Abstract
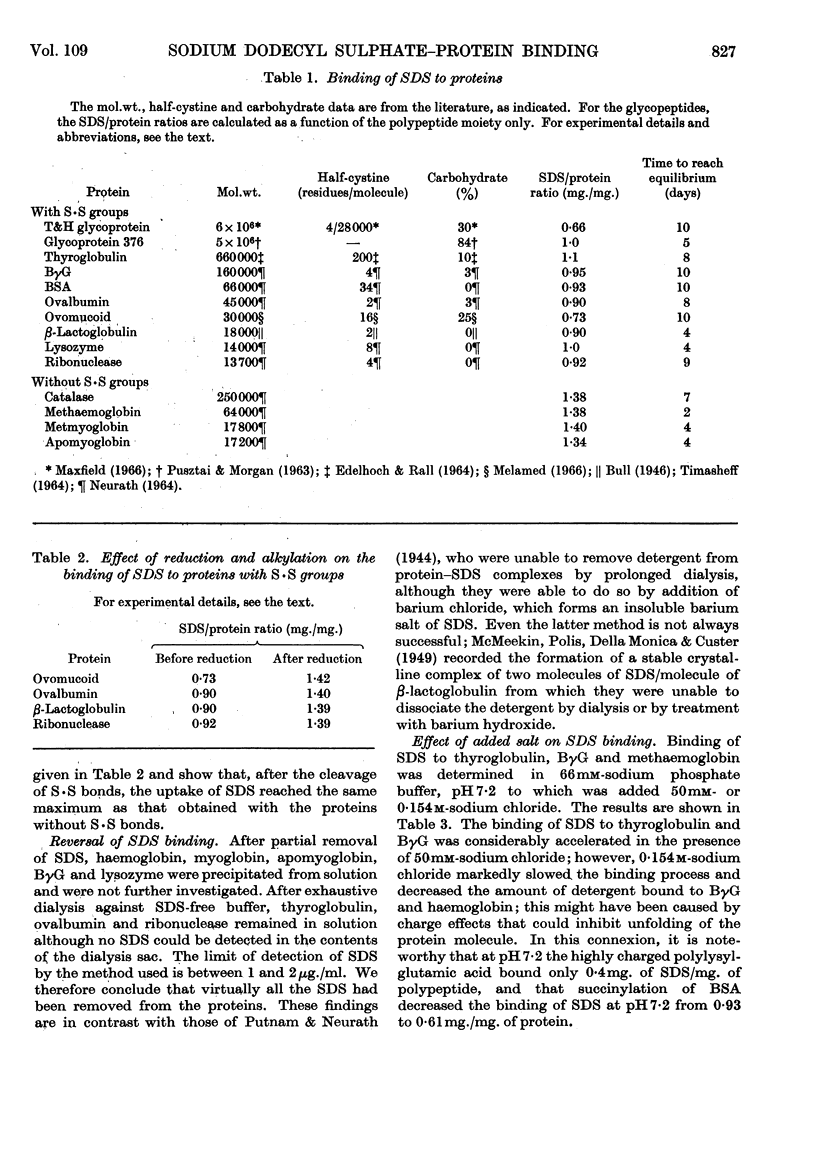
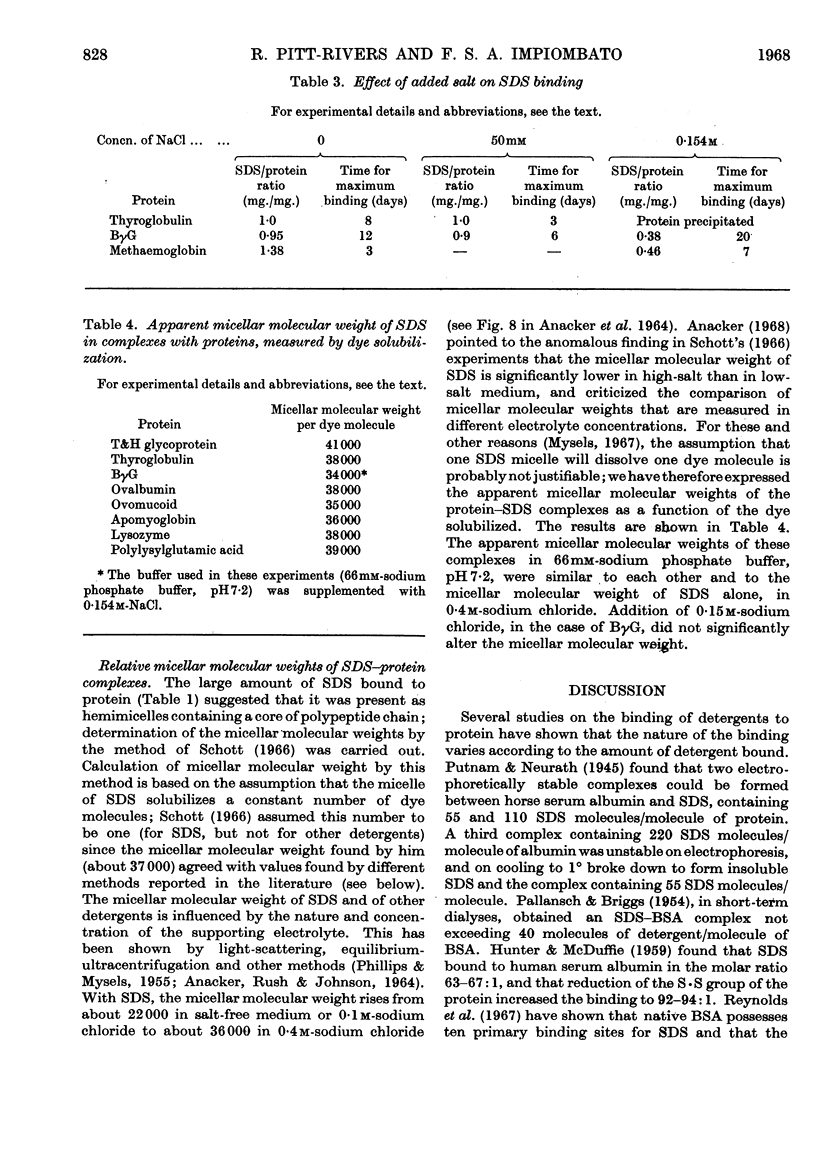
1. The binding of sodium dodecyl sulphate to proteins by equilibrium dialysis was investigated. 2. Most of the proteins studied bound 90–100% of their weight of sodium dodecyl sulphate. 3. The glycoproteins studied bound 70–100% of their weight of sodium dodecyl sulphate, calculated in terms of the polypeptide moiety of the molecule. 4. Proteins not containing S·S groups bound about 140% of their weight of sodium dodecyl sulphate. 5. Reduction of four proteins containing S·S groups caused a rise in sodium dodecyl sulphate binding to 140% of the weight of protein. 6. The apparent micellar molecular weights of the protein–sodium dodecyl sulphate complexes were measured by the dye-solubilization method; they were all found to have approximately the same micellar molecular weight (34000–41000) irrespective of the molecular weight of the protein to which they were attached.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Creeth J. M., Knight C. G. The macromolecular properties of blood-group substances. Sedimentation-velocity and viscosity measurements. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1135–1145. doi: 10.1042/bj1051135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELHOCH H., LIPPOLDT R. E. The properties of thyroglobulin. II. The effects of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1335–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABEEB A. F., CASSIDY H. G., SINGER S. J. Molecular structural effects produced in proteins by reaction with succinic anhydride. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):587–593. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUSZTAI A., MORGAN W. T. STUDIES IN IMMUNOCHEMISTRY. 22. THE AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF THE HUMAN BLOOD-GROUP A, B, H AND LE-A SPECIFIC SUBSTANCES. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:546–555. doi: 10.1042/bj0880546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Herbert S., Polet H., Steinhardt J. The binding of divers detergent anions to bovine serum albumin. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):937–947. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


