Abstract
1. A glycoprotein extracted by cold alkali from the walls of human aorta was purified by chromatography on DEAE-cellulose. 2. The compound was electrophoretically homogeneous and essentially so by chromatography on DEAE-cellulose. Ultracentrifugal examination revealed two components, and it is suggested that the faster-sedimenting component represents an aggregated form of the glycoprotein. 3. Glycoprotein preparations contained approx. 8% of carbohydrate. Digestion with Pronase yielded a glycopeptide fraction containing all the carbohydrate of the glycoprotein. The glycopeptide, of molecular weight about 7800, contained sialic acid, galactose, mannose, fucose and hexosamine in the approximate molar proportions 5:10:5:2:11. Sialic acid was terminal with respect to the polysaccharide chains. 4. Both elastase and elastomucoproteinases exhibited proteolytic activity towards the glycoprotein. Studies by other investigators have led to the conclusion that elastomucoproteinases attack protein–carbohydrate complexes occurring in intimate association with elastin in aorta and other tissues, and it is suggested that the glycoprotein may be identified with one of these compounds.
Full text
PDF


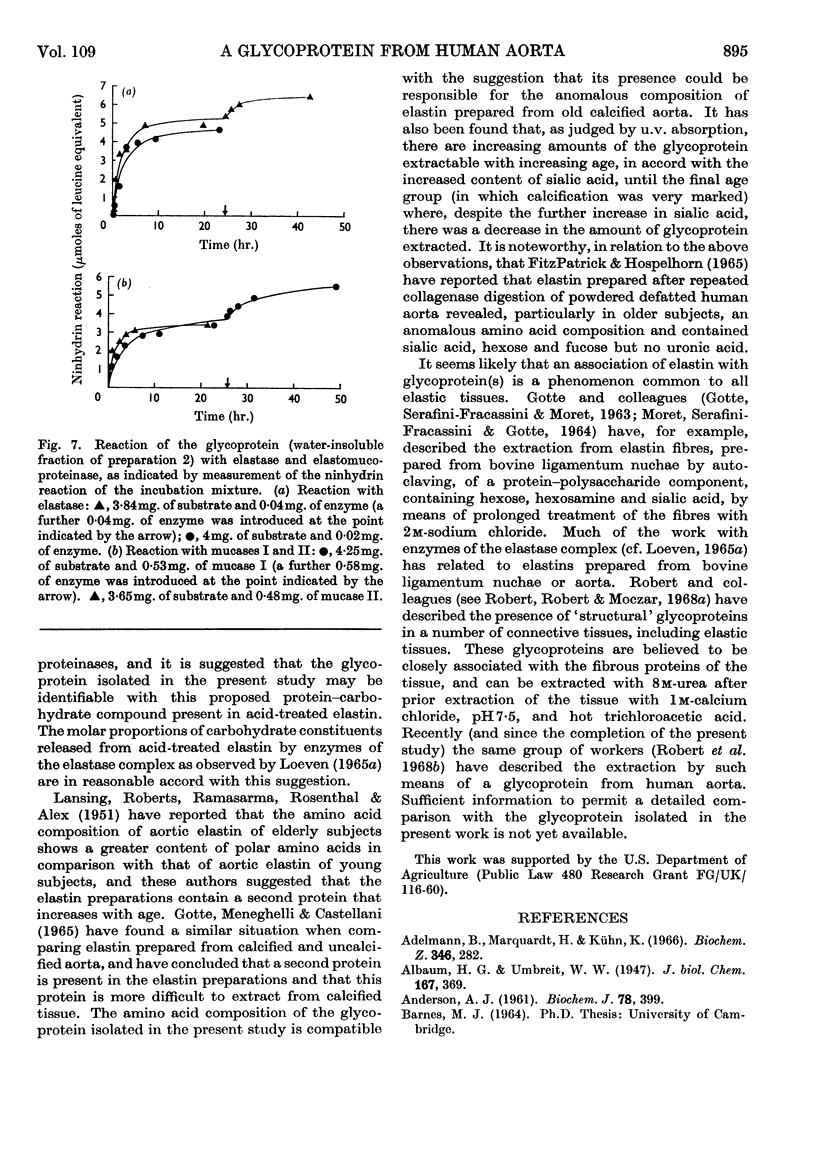

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON A. J. Some studies on the occurrence of sialic acid in human cartilage. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:399–409. doi: 10.1042/bj0780399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTELSEN S., JENSEN C. E. Histochemical studies on human aortic tissue. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1960;48:305–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1960.tb04770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOAS N. F. Distribution of hexosamine in electrophoretically separated extracts of rat connective tissue. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Aug;57(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOWES J. H., MOSS J. A. The effect of gamma radiation on collagen. Radiat Res. 1962 Mar;16:211–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenson G. S., Radhakrishnamurthy B., Fishkin A. F., Dessauer H., Arquembourg P. Individuality of glycoproteins in human aorta. J Atheroscler Res. 1966 May-Jun;6(3):214–223. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(66)80002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd B., Napier E. J., Somerfield G. A. The demethylation of griseofulvin by fungi. Biochem J. 1961 Jul;80(1):34–37. doi: 10.1042/bj0800034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S. Determination of inorganic sulphate in studies on the enzymic and non-enzymic hydrolysis of carbohydrate and other sulphate esters. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:312–319. doi: 10.1042/bj0780312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., PRICE R. G. A note on the determination of the ester sulphate content of sulphated polysaccharides. Biochem J. 1962 Jul;84:106–110. doi: 10.1042/bj0840106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENSELME J., FREY J., HENRY J. C. [Comparison of the composition of normal and atheromatous aortic tissue]. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1961 Nov 28;43:1085–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson L. A., Morgan W. T. A colorimetric method for the determination of glucosamine and chondrosamine. Biochem J. 1933;27(6):1824–1828. doi: 10.1042/bj0271824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEENEY R. E., RHODES M. B., ANDERSON J. S. The distribution and role of sialic acid in chicken egg white. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2633–2637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTE L. Sulla sostanza metacromatica dell'aorta umana in rapporto all'accrescimento ed alla senescenza. Arch Ital Anat Embriol. 1952;57(2):225–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H., NEUBERGER A., PERKINS D. J. Observations on the presence of plasma proteins in skin and tendon. Biochem J. 1957 Jul;66(3):390–399. doi: 10.1042/bj0660390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAO K. Y., HITT W. E., DAWSON R. L., McGAVACK T. H. Connective tissue. VII. Changes in protein and hexosamine content of bone and cartilage of rats at different ages. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Jul;110:538–543. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANSING A. I., ROBERTS E., RAMASARMA G. B., ROSENTHAL T. B., ALEX M. Changes with age in amino acid composition of arterial elastin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Apr;76(4):714–717. doi: 10.3181/00379727-76-18604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEVEN W. A. Elastolysis. Remarks on some properties of elastomucase and elastoproteinase purified by means of starch column electrophoresis. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Neerl. 1960;9:473–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeven W. A. Elastolysis. 3. The release of carbohydrate moieties during the incubation of acid- and alkali-treated elastin with the enzymes of the elastase complex. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Neerl. 1965;13(3):278–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTENSSON E., RAAL A., SVENNERHOLM L. Sialic acids in blood serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Oct;30(1):124–129. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTREUIL J., BISERTE G. [Sialic acid and specificity of the periodic acid-Schiff's fuchsin reaction as applied to paper electrophoresis. Special example of orosomucoid]. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1959;41:959–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORET V., SERAFINI-FRACASSINI A., GOTTE L. THE CARBOHYDRATE COMPOSITION OF THE NAC1-SOLUBLE FRACTION FROM AUTOCLAVED ELASTIN. J Atheroscler Res. 1964 Mar-Apr;4:184–188. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(64)80038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUBERGER A., PAPKOFF H. Carbohydrates in protein. 7. The nature of the carbohydrate in ovomucoid. Biochem J. 1963 Jun;87:581–585. doi: 10.1042/bj0870581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARTRIDGE S. M., DAVIS H. F. The chemistry of connective tissues. 4. The presence of a non-collagenous protein in cartilage. Biochem J. 1958 Feb;68(2):298–305. doi: 10.1042/bj0680298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPORT M. M., ALONZO N. Photometric determination of fatty acid ester groups in phospholipides. J Biol Chem. 1955 Nov;217(1):193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. The free amino groups of insulin. Biochem J. 1945;39(5):507–515. doi: 10.1042/bj0390507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. The influence of post-mortem conditions on the solubilities of muscle proteins. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):201–207. doi: 10.1042/bj0910201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YEMM E. W., WILLIS A. J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):508–514. doi: 10.1042/bj0570508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


