Abstract
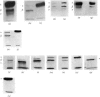
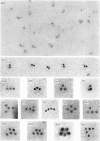
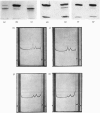
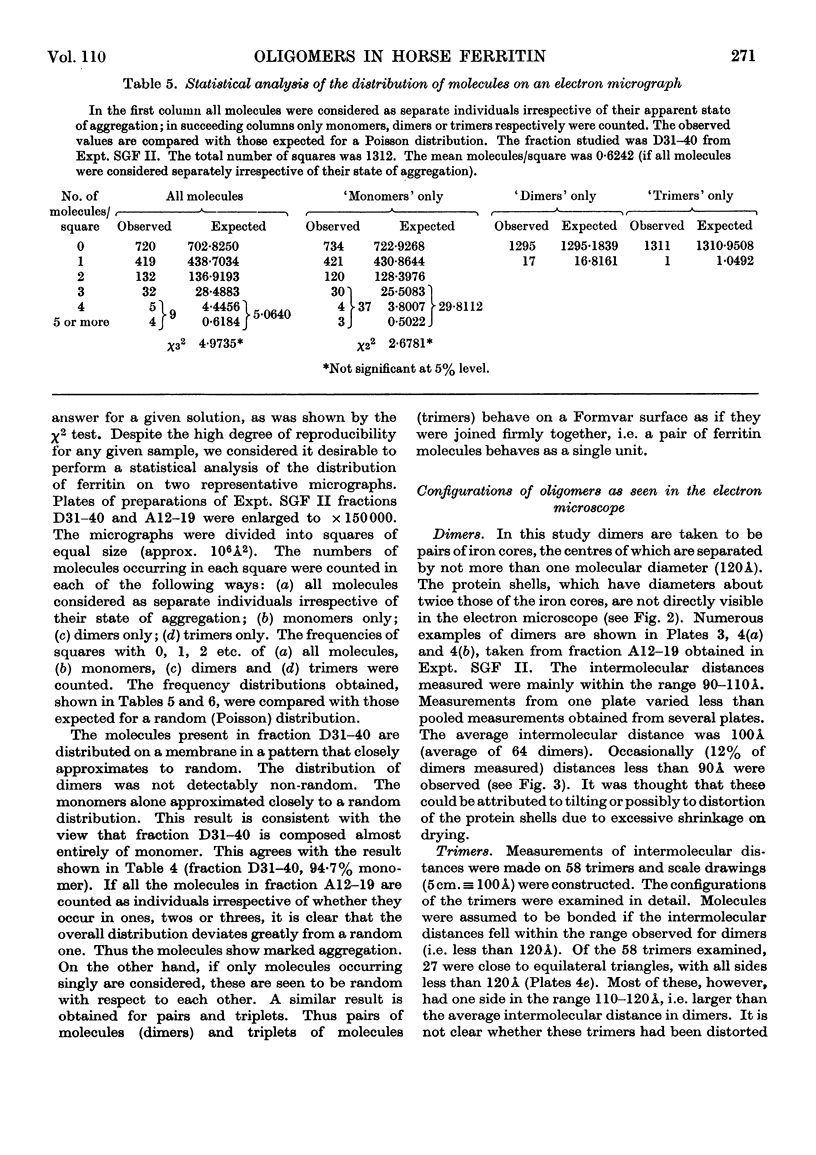
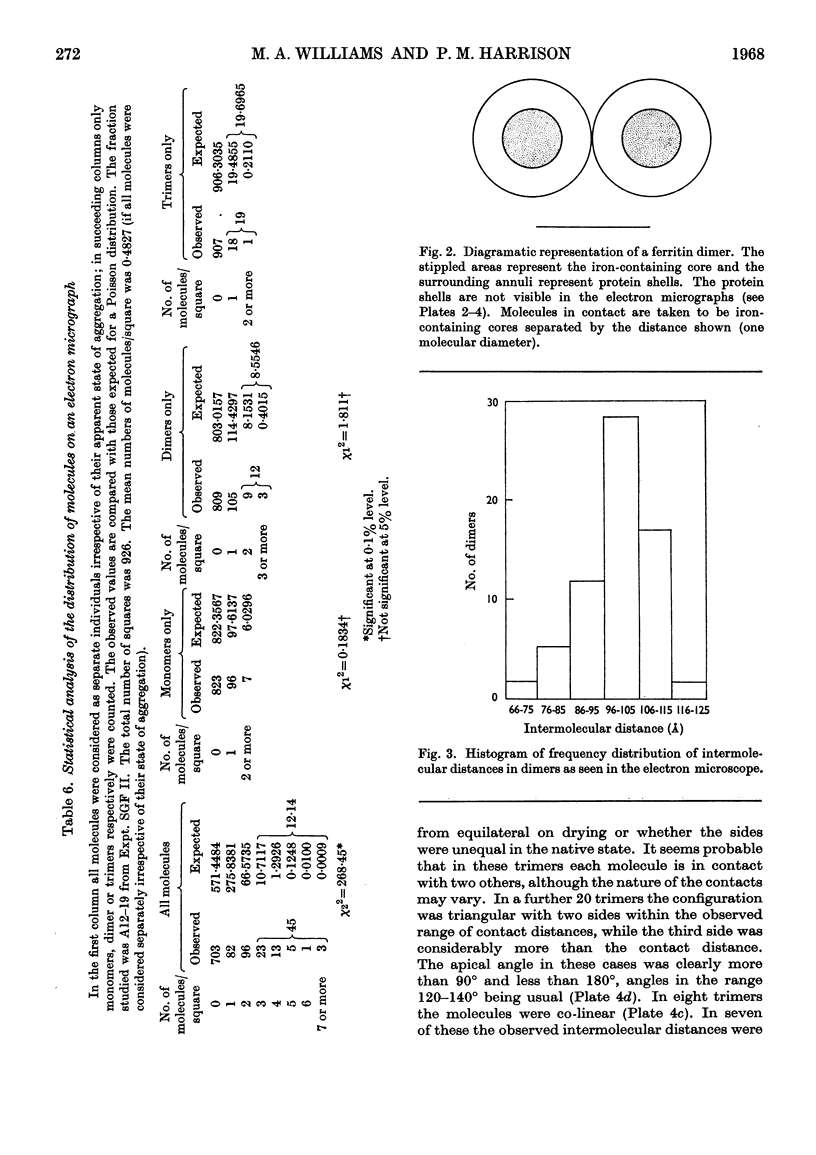
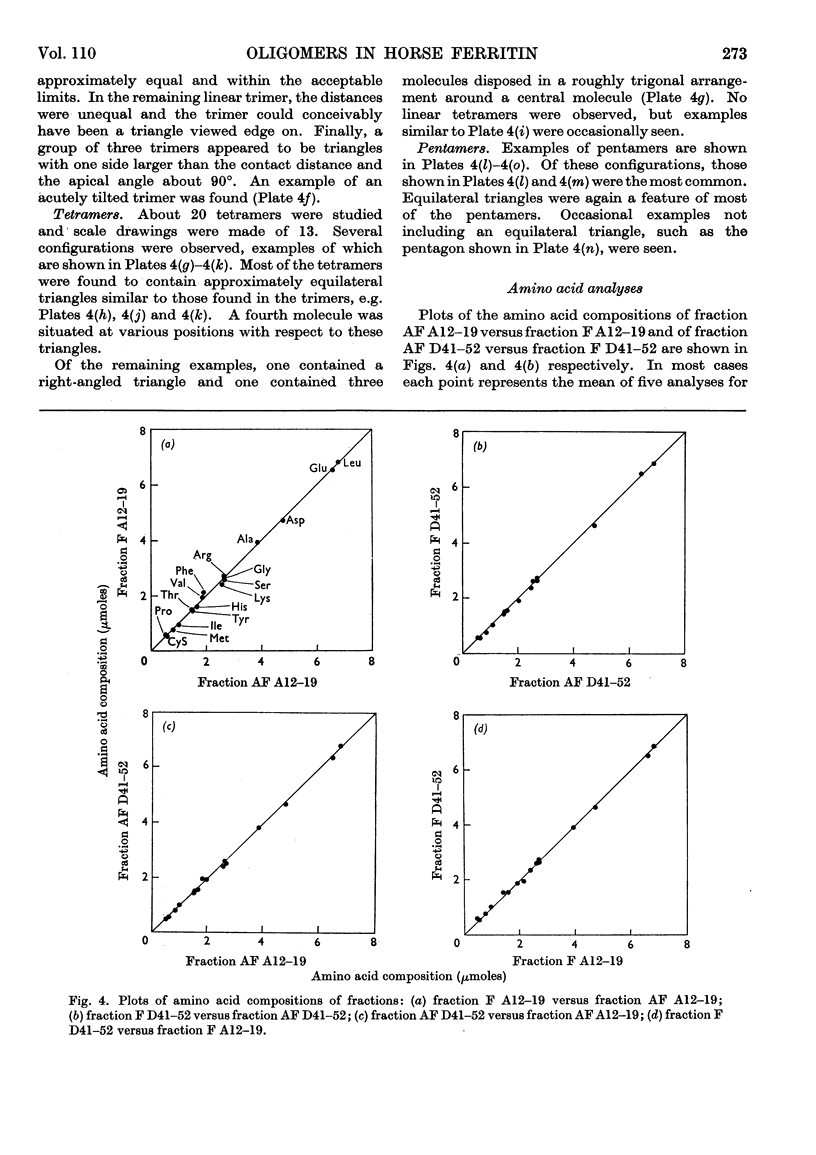
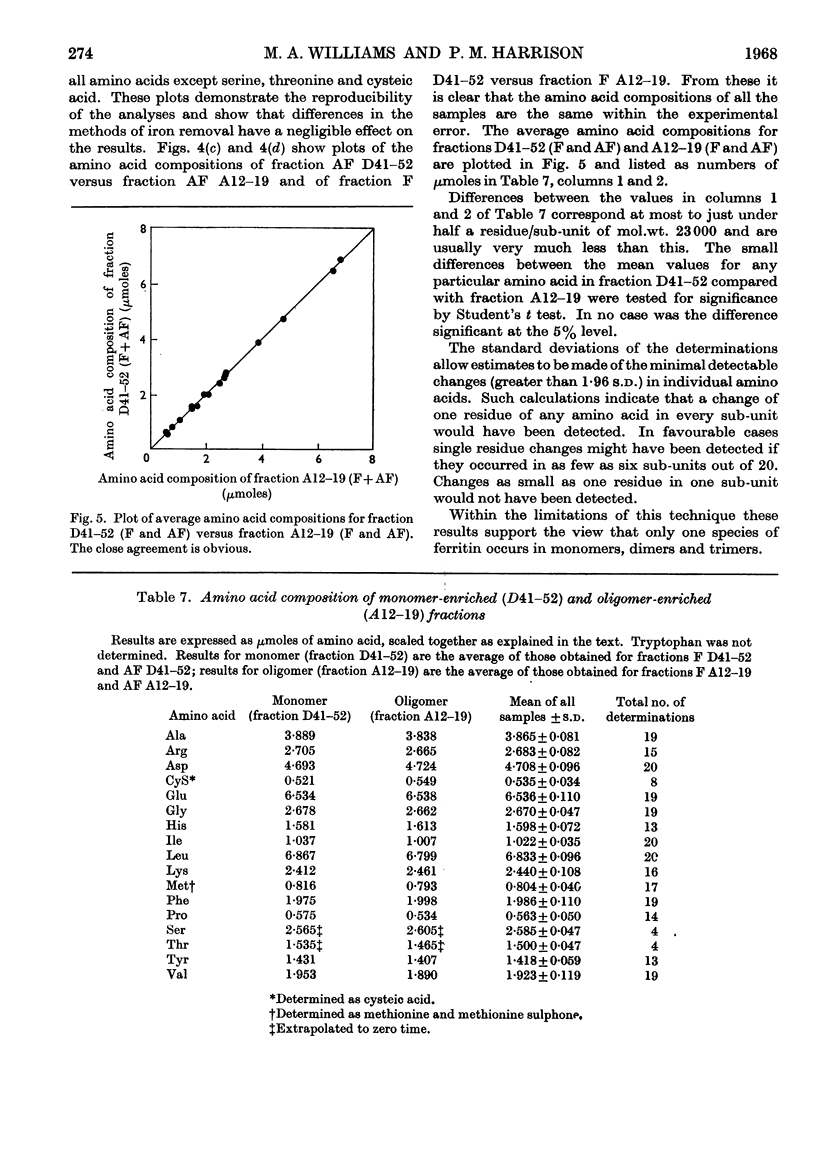
Horse ferritin was fractionated both by starch-gel electrophoresis and by gel filtration on Sephadex G-200. Monomer fractions contained up to 98% of monomer and oligomer fractions up to 76% of oligomers as determined by quantitative electron microscopy. Percentages obtained from electron micrographs correlated well with analytical starch-gel electrophoretograms and ultracentrifuge patterns. Amino acid analyses of monomer- and oligomer-enriched fractions showed no significant differences. Ferritin oligomers did not apparently dissociate on dilution for electron microscopy or on storage. Apoferritin dimers were stable in 0·01m-phosphate buffer at dilutions down to 0·19mg./ml. as shown by ultracentrifugation. Chemical studies indicated that the intermolecular bonds in oligomers are resistant to a variety of reagents and conditions, including those that would be expected to attack disulphide, peptide and ester linkages respectively. Partial disaggregation was achieved at high pH values and in 67% (v/v) acetic acid. Centre-to-centre intermolecular distances in dimers were found to be about 100å. Three main types of trimer configuration were found and a variety of tetramers and pentamers. These configurations are described and discussed.
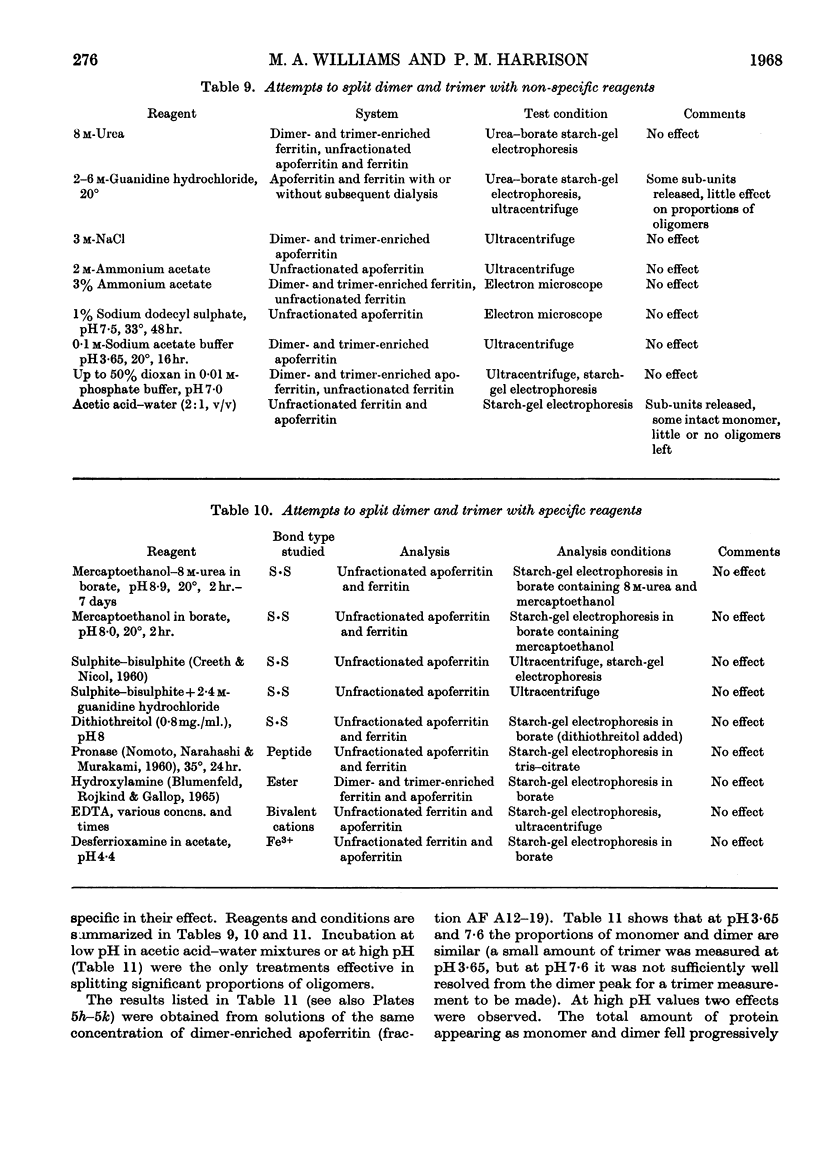
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARNEVALI F., TECCE G. APOFERRITIN HETEROGENEITY. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Apr;105:207–207. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90254-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREETH J. M., NICHOL L. W. Evidence for the chemical interaction of urease in solution. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:230–239. doi: 10.1042/bj0770230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURELL J., ANDERSON D. G., CANTONI G. L. The synthesis of methionine by enzymic transmethylation. I. Purification and properties of thetin homocysteine methylpherase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Nov;26(2):270–281. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARRANT J. L. An electron microscopic study of ferritin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Apr;13(4):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINE J. M., HARRIS G. ELECTROPHORETIC AND IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES OF HORSE AND HUMAN FERRITIN. Clin Chim Acta. 1963 Sep;8:794–798. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(63)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H. Degradation of tobacco mosaic virus with acetic acid. Virology. 1957 Aug;4(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory D. W., Williams M. A. The preparation of ferritin-labelled antibodies and other protein-protein conjugates with bis-diazotized benzidine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):319–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON P. M., HOFMANN T., MAINWARING W. I. The structure of apoferritin: amino acid composition and end-groups. J Mol Biol. 1962 Apr;4:251–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN T., HARRISON P. M. The structure of apoferritin: degradation into and molecular weight of subunits. J Mol Biol. 1963 Apr;6:256–267. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. M., Gregory D. W. Evidence for the existence of stable "aggregates" in horse ferritin and apoferritin. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):626–629. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPP R., VOGT A., MAASS G. 'FREE' APOFERRITIN AND APOFERRITIN OBTAINED BY REDUCTION OF IRON-CONTAINING FERRITIN. Nature. 1964 Jun 20;202:1211–1212. doi: 10.1038/2021211b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPP R., VOGT A., MAASS G. Separation of iron-containing ferritin from horse-spleen into three distinct fractions by starch-gel electrophoresis. Nature. 1963 Jun 1;198:892–893. doi: 10.1038/198892a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABAW L. W., WYCKOFF R. W. The electron microscopy of ferritin crystals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Aug;25(2):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luftig R. An accurate measurement of the catalase crystal period and its use as an internal marker for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Sep;20(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULIK M. D. Starch gel electrophoresis in a discontinous system of buffers. Nature. 1957 Dec 28;180(4600):1477–1479. doi: 10.1038/1801477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHTER G. W. ON FERRITIN AND ITS PRODUCTION BY CELLS GROWING. Lab Invest. 1963 Oct;12:1026–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter G. W., Walker G. F. Reversible association of apoferritin molecules. Comparison of light-scattering and other data. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2871–2880. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SADDI R. [Ferritin and idiopathic hemochromatosis]. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1962 Apr;7:408–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinjyo S., Kume M., Danjo T. [Heterogeneity of horse spleen ferritin. I. Comparison of "free" apoferritin and alfa-ferritin]. Seikagaku. 1967 Jan;39(1):23–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suran A. A., Tarver H. Heterogeneity of horse spleen ferritin and apoferritin: comparison of electrophoretic and chromatographic fractions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Aug;111(2):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THERON J. J., HAWTREY A. O., SCHIRREN V. Characterization of human liver ferritin by starch-gel electrophoresis. Clin Chim Acta. 1963 Jan;8:165–167. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(63)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamiri I., Mason J. Electrophoresis of ferritins. Nature. 1968 Jan 20;217(5125):258–259. doi: 10.1038/217258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]