Abstract
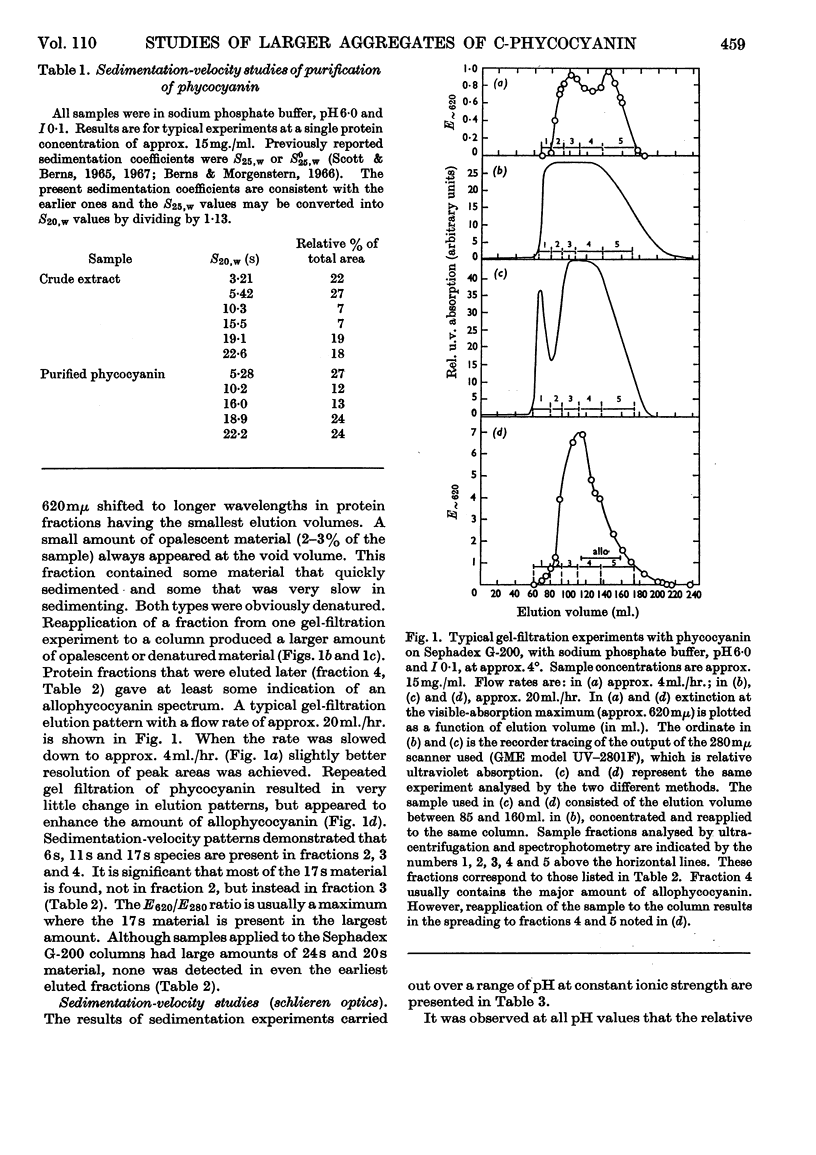
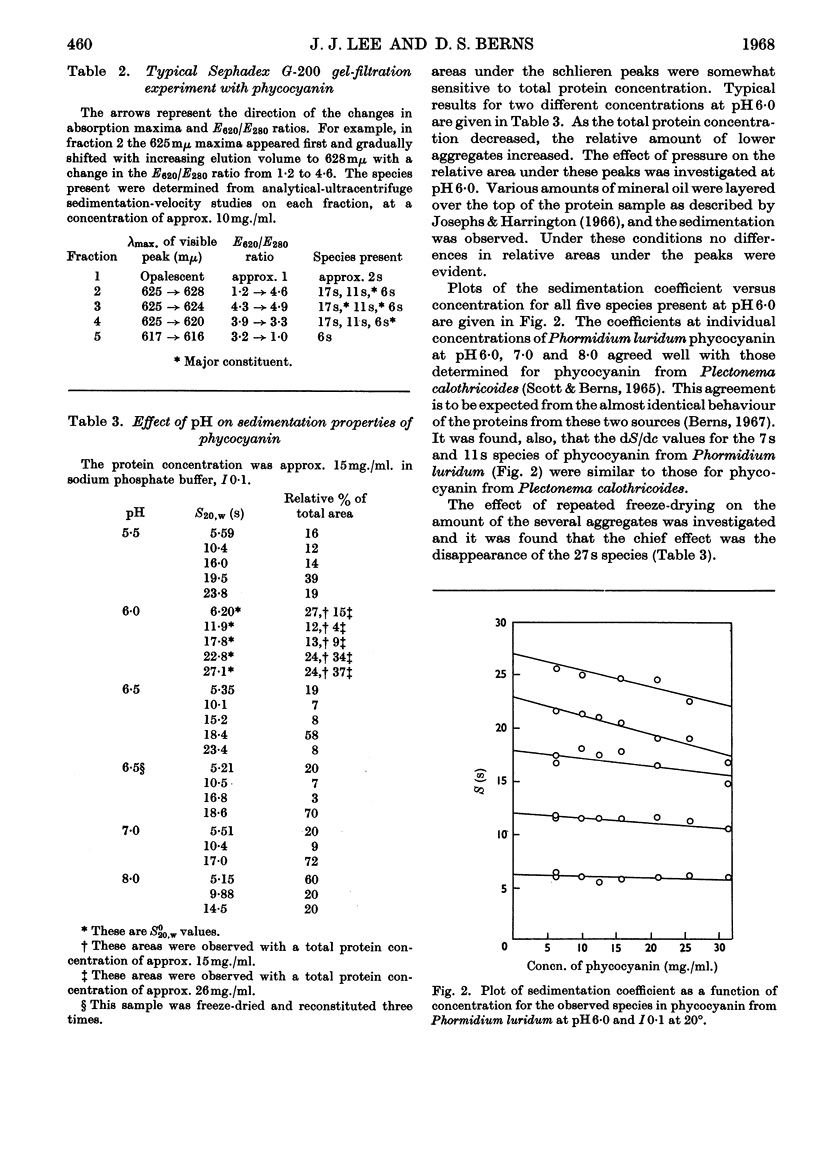
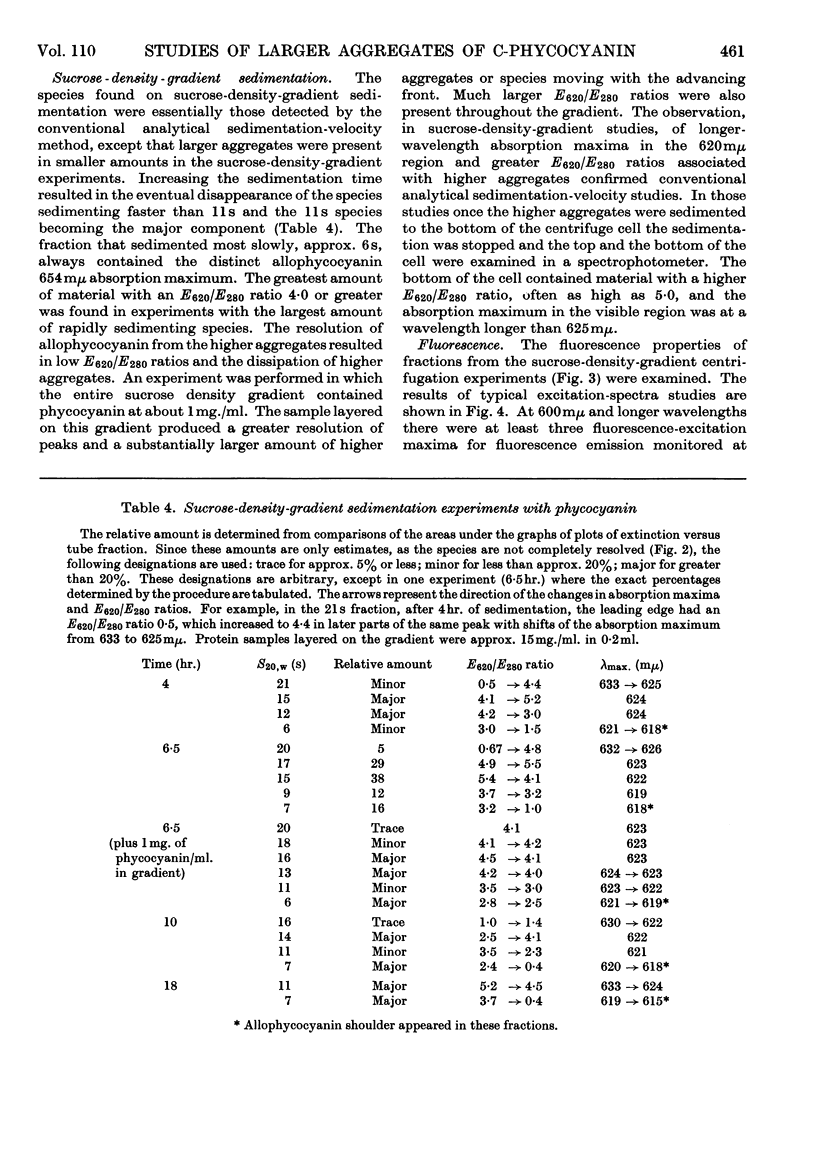
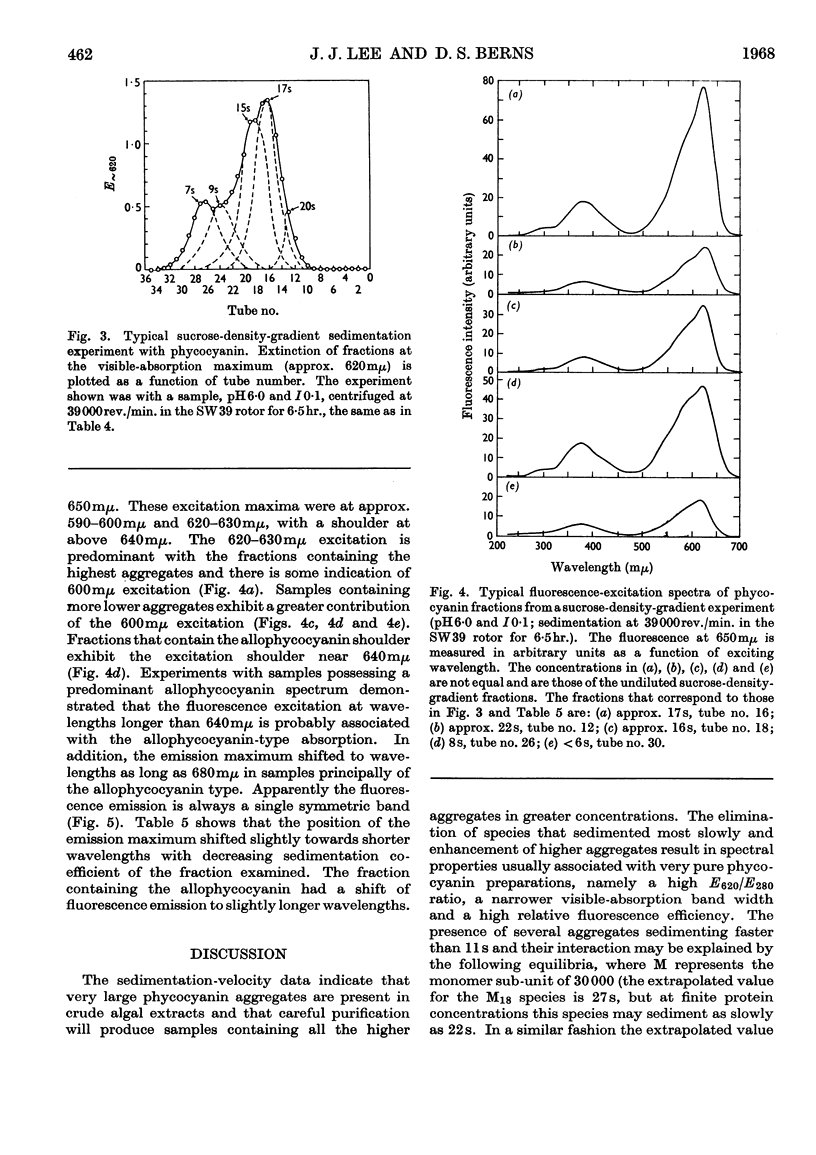
Aggregates of phycocyanin sedimenting at 17s, 22s and 27s are demonstrated to constitute more than 40% of crude blue–green-algal extracts, pH6·0 and I0·1, and are retained in highly purified preparations. Sedimentation-velocity studies of the large aggregates as a function of pH are reported. Sucrose-density-gradient experiments performed as a function of time of sedimentation indicate that: (1) with increasing time of sedimentation, the largest aggregates are dissipated at the leading protein boundary and the several phycocyanin species present are not completely resolved; (2) phycocyanin fractions with the largest aggregates exhibit the highest E620/E280 ratio and the largest relative fluorescence efficiency. Gel-filtration experiments with Sephadex G-200 do not resolve the species completely, and reapplication of phycocyanin gel-filtration fractions to the column results in an elution pattern similar to the original, except that there is an enhancement of the allophycocyanin fraction and the amount of denatured protein. Increasing the sedimentation times in a sucrose density gradient also enhances the allophycocyanin fraction. Fluorescence results demonstrate that there are possibly three excitation maxima, one corresponding to the monomer (approx. 600mμ), one for higher aggregates (625–630mμ) and one for the allophycocyanin fraction (approx. 650mμ). Only a single fluorescence-emission band is detected, which is fairly symmetrical and which has a red shift with higher aggregation and with the appearance of allophycocyanin. The appearance of allophycocyanin may be correlated with the irreversible disaggregation of the largest phycocyanin species. It is suggested that the largest protein aggregates are in the size range of the biliprotein aggregates reported in electron microscopy of algal cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns D. S. Immunochemistry of biliproteins. Plant Physiol. 1967 Nov;42(11):1569–1586. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.11.1569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns D. S., Morgenstern A. Ultracentrifuge investigation of protein aggregation in dilute solutions of C-phycocyanin. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2985–2990. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns D. S., Scott E. Protein aggregation in a thermophilic protein. Phycocyanin from Synechococcus lividus. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1528–1533. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson-Quensel I. B. The molecular weights of phycoerythrin and phycocyan. I. Biochem J. 1938 Mar;32(3):585–589. doi: 10.1042/bj0320585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt E., Conti S. F. Phycobiliprotein localization in algae. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1966;19:393–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs R., Harrington W. F. Studies on the formation and physical chemical properties of synthetic myosin filaments. Biochemistry. 1966 Nov;5(11):3474–3487. doi: 10.1021/bi00875a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luftig R., Haselkorn R. Morphology of a virus of blue-green algae and properties of its deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):344–361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.2.344-361.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E., Berns D. S. Completely deuterated proteins. 3. Deuteration effects on protein-protein interaction in phycocyanin. Biochemistry. 1967 May;6(5):1327–1334. doi: 10.1021/bi00857a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E., Berns D. S. Protein-protein interaction. The phycocyanin system. Biochemistry. 1965 Dec;4(12):2597–2606. doi: 10.1021/bi00888a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


