Abstract
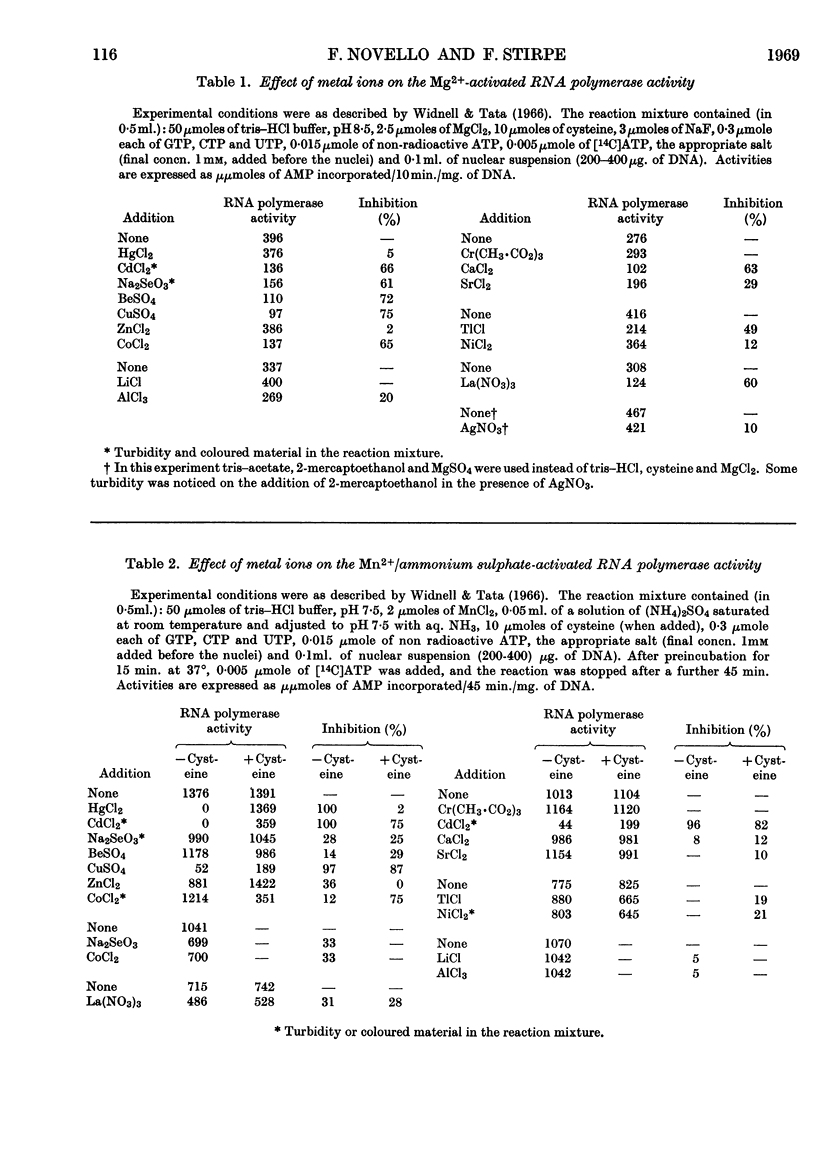
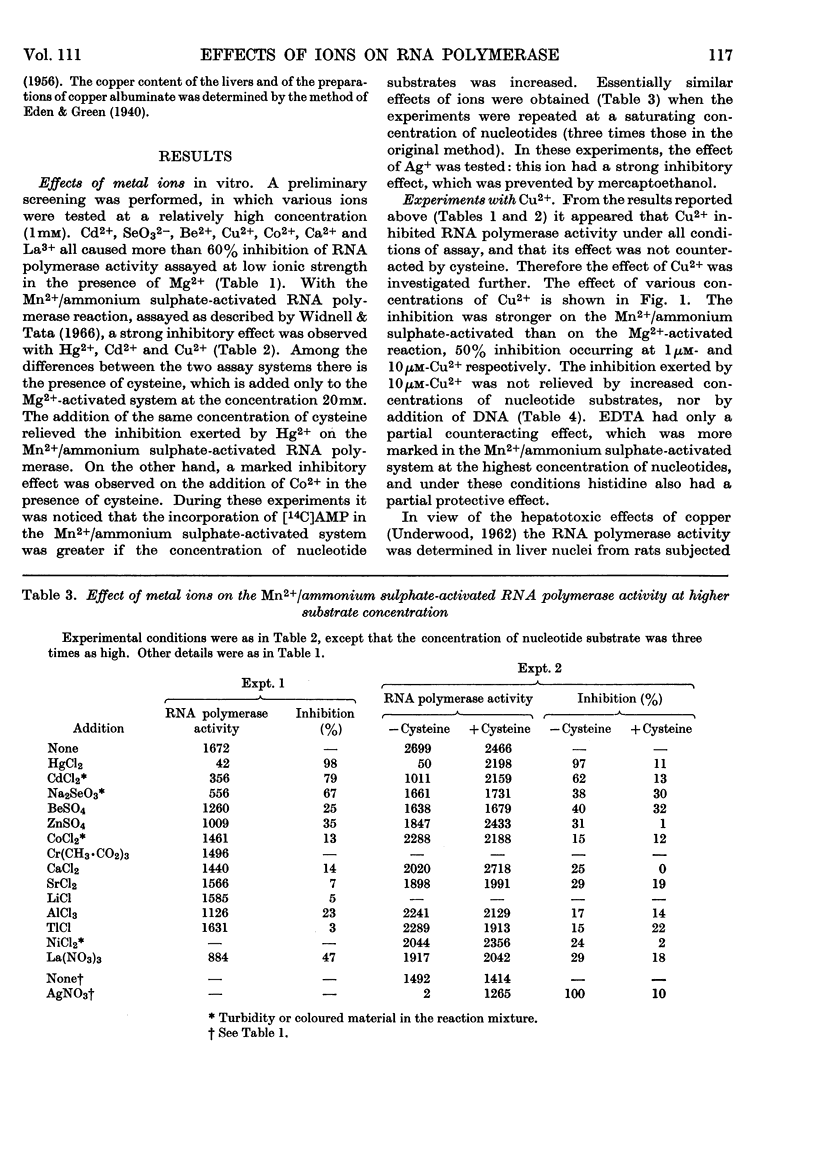
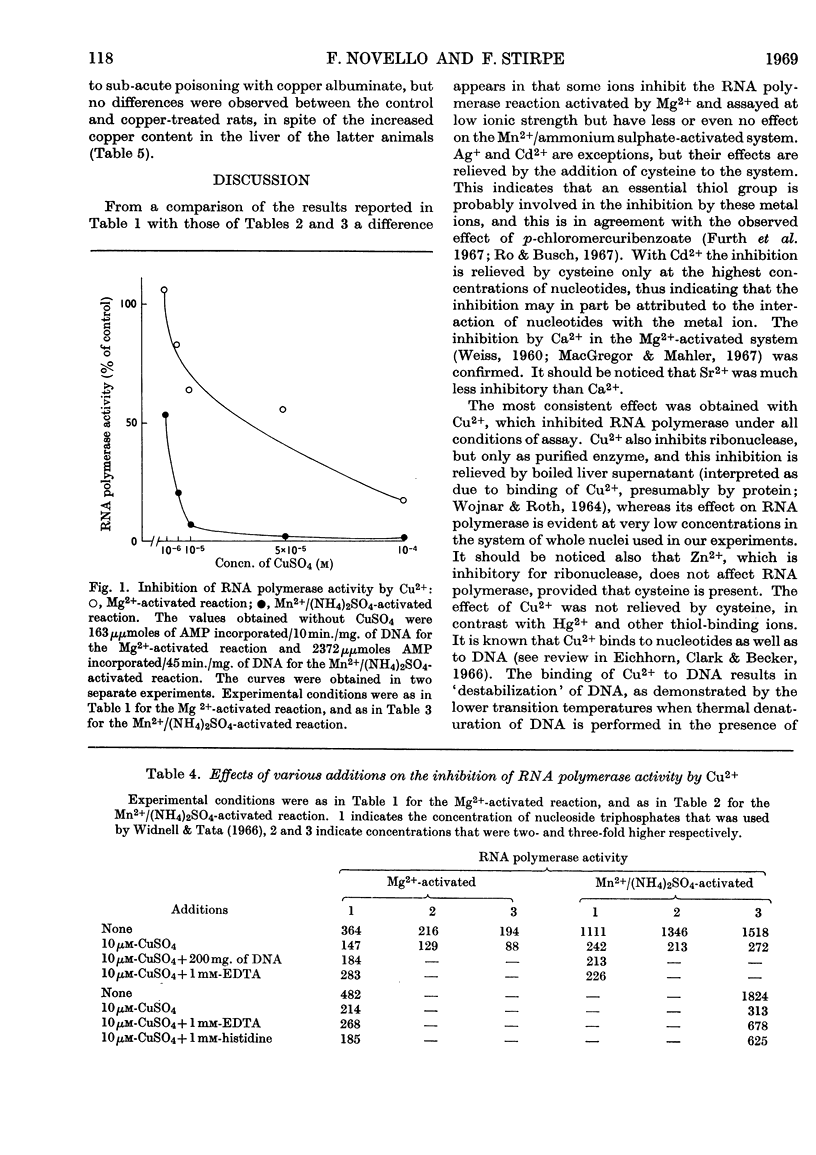
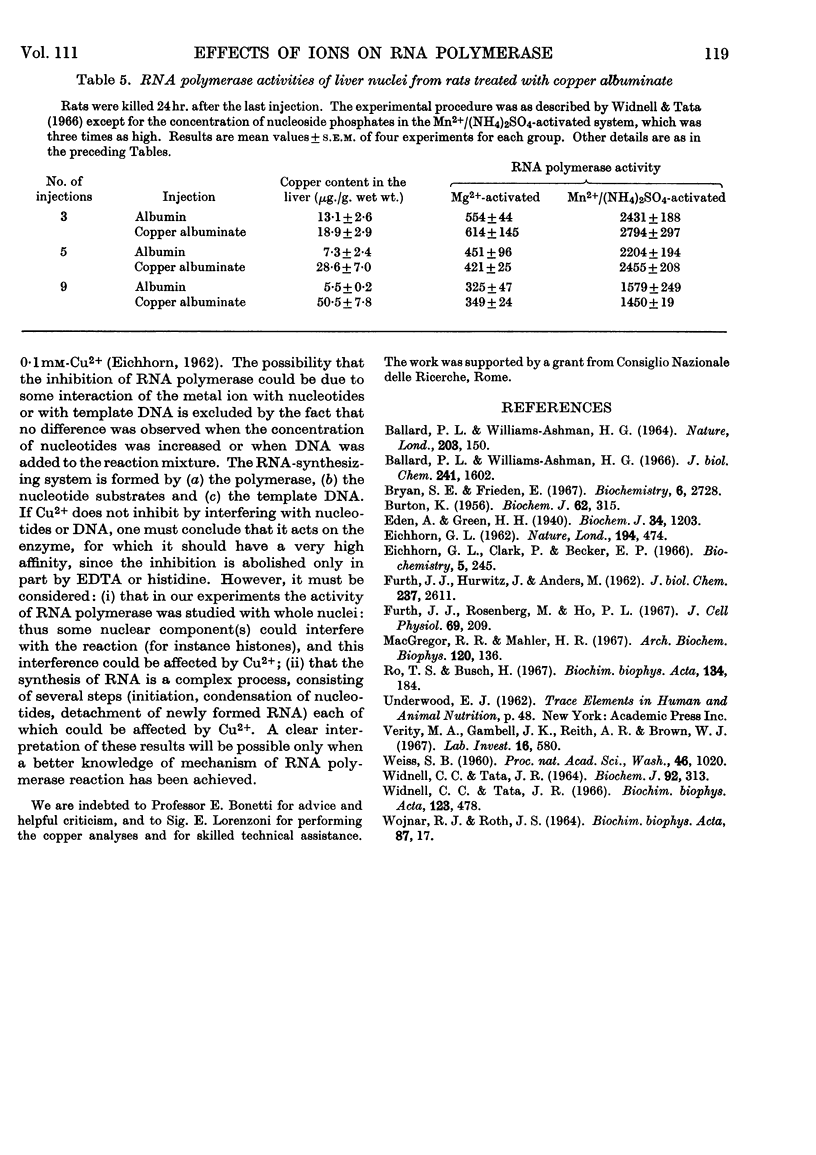
1. The effects of various ions on the Mg2+- and Mn2+/ammonium sulphate-activated RNA polymerase activities of isolated liver nuclei were studied. 2. The Mg2+-activated RNA polymerase reaction was inhibited by more than 60% by Cd2+, SeO32−, Be2+, Cu2+, Co2+, Ca2+ and La3+, all at 1mm concentrations. 3. The Mn2+/ammonium sulphate-activated RNA polymerase reaction was strongly inhibited by Hg2+, Cd2+, Cu2+ and Ag+. The effect of Hg2+, Cd2+ and Ag+ was relieved by cysteine or mercaptoethanol. 4. Inhibition by Cu2+ was not affected by addition of DNA, and was relieved only partially by EDTA or histidine. 5. No changes of RNA polymerase activities were observed in nuclei isolated from the liver of rats treated with copper albuminate.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALLARD P., WILLIAMS-ASHMAN H. G. ISOLATION OF A SOLUBLE RNA POLYMERASE FROM RAT TESTIS. Nature. 1964 Jul 11;203:150–151. doi: 10.1038/203150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard P. L., Williams-Ashman H. G. Isolation and properties of a testicular ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 10;241(7):1602–1615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan S. E., Frieden E. Interaction of copper(II) with deoxyribonucleic acid below 30 degrees. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2728–2734. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICHHORN G. L. Metal ions as stabilizers or destabilizers of the deoxyriboucleic acid structure. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:474–475. doi: 10.1038/194474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichhorn G. L., Clark P., Becker E. D. Interactions of metal ions with polynucleotides and related compounds. VII. The binding of copper(II) to nucleosides, nucleotides, and deoxyribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):245–253. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURTH J. J., HURWITZ J., ANDERS M. The role of deoxyribonucleic acid in ribonucleic acid synthesis. I. The purification and properties of ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2611–2619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth J. J., Rosenberg M., Ho P. L. Comparison of the requirements for ribonucleic acid synthesis with the requirements for deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in animal tissues. J Cell Physiol. 1967 Apr;69(2):209–217. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040690211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Mahler H. R. RNA synthesis in intact rat liver nuclei. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Apr;120(1):136–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90607-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verity M. A., Gambell J. K., Reith A. R., Brown W. J. Subcellular distribution and enzyme changes following subacute copper intoxication. Lab Invest. 1967 Apr;16(4):580–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOJNAR R. J., ROTH J. S. METAL IONS IN RIBONUCLEIC ACID: THEIR NATURE AND INTERFERENCE WITH THE ASSAY FOR RIBONUCLEASE AND RIBONUCLEASE INHIBITOR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 18;87:17–27. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. A procedure for the isolation of enzymically active rat-liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):313–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0920313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. Studies on the stimulation by ammonium sulphate of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of isolated rat-liver nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Sep;123(3):478–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


