Abstract
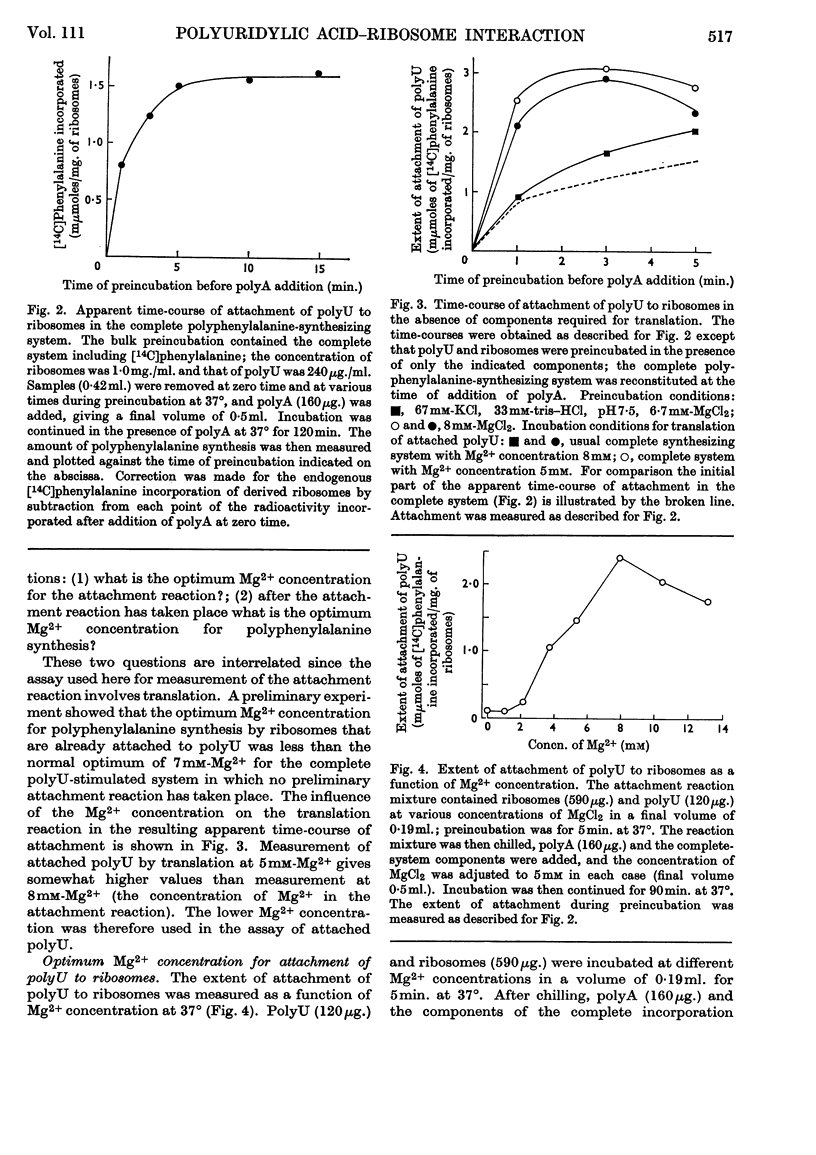
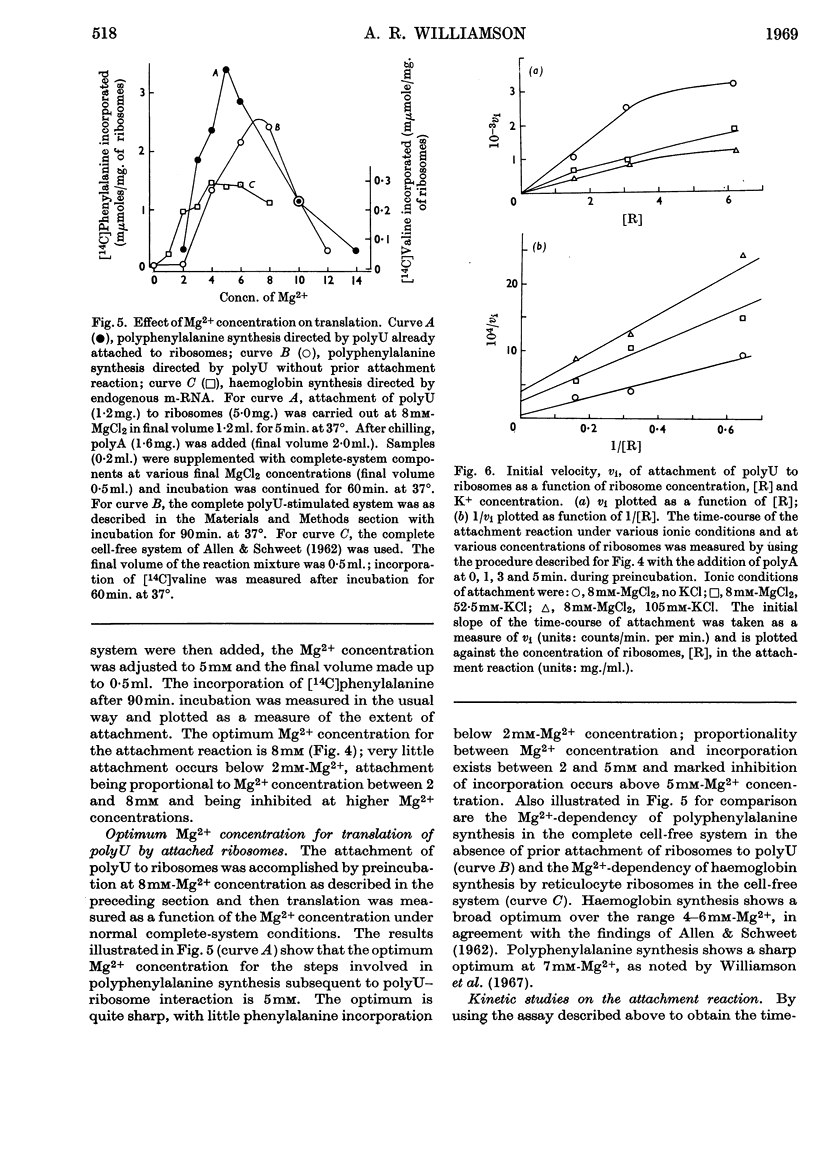
The attachment of polyuridylic acid to reticulocyte ribosomes was studied by using polyadenylic acid, which inhibits the attachment reaction only, while permitting translation of polyuridylic acid bound to ribosomes. After addition of polyadenylic acid the amount of polyphenylalanine synthesized under standard conditions was taken as a measure of the bound polyuridylic acid. In this way certain parameters of the attachment reaction and the subsequent translation of attached polyuridylic acid were defined: (1) polyuridylic acid–ribosome interaction at 37° requires only Mg2+ at an optimum concentration of 8mm; (2) K+ (required for translation) is a non-competitive inhibitor of the attachment reaction; (3) optimum polyphenylalanine synthesis directed by attached polyuridylic acid occurs at 5mm-Mg2+ concentration; (4) from kinetic studies single ribosomes appear to participate in the attachment reaction.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN E. H., SCHWEET R. S. Synthesis of hemoglobin in a cell-free system. I. Properties of the complete system. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:760–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARLINGHAUS R., SHAEFER J., SCHWEET R. MECHANISM OF PEPTIDE BOND FORMATION IN POLYPEPTIDE SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1291–1299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARNSTEIN H. R., COX R. A., HUNT J. A. Function of polyuridylic acid and ribonucleic acid in protein biosynthesis by ribosomes from mammalian reticulocytes. Nature. 1962 Jun 16;194:1042–1044. doi: 10.1038/1941042a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Haselkorn R. The ribosome-binding sites in turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1269–1276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT W. Polypeptide synthesis in Escherichia coli. I. Ribosomes and the active complex. J Mol Biol. 1963 May;6:374–388. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN H. M., RICH A. MECHANISM OF POLYRIBOSOME ACTION DURING PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Nature. 1963 Jul 27;199:318–322. doi: 10.1038/199318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDESTY B., HUTTON J. J., ARLINGHAUS R., SCHWEET R. POLYRIBOSOME FORMATION AND HEMOGLOBIN SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1078–1085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEDERSEN S., HULTIN T. The interaction between polyuridylic acid and isolated microsomes from Ehrlich ascitic tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 26;68:328–330. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REVEL M., HIATT H. H. MAGNESIUM REQUIREMENT FOR THE FORMATION OF AN ACTIVE MESSENGER RNA-RIBOSOME-S-RNA COMPLEX. J Mol Biol. 1965 Mar;11:467–475. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson A. R., Askonas B. A. Biosynthesis of immunoglobulins: the separate classes of polyribosomes synthesizing heavy and light chains. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jan 28;23(2):201–216. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson A. R., Hausmann E., Heintz R., Schweet R. Homopolynucleotide inhibition of poly U-dependent polyphenylalanine synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):267–278. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


