Abstract
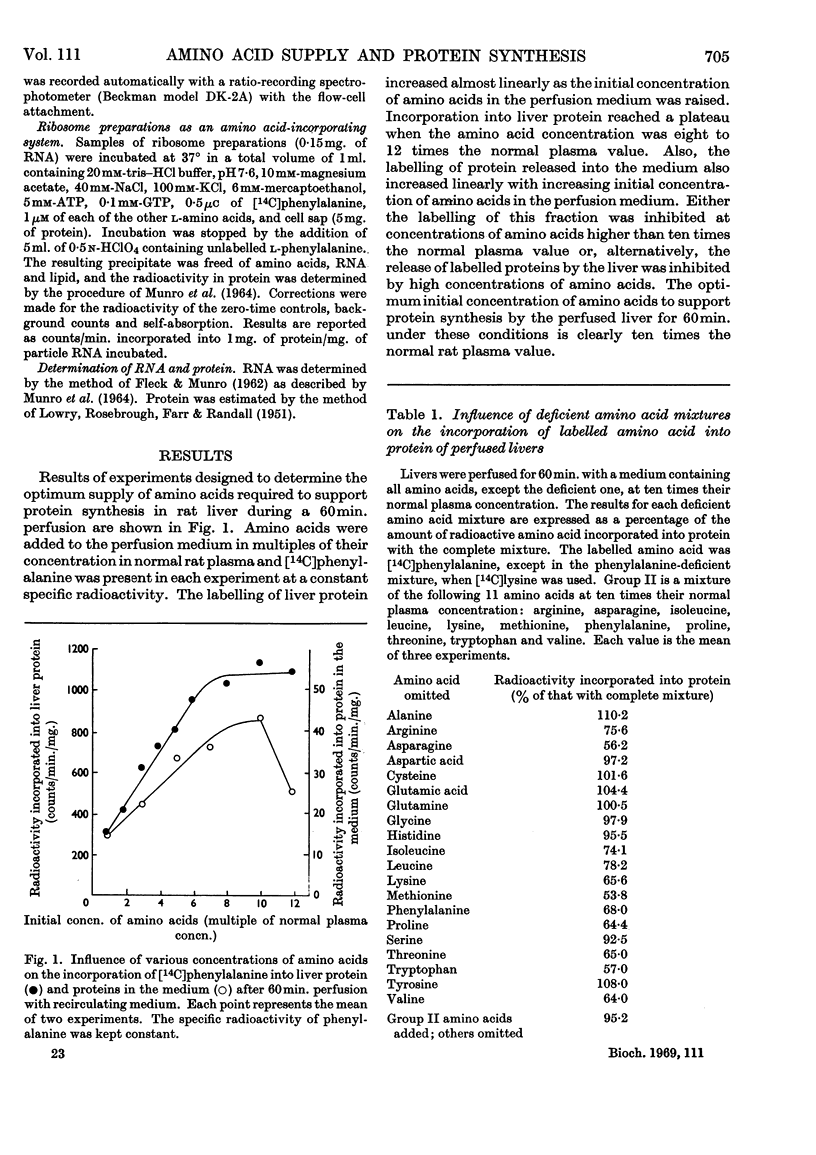
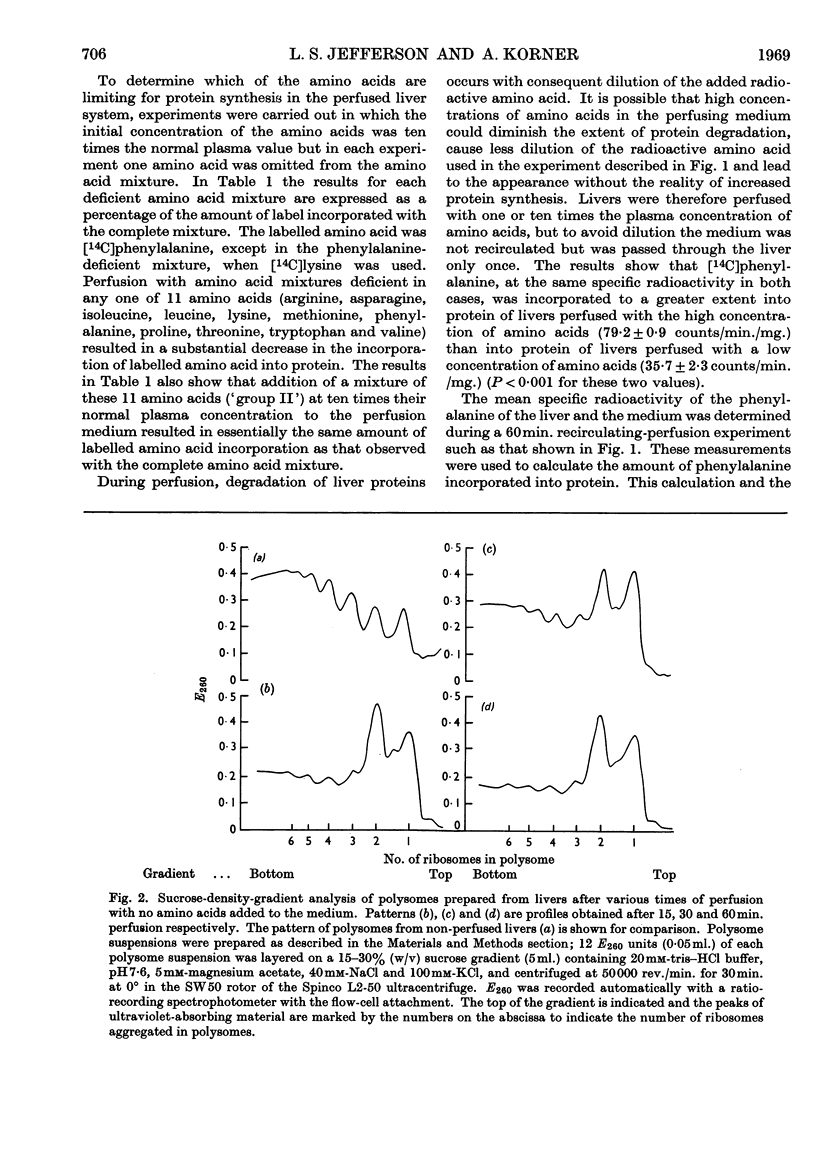
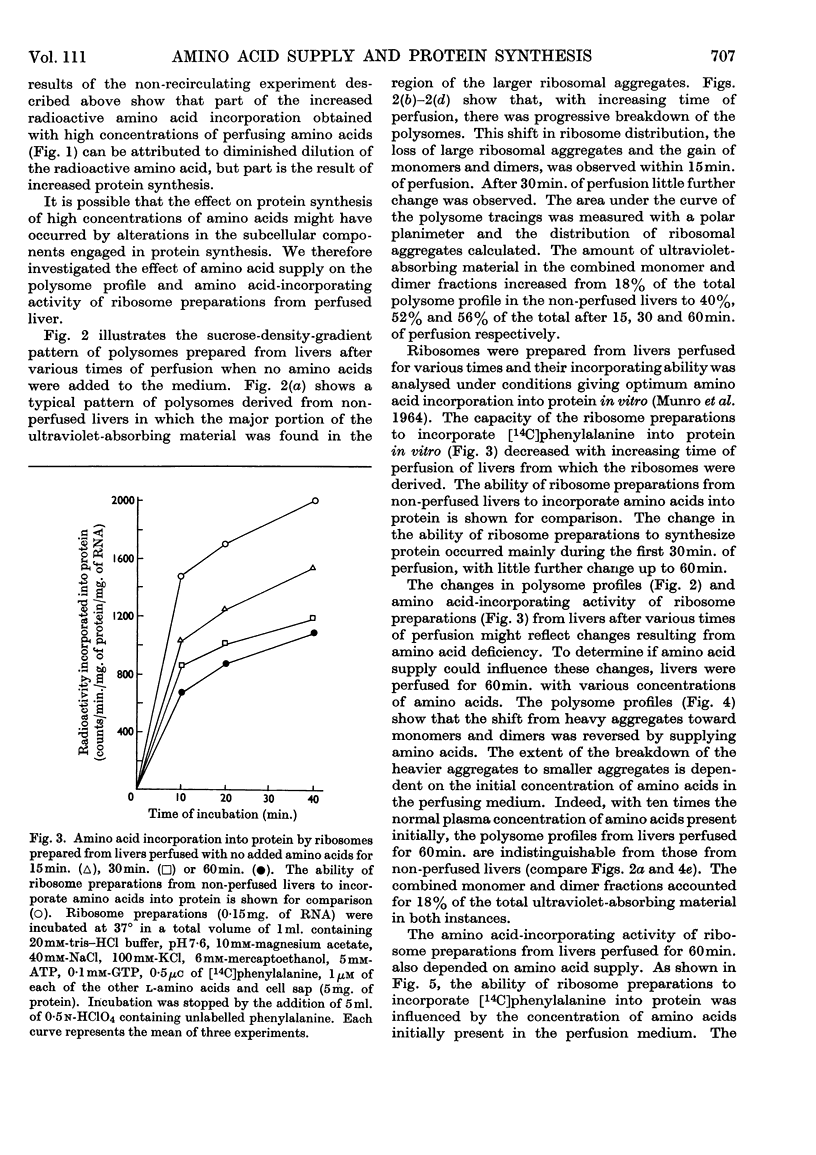
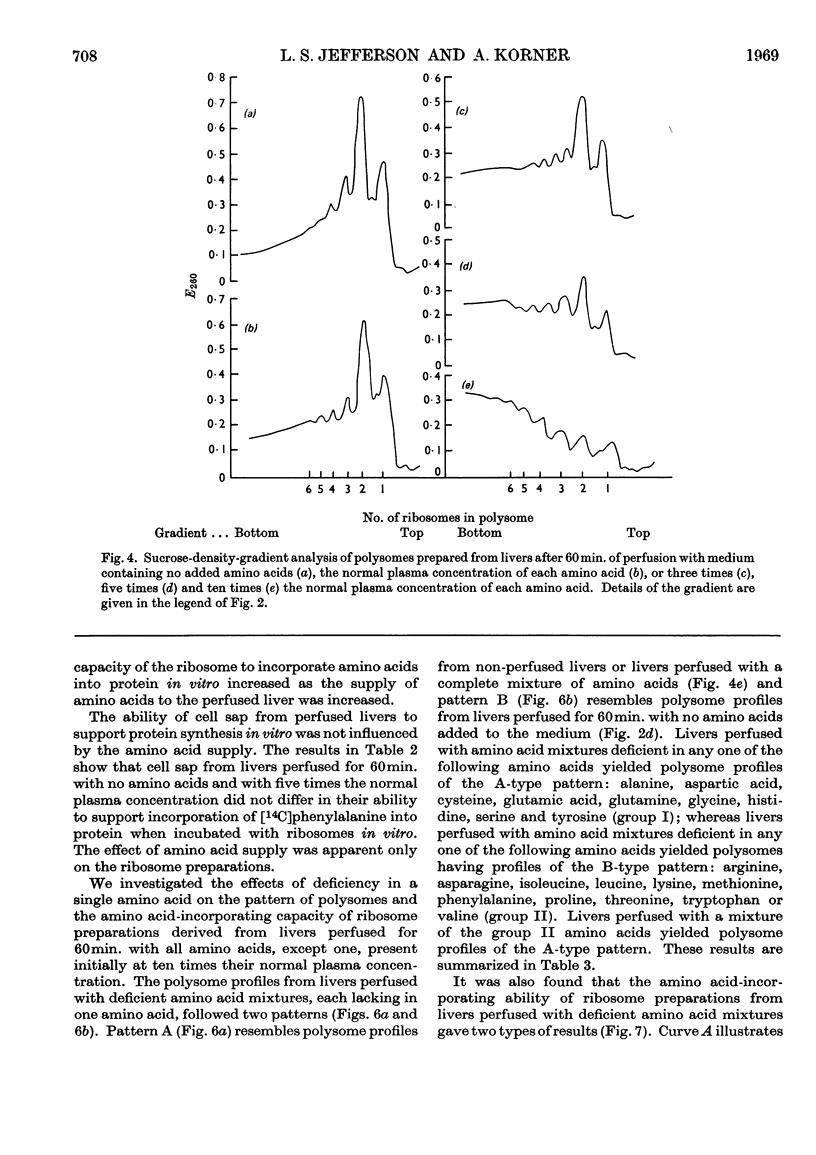
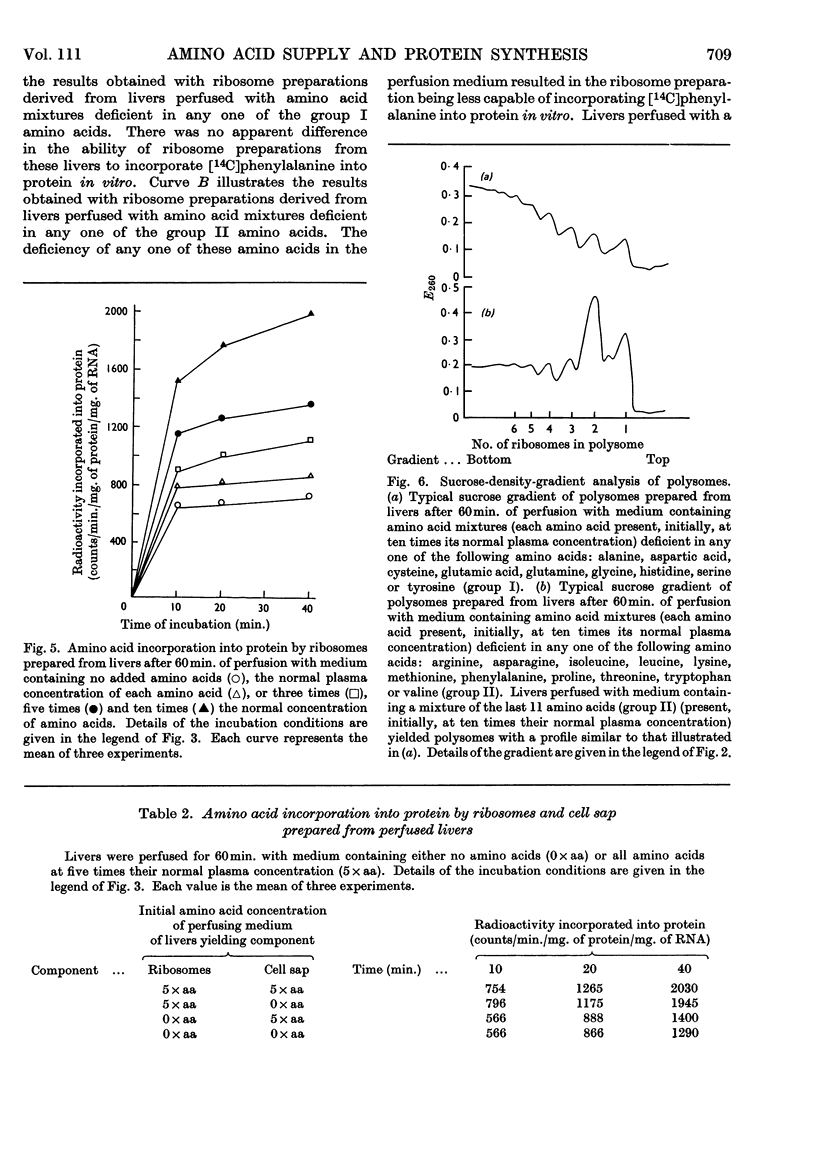
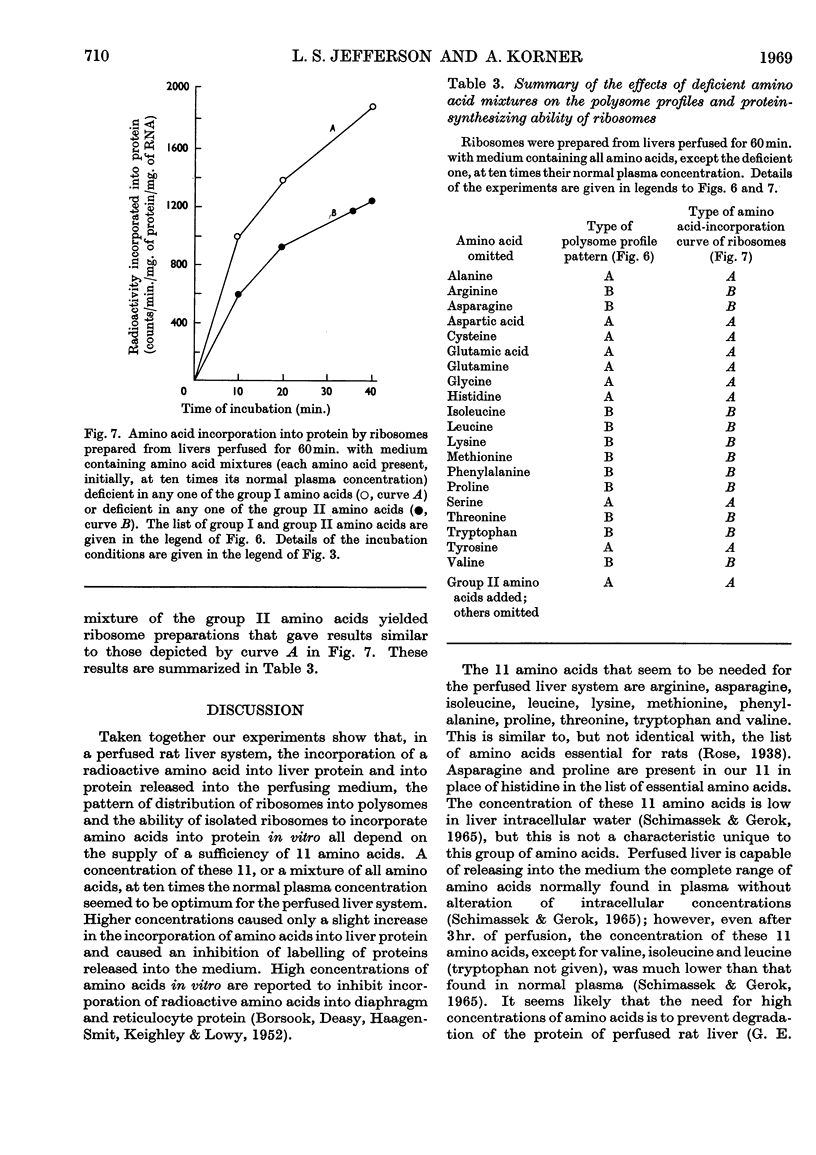
1. The livers of rats were perfused in situ with medium containing mixtures of amino acids in multiples of their concentration in normal rat plasma. The incorporation of labelled amino acid into protein of the liver and of the perfusing medium increased with increasing amino acid concentration. During 60min. perfusions, labelling of liver protein reached a plateau, and labelling of medium protein was inhibited when the initial concentration of the amino acid mixture was more than ten times the normal plasma value. 2. Examination of polysome profiles derived from livers perfused without amino acids in the medium showed that the number of large aggregates was decreased and the number of small aggregates, particularly monomers and dimers, was increased with time of perfusion. The addition of amino acids to the perfusion medium reversed this polysome shift to an extent that was dependent on the initial concentration of amino acids. Polysome profiles derived from livers perfused for 60min. with ten times the normal plasma concentration of amino acids were essentially the same as the polysome profiles of normal non-perfused livers. 3. The ability of ribosome preparations from perfused livers to incorporate amino acids into protein in vitro decreased with increasing time of perfusion when no amino acids were added to the medium, but increased as the concentration of amino acids in the perfusion medium was increased. 4. The ability of cell sap from perfused livers to support protein synthesis in vitro was not influenced by the amino acid concentration of the perfusion medium. 5. Livers were perfused for 60min. with medium containing amino acid mixtures at ten times the normal plasma concentration but deficient in one amino acid. Maximal incorporation of labelled amino acid into liver protein, the stability of the polysome profile and the ability of ribosome preparations to incorporate amino acids into protein were found to depend on the presence of 11 amino acids: arginine, asparagine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, threonine, tryptophan and valine. A mixture of these 11 amino acids, at ten times their normal plasma concentration, stimulated the incorporation of labelled amino acid into liver protein, stabilized the polysome profile and increased the ability of ribosome preparations to incorporate amino acids into protein to the same extent as the complete mixture. 6. It is concluded that the availability of certain amino acids plays an important role in the control of protein synthesis, possibly by stimulating the ability of ribosomes to become, and to remain, attached to messenger RNA.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORSOOK H., DEASY C. L., HAAGENSMIT A. J., KEIGHLEY G., LOWY P. H. Incorporation in vitro of labeled amino acids into proteins of rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(2):669–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baliga B. S., Pronczuk A. W., Munro H. N. Regulation of polysome aggregation in a cell-free system through amino acid supply. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):199–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Park C. R. Control of gluconeogenesis in liver. I. General features of gluconeogenesis in the perfused livers of rats. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2622–2636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLECK A., MUNRO H. N. The precision of ultraviolet absorption measurements in the Schmidt-Thannhauser procedure for nucleic acid estimation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 14;55:571–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90836-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck A., Shepherd J., Munro H. N. Protein synthesis in rat liver: influence of amino acids in diet on microsomes and polysomes. Science. 1965 Oct 29;150(3696):628–629. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3696.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanking B. M., Roberts S. Influence of alterations in intracellular levels of amino-acids on protein-synthesizing activity of isolated ribosomes. Nature. 1965 Aug 21;207(999):862–864. doi: 10.1038/207862a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanking B. M., Roberts S. Stimulation of protein synthesis in vitro by elevated levels of amino acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 8;104(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori M., Fisher J. M., Rabinovitz M. Tryptophan deficiency in rabbit reticulocytes: polyribosomes during interrupted growth of hemoglobin chains. Science. 1967 Jan 6;155(3758):83–84. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3758.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Korner A. A direct effect of growth hormone on the incorporation of precursors into proteins and nucleic acids of perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):826–832. doi: 10.1042/bj1040826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner A., Gumbley J. M. Impaired ability of ribosomes to react with polyuridylic acid after hypophysectomy of the rat: removal of the disability by a cell sap factor. Nature. 1966 Jan 29;209(5022):505–506. doi: 10.1038/209505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTIMORE G. E. Effect of insulin on potassium transfer in isolated rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1315–1319. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro A. J., Jackson R. J., Korner A. Studies on the nature of polysomes. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):289–299. doi: 10.1042/bj0920289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHARFF R., WOOL I. G. CONCENTRATION OF AMINO ACIDS IN RAT MUSCLE AND PLASMA. Nature. 1964 May 9;202:603–604. doi: 10.1038/202603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON M. V., TARVER H. Studies on protein synthesis in vitro; further observations on the incorporation of methionine into liver protein. Arch Biochem. 1950 Feb;25(2):384–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimassek H., Gerok W. Control of the levels of free amino acids in plasma by the liver. Biochem Z. 1965 Dec 31;343(4):407–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidransky H., Bongiorno M., Sarma D. S., Verney E. The influence of tryptophan on hepatic polyribosomes and protein synthesis in fasted mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):242–248. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin T., Verney E., Sidransky H. The influence of nutritional change on polyribosomes of the liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 22;145(1):105–119. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90659-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirewalt W. S., Wool I. G., Cavicchi P. The relation of RNA and protein synthesis to the sedimentation of muscle ribosomes: effect of diabetes and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1885–1892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLA-TREVINO S., FARBER E., STAEHELIN T., WETTSTEIN F. O., NOLL H. BREAKDOWN AND REASSEMBLY OF RAT LIVER ERGOSOMES AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF ETHIONINE OR PUROMYCIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3826–3833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WETTSTEIN F. O., STAEHELIN T., NOLL H. Ribosomal aggregate engaged in protein synthesis: characterization of the ergosome. Nature. 1963 Feb 2;197:430–435. doi: 10.1038/197430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G., Kurihara K. Determination of the number of active muscle ribosomes: effect of diabetes and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2401–2407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Bell J., Munro H. N. The effect of feeding with a tryptophan-free amino acid mixture on rat-liver polysomes and ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):417–428. doi: 10.1042/bj1010417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


