Abstract
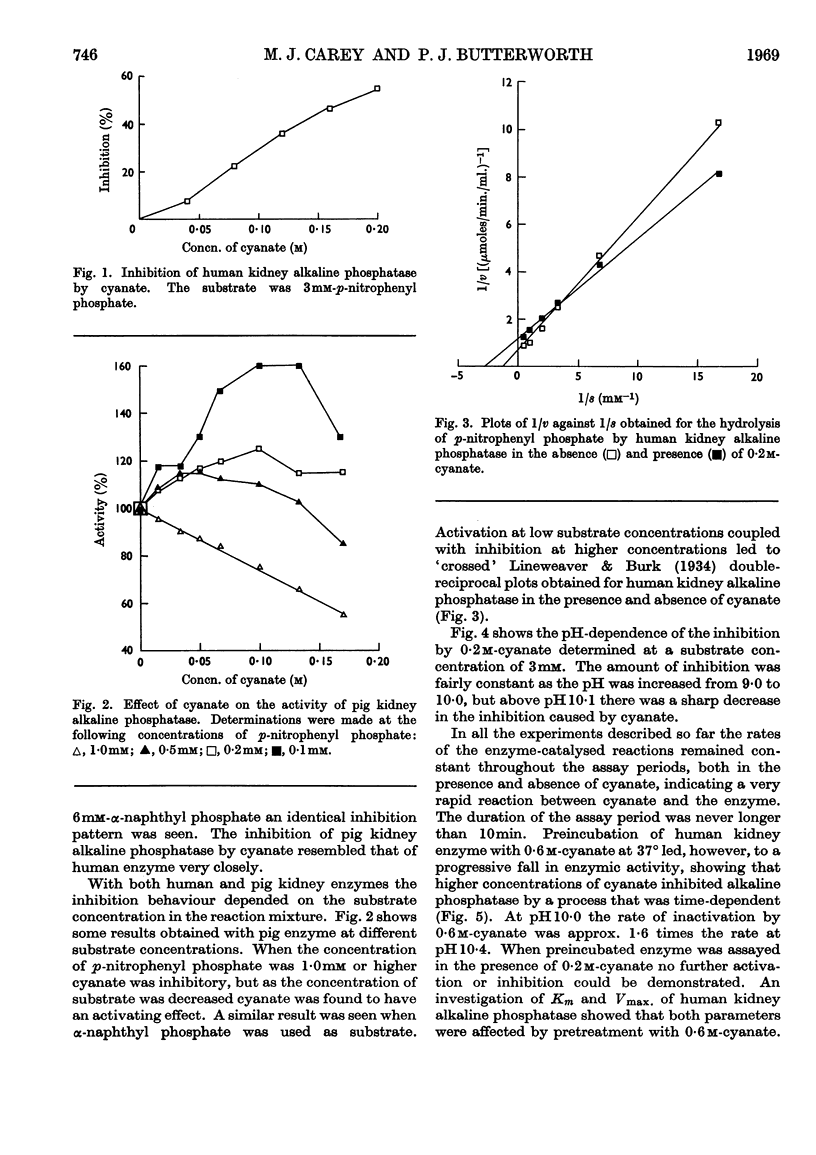
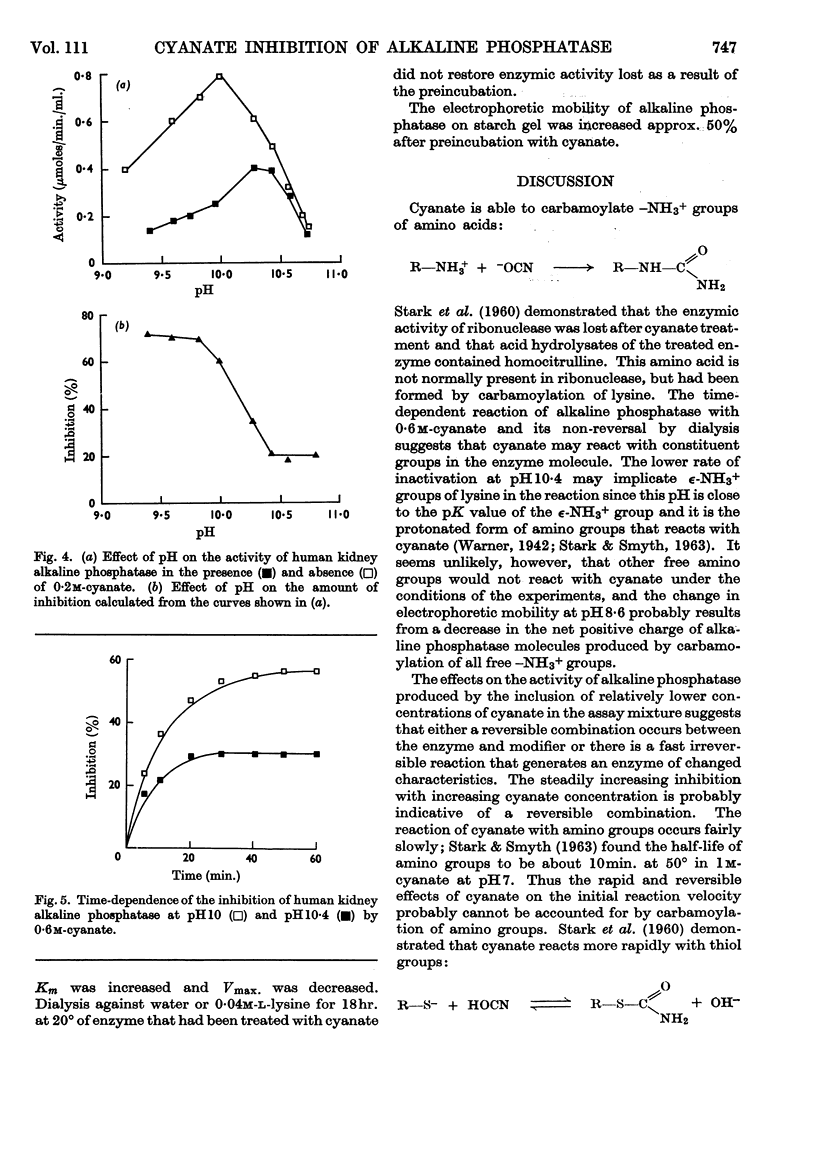
1. At concentrations of cyanate up to 0·2m there is an apparently reversible combination with alkaline phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1), but higher concentrations inhibit alkaline phosphatase irreversibly by a process that is time-dependent. 2. The effect of 0·2m-cyanate on the enzymic reaction velocity depends on the substrate concentration. There is inhibition when the substrate concentration is 1·0mm or higher, but at lower substrate concentrations cyanate has an activating effect. 3. The pH-dependence of the reversible reaction suggests that cyanate may react with a thiol group at or near the active site of the enzyme, preventing a conformational change that is believed to be important in the mechanism of action of alkaline phosphatase. 4. Prolonged treatment with 0·6m-cyanate probably carbamoylates all free amino groups in the enzyme molecule and generates a new enzyme with decreased Vmax. and increased Km.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butterworth P. J. Human kidney and urinary alkaline phosphatases. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(4):467–472. doi: 10.1042/bj1070467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth P. J. The reversible inactivation of pig kidney alkaline phosphatase at low pH. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(2):243–246. doi: 10.1042/bj1080243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernley H. N., Walker P. G. Kinetic behaviour of calf-intestinal alkaline phosphatase with 4-methylumbelliferyl phosphate. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):95–103. doi: 10.1042/bj0970095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H., Ghosh N. K. Influence of reagents reacting with metal, thiol and amino sites of catalytic activity and l-phenylalanine inhibition of rat intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1163–1170. doi: 10.1042/bj1051163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULIK M. D. Starch gel electrophoresis in a discontinous system of buffers. Nature. 1957 Dec 28;180(4600):1477–1479. doi: 10.1038/1801477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARK G. R. ON THE REVERSIBLE REACTION OF CYANATE WITH SULFHYDRYL GROUPS AND THE DETERMINATION OF NH2-TERMINAL CYSTEINE AND CYSTINE IN PROTEINS. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1411–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARK G. R., SMYTH D. G. The use of cyanate for the determination of NH2-terminal residues in proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:214–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


