Abstract
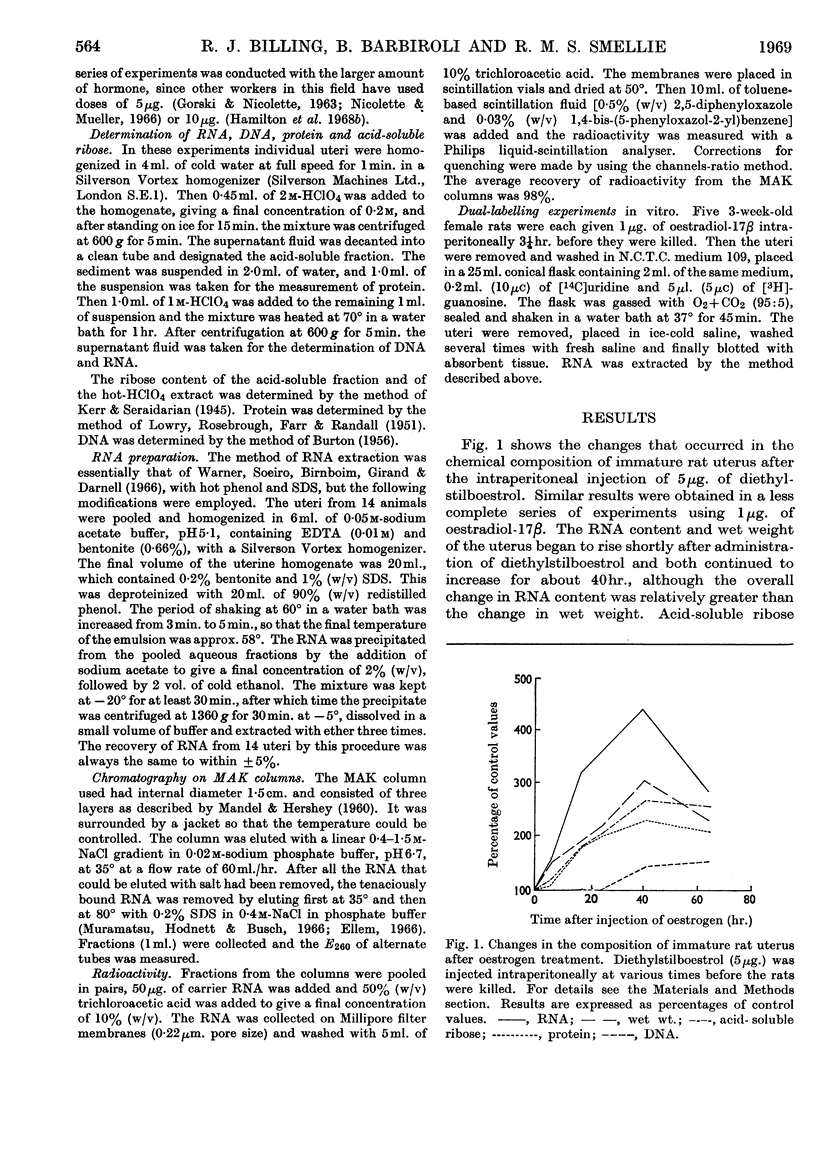
1. After treatment of immature rats with diethylstilboestrol, the wet weight and RNA content of uterine tissue increased rapidly, reaching a peak at 40hr. After an initial lag of a few hours, the acid-soluble ribose and protein contents also rose to maxima at 40hr. No increase in DNA content occurred until at least 24hr. after treatment. 2. The RNA from immature rat uterus isolated at various times up to 6hr. after administration of oestradiol-17β was labelled by injecting [3H]uridine and [3H]guanosine intraperitoneally 30min. before the animals were killed. It was fractionated on columns of kieselguhr coated with methylated serum albumin and the radioactivity in fractions corresponding to transfer RNA, 7s RNA, ribosomal RNA, Q1-RNA, Q2-RNA and DNA-like RNA was determined. 3. The radioactivity of the whole RNA increased steadily for 6hr. after hormone treatment. The earliest changes occurred in the Q1-RNA (ribosomal RNA precursor), whereas at longer time-intervals the radioactivity of the ribosomal RNA, 7s RNA and transfer RNA increased by four- to five-fold. The radioactivity of the DNA-like RNA increased by about 50%, but only at the longer time-intervals. 4. It is concluded that one of the earliest changes in response to oestradiol treatment is a major increase in synthesis of ribosomal RNA followed later by a similar increase in synthesis of transfer RNA and by a much smaller increase in synthesis of DNA-like RNA. The change in synthesis of ribosomal RNA in immature rat uterus may represent one of the most important responses to oestradiol treatment.
Full text
PDF

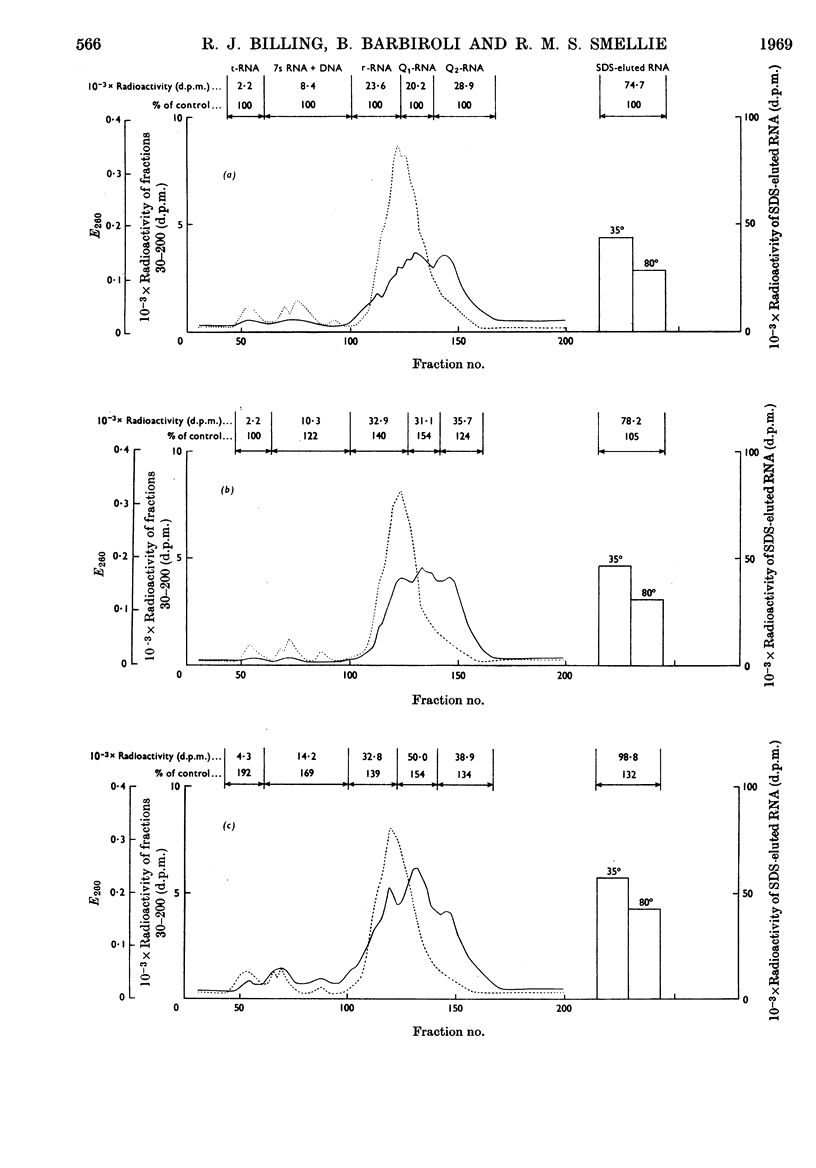
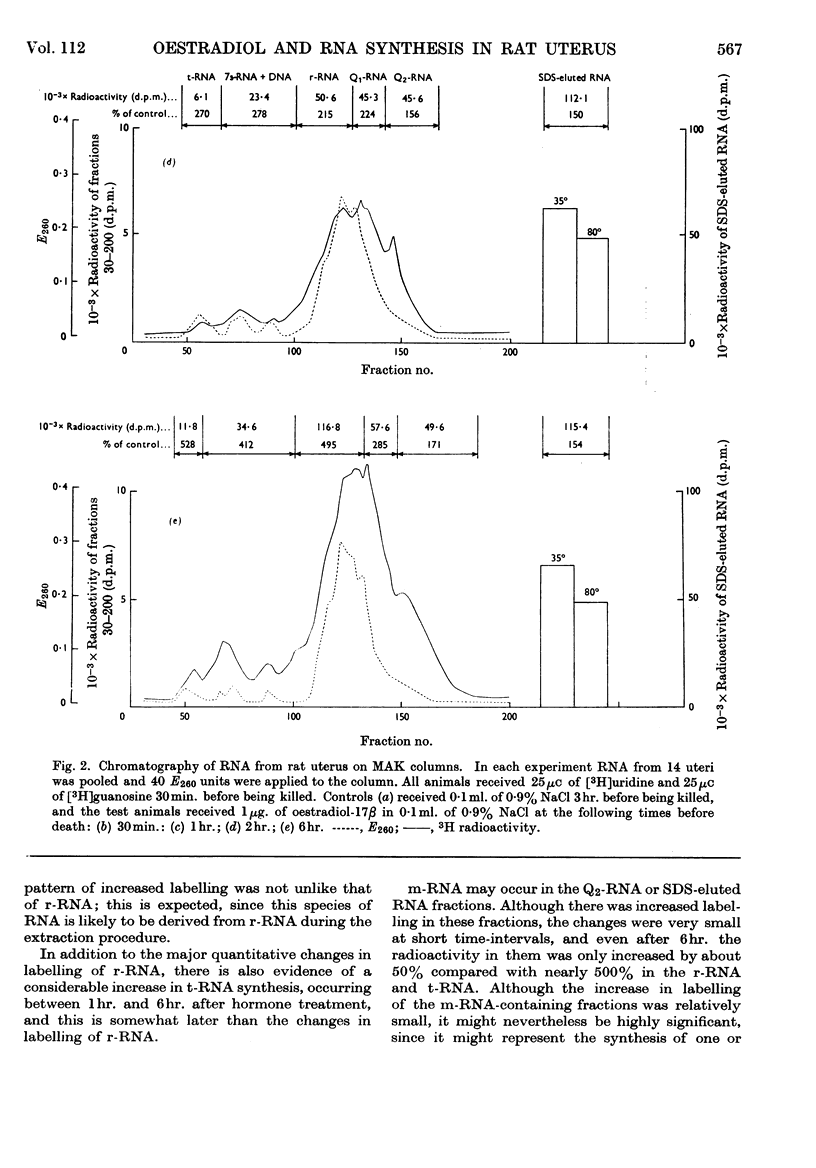
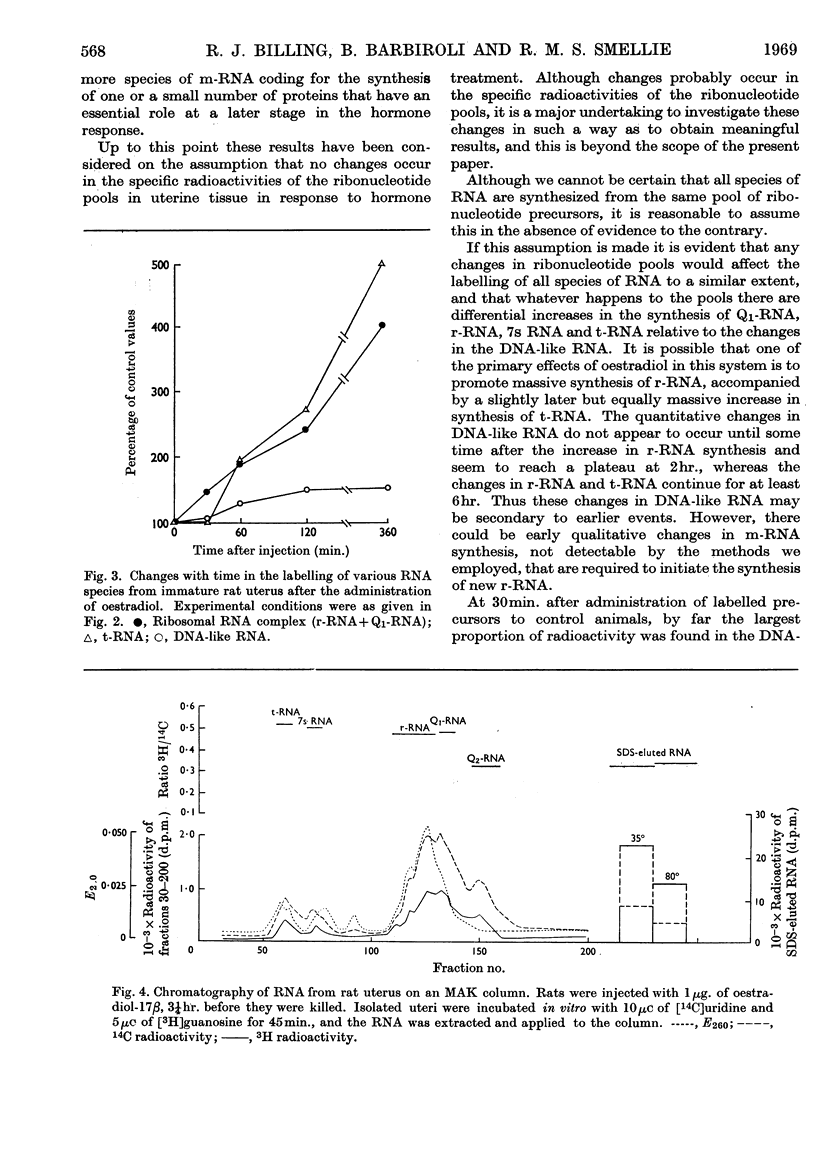

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellem K. A. Some properties of mammalian DNA-like RNA isolated by chromatography on methylated bovine serum albumin-kieselguhr columns. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):283–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORSKI J. EARLY ESTROGEN EFFECTS ON THE ACTIVITY OF UTERINE RIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:889–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORSKI J., NICOLETTE J. A. EARLY ESTROGEN EFFECTS ON NEWLY SYNTHESIZED RNA AND PHOSPHOLIPID IN SUBCELLULAR FRACTIONS OF RAT UTERI. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Dec;103:418–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90431-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. H., Teng C. S., Means A. R. Early estrogen action: nuclear synthesis and accumulation of protein correlated with enhancement of two DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1265–1272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. H., Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. Synthesis of ribonucleic acid during early estrogen action. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 25;243(2):408–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., HERSHEY A. D. A fractionating column for analysis of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. R., Hamilton T. H. Evidence for depression of nuclear protein synthesis and concomitant stimulation of nuclear RNA synthesis during early estrogen action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):686–693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Hodnett J. L., Busch H. Base composition of fractions of nuclear and nucleolar ribonucleic acid obtained by sedimentation and chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 10;241(7):1544–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolette J. A., Mueller G. C. In vitro regulation of RNA polymerase in estrogen-treated uteri. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 22;24(6):851–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pene J. J., Knight E., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Characterization of a new low molecular weight RNA in HeLa cell ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):609–623. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. Hormonal regulation of growth and protein synthesis. Nature. 1968 Jul 27;219(5152):331–337. doi: 10.1038/219331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. Hormones and the synthesis and utilization of ribonucleic acids. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1966;5:191–250. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng C. S., Hamilton T. H. Regulation of polyribosome formation and protein synthesis in the uterus. Effect of ovariectomy and administration of oestradiol-17beta on the amino acid-incorporation activity in vitro and the cytoplasmic concentration in vivo of polyribosomal preparation. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1101–1109. doi: 10.1042/bj1051101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Soeiro R., Birnboim H. C., Girard M., Darnell J. E. Rapidly labeled HeLa cell nuclear RNA. I. Identification by zone sedimentation of a heterogeneous fraction separate from ribosomal precursor RNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):349–361. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


