Abstract
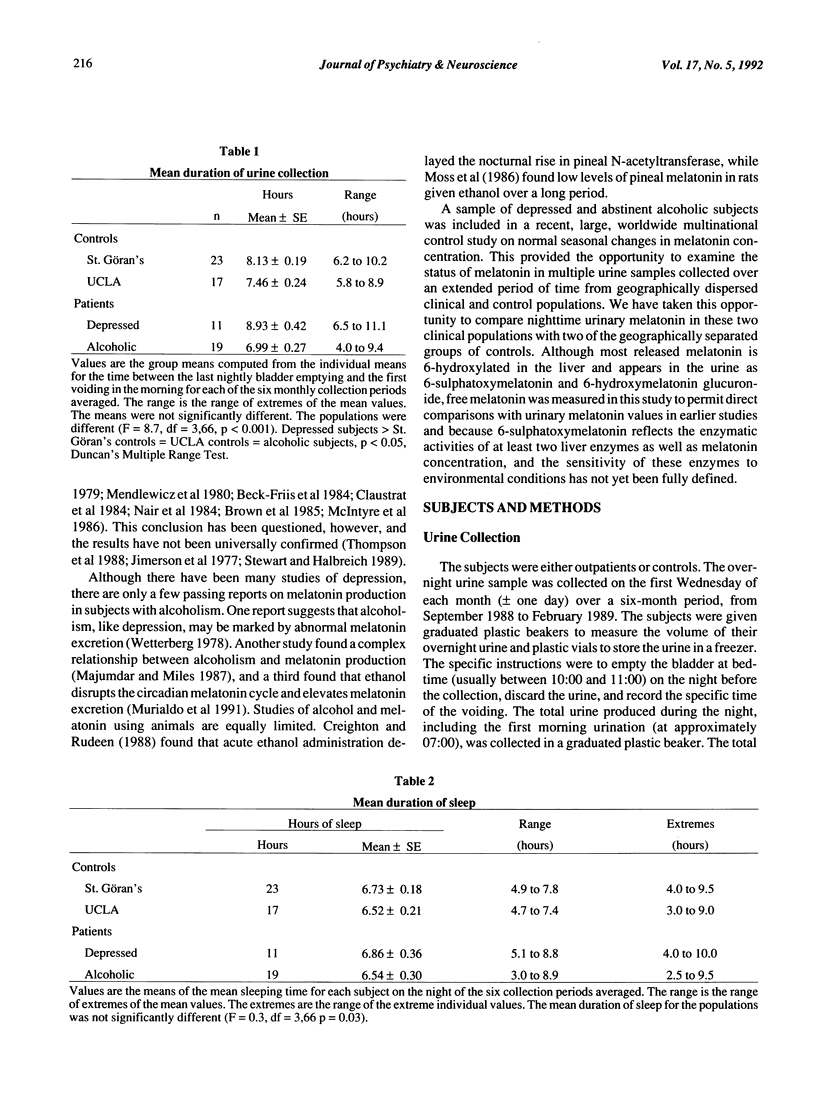
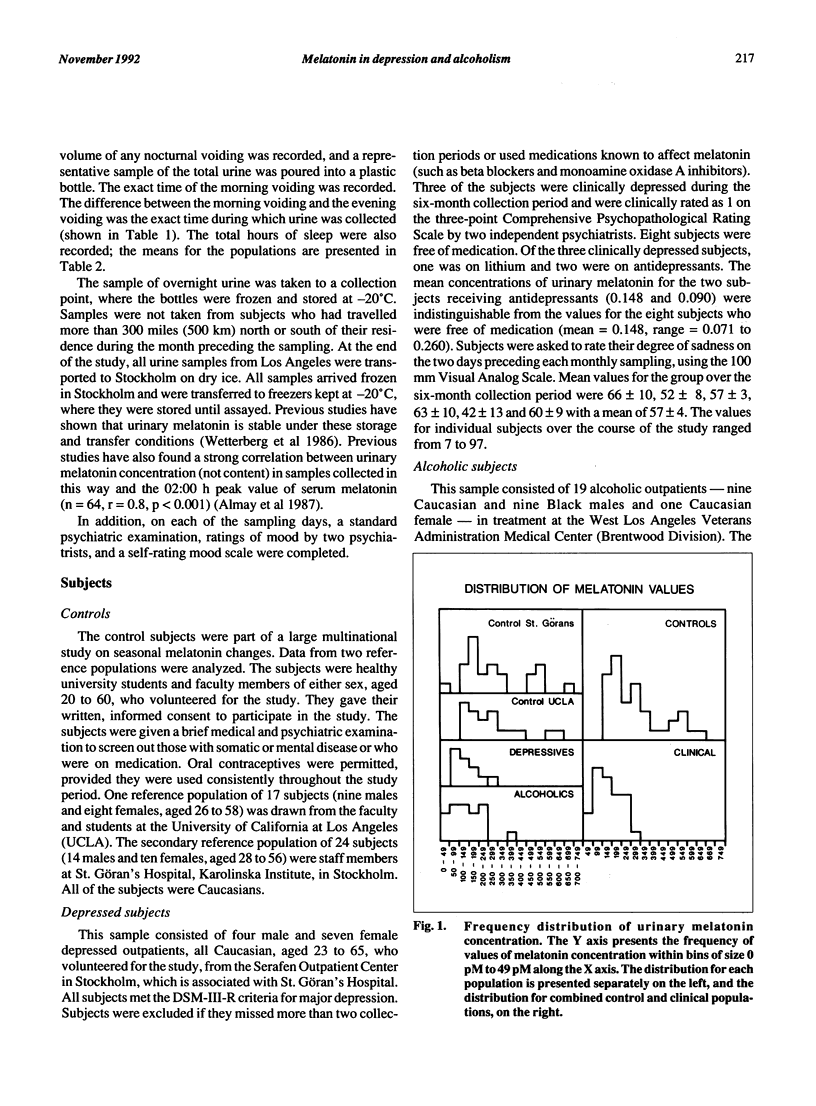
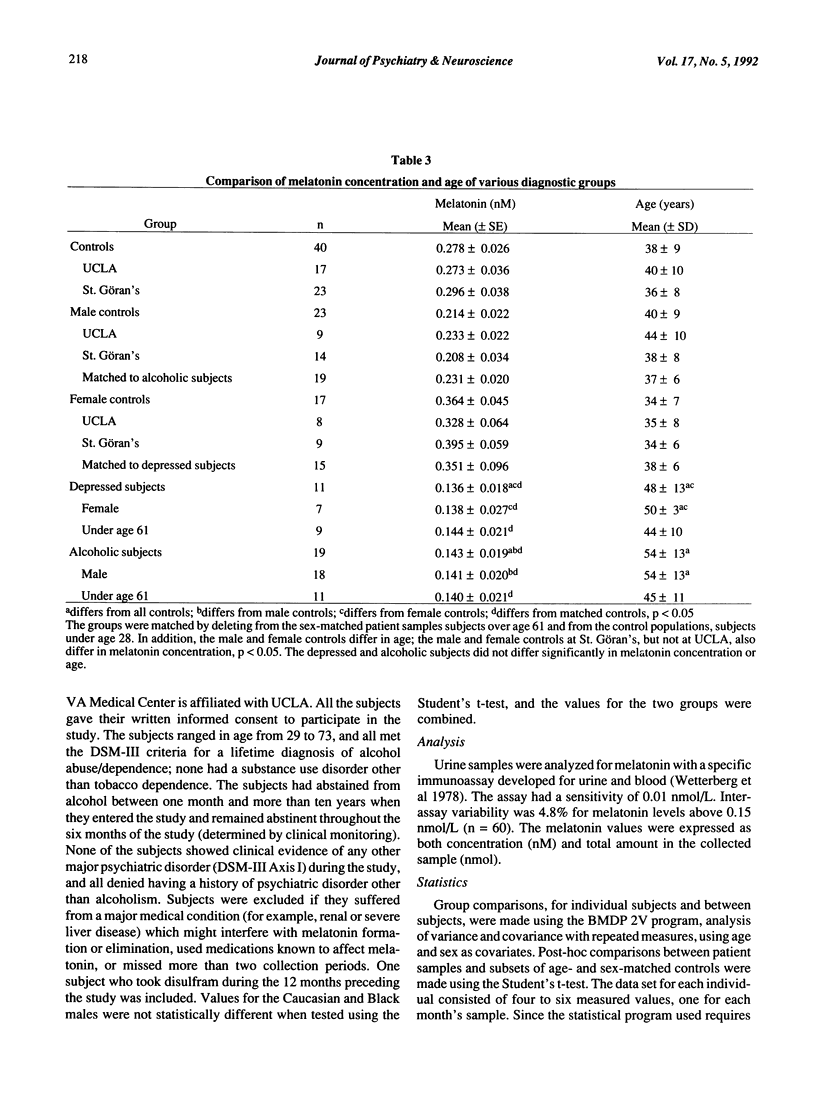
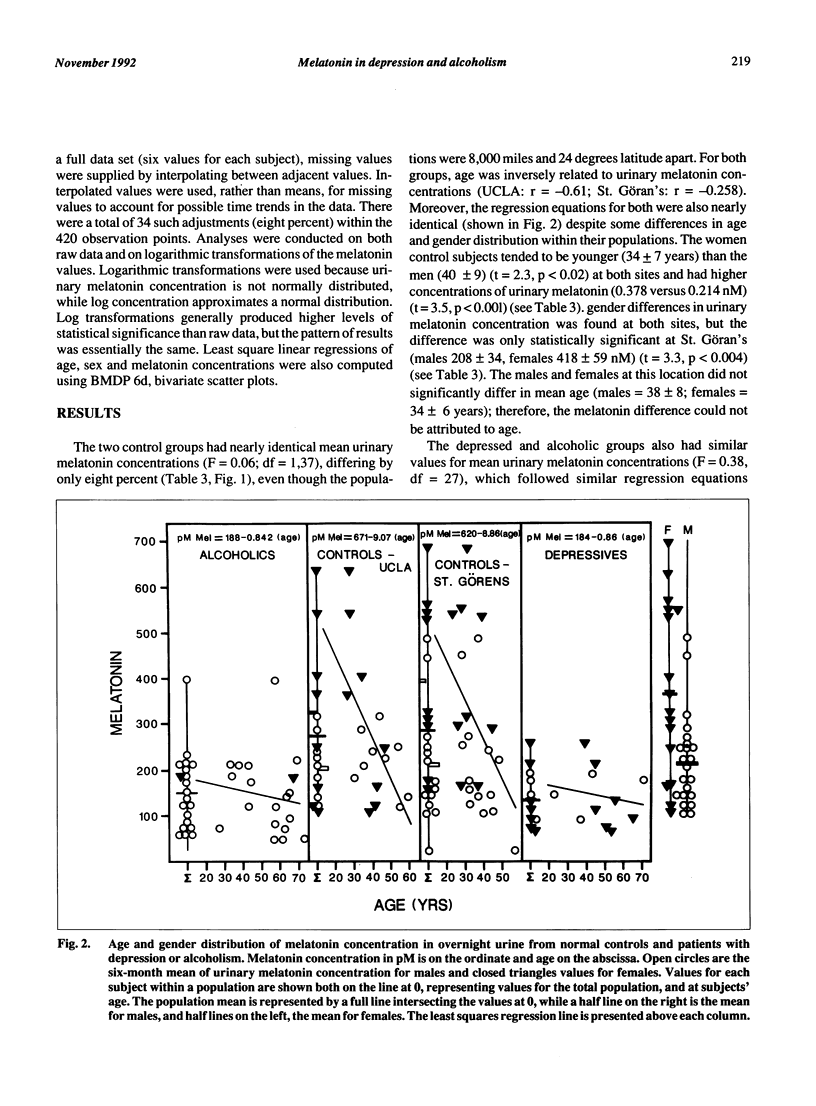
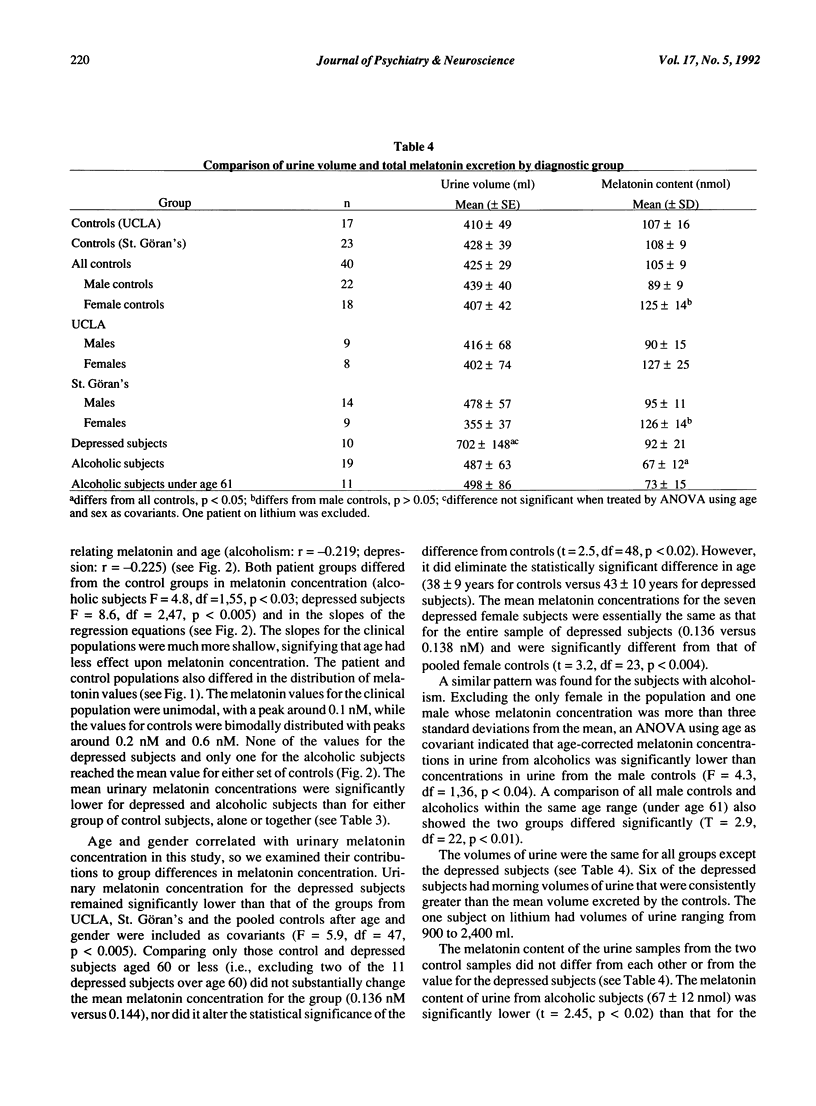
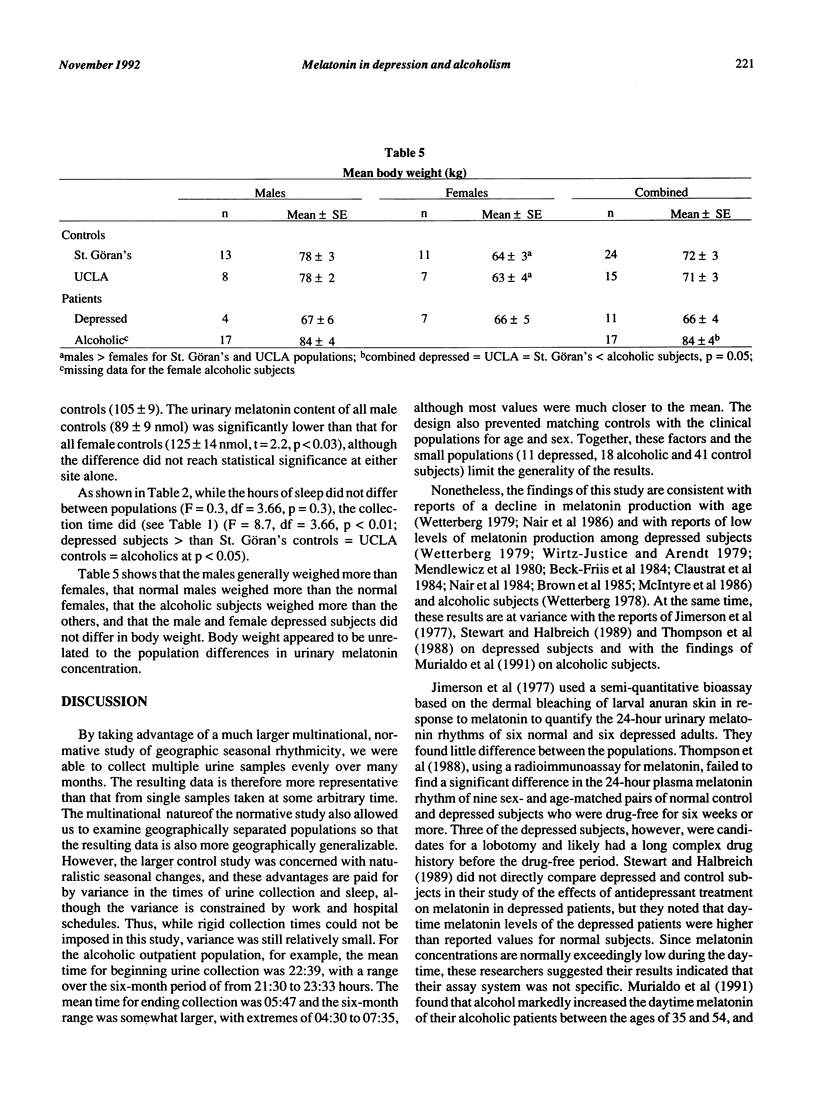
Two normal control populations, separated by 8,000 miles and 24 degrees of latitude, had similar six-month mean values for overnight urinary melatonin concentrations. These values were significantly higher than six-month values for depressed subjects and abstinent alcoholic subjects, while the means for the two clinical populations were similar. Age and urinary melatonin concentration in the control and clinical populations were inversely related, but the slopes of the linear regression equations were ten times steeper for the control populations than for the clinical populations. Differences in age and sex distributions accounted for some of the differences in values between controls and the clinical populations, although controls still differed from the clinical populations, even after sex and age were factored out. The disparate slopes for age and melatonin concentrations may contribute to some of the conflicting findings of studies comparing populations of different ages. The total melatonin content in the samples from alcoholic subjects, but not the depressed subjects, was lower than that for controls. The difference in the urinary melatonin concentration between the controls and the two patient groups was not accounted for by difference in duration of urine collection period, hours of sleep or body weight.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almay B. G., von Knorring L., Wetterberg L. Melatonin in serum and urine in patients with idiopathic pain syndromes. Psychiatry Res. 1987 Nov;22(3):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(87)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arendt J., Hampton S., English J., Kwasowski P., Marks V. 24-hour profiles of melatonin, cortisol, insulin, C-peptide and GIP following a meal and subsequent fasting. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1982 Jan;16(1):89–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1982.tb03151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck-Friis J., von Rosen D., Kjellman B. F., Ljunggren J. G., Wetterberg L. Melatonin in relation to body measures, sex, age, season and the use of drugs in patients with major affective disorders and healthy subjects. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1984;9(3):261–277. doi: 10.1016/0306-4530(84)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R., Kocsis J. H., Caroff S., Amsterdam J., Winokur A., Stokes P. E., Frazer A. Differences in nocturnal melatonin secretion between melancholic depressed patients and control subjects. Am J Psychiatry. 1985 Jul;142(7):811–816. doi: 10.1176/ajp.142.7.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claustrat B., Chazot G., Brun J., Jordan D., Sassolas G. A chronobiological study of melatonin and cortisol secretion in depressed subjects: plasma melatonin, a biochemical marker in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 1984 Aug;19(8):1215–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton J. A., Rudeen P. K. Effects of acute ethanol administration on nocturnal pineal serotonin N-acetyltransferase activity. Life Sci. 1988;43(24):2007–2014. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90574-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier I. N., Arendt J., Johnstone E. C., Crow T. J. Reduced nocturnal melatonin secretion in chronic schizophrenia: relationship to body weight. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1982 Aug;17(2):181–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1982.tb01577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson P. H., Sarna G. S., Kantamaneni B. D., Curzon G. Monitoring the effect of a tryptophan load on brain indole metabolism in freely moving rats by simultaneous cerebrospinal fluid sampling and brain dialysis. J Neurochem. 1985 Apr;44(4):1266–1273. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb08753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimerson D. C., Lynch H. J., Post R. M., Wurtman R. J., Bunney W. E., Jr Urinary melatonin rhythms during sleep deprivation in depressed patients and normals. Life Sci. 1977 May 1;20(9):1501–1508. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90441-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPPERS J. A. The development, topographical relations and innervation of the epiphysis cerebri in the albino rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1960;52:163–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00338980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar S. K., Miles A. Disturbed melatonin secretion in chronic alcoholism and withdrawal. Clin Chem. 1987 Jul;33(7):1291–1291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre I. M., Judd F. K., Norman T. R., Burrows G. D. Plasma melatonin concentrations in depression. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 1986 Sep;20(3):381–383. doi: 10.3109/00048678609158887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlewicz J., Branchey L., Weinberg U., Branchey M., Linkowski P., Weitzman E. D. The 24 hour pattern of plasma melatonin in depressed patients before and after treatment. Commun Psychopharmacol. 1980;4(1):49–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles A., Philbrick D. R. Melatonin and psychiatry. Biol Psychiatry. 1988 Feb 15;23(4):405–425. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(88)90291-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Eichler V. B. Loss of a circadian adrenal corticosterone rhythm following suprachiasmatic lesions in the rat. Brain Res. 1972 Jul 13;42(1):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Heller A., Wurtman R. J., Axelrod J. Visual pathway mediating pineal response to environmental light. Science. 1967 Jan 13;155(3759):220–223. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3759.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss H. B., Tamarkin L., Majchrowicz E., Martin P. R., Linnoila M. Pineal function during ethanol intoxication, dependence, and withdrawal. Life Sci. 1986 Dec 8;39(23):2209–2214. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murialdo G., Filippi U., Costelli P., Fonzi S., Bo P., Polleri A., Savoldi F. Urine melatonin in alcoholic patients: a marker of alcohol abuse? J Endocrinol Invest. 1991 Jun;14(6):503–507. doi: 10.1007/BF03346853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair N. P., Hariharasubramanian N., Pilapil C. Circadian rhythm of plasma melatonin in endogenous depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1984;8(4-6):715–718. doi: 10.1016/0278-5846(84)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair N. P., Hariharasubramanian N., Pilapil C., Isaac I., Thavundayil J. X. Plasma melatonin--an index of brain aging in humans? Biol Psychiatry. 1986 Feb;21(2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(86)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. W., Halbreich U. Plasma melatonin levels in depressed patients before and after treatment with antidepressant medication. Biol Psychiatry. 1989 Jan;25(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(89)90144-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C., Franey C., Arendt J., Checkley S. A. A comparison of melatonin secretion in depressed patients and normal subjects. Br J Psychiatry. 1988 Feb;152:260–265. doi: 10.1192/bjp.152.2.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterberg L. Clinical importance of melatonin. Prog Brain Res. 1979;52:539–547. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)62962-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterberg L., Eriksson O., Friberg Y., Vangbo B. A simplified radioimmunoassay for melatonin and its application to biological fluids. Preliminary observations on the half-life of plasma melatonin in man. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Jun;86(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterberg L. Melatonin in humans physiological and clinical studies. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1978;(13):289–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterberg L. The relationship between the pineal gland and the pituitary--adrenal axis in health, endocrine and psychiatric conditions. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1983;8(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0306-4530(83)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yie S. M., Liu G. Y., Johansson E., Brown C., Brown G. M. Age-associated changes and sex differences in urinary 6-sulphatoxymelatonin circadian rhythm in the rat. Life Sci. 1992;50(17):1235–1242. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90323-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuwiler A. Effects of steroids on serotonin-N-acetyltransferase activity of pineals in organ culture. J Neurochem. 1989 Jan;52(1):46–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb10896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


