Abstract
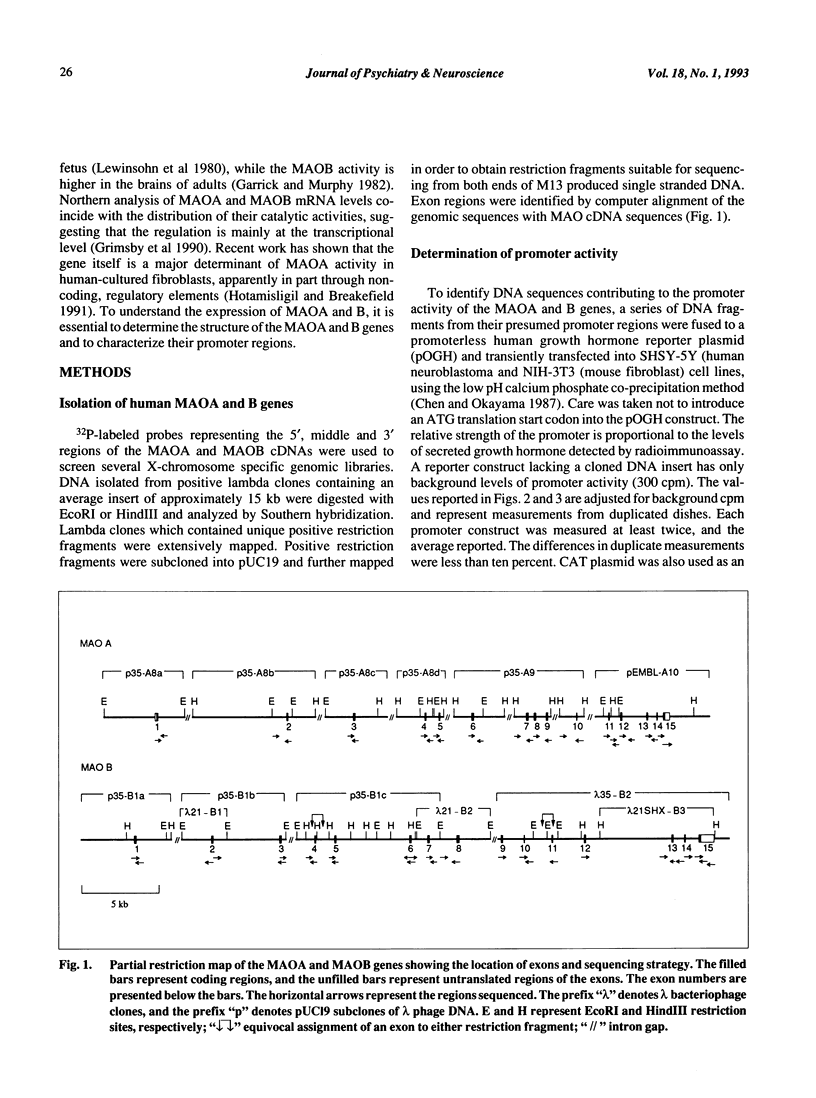
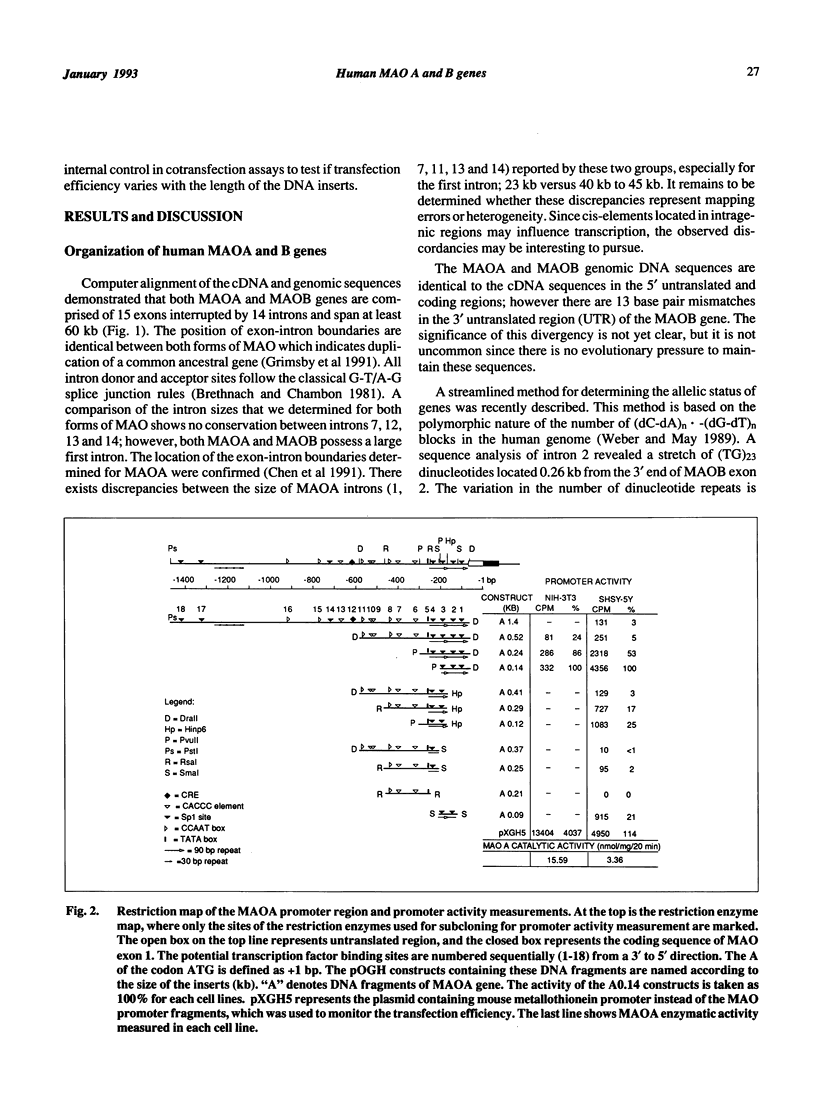
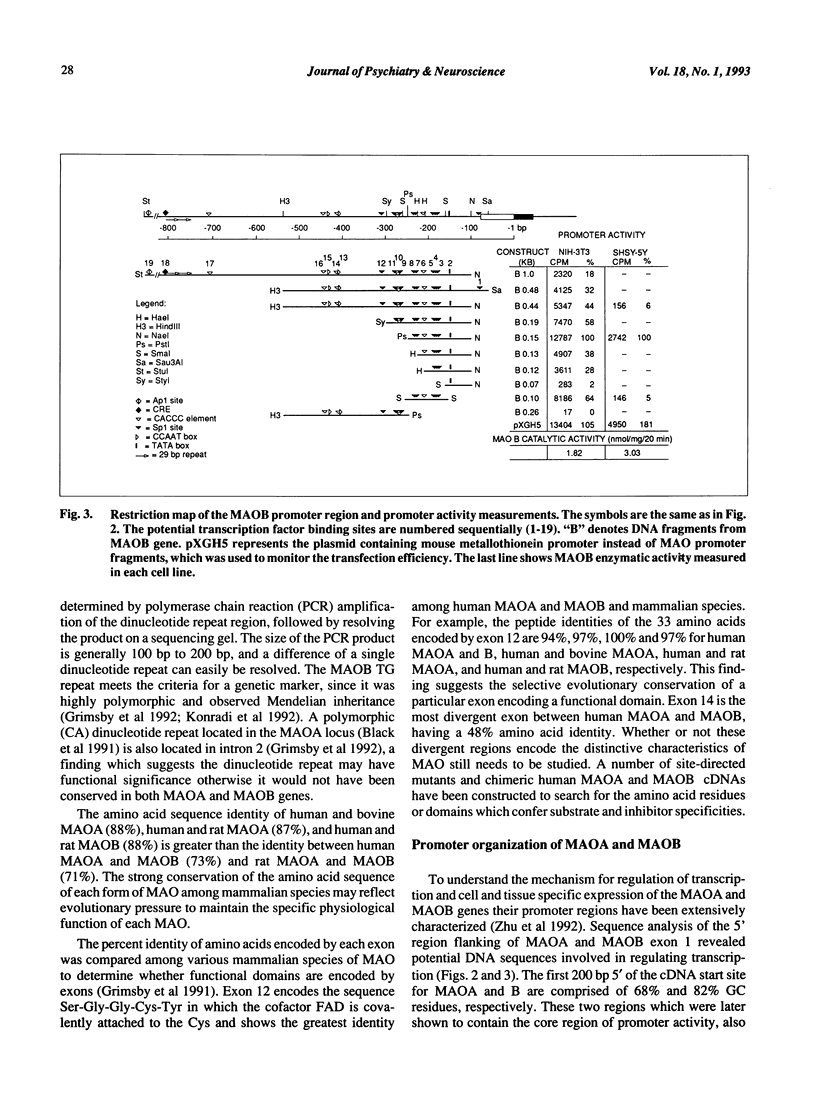
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) A and B play an important role in regulating levels of biogenic amines. MAO A and B cDNAs have been cloned and the deduced amino acids share 73% sequence identity. The genes for MAOA and B are comprised of 15 exons interspersed by 14 introns, span at least 60 kb and exhibit identical exon-intron organization. These findings suggest that the MAOA and MAOB genes are derived from the duplication of a common ancestral gene. The core promoter region of MAOA is comprised of two 90 bp repeats, each of which contains two Spl elements and lacks a TATA box. The MAOB core promoter region contains two sets of overlapping Spl sites which flank a CACCC element all upstream of a TATA box. The different organization of the MAOA and MAOB promoters may underlie their different cell and tissue specific expression.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach A. W., Lan N. C., Johnson D. L., Abell C. W., Bembenek M. E., Kwan S. W., Seeburg P. H., Shih J. C. cDNA cloning of human liver monoamine oxidase A and B: molecular basis of differences in enzymatic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4934–4938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black G. C., Chen Z. Y., Craig I. W., Powell J. F. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the MAOA locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):689–689. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.689-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond P. A., Cundall R. L. Properties of monoamine oxidase (MAO) in human blood platelets, plasma, lymphocytes and granulocytes. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Oct 15;80(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Y., Hotamisligil G. S., Huang J. K., Wen L., Ezzeddine D., Aydin-Muderrisoglu N., Powell J. F., Huang R. H., Breakefield X. O., Craig I. Structure of the human gene for monoamine oxidase type A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4537–4541. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba K., Trevor A., Castagnoli N., Jr Metabolism of the neurotoxic tertiary amine, MPTP, by brain monoamine oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 30;120(2):574–578. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly C. H., Murphy D. L. Substrate- and inhibitor-related characteristics of human platelet monoamine oxidase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 May 1;26(9):853–858. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egashira T., Yamanaka Y. Further studies on the synthesis of A-form monoamine oxidase. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct;31(5):763–770. doi: 10.1254/jjp.31.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler J. S., MacGregor R. R., Wolf A. P., Arnett C. D., Dewey S. L., Schlyer D., Christman D., Logan J., Smith M., Sachs H. Mapping human brain monoamine oxidase A and B with 11C-labeled suicide inactivators and PET. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):481–485. doi: 10.1126/science.3099392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrick N. A., Murphy D. L. Monoamine oxidase type A: differences in selectivity towards l-norepinephrine compared to serotonin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 15;31(24):4061–4066. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90656-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenawalt J. W., Schnaitman C. An appraisal of the use of monoamine oxidase as an enzyme marker for the outer membrane of rat liver mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jul;46(1):173–179. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimsby J., Chen K., Devor E. J., Cloninger C. R., Shih J. C. Dinucleotide repeat (TG)23 polymorphism in the MAOB gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):924–924. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimsby J., Chen K., Wang L. J., Lan N. C., Shih J. C. Human monoamine oxidase A and B genes exhibit identical exon-intron organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimsby J., Lan N. C., Neve R., Chen K., Shih J. C. Tissue distribution of human monoamine oxidase A and B mRNA. J Neurochem. 1990 Oct;55(4):1166–1169. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb03121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotamisligil G. S., Breakefield X. O. Human monoamine oxidase A gene determines levels of enzyme activity. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):383–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu Y. P., Weyler W., Chen S., Sims K. B., Rinehart W. B., Utterback M. C., Powell J. F., Breakefield X. O. Structural features of human monoamine oxidase A elucidated from cDNA and peptide sequences. J Neurochem. 1988 Oct;51(4):1321–1324. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito A., Kuwahara T., Inadome S., Sagara Y. Molecular cloning of a cDNA for rat liver monoamine oxidase B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):970–976. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80969-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konradi C., Ozelius L., Breakefield X. O. Highly polymorphic (GT)n repeat sequence in intron II of the human MAOB gene. Genomics. 1992 Jan;12(1):176–177. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90426-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara T., Takamoto S., Ito A. Primary structure of rat monoamine oxidase A deduced from cDNA and its expression in rat tissues. Agric Biol Chem. 1990 Jan;54(1):253–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan N. C., Heinzmann C., Gal A., Klisak I., Orth U., Lai E., Grimsby J., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., Shih J. C. Human monoamine oxidase A and B genes map to Xp 11.23 and are deleted in a patient with Norrie disease. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):552–559. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90279-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E. R., Powell J. F., Buckle V. J., Hsu Y. P., Breakefield X. O., Craig I. W. Localization of human monoamine oxidase-A gene to Xp11.23-11.4 by in situ hybridization: implications for Norrie disease. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):368–370. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewinsohn R., Glover V., Sandler M. Development of benzylamine oxidase and monoamine oxidase A and B in man. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 May 1;29(9):1221–1230. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. L., Donnelly C. H. Monoamine oxidase in man: enzyme characteristics in platelets, plasma, and other human tissues. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1974;12(0):71–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozelius L., Hsu Y. P., Bruns G., Powell J. F., Chen S., Weyler W., Utterback M., Zucker D., Haines J., Trofatter J. A. Human monoamine oxidase gene (MAOA): chromosome position (Xp21-p11) and DNA polymorphism. Genomics. 1988 Jul;3(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. F., Hsu Y. P., Weyler W., Chen S. A., Salach J., Andrikopoulos K., Mallet J., Breakefield X. O. The primary structure of bovine monoamine oxidase type A. Comparison with peptide sequences of bovine monoamine oxidase type B and other flavoenzymes. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):407–413. doi: 10.1042/bj2590407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih J. C. Molecular basis of human MAO A and B. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1991 Jan;4(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims K. B., de la Chapelle A., Norio R., Sankila E. M., Hsu Y. P., Rinehart W. B., Corey T. J., Ozelius L., Powell J. F., Bruns G. Monoamine oxidase deficiency in males with an X chromosome deletion. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1069–1076. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. L., Cavenar J. O., Jr, Maltbie A. A., Lister P., Zung W. W. Familial biochemical and clinical correlates of alcoholics with low platelet monoamine oxidase activity. Biol Psychiatry. 1979 Apr;14(2):385–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K., Shih J., Fong T., Young H., Gelfand R., Boyd J., Simpson G., Sloane R. B. Elevated platelet monoamine oxidase activity in patients wth nonendogenous depression. Am J Psychiatry. 1980 Oct;137(10):1258–1259. doi: 10.1176/ajp.137.10.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. J., Murphy D. L. Low platelet monoamine oxidase activity and schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1976;2(1):77–89. doi: 10.1093/schbul/2.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Q. S., Grimsby J., Chen K., Shih J. C. Promoter organization and activity of human monoamine oxidase (MAO) A and B genes. J Neurosci. 1992 Nov;12(11):4437–4446. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-11-04437.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


