Abstract
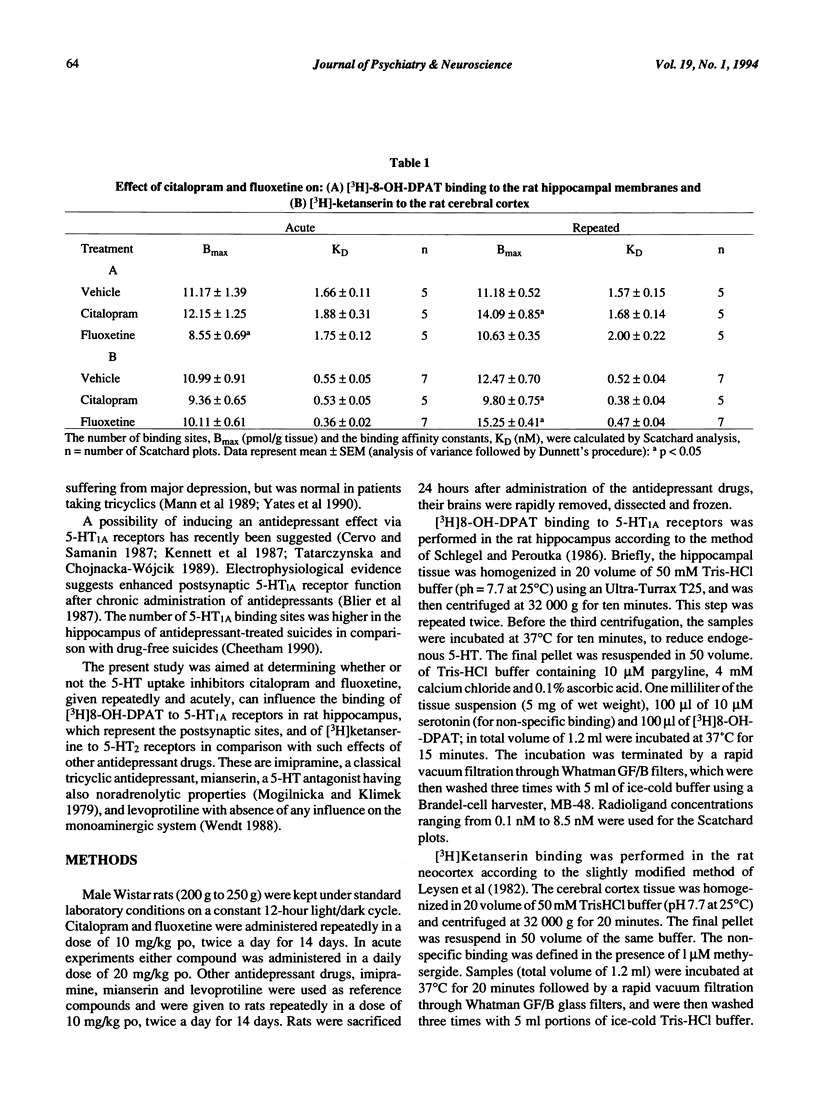
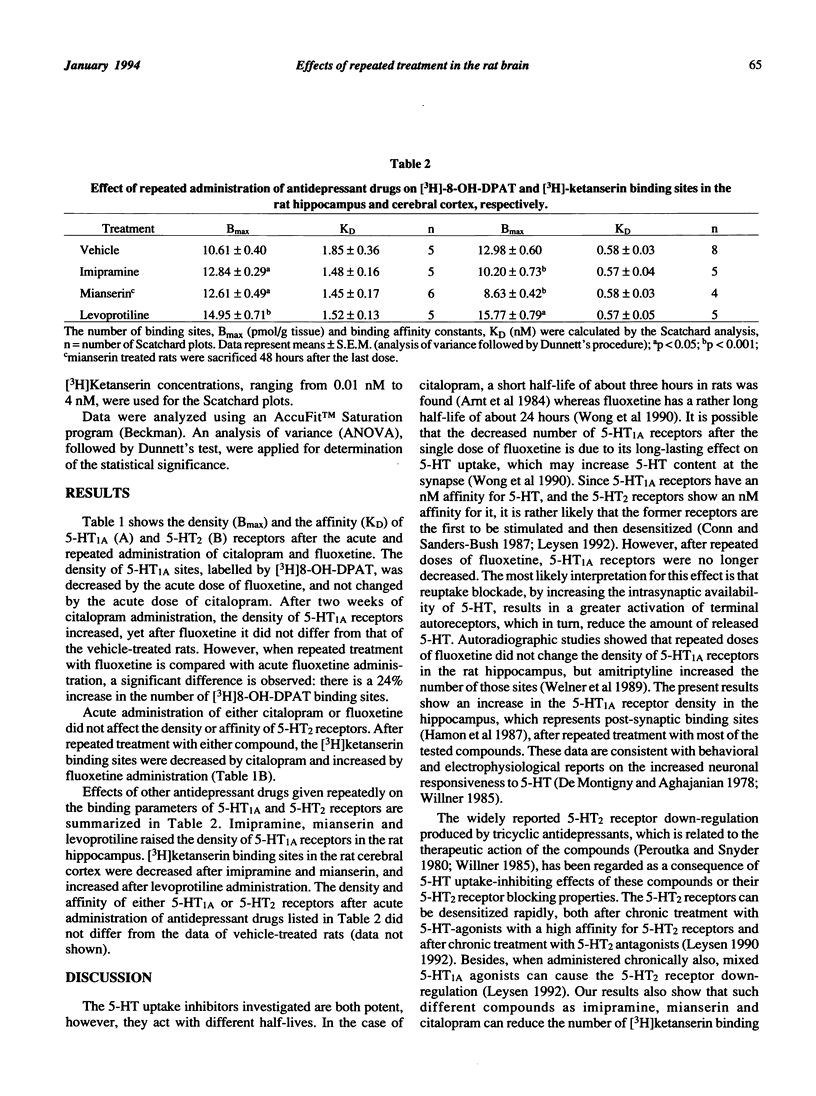
Repeated treatment with fluoxetine and citalopram, which are potent 5-HT reuptake inhibitors, resulted in different regulation of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors in the rat brain. Their effects were compared with those of other antidepressants: imipramine, mianserin and levoprotiline. The density of 5-HT1A receptors, labelled with [3H]8-OH-DPAT, in the rat hippocampus was enhanced after citalopram, imipramine, mianserin and levoprotiline, but not altered after fluoxetine administration. [3H]Ketanserin binding sites, which label 5-HT2 receptors, were increased after fluoxetine and levoprotiline, but decreased after citalopram, imipramine and mianserin in the rat cerebral cortex. Acute administration of fluoxetine, but not citalopram, resulted in a decreased density of 5-HT1A receptors. 5-HT2 receptors were not changed by acute administration of either fluoxetine or citalopram. The obtained results indicate that besides 5-HT reuptake inhibiting properties of both compounds, there may exist an additional mechanism(s) of their action, which leads to different regulation of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnt J., Hyttel J., Overø K. F. Prolonged treatment with the specific 5-HT-uptake inhibitor citalopram: effect on dopaminergic and serotonergic functions. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm. 1984 Mar-Jun;36(2-3):221–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldecott-Hazard S., Morgan D. G., DeLeon-Jones F., Overstreet D. H., Janowsky D. Clinical and biochemical aspects of depressive disorders: II. Transmitter/receptor theories. Synapse. 1991 Dec;9(4):251–301. doi: 10.1002/syn.890090404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervo L., Samanin R. Potential antidepressant properties of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin, a selective serotonin1A receptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 1;144(2):223–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90523-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheetham S. C., Crompton M. R., Katona C. L., Horton R. W. Brain 5-HT1 binding sites in depressed suicides. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1990;102(4):544–548. doi: 10.1007/BF02247138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn P. J., Sanders-Bush E. Central serotonin receptors: effector systems, physiological roles and regulation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1987;92(3):267–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00210830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. M., Green A. R., Johnson P. 5-HT2 receptor characteristics in frontal cortex and 5-HT2 receptor-mediated head-twitch behaviour following antidepressant treatment to mice. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;83(1):235–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R. Evolving concepts on the interactions between antidepressant treatments and monoamine neurotransmitters. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Jul;26(7B):815–822. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., Heal D. J., Johnson P., Laurence B. E., Nimgaonkar V. L. Antidepressant treatments: effects in rodents on dose-response curves of 5-hydroxytryptamine- and dopamine-mediated behaviours and 5-HT2 receptor number in frontal cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct;80(2):377–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellar K. J., Cascio C. S., Butler J. A., Kurtzke R. N. Differential effects of electroconvulsive shock and antidepressant drugs on serotonin-2 receptors in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Feb 19;69(4):515–518. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90460-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett G. A., Dourish C. T., Curzon G. Antidepressant-like action of 5-HT1A agonists and conventional antidepressants in an animal model of depression. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb 24;134(3):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leysen J. E. Gaps and peculiarities in 5-HT2 receptor studies. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1990 Oct-Dec;3(5-6):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leysen J. E., Niemegeers C. J., Van Nueten J. M., Laduron P. M. [3H]Ketanserin (R 41 468), a selective 3H-ligand for serotonin2 receptor binding sites. Binding properties, brain distribution, and functional role. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;21(2):301–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maj J., Moryl E. Effects of fluoxetine given chronically on the responsiveness of 5-HT receptor subpopulations to their agonists. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 1993 Jun;3(2):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0924-977x(93)90259-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maj J., Moryl E. Effects of sertraline and citalopram given repeatedly on the responsiveness of 5-HT receptor subpopulations. J Neural Transm Gen Sect. 1992;88(2):143–156. doi: 10.1007/BF01244819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. J., Arango V., Marzuk P. M., Theccanat S., Reis D. J. Evidence for the 5-HT hypothesis of suicide. A review of post-mortem studies. Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 1989 Dec;(8):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogilnicka E., Klimek V. Mianserin, danitracen and amitriptyline withdrawal increases the behavioural responses of rats to L-5-HTP. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;31(10):704–705. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1979.tb13634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J., Snyder S. H. Long-term antidepressant treatment decreases spiroperidol-labeled serotonin receptor binding. Science. 1980 Oct 3;210(4465):88–90. doi: 10.1126/science.6251550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel J. R., Peroutka S. J. Nucleotide interactions with 5-HT1A binding sites directly labeled by [3H]-8-hydroxy-2-(DI-n-propylamino)tetralin ([3H]-8-OH-DPAT). Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 15;35(12):1943–1949. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90725-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatarczyńska E., Chojnacka-Wójcik E. Effects of 8-OH-DPAT and ipsapirone in the tests used for evaluation of the antidepressant action. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm. 1989 Jul-Aug;41(4):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetulani J., Lebrecht U., Pilc A. Enhancement of responsiveness of the central serotonergic system and serotonin-2 receptor density in rat frontal cortex by electroconvulsive treatment. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov 19;76(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welner S. A., De Montigny C., Desroches J., Desjardins P., Suranyi-Cadotte B. E. Autoradiographic quantification of serotonin1A receptors in rat brain following antidepressant drug treatment. Synapse. 1989;4(4):347–352. doi: 10.1002/syn.890040410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willner P. Antidepressants and serotonergic neurotransmission: an integrative review. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1985;85(4):387–404. doi: 10.1007/BF00429653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. T., Fuller R. W., Robertson D. W. Fluoxetine and its two enantiomers as selective serotonin uptake inhibitors. Acta Pharm Nord. 1990;2(3):171–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates M., Leake A., Candy J. M., Fairbairn A. F., McKeith I. G., Ferrier I. N. 5HT2 receptor changes in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 1990 Mar 1;27(5):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(90)90440-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Montigny C., Aghajanian G. K. Tricyclic antidepressants: long-term treatment increases responsivity of rat forebrain neurons to serotonin. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.725608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Praag H. M., Korf J. A pilot study of some kinetic aspects of the metabolism of 5-hydroxytryptamine in depressive patients. Biol Psychiatry. 1971;3(2):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


