Abstract
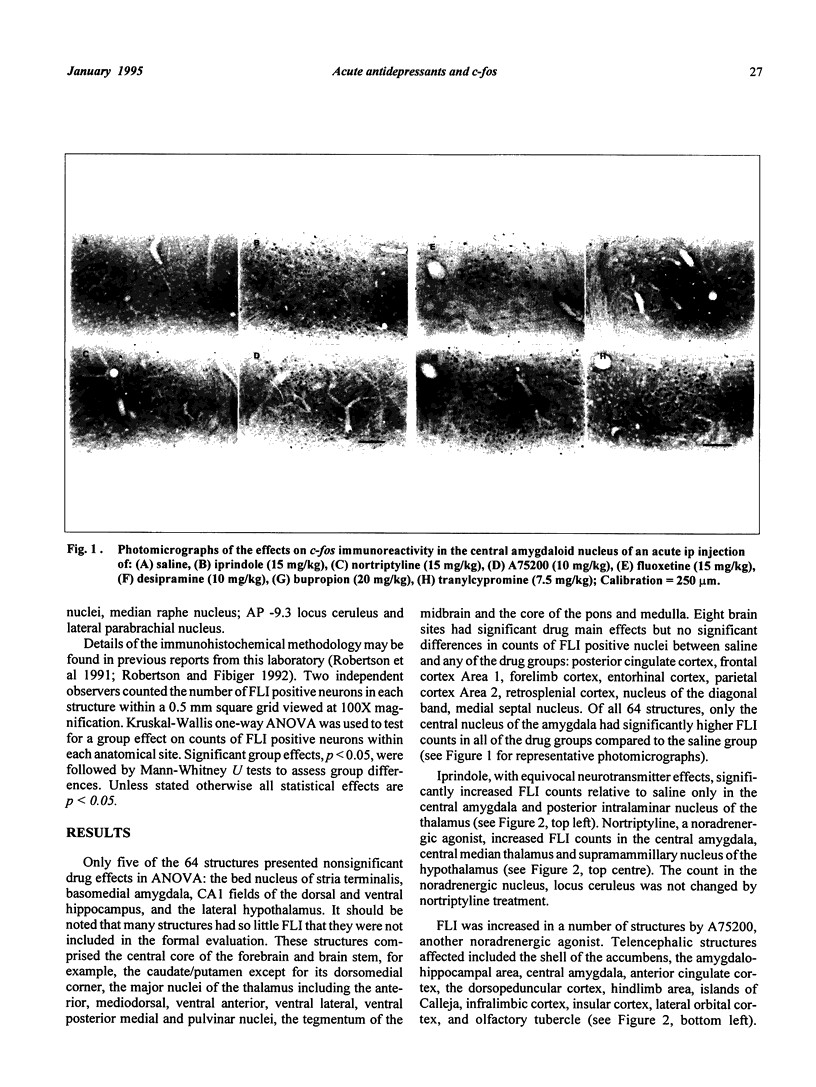
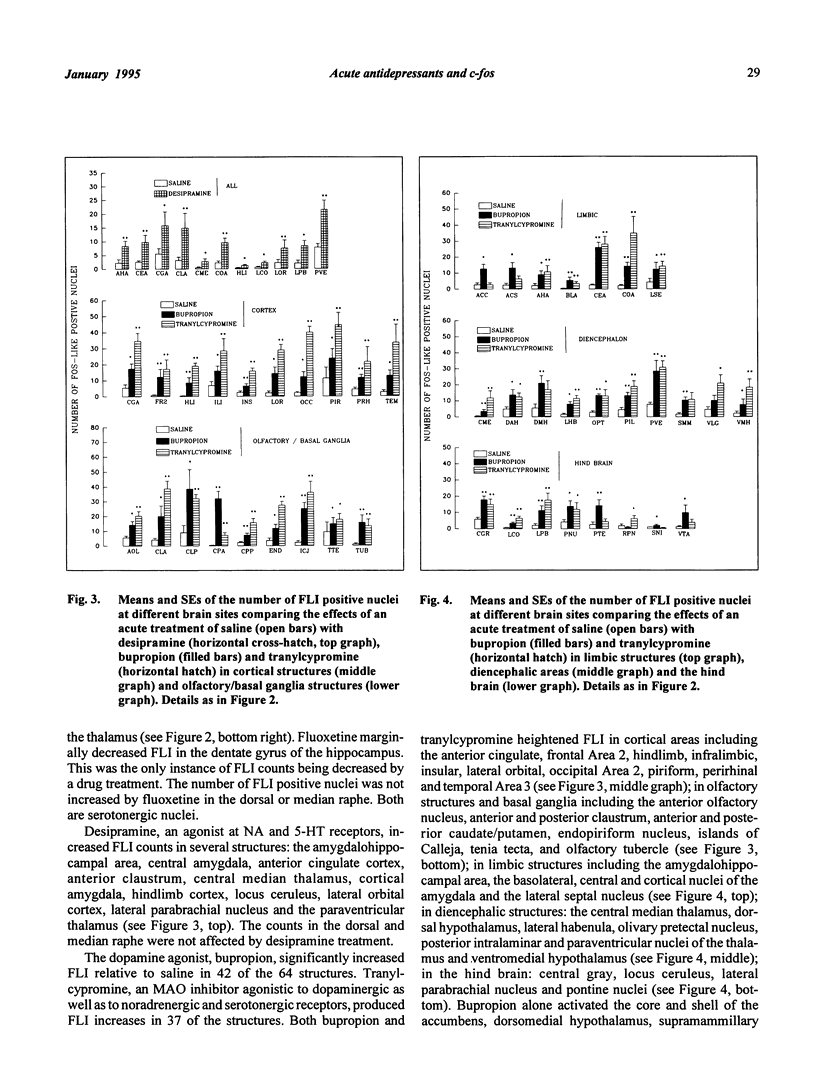
Rats were treated acutely, ip, with saline vehicle or an antidepressant: iprindole (15 mg/kg), nortriptyline (15 mg/kg), A75200 (10 mg/kg), fluoxetine (15 mg/kg), desipramine (10 mg/kg), bupropion (20 mg/kg) or tranylcypromine (7.5 mg/kg). Mapping the neuroanatomical distribution at 64 sites of the immediate early gene, c-fos revealed several patterns: first, increased counts of Fos-like neurons were found in all but one instance; second, drugs which had dopaminergic effects (bupropion and tranylcypromine) were more likely to potentiate c-fos reactivity than were the other drugs; third, Fos-like counts were more likely to be significantly elevated in structures bordering brain ventricles; fourth, only in the central amygdala were the Fos-like counts higher in all seven drug groups relative to the saline group. It remains to be seen whether or not this shared substrate is therapeutically significant.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asberg M., Crönholm B., Sjöqvist F., Tuck D. Relationship between plasma level and therapeutic effect of nortriptyline. Br Med J. 1971 Aug 7;3(5770):331–334. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5770.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker G. B., Coutts R. T., McKenna K. F., Sherry-McKenna R. L. Insights into the mechanisms of action of the MAO inhibitors phenelzine and tranylcypromine: a review. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1992 Nov;17(5):206–214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäckström I. T., Ross S. B., Marcusson J. O. [3H]desipramine binding to rat brain tissue: binding to both noradrenaline uptake sites and sites not related to noradrenaline neurons. J Neurochem. 1989 Apr;52(4):1099–1106. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb01853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campeau S., Hayward M. D., Hope B. T., Rosen J. B., Nestler E. J., Davis M. Induction of the c-fos proto-oncogene in rat amygdala during unconditioned and conditioned fear. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 29;565(2):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91669-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccatelli S., Villar M. J., Goldstein M., Hökfelt T. Expression of c-Fos immunoreactivity in transmitter-characterized neurons after stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9569–9573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chastrette N., Pfaff D. W., Gibbs R. B. Effects of daytime and nighttime stress on Fos-like immunoreactivity in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, the habenula, and the posterior paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 1;563(1-2):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91559-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. J., Bhat R. V., Patt C., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M. D1 dopamine receptor activation of multiple transcription factor genes in rat striatum. J Neurochem. 1992 Apr;58(4):1420–1426. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb11358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson T. M., Wamsley J. K. Autoradiographic localization of [3H]-imipramine binding sites: association with serotonergic neurons. Brain Res Bull. 1983 Sep;11(3):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(83)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritschy J. M., Frondoza C. G., Grzanna R. Differential effects of reserpine on brainstem catecholaminergic neurons revealed by Fos protein immunohistochemistry. Brain Res. 1991 Oct 18;562(1):48–56. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Hrdina P. D. Effects of tricyclic antidepressants on the content and metabolism of dopamine in the rat striatum. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;55(3):383–388. doi: 10.1139/y77-054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D. D., Manier D. H., Sanders-Bush E., Sulser F. The serotonin/norepinephrine-link in brain. II. Role of serotonin in the regulation of beta adrenoceptors in the low agonist affinity conformation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jan;244(1):154–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriadis D. E., Pearsall D., De Souza E. B. Effects of chronic antidepressant and benzodiazepine treatment on corticotropin-releasing-factor receptors in rat brain and pituitary. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1989 Mar;2(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0893-133x(89)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendley E. D., Snyder S. H. Relationship between the action of monoamine oxidase inhibitors on the noradrenaline uptake system and their antidepressant efficacy. Nature. 1968 Dec 28;220(5174):1330–1331. doi: 10.1038/2201330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrdina P. D., Ling G. M., Maneckjee A. Desipramine (DMI): effect on the levels of acetylcholine (ACH) in whole brain and in striatum of rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;15(1):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon G. A., Lawlor P. A., Bravo R., Dragunow M. Clozapine and haloperidol produce a differential pattern of immediate early gene expression in rat caudate-putamen, nucleus accumbens, lateral septum and islands of Calleja. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Apr;23(1-2):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElroy J. F., Du Pont A. F., Feldman R. S. The effects of fenfluramine and fluoxetine on the acquisition of the conditioned avoidance response in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1982;77(4):356–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00432770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi K., Kowalski K., Traub R., Solodkin A., Iadarola M. J., Ruda M. A. Dynorphin expression and Fos-like immunoreactivity following inflammation induced hyperalgesia are colocalized in spinal cord neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Jun;10(3):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty F., Sherman A. D. Regional aspects of the prevention of learned helplessness by desipramine. Life Sci. 1980 Apr 28;26(17):1447–1452. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzone M. A., Lee W. S., Hoffman G. E., Rabin B. S. Induction of c-Fos immunoreactivity in the rat forebrain by conditioned and unconditioned aversive stimuli. Brain Res. 1992 Nov 27;597(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91503-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G. S., Fibiger H. C. Neuroleptics increase c-fos expression in the forebrain: contrasting effects of haloperidol and clozapine. Neuroscience. 1992;46(2):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G. S., Herrera D. G., Dragunow M., Robertson H. A. L-dopa activates c-fos in the striatum ipsilateral to a 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of the substantia nigra. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 2;159(1):99–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G. S., Pfaus J. G., Atkinson L. J., Matsumura H., Phillips A. G., Fibiger H. C. Sexual behavior increases c-fos expression in the forebrain of the male rat. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 15;564(2):352–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91477-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut J. J. Tranylcypromine: effects on norepinephrine metabolism in rat brain. Am J Psychiatry. 1970 Jan;126(7):925–931. doi: 10.1176/ajp.126.7.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp F. R., Sagar S. M., Hicks K., Lowenstein D., Hisanaga K. c-fos mRNA, Fos, and Fos-related antigen induction by hypertonic saline and stress. J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2321–2331. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02321.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone E. A., Zhang Y., John S. M., Bing G. c-Fos response to administration of catecholamines into brain by microdialysis. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Nov 25;133(1):33–35. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulser F. New perspectives on the molecular pharmacology of affective disorders. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci. 1989;238(5-6):231–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00449803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. T., Horng J. S., Bymaster F. P., Hauser K. L., Molloy B. B. A selective inhibitor of serotonin uptake: Lilly 110140, 3-(p-trifluoromethylphenoxy)-N-methyl-3-phenylpropylamine. Life Sci. 1974 Aug 1;15(3):471–479. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90345-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yavin Z., Biegon A., Segal M., Samuel D. The in vivo binding of [3H]-desipramine and [3H]-chlorpromazine to areas in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Sep 15;51(2):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. T., Porrino L. J., Iadarola M. J. Cocaine induces striatal c-fos-immunoreactive proteins via dopaminergic D1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1291–1295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zis A. P., Goodwin F. K. Novel antidepressants and the biogenic amine hypothesis of depression. The case for iprindole and mianserin. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1979 Sep;36(10):1097–1107. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1979.01780100067006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]