Abstract
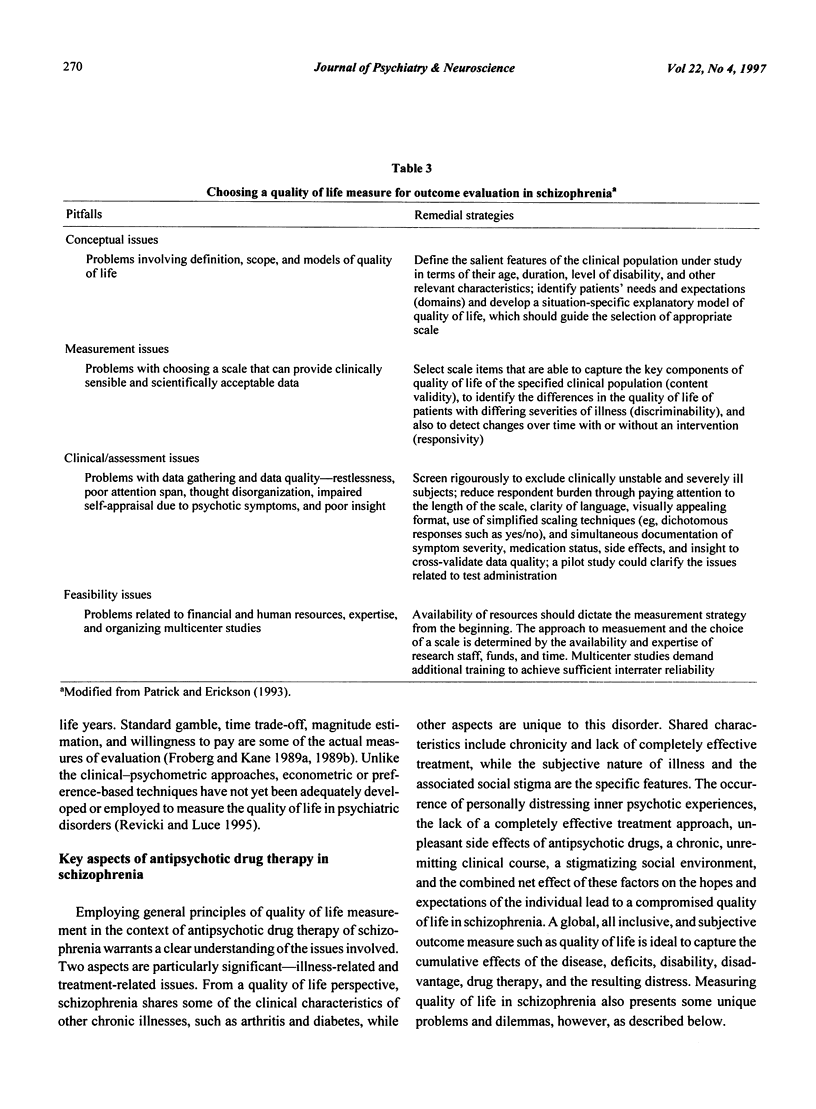
The strategy for measuring quality of life and the choice of a rating scale should follow a rational scheme aimed at capturing the key components of quality of life of a specified clinical population. This is achieved through defining the purpose of the study, identifying the clinical population and its needs, developing a situation-specific quality of life model, and choosing a battery of psychometrically sound and user-friendly rating scales based on the model. Patients' self-reports and subjective feelings should be central to quality of life measurement, which should also monitor symptom severity, drug side effects, and psychosocial adjustment. This article describes the application of these principles in the context of antipsychotic drug therapy of schizophrenia and identifies potential problems that may arise from the conceptual, psychometric, clinical, and other feasibility issues. The highly subjective nature of the disorder, together with the poor insight, lack of motivation, and neurocognitive deficits of those who are afflicted, poses special difficulties for obtaining and interpreting patients' quality of life appraisals in schizophrenia.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amador X. F., Strauss D. H., Yale S. A., Flaum M. M., Endicott J., Gorman J. M. Assessment of insight in psychosis. Am J Psychiatry. 1993 Jun;150(6):873–879. doi: 10.1176/ajp.150.6.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M., Zibin S., Chuang H. Characterizing quality of life among patients with chronic mental illness: a critical examination of the self-report methodology. Am J Psychiatry. 1997 Jan;154(1):99–105. doi: 10.1176/ajp.154.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
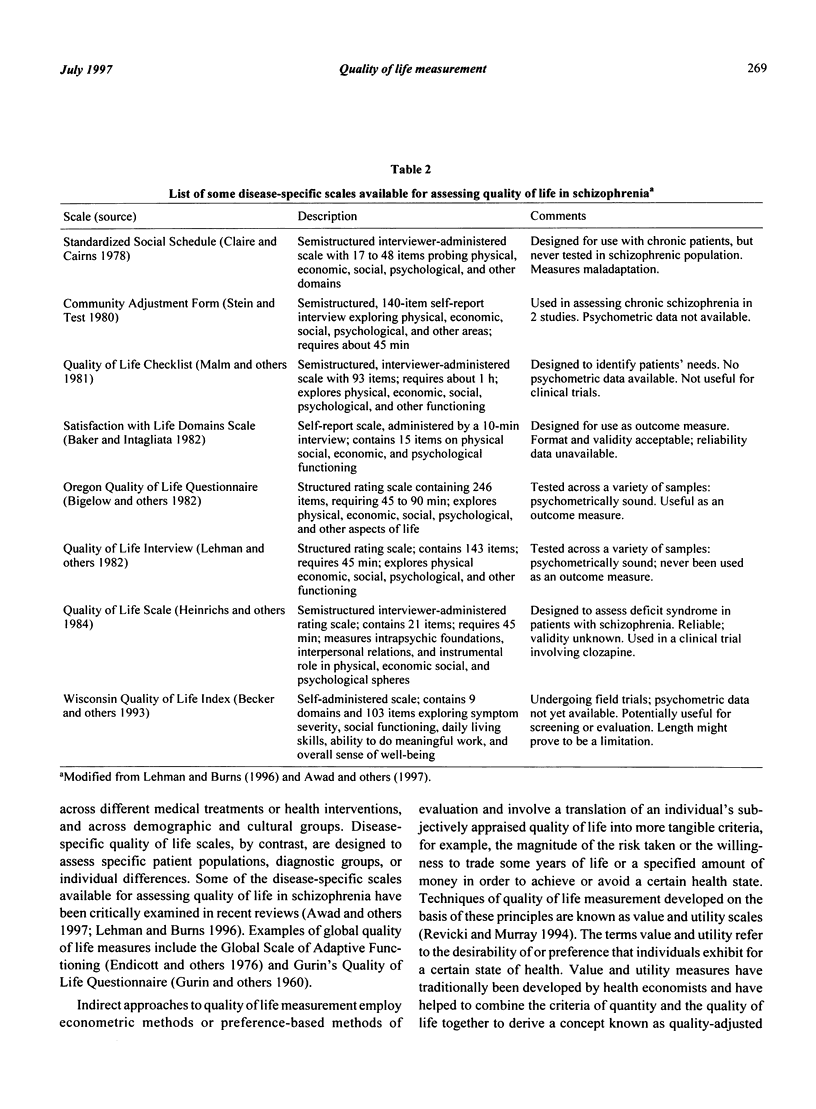
- Awad A. G. Quality of life of schizophrenic patients on medications and implications for new drug trials. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1992 Mar;43(3):262–265. doi: 10.1176/ps.43.3.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awad A. G. Subjective response to neuroleptics in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1993;19(3):609–618. doi: 10.1093/schbul/19.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awad A. G., Voruganti L. N., Heslegrave R. J. Measuring quality of life in patients with schizophrenia. Pharmacoeconomics. 1997 Jan;11(1):32–47. doi: 10.2165/00019053-199711010-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker F., Intagliata J. Quality of life in the evaluation of community support systems. Eval Program Plann. 1982;5(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0149-7189(82)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker M., Diamond R., Sainfort F. A new patient focused index for measuring quality of life in persons with severe and persistent mental illness. Qual Life Res. 1993 Aug;2(4):239–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00434796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergner M., Bobbitt R. A., Carter W. B., Gilson B. S. The Sickness Impact Profile: development and final revision of a health status measure. Med Care. 1981 Aug;19(8):787–805. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198108000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare A. W., Cairns V. E. Design, development and use of a standardized interview to assess social maladjustment and dysfunction in community studies. Psychol Med. 1978 Nov;8(4):589–604. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700018808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J., Spitzer R. L., Fleiss J. L., Cohen J. The global assessment scale. A procedure for measuring overall severity of psychiatric disturbance. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1976 Jun;33(6):766–771. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1976.01770060086012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froberg D. G., Kane R. L. Methodology for measuring health-state preferences--I: Measurement strategies. J Clin Epidemiol. 1989;42(4):345–354. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(89)90039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froberg D. G., Kane R. L. Methodology for measuring health-state preferences--II: Scaling methods. J Clin Epidemiol. 1989;42(5):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(89)90136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill T. M., Feinstein A. R. A critical appraisal of the quality of quality-of-life measurements. JAMA. 1994 Aug 24;272(8):619–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrichs D. W., Hanlon T. E., Carpenter W. T., Jr The Quality of Life Scale: an instrument for rating the schizophrenic deficit syndrome. Schizophr Bull. 1984;10(3):388–398. doi: 10.1093/schbul/10.3.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman A. F. The well-being of chronic mental patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983 Apr;40(4):369–373. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790040023003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman A. F., Ward N. C., Linn L. S. Chronic mental patients: the quality of life issue. Am J Psychiatry. 1982 Oct;139(10):1271–1276. doi: 10.1176/ajp.139.10.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn-Thomas H., Sutherland H. J., Tibshirani R., Ciampi A., Till J. E., Boyd N. F. Describing health states. Methodologic issues in obtaining values for health states. Med Care. 1984 Jun;22(6):543–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malm U., May P. R., Dencker S. J. Evaluation of the quality of life of the schizophrenic outpatient: a checklist. Schizophr Bull. 1981;7(3):477–487. doi: 10.1093/schbul/7.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer H. Y., Burnett S., Bastani B., Ramirez L. F. Effects of six months of clozapine treatment on the quality of life of chronic schizophrenic patients. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1990 Aug;41(8):892–897. doi: 10.1176/ps.41.8.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick D. L., Bush J. W., Chen M. M. Methods for measuring levels of well-being for a health status index. Health Serv Res. 1973 Fall;8(3):228–245. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revicki D. A., Luce B. R. Methods of pharmacoeconomic evaluation of new medical treatments in psychiatry. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1995;31(1):57–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L. I., Test M. A. Alternative to mental hospital treatment. I. Conceptual model, treatment program, and clinical evaluation. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980 Apr;37(4):392–397. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1980.01780170034003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrance G. W., Feeny D. Utilities and quality-adjusted life years. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 1989;5(4):559–575. doi: 10.1017/s0266462300008461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrance G. W., Furlong W., Feeny D., Boyle M. Multi-attribute preference functions. Health Utilities Index. Pharmacoeconomics. 1995 Jun;7(6):503–520. doi: 10.2165/00019053-199507060-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


