Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Currently, there is no documentation of the efficacy of venlafaxine (a serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor) in the treatment of dysthymia. This open-label pilot investigation examined the efficacy and tolerability of venlafaxine in patients with primary dysthymia without concomitant major depression. METHODS: Fifteen patients were treated with venlafaxine for 12 weeks, with a dose range of 75 mg to 225 mg daily (taken orally), and symptom changes were measured using standard instruments including the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D). RESULTS: Significant changes from pretreatment to posttreatment were observed (p < 0.001). Using the standard criteria of a 50% reduction in HAM-D scores, 73.3% of patients were rated as responders. About two-thirds of the patients reported adverse events, which were mostly mild and brief in duration. CONCLUSION: Venlafaxine may be useful in the treatment of primary dysthymia but placebo-controlled studies are required for confirmation.
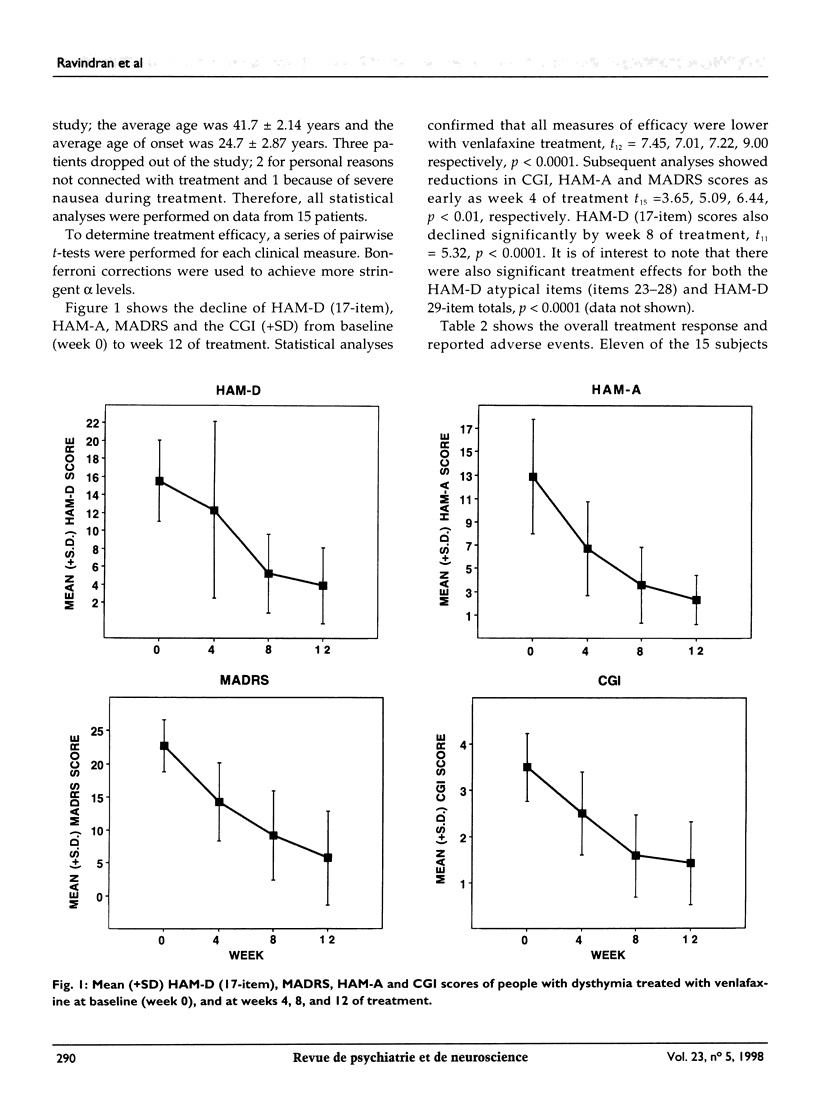
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cunningham L. A., Borison R. L., Carman J. S., Chouinard G., Crowder J. E., Diamond B. I., Fischer D. E., Hearst E. A comparison of venlafaxine, trazodone, and placebo in major depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1994 Apr;14(2):99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunner D. L., Hendrickson H. E., Bea C., Budech C. B. Venlafaxine in dysthymic disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 1997 Dec;58(12):528–531. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v58n1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entsuah A. R., Rudolph R. L., Chitra R. Effectiveness of venlafaxine treatment in a broad spectrum of depressed patients: a meta-analysis. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1995;31(4):759–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol. 1959;32(1):50–55. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8341.1959.tb00467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton M. Development of a rating scale for primary depressive illness. Br J Soc Clin Psychol. 1967 Dec;6(4):278–296. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8260.1967.tb00530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howland R. H. General health, health care utilization, and medical comorbidity in dysthymia. Int J Psychiatry Med. 1993;23(3):211–238. doi: 10.2190/AXCU-P704-23XQ-CQTR. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller M. B. The difficult depressed patient in perspective. J Clin Psychiatry. 1993 Feb;54 (Suppl):4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendels J., Johnston R., Mattes J., Riesenberg R. Efficacy and safety of b.i.d. doses of venlafaxine in a dose-response study. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1993;29(2):169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton W. A., Sonne S. C., Verga M. A. Venlafaxine: a structurally unique and novel antidepressant. Ann Pharmacother. 1995 Apr;29(4):387–395. doi: 10.1177/106002809502900410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muth E. A., Haskins J. T., Moyer J. A., Husbands G. E., Nielsen S. T., Sigg E. B. Antidepressant biochemical profile of the novel bicyclic compound Wy-45,030, an ethyl cyclohexanol derivative. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Dec 15;35(24):4493–4497. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90769-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierenberg A. A., Feighner J. P., Rudolph R., Cole J. O., Sullivan J. Venlafaxine for treatment-resistant unipolar depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1994 Dec;14(6):419–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravindran A. V., Bialik R. J., Lapierre Y. D. Therapeutic efficacy of specific serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in dysthymia. Can J Psychiatry. 1994 Feb;39(1):21–26. doi: 10.1177/070674379403900106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. W., McGrath P. J., Quitkin F. M., Rabkin J. G., Harrison W., Wager S., Nunes E., Ocepek-Welikson K., Tricamo E. Chronic depression: response to placebo, imipramine, and phenelzine. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1993 Dec;13(6):391–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman M. M., Leaf P. J., Bruce M. L., Florio L. The epidemiology of dysthymia in five communities: rates, risks, comorbidity, and treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 1988 Jul;145(7):815–819. doi: 10.1176/ajp.145.7.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


