Abstract
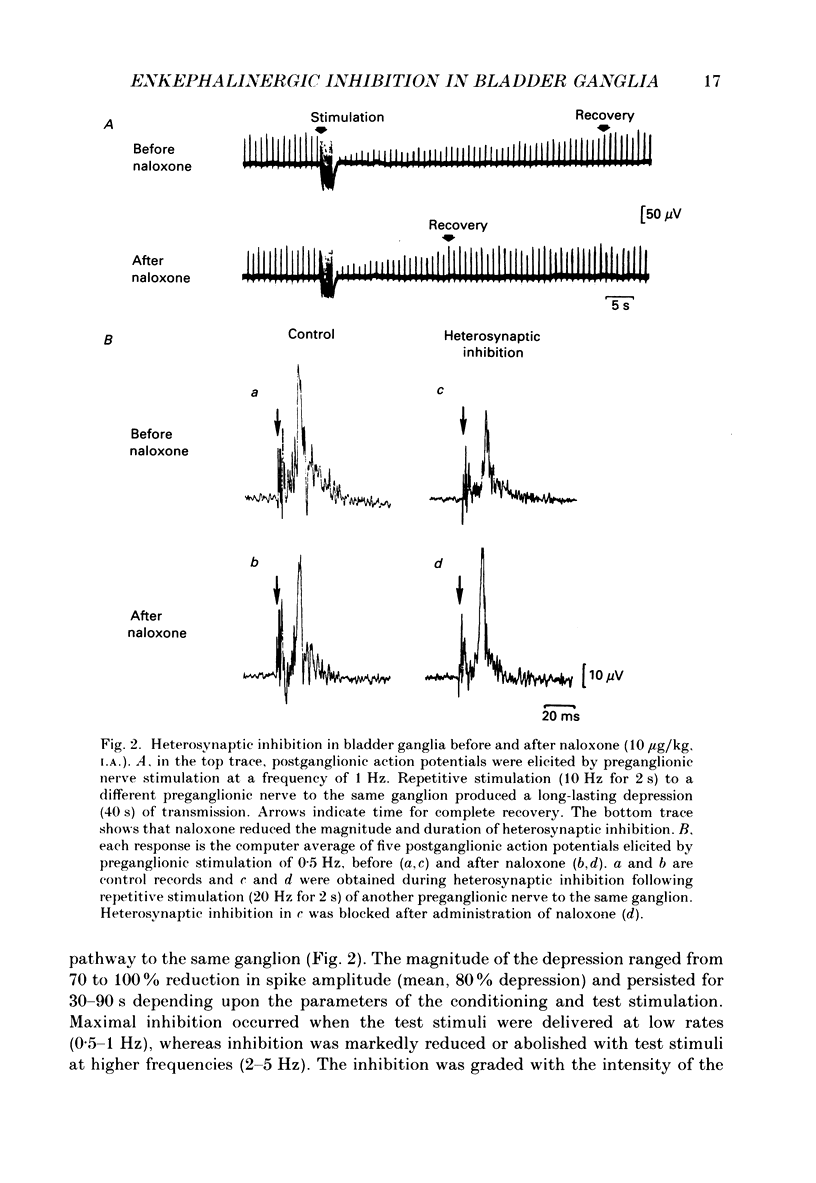
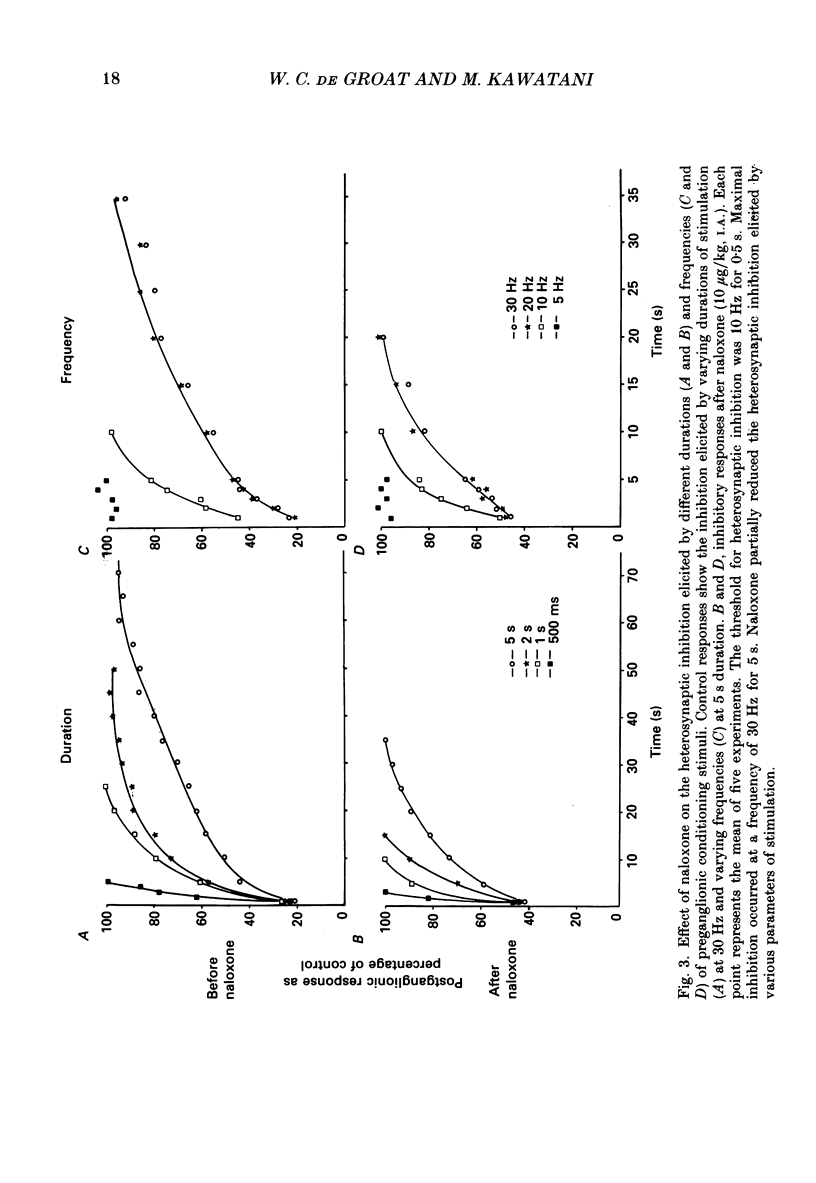
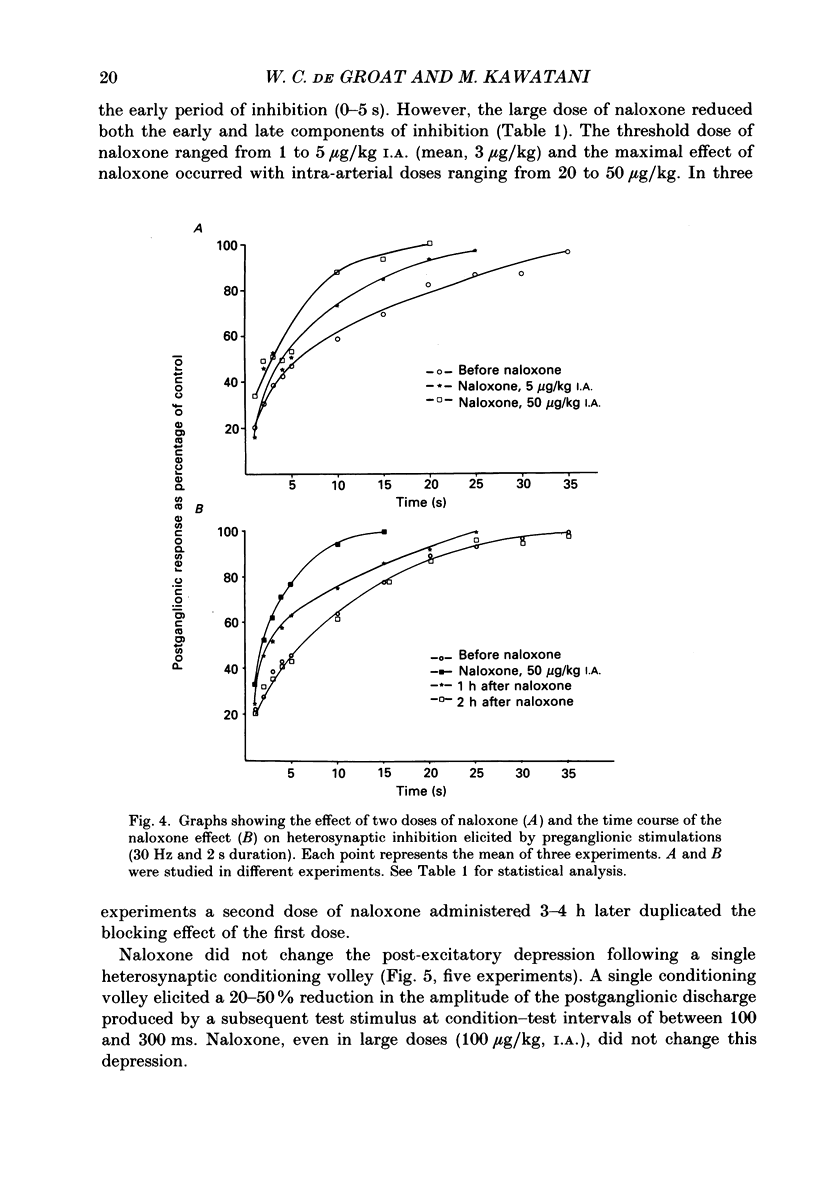
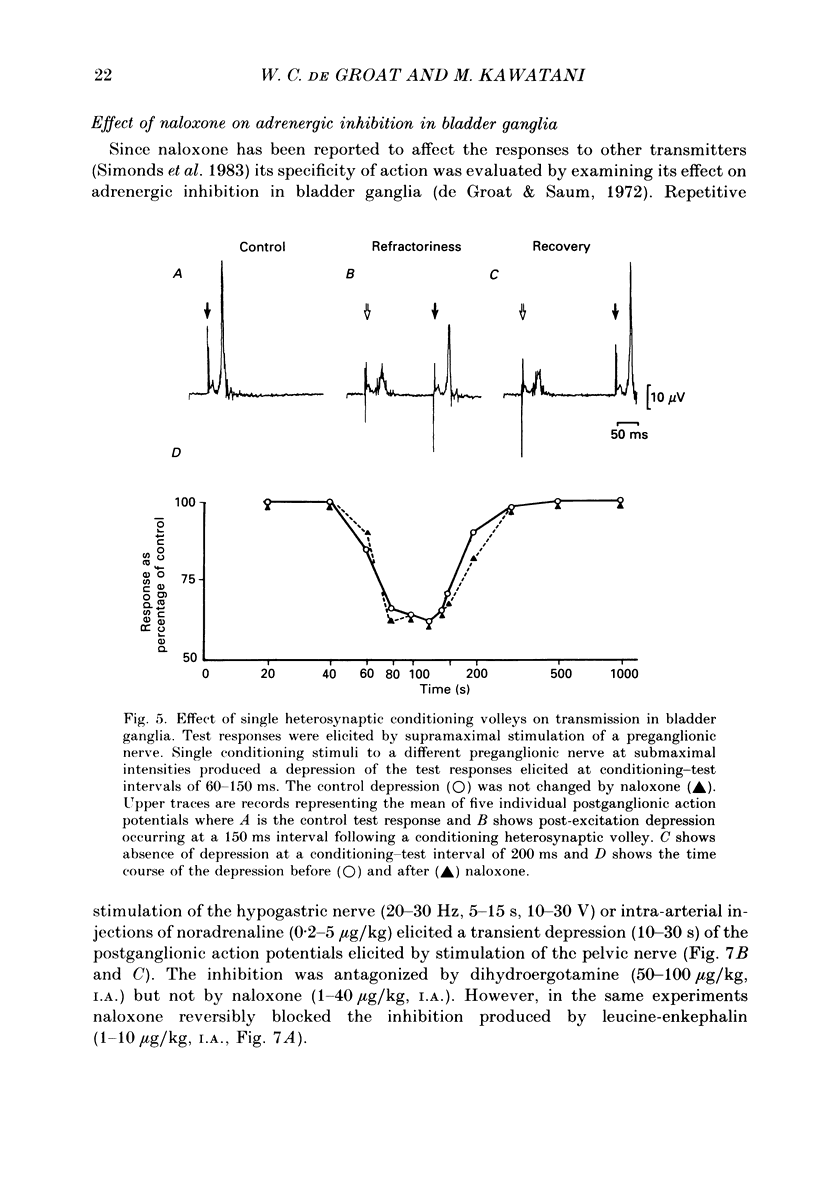
1. Repetitive stimulation (10-20 Hz, 0.5-5 s duration) of the preganglionic nerves to ganglia on the surface of the urinary bladder of the cat produced a prolonged inhibition (duration, 30-65 s) of the postganglionic action potentials, elicited by low-frequency stimulation (0.25-1 Hz) of another preganglionic nerve to the same ganglion. 2. Intra-arterial administration of naloxone, an opiate antagonist (20-50 micrograms/kg), reduced the magnitude and duration of this heterosynaptic inhibition and also blocked the depression of ganglionic transmission elicited by the intra-arterial administration of leucine-enkephalin (0.1-10 micrograms/kg). 3. Naloxone did not alter adrenergic inhibition elicited by repetitive stimulation of the hypogastric nerve or exogenous noradrenaline. Naloxone did not alter the postganglionic firing elicited by single stimuli or trains of low-frequency (1-3 Hz) stimuli to the preganglionic nerves. 4. Heterosynaptic inhibition was not altered by the administration of antagonists for alpha-adrenergic (dihydroergotamine, prazosin, yohimbine), muscarinic (atropine), purinergic (theophylline) or GABAergic (picrotoxin) receptors. 5. A delta-selective opiate receptor agonist, DSLET (D-Ser2-leucine-enkephalin-Thr), inhibited parasympathetic ganglionic transmission in low doses (mean threshold dose, 0.02 microgram/kg, I.A.), whereas a mu-opiate receptor agonist, morphine sulphate, produced only a small depression in larger doses (mean threshold dose, 100 micrograms/kg, I.A.). Ethylketocyclazocine, which has an affinity for kappa-receptors did not alter transmission in relatively large doses (1 mg/kg, I.A.). 6. These findings coupled with previous immunocytochemical demonstrations of leucine-enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in preganglionic nerve terminals in bladder ganglia suggest that opioid peptides released endogenously from preganglionic nerves are involved in delta-receptor-mediated inhibitory mechanisms at cholinergic synapses in bladder ganglia.
Full text
PDF





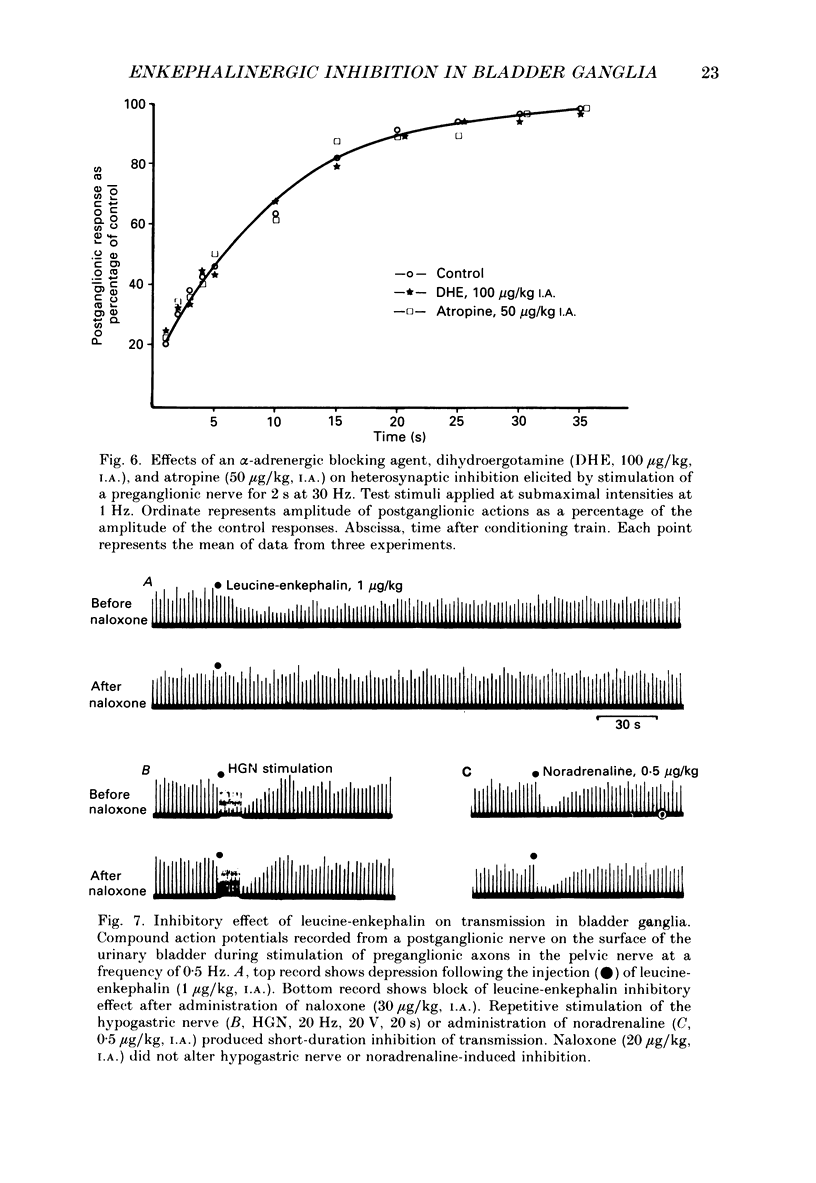
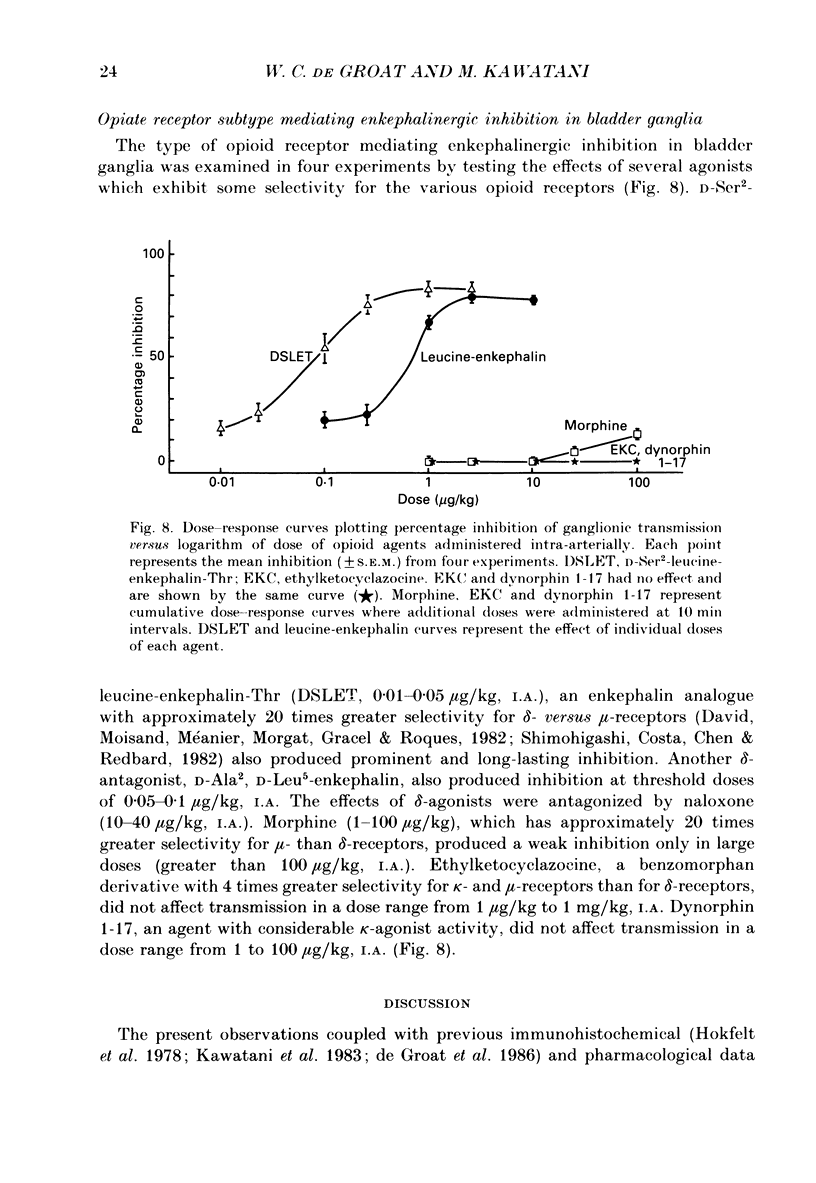





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akasu T., Shinnick-Gallagher P., Gallagher J. P. Adenosine mediates a slow hyperpolarizing synaptic potential in autonomic neurones. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):62–65. doi: 10.1038/311062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akasu T., Shinnick-Gallagher P., Gallagher J. P. Evidence for a catecholamine-mediated slow hyperpolarizing synaptic response in parasympathetic ganglia. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 19;365(2):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91651-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Neale J. H., Smith T. G., Jr, Macdonald R. L. Opiate peptide modulation of amino acid responses suggests novel form of neuronal communication. Science. 1978 Mar 31;199(4336):1451–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.204016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixby J. L., Spitzer N. C. Enkephalin reduces quantal content at the frog neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):431–432. doi: 10.1038/301431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carette B., Poulain P. Postsynaptic inhibitory effects of Met- and Leu-enkephalin on endocrine and adjacent neurones in the preoptic-septal region of the guinea pig. Regul Pept. 1982 Feb;3(2):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(82)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Hökfelt T., Schultzberg M., Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Dockray G. J., Goldstein M. Origin of peptide-containing fibers in the inferior mesenteric ganglion of the guinea-pig: immunohistochemical studies with antisera to substance P, enkephalin, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, cholecystokinin and bombesin. Neuroscience. 1983 May;9(1):191–211. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Moisand C., Meunier J. C., Morgat J. L., Gacel G., Roques B. P. [3H]Tyr-D-Ser-Gly-Phe-Leu-Thr: a specific probe for the delta-opiate receptor subtype in brain membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Mar 12;78(3):385–387. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groat W. C., Saum W. R. Sympathetic inhibition of the urinary bladder and of pelvic ganglionic transmission in the cat. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(2):297–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGroat W. C., Saum W. R. Synaptic transmission in parasympathetic ganglia in the urinary bladder of the cat. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;256(1):137–158. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubocovich M. L., Langer S. Z. Pharmacological differentiation of presynaptic inhibitory alpha-adrenoceptors and opiate receptors in the cat nictitating membrane. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;70(3):383–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb08714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erichsen J. T., Reiner A., Karten H. J. Co-occurrence of substance P-like and Leu-enkephalin-like immunoreactivities in neurones and fibres of avian nervous system. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):407–410. doi: 10.1038/295407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. P., Griffith W. H., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Cholinergic transmission in cat parasympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:473–486. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer E. J., Basbaum A. I. Leucine enkephalin: localization in and axoplasmic transport by sacral parasympathetic preganglionic neurons. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1479–1481. doi: 10.1126/science.6155697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisamitsu T., de Groat W. C. The inhibitory effect of opioid peptides and morphine applied intrathecally and intracerebroventricularly on the micturition reflex in the cat. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 23;298(1):51–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Schultzberg M., Elde R., Nilsson G., Terenius L., Said S., Goldstein M. Peptide neurons in peripheral tissues including the urinary tract: immunohistochemical studies. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1978;43 (Suppl 2):79–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1978.tb03224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOELLE G. B. The elimination of enzymatic diffusion artifacts in the histochemical localization of cholinesterases and a survey of their cellular distributions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1951 Oct;103(2):153–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawatani M., Lowe I. P., Booth A. M., Backes M. G., Erdman S. L., De Groat W. C. The presence of leucine-enkephalin in the sacral preganglionic pathway to the urinary bladder of the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Aug 29;39(2):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi S., Tsunoo A., Otsuka M. Enkephalin as a transmitter for presynaptic inhibition in sympathetic ganglia. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):80–82. doi: 10.1038/294080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi S., Tsunoo A., Otsuka M. Enkephalins presynaptically inhibit cholinergic transmission in sympathetic ganglia. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):515–516. doi: 10.1038/282515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumakura K., Karoum F., Guidotti A., Costa E. Modulation of nicotinic receptors by opiate receptor agonists in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):489–492. doi: 10.1038/283489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo D. C., Hisamitsu T., de Groat W. C. A sympathetic projection from sacral paravertebral ganglia to the pelvic nerve and to postganglionic nerves on the surface of the urinary bladder and large intestine of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jun 10;226(1):76–86. doi: 10.1002/cne.902260106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machová J., Kvaltínová Z. The actions of [Leu5]enkephalin and morphine in cat sympathetic ganglion. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Feb 18;87(2-3):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadelhaft I., Degroat W. C., Morgan C. Location and morphology of parasympathetic preganglionic neurons in the sacral spinal cord of the cat revealed by retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Sep 1;193(1):265–281. doi: 10.1002/cne.901930118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Yoshimura M., Shinnick-Gallagher P., Gallagher J. P., Akasu T. alpha 2 and alpha 1-Adrenoceptors mediate opposing actions on parasympathetic neurons. Brain Res. 1984 Dec 10;323(2):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90312-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Katayama Y., Williams J. T. Actions of peptides on enteric neurones. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1980;22:83–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper C. M., Henderson G. Opiates and opioid peptides hyperpolarize locus coeruleus neurons in vitro. Science. 1980 Jul 18;209(4454):394–395. doi: 10.1126/science.7384811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saum W. R., De Groat W. C. Parasympathetic ganglia: activation of an adrenergic inhibitory mechanism by cholinomimetic agents. Science. 1972 Feb 11;175(4022):659–661. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4022.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimohigashi Y., Costa T., Chen H. C., Rodbard D. Dimeric tetrapeptide enkephalins display extraordinary selectivity for the delta opiate receptor. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):333–335. doi: 10.1038/297333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Booth A. M., Thor K. B., Ostrowski N. L., Nagel J. R., de Groat W. C. Parasympathetic ganglia: naloxone antagonizes inhibition by leucine-enkephalin and GABA. Brain Res. 1983 Jul 25;271(2):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90303-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Egan T. M., North R. A. Enkephalin opens potassium channels on mammalian central neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):74–77. doi: 10.1038/299074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., Bayerl H. The mechanism of inhibition of neuronal activity by opiates in the spinal cord of cat. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 8;115(1):111–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90826-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groat W. C., Booth A. M. Inhibition and facilitation in parasympathetic ganglia of the urinary bladder. Fed Proc. 1980 Oct;39(12):2990–2996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groat W. C., Kawatani M., Hisamitsu T., Lowe I., Morgan C., Roppolo J., Booth A. M., Nadelhaft I., Kuo D., Thor K. The role of neuropeptides in the sacral autonomic reflex pathways of the cat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Mar-Apr;7(3-4):339–350. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groat W. C., Nadelhaft I., Milne R. J., Booth A. M., Morgan C., Thor K. Organization of the sacral parasympathetic reflex pathways to the urinary bladder and large intestine. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1981 Apr;3(2-4):135–160. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(81)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




