Abstract
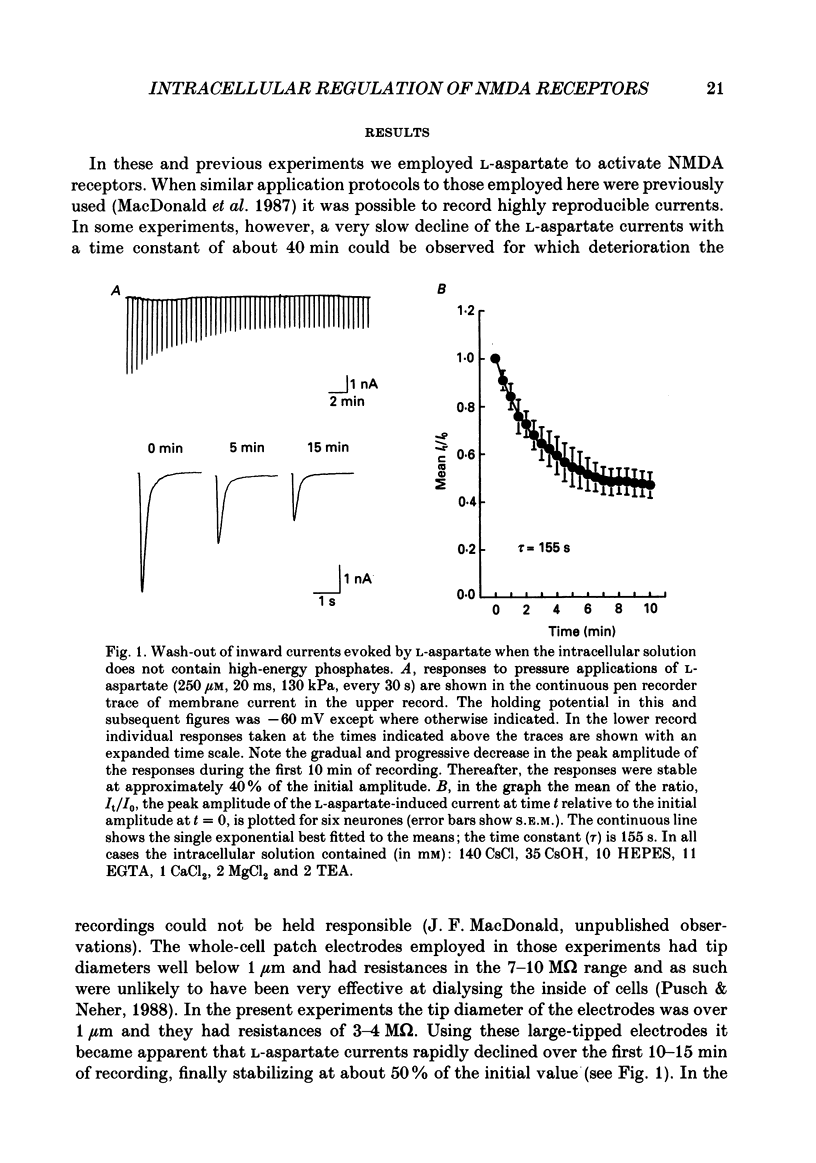
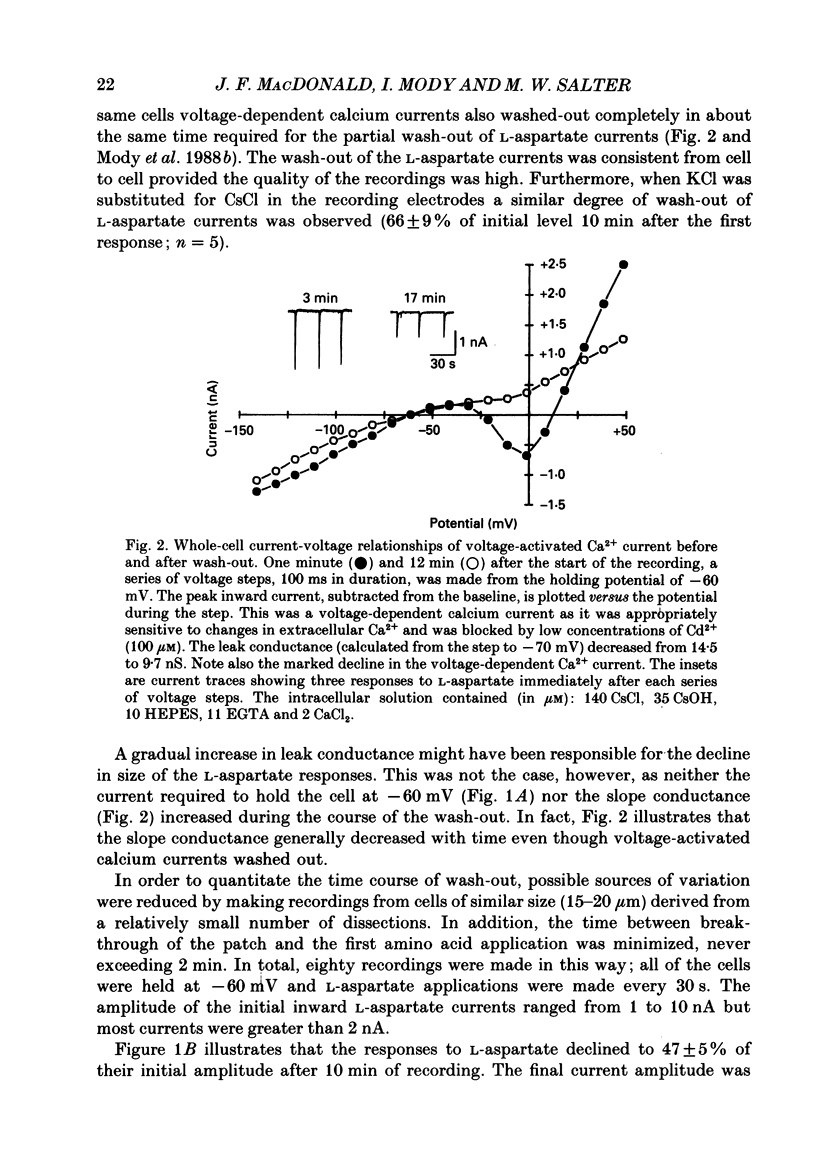
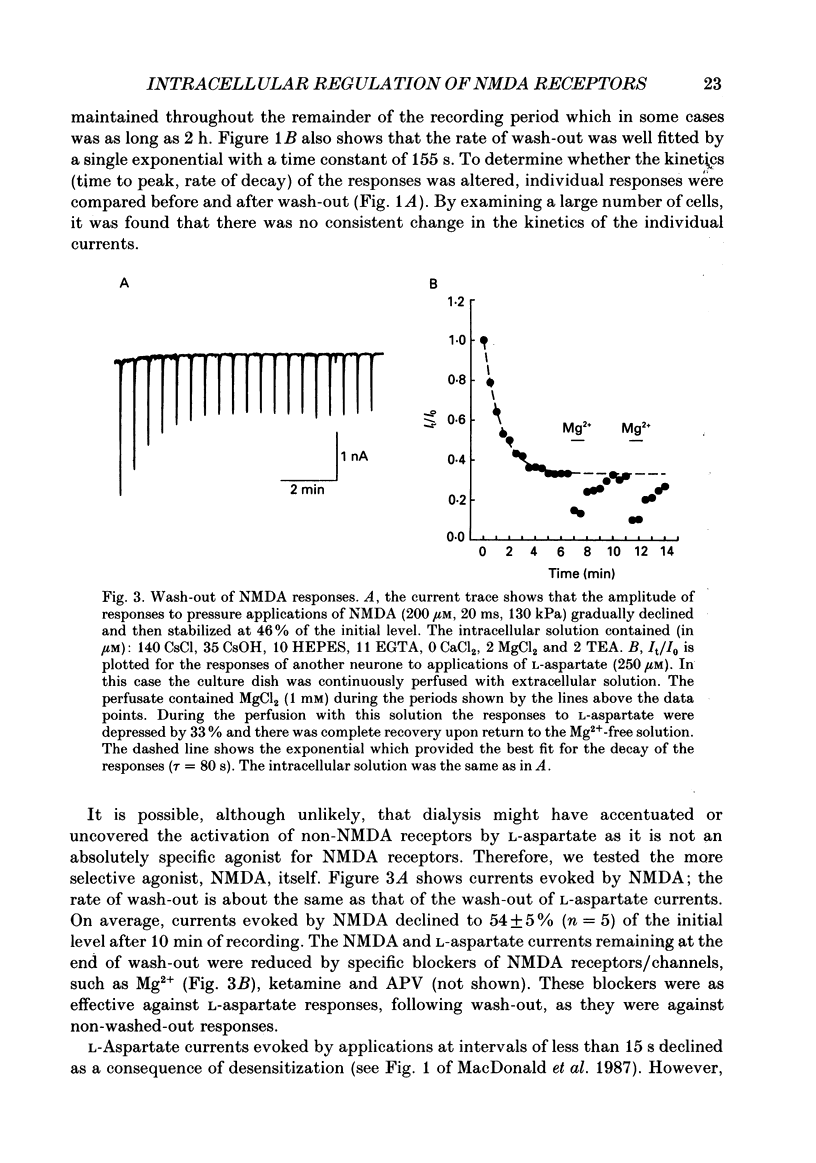
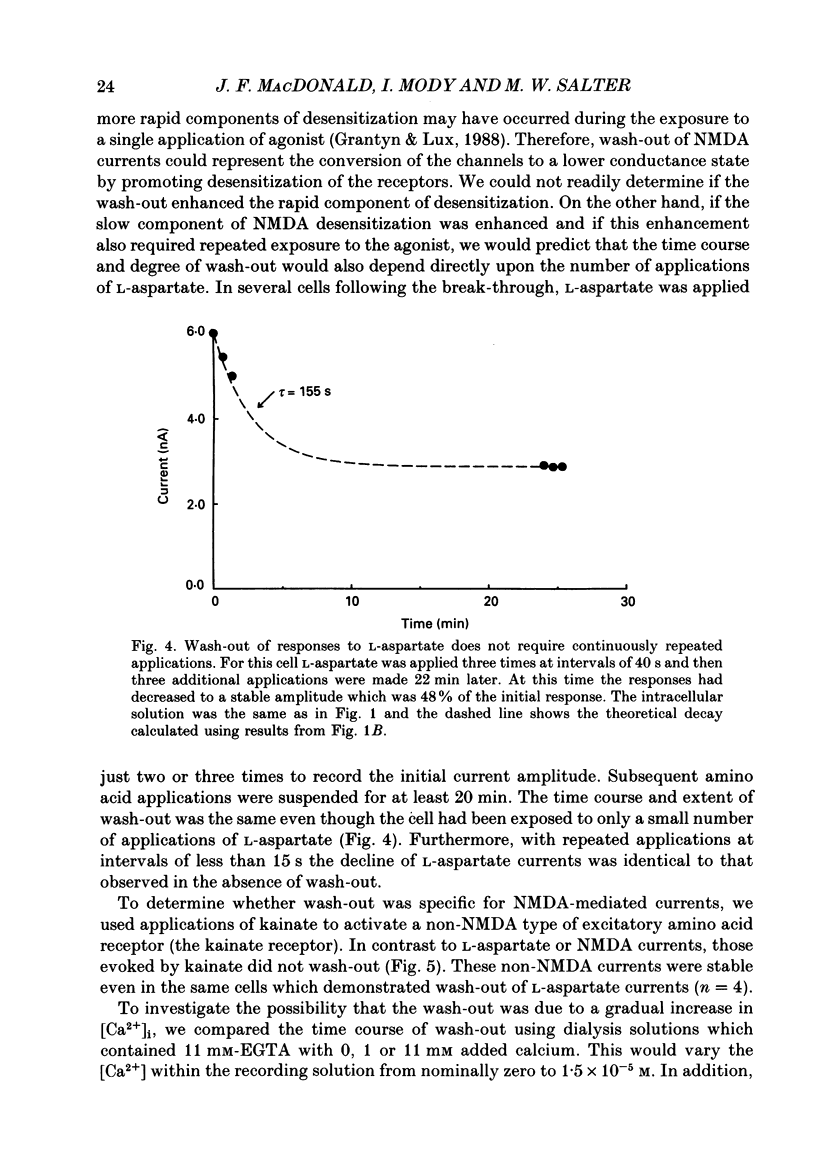
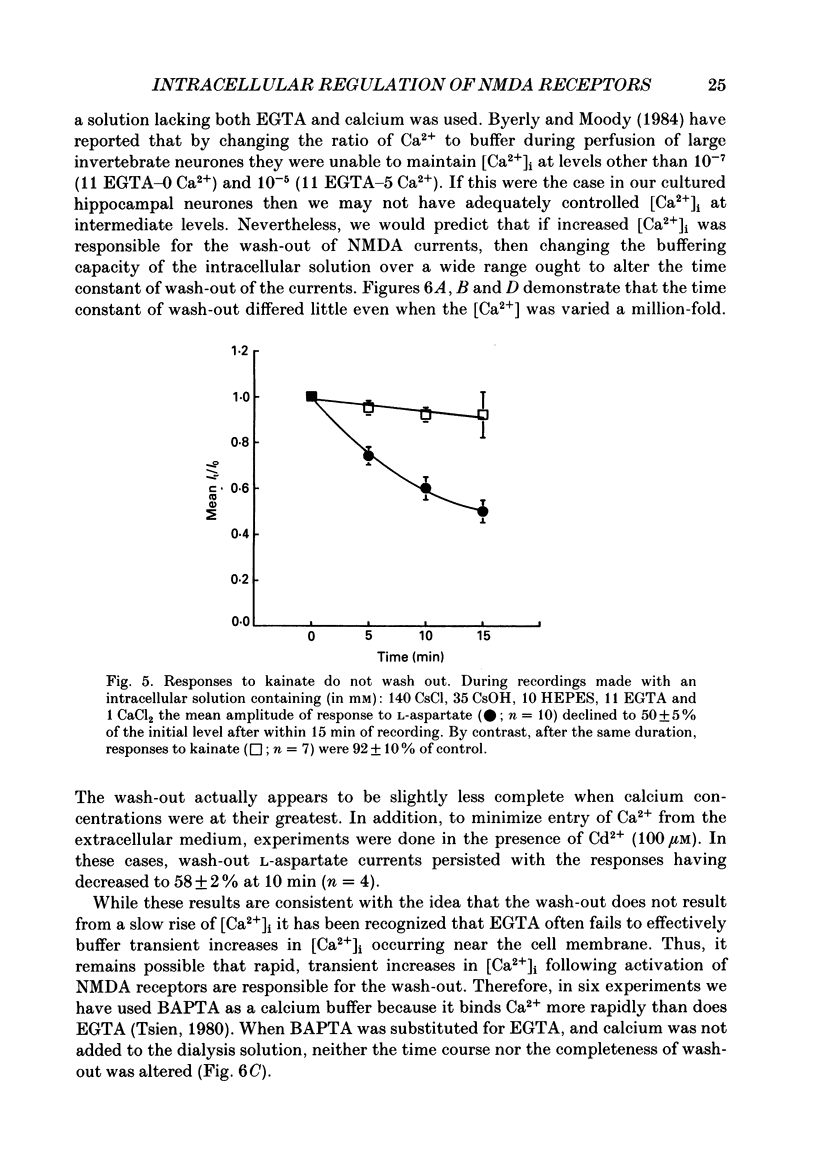
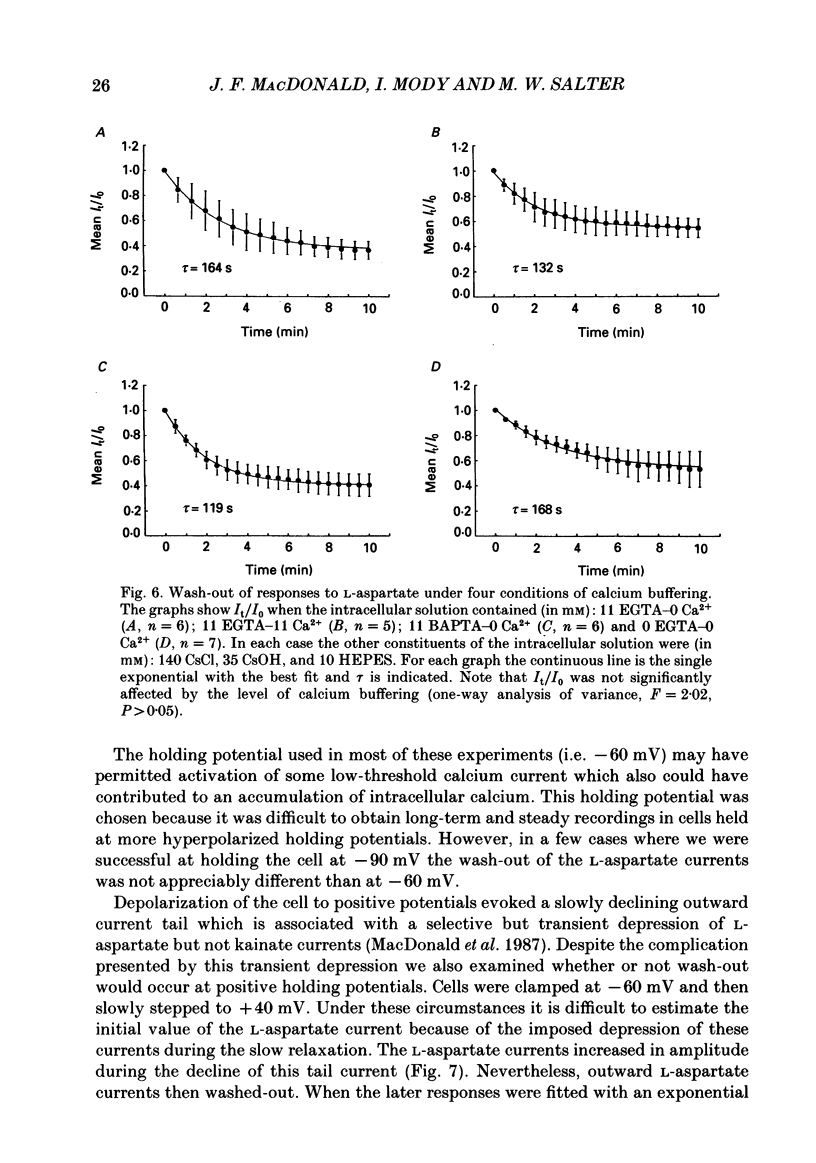
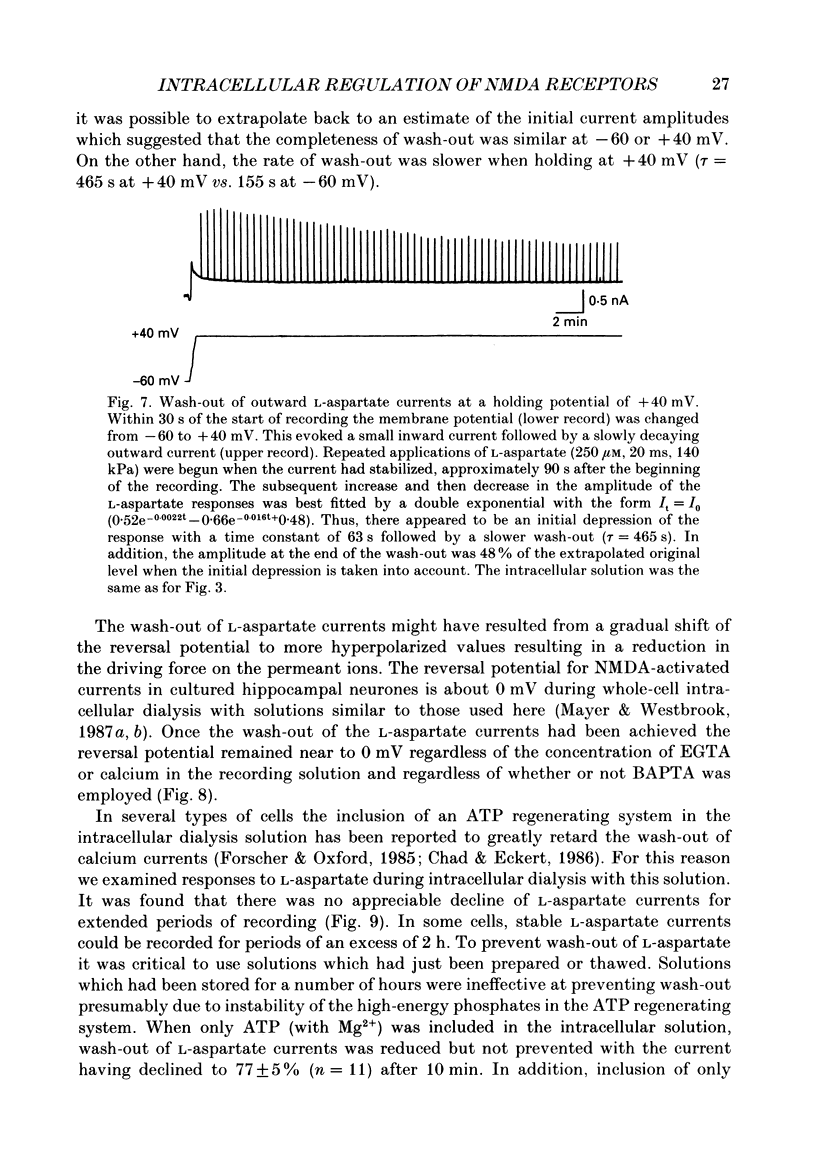
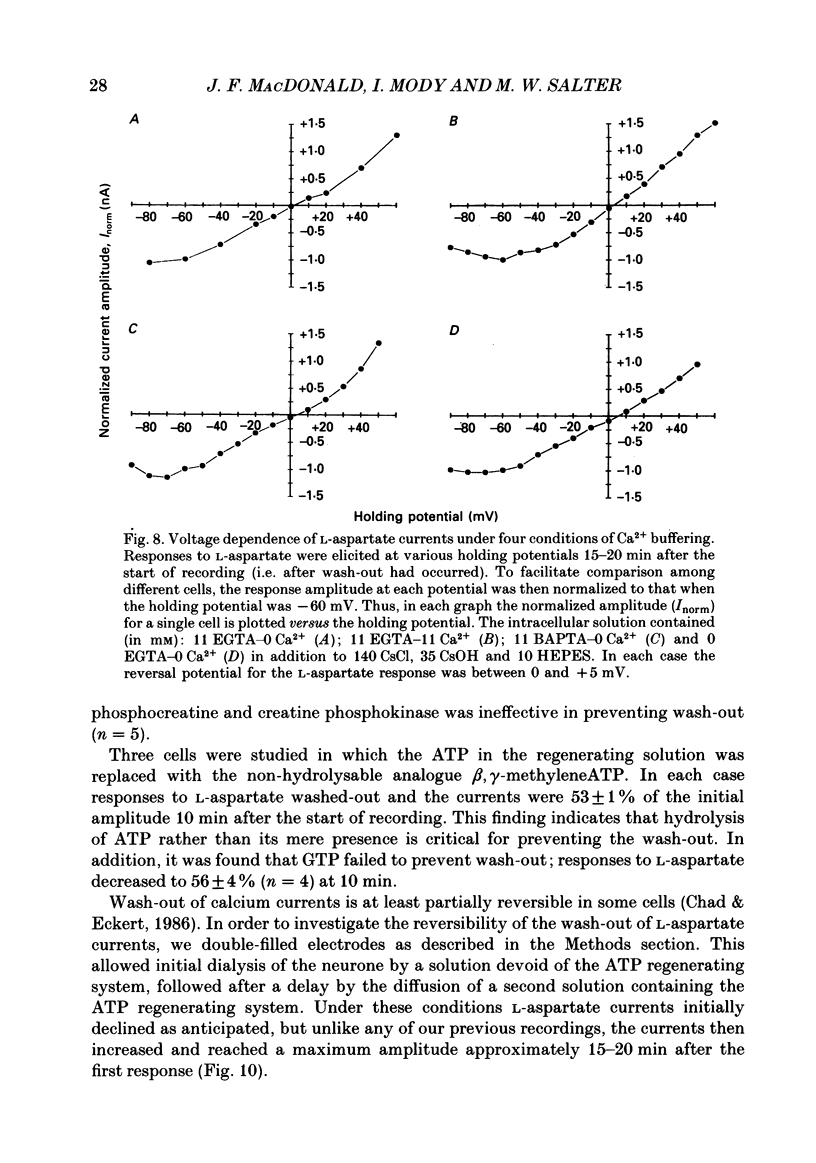
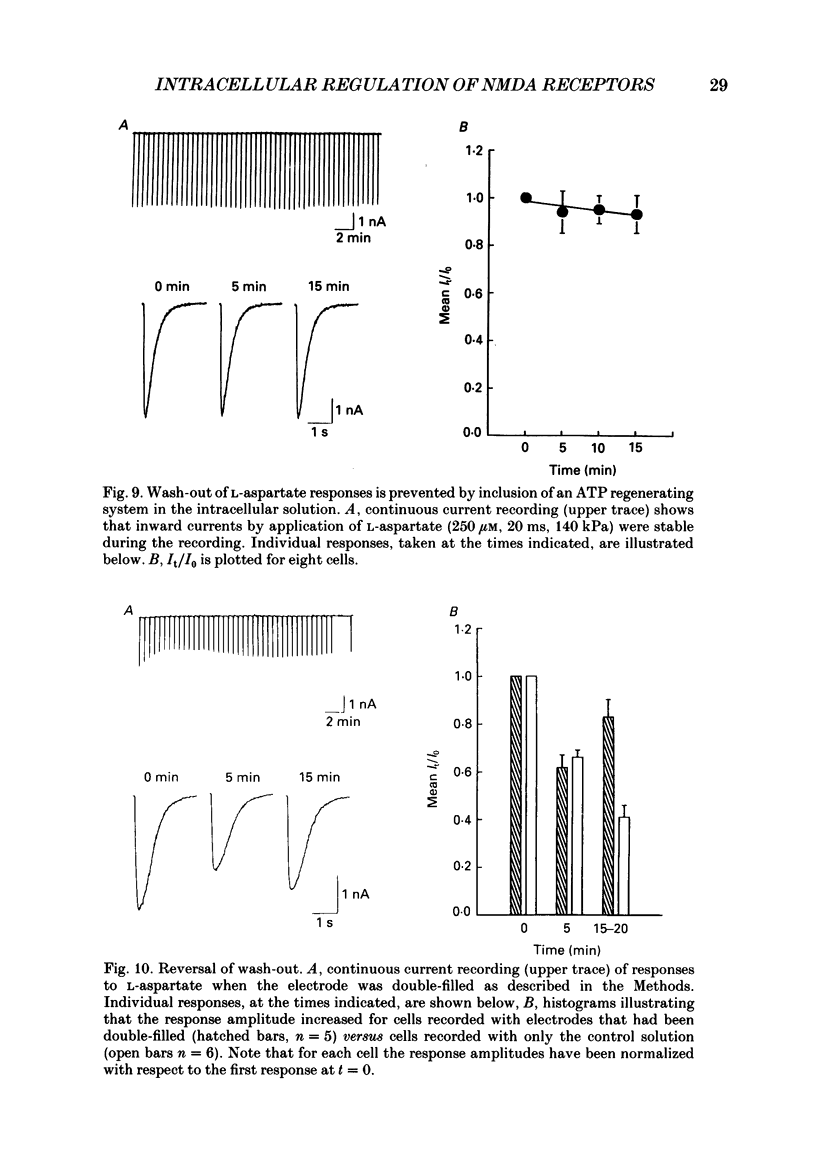
1. The whole-cell patch clamp recording technique was employed to investigate the intracellular regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in cultured murine hippocampal neurones. Excitatory amino acids were repeatedly applied at regular intervals during intracellular dialysis with solutions of various composition. 2. Currents evoked by L-aspartate, an agonist of NMDA receptors, gradually 'washed out' to approximately 50% of their initial amplitude during dialysis with an intracellular solution containing CsCl and EGTA as a calcium buffer. In contrast, responses to kainate did not wash out. The wash-out of L-aspartate currents followed an exponential time course with a time constant of about 150 s. Wash-out did not appear to be related to desensitization of NMDA receptors. 3. Following wash-out, L-aspartate responses were blocked by Mg2+, ketamine or D-2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate indicating that these responses were still mediated by NMDA receptors. Furthermore, responses to NMDA itself showed wash-out to the same extent and with a time course similar to that for L-aspartate responses. 4. Neither the time course nor the extent of the wash-out of responses to L-aspartate was affected when the Ca2+ concentration of the dialysate was varied from zero to 1.5 x 10(-5) M. In addition, wash-out was unaffected by substitution of BAPTA for EGTA, indicating that wash-out was not a consequence of changes in intracellular pH related to the binding of Ca2+ to the buffer or to the kinetics of this binding. Therefore, the wash-out of NMDA currents could not be attributed to a gradual elevation of the concentration of intracellular Ca2+. 5. The extent of the wash-out of L-aspartate currents was similar for cells held at +40 versus -60 mV although the rate of wash-out was slower at the depolarized potential. In addition, the reversal potential of these currents was not altered, demonstrating that a change in driving force did not account for a component of the wash-out. 6. Inclusion of an ATP regeneration solution (Forscher & Oxford, 1985) in the dialysate prevented the wash-out of L-aspartate currents. ATP alone was less effective in preventing wash-out whereas phosphocreatine and creatine phosphokinase were ineffective by themselves. Wash-out also occurred when ATP was replaced with the non-hydrolysable analogue, beta, gamma-methyleneATP, or with GTP. In cells where wash-out of L-aspartate currents had been established, subsequent dialysis with the ATP regenerating solution partially reversed this wash-out.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaike N., Kaneda M., Hori N., Krishtal O. A. Blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate response in enzyme-treated rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Apr 22;87(1-2):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akers R. F., Lovinger D. M., Colley P. A., Linden D. J., Routtenberg A. Translocation of protein kinase C activity may mediate hippocampal long-term potentiation. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):587–589. doi: 10.1126/science.3003904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen C. N., Brady R., Swann J., Hori N., Carpenter D. O. N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are inactivated by trypsin. Brain Res. 1988 Aug 16;458(1):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90507-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Eckert R. Voltage-activated calcium channels that must be phosphorylated to respond to membrane depolarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2518–2522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Nowak L. The role of divalent cations in the N-methyl-D-aspartate responses of mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:247–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balázs R., Hack N., Jørgensen O. S. Stimulation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor has a trophic effect on differentiating cerebellar granule cells. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Apr 22;87(1-2):80–86. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Moody W. J. Intracellular calcium ions and calcium currents in perfused neurones of the snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:637–652. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chad J. E., Eckert R. An enzymatic mechanism for calcium current inactivation in dialysed Helix neurones. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:31–51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Howe J. R., Ogden D. C. Noise and single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:189–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Usowicz M. M. Multiple-conductance channels activated by excitatory amino acids in cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):525–528. doi: 10.1038/325525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forscher P., Oxford G. S. Modulation of calcium channels by norepinephrine in internally dialyzed avian sensory neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1985 May;85(5):743–763. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.5.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantyn R., Lux H. D. Similarity and mutual exclusion of NMDA- and proton-activated transient Na+-currents in rat tectal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jun 29;89(2):198–203. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90381-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Iontophoretic studies of neurones in the mammalian cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Feb;165:274–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauer J. A., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. NMDA application potentiates synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):250–252. doi: 10.1038/334250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger D. M., Wong K. L., Murakami K., Routtenberg A. Protein kinase C inhibitors eliminate hippocampal long-term potentiation. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 8;436(1):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91573-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Miljkovic Z., Pennefather P. Use-dependent block of excitatory amino acid currents in cultured neurons by ketamine. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Aug;58(2):251–266. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Wojtowicz J. M. The effects of L-glutamate and its analogues upon the membrane conductance of central murine neurones in culture. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;60(3):282–296. doi: 10.1139/y82-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson M. P., Dou P., Kater S. B. Outgrowth-regulating actions of glutamate in isolated hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 1988 Jun;8(6):2087–2100. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-06-02087.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., MacDermott A. B., Westbrook G. L., Smith S. J., Barker J. L. Agonist- and voltage-gated calcium entry in cultured mouse spinal cord neurons under voltage clamp measured using arsenazo III. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3230–3244. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03230.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Permeation and block of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor channels by divalent cations in mouse cultured central neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:501–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mody I., Heinemann U. NMDA receptors of dentate gyrus granule cells participate in synaptic transmission following kindling. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):701–704. doi: 10.1038/326701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mody I., Salter M. W., MacDonald J. F. Requirement of NMDA receptor/channels for intracellular high-energy phosphates and the extent of intraneuronal calcium buffering in cultured mouse hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Oct 31;93(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mody I., Stanton P. K., Heinemann U. Activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors parallels changes in cellular and synaptic properties of dentate gyrus granule cells after kindling. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Mar;59(3):1033–1054. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.3.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris M. E., Friedlich J. J., MacDonald J. F. Intracellular calcium in mammalian brain cells: fluorescence measurements with quin2. Exp Brain Res. 1987;65(3):520–526. doi: 10.1007/BF00235975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. N., Thayer S. A., Miller R. J. The effects of excitatory amino acids on intracellular calcium in single mouse striatal neurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1987 Dec;7(12):4145–4158. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-12-04145.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce I. A., Cambray-Deakin M. A., Burgoyne R. D. Glutamate acting on NMDA receptors stimulates neurite outgrowth from cerebellar granule cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80525-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Neher E. Rates of diffusional exchange between small cells and a measuring patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):204–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00582316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelzer A., Kay A. R., Wong R. K. GABAA-receptor function in hippocampal cells is maintained by phosphorylation factors. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):339–341. doi: 10.1126/science.2455347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockbridge N. EGTA. Comput Biol Med. 1987;17(5):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(87)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyklicky L., Jr, Krusek J., Edwards C. Differences in the pore sizes of the N-methyl-D-aspartate and kainate cation channels. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jul 8;89(3):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90545-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount R. G. ATP analogs. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:1–56. doi: 10.1002/9780470122884.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


