Abstract
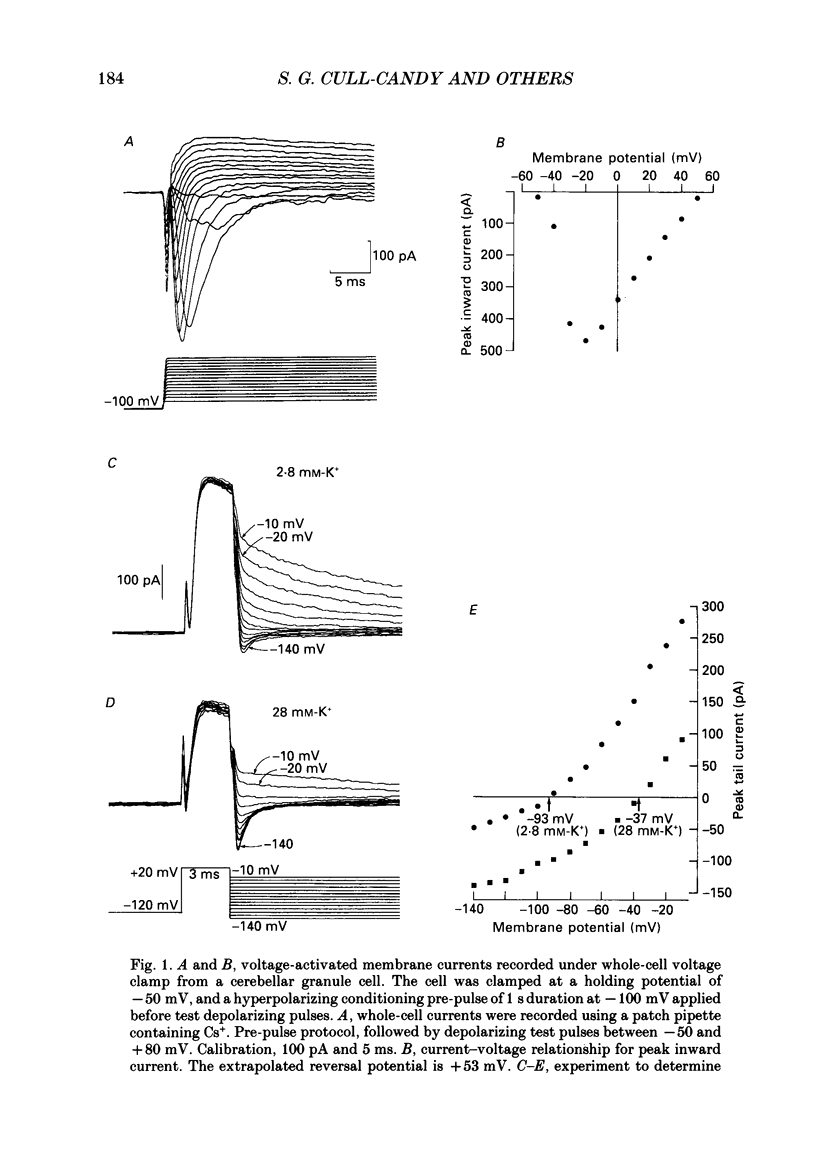
1. Voltage-activated currents have been recorded from cerebellar granule neurones in explant cultures from young rats (1-9 days old). Cells were examined with whole-cell patch-clamp methods. Depolarizing pulses from a pre-pulse potential of -100 mV evoked a rapidly activated transient inward current, and an outward current which decayed in two phases. The ionic dependence, kinetics and pharmacological properties of these currents have been studied. 2. Peak inward Na+ currents in cells from 7-day-old rats were in the range 350-450 pA. No evidence was found for the presence of calcium currents. Thus, inward current was unchanged in zero Ca2+, 1 mM-EGTA solution. No inward current was obtained in medium containing 10 mM-Ba2+ and tetrodotoxin (TTX). Supplementing the pipette (i.e. intracellular) solution with Mg-ATP did not reveal any Ca2+ current. 3. Depolarizing steps (from -100 mV) in TTX-containing solution gave an early transient outward current and a late outward current. The transient current resembled IA described in other cells, and reversed close to EK in both normal and elevated potassium concentrations, indicating that K+ is the predominant charge carrier. Depolarizing steps from -50 mV failed to give a transient outward current, and gave only a slowly rising current which resembled the late potassium current, IK. 4. Inactivation of the transient current was examined by applying test depolarizations from increasingly negative pre-pulse potentials (-50 to -120 mV): half-inactivation occurred at -72 mV. Transient outward currents decayed exponentially with time constants, tau, of 7.3-25.3 ms at 0 mV. The time course of removal of inactivation in cells held at -50 mV, and given increasingly long pre-pulses to -100 mV, was exponential with tau = 35 ms. 5. Both transient and late outward currents were reversibly abolished by addition to the bathing medium of 10 mM-Ba2+ or 1 mM-quinine. Outward K+ current was not dependent on external calcium. Tetraethylammonium (20 mM) selectively reduced the late outward current; the peak transient current was reduced by less than 20%. 4-Aminopyridine (2 mM) showed little selectivity between transient and late outward currents. 6. It is concluded that cerebellar granule cells from young rats possess voltage-activated inward Na+ current as well as two types of K+ current, IA and IK. In terms of neuronal functioning, the properties of the transient outward current may confer a role in regulating excitability and in repolarization, but a definitive statement will require knowledge of the cellular location and relative densities of channels in granule cells in vivo.
Full text
PDF





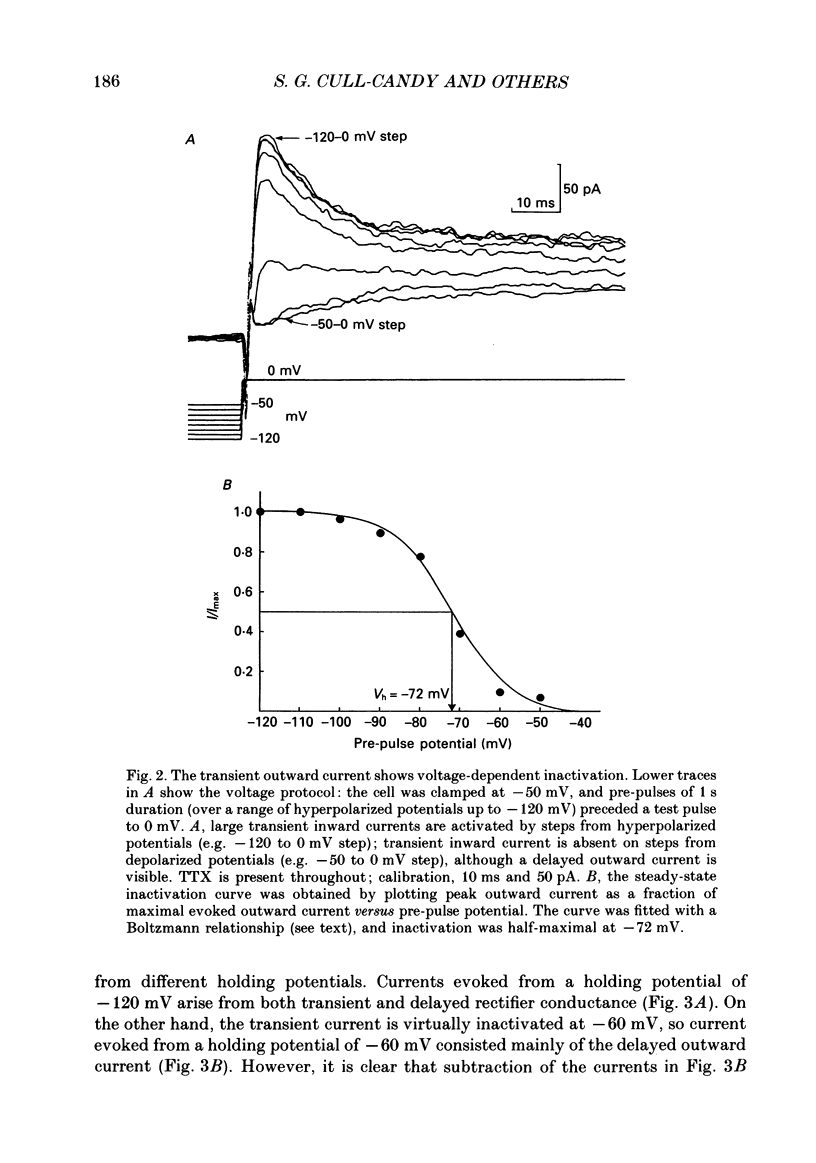
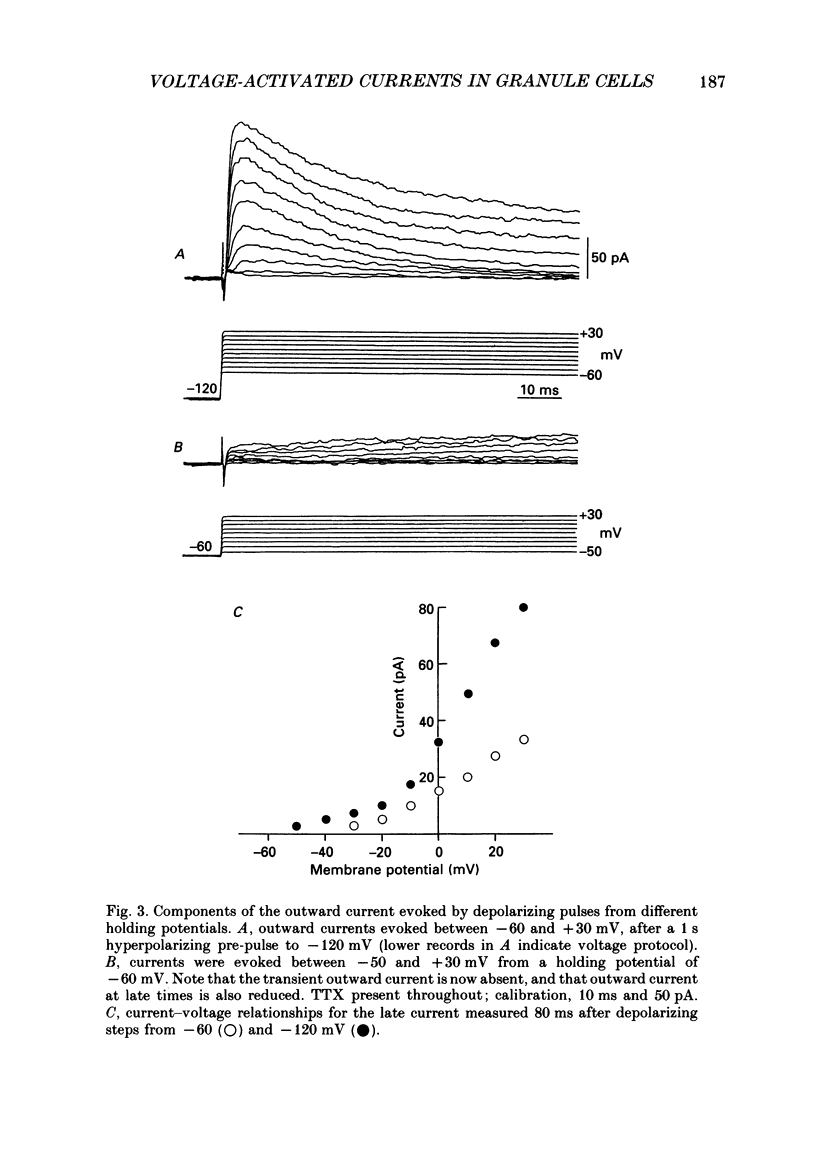
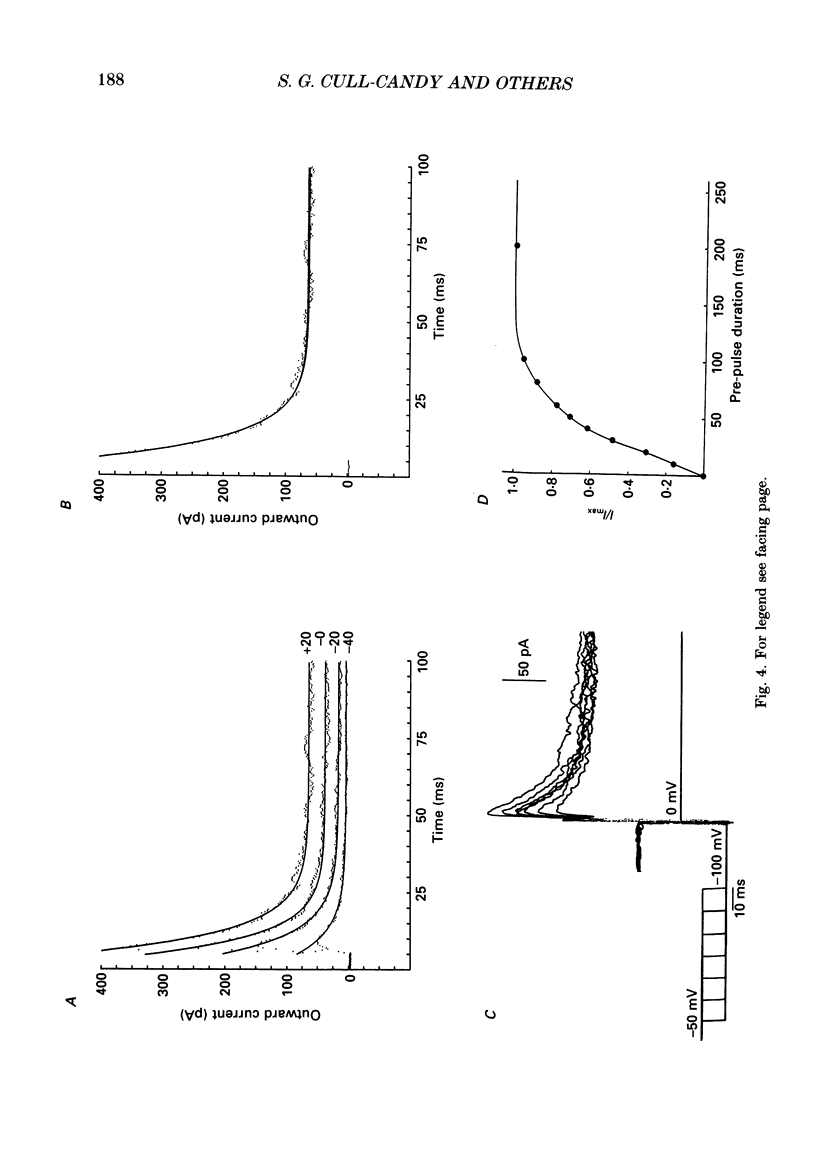









Selected References
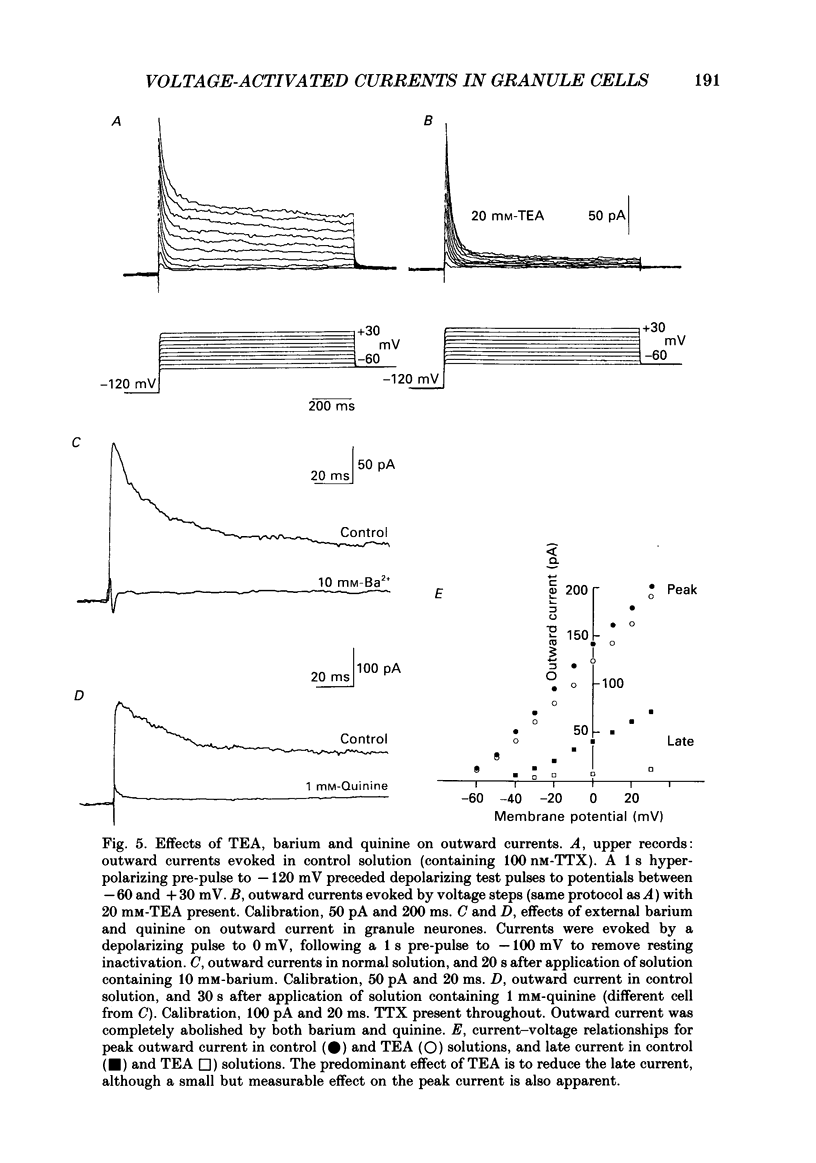
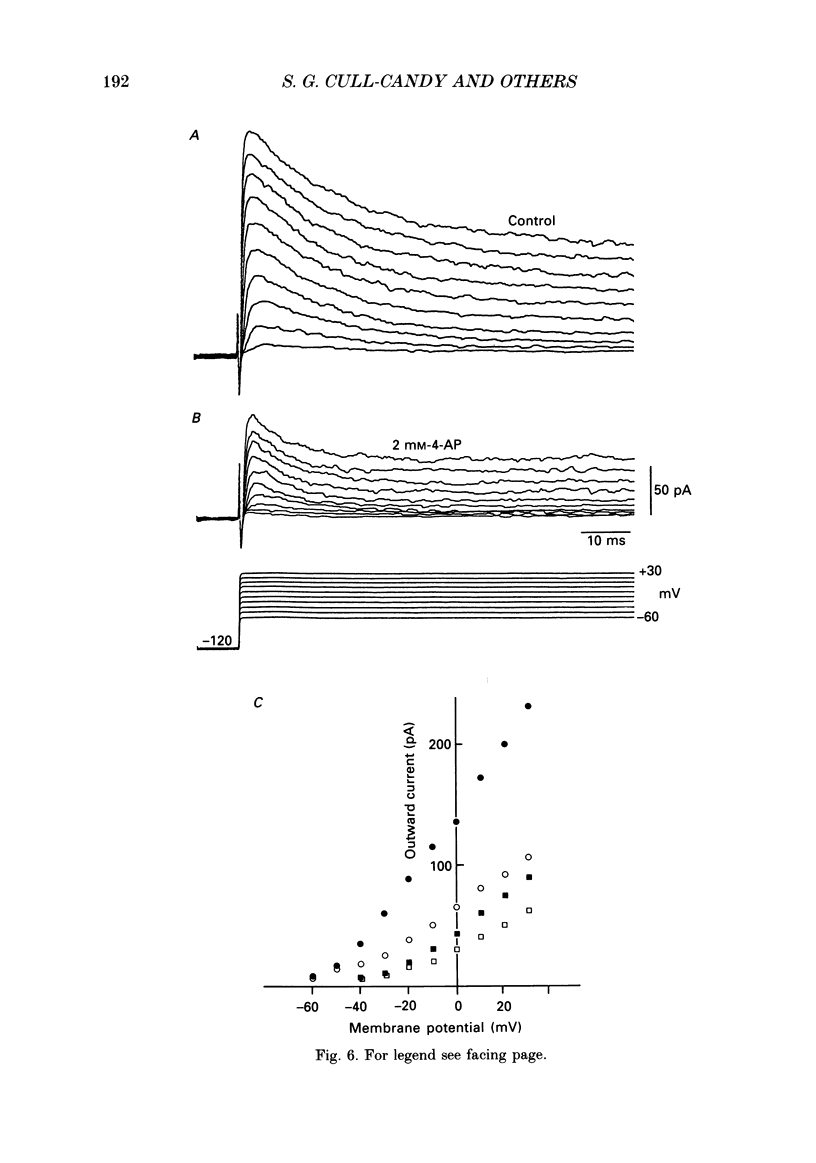
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aghajanian G. K. Modulation of a transient outward current in serotonergic neurones by alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):501–503. doi: 10.1038/315501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman J. Postnatal development of the cerebellar cortex in the rat. 3. Maturation of the components of the granular layer. J Comp Neurol. 1972 Aug;145(4):465–513. doi: 10.1002/cne.901450403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., Bertrand D., Dupin E. Voltage-dependent potassium currents in developing neurones from quail mesencephalic neural crest. J Physiol. 1985 Sep;366:129–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale R., Dutton G. R., Currie D. N. An ion flux assay of action potential sodium channels in neuron- and glia-enriched cultures of cells dissociated from rat cerebellum. Brain Res. 1980 Feb 3;183(1):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belluzzi O., Sacchi O., Wanke E. A fast transient outward current in the rat sympathetic neurone studied under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:91–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Yazejian B. Intracellular factors for the maintenance of calcium currents in perfused neurones from the snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:631–650. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., Balázs R., Hajós F., Currie D. N., Dutton G. R. Separation of cell types from the developing cerebellum. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 16;148(2):313–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90722-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Tseng H. Y., Hockberger P. E. Depolarization- and transmitter-induced changes in intracellular Ca2+ of rat cerebellar granule cells in explant cultures. J Neurosci. 1987 May;7(5):1384–1400. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-05-01384.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Howe J. R., Ogden D. C. Noise and single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:189–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Ogden D. C. Ion channels activated by L-glutamate and GABA in cultured cerebellar neurons of the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 May 22;224(1236):367–373. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Galvan M., Grafe P., Wigström H. A transient outward current in a mammalian central neurone blocked by 4-aminopyridine. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):252–254. doi: 10.1038/299252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ohmori H. Studies of single calcium channel currents in rat clonal pituitary cells. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:649–661. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Gorman A. L. Effects of 4-aminopyridine on potassium currents in a molluscan neuron. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jul;78(1):63–86. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Kubo Y., Wu M. M. Cerebellar granule cells in culture: monosynaptic connections with Purkinje cells and ionic currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4957–4961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockberger P. E., Tseng H. Y., Connor J. A. Immunocytochemical and electrophysiological differentiation of rat cerebellar granule cells in explant cultures. J Neurosci. 1987 May;7(5):1370–1383. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-05-01370.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen J., Kleinhaus A. L. Transient and delayed potassium currents in the Retzius cell of the leech, Macrobdella decora. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Sep;56(3):812–822. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.56.3.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Kameyama M., Yamaguchi K., Fukuda J. Single transient K channels in mammalian sensory neurons. Biophys J. 1986 Jun;49(6):1243–1247. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83754-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. R., Wong R. K. Calcium current activation kinetics in isolated pyramidal neurones of the Ca1 region of the mature guinea-pig hippocampus. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:603–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi G., Gallo V. Release studies related to the neurotransmitter role of glutamate in the cerebellum: an overview. Neurochem Res. 1986 Dec;11(12):1627–1642. doi: 10.1007/BF00967741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Calcium conductances in Purkinje cell dendrites: their role in development and integration. Prog Brain Res. 1979;51:323–334. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)61312-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Westbrook G. L. Early development of voltage-dependent sodium currents in cultured mouse spinal cord neurons. Dev Biol. 1986 Feb;113(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Leonard R. J., Yamaguchi K. Acetylcholine raises excitability by inhibiting the fast transient potassium current in cultured hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3022–3026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jul;58(1):36–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerbonne J. M., Gurney A. M., Rayburn H. B. Development of the fast, transient outward K+ current in embryonic sympathetic neurones. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 16;378(1):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Wroblewski J. T., Novelli A., Alho H., Guidotti A., Costa E. The activation of inositol phospholipid metabolism as a signal-transducing system for excitatory amino acids in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci. 1986 Jul;6(7):1905–1911. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-07-01905.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numann R. E., Wadman W. J., Wong R. K. Outward currents of single hippocampal cells obtained from the adult guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:331–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Multiple potassium-channel components are produced by alternative splicing at the Shaker locus in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):137–142. doi: 10.1038/331137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Barker J. L. Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: potassium conductances. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Jun;51(6):1409–1433. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.6.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Rogawski M. A., Barker J. L. A transient potassium conductance regulates the excitability of cultured hippocampal and spinal neurons. J Neurosci. 1984 Feb;4(2):604–609. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-02-00604.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solc C. K., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Single-channel and genetic analyses reveal two distinct A-type potassium channels in Drosophila. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1094–1098. doi: 10.1126/science.2437657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Anderton B. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mammalian neurofilaments. Biosci Rep. 1981 Mar;1(3):263–268. doi: 10.1007/BF01114913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


