Abstract
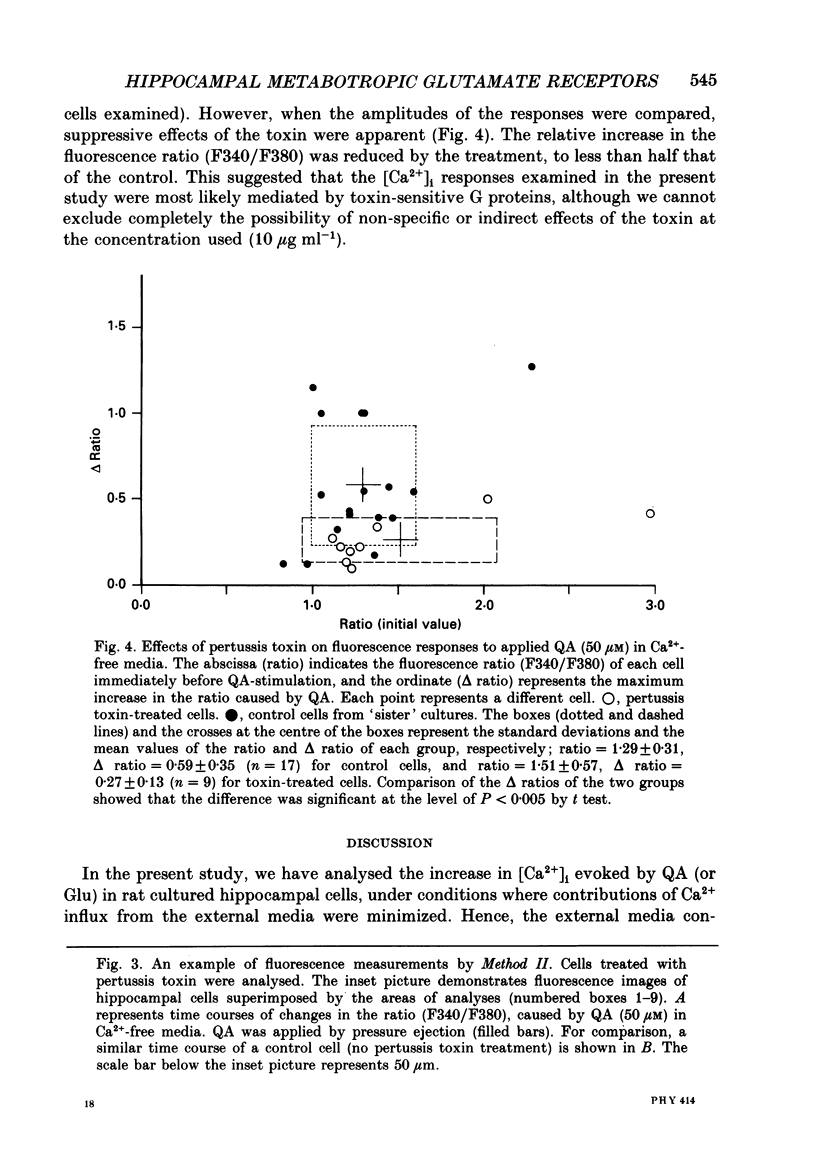
1. Intracellular free calcium ([Ca2+]i) was monitored by means of Fura-2 fluorescence measurements in hippocampal cells in primary cultures from newborn rats. 2. In external media containing 200 microM-DL-2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate and 1 mM-kynurenate, but no added Ca2+, an increase in [Ca2+]i was observed in 30-40% of cells examined in response to quisqualate or L-glutamate. 3. Under such conditions, [Ca2+]i often increased gradually with a latency of a few seconds after application of the agonists. 4. Pre-treatment of the cultured cells with pertussis toxin reduced the extent of quisqualate-stimulated [Ca2+]i increase in Ca2+-free media, but the percentage of the responsive cells was not affected appreciably. 5. It is concluded that quisqualate and L-glutamate can trigger the release of Ca2+ from intracellular Ca2+ stores, most likely by activating a glutamate receptor coupled to a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein.
Full text
PDF


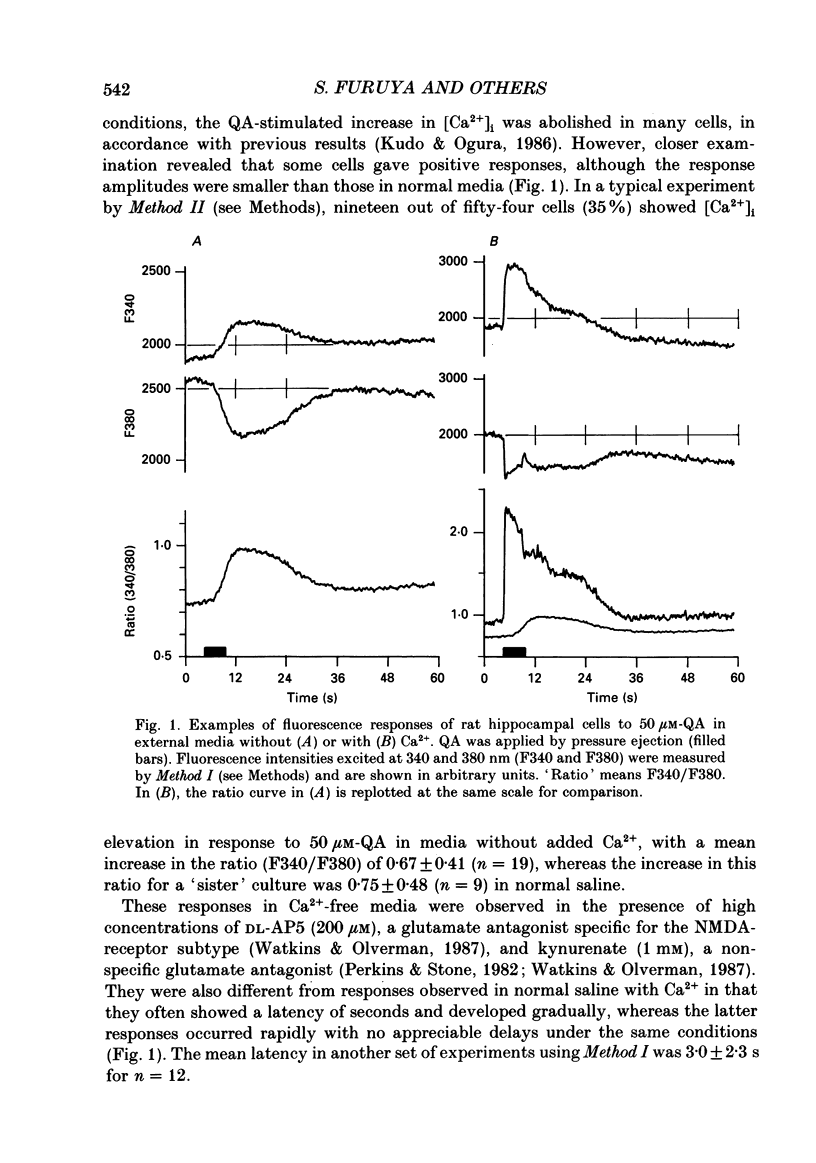
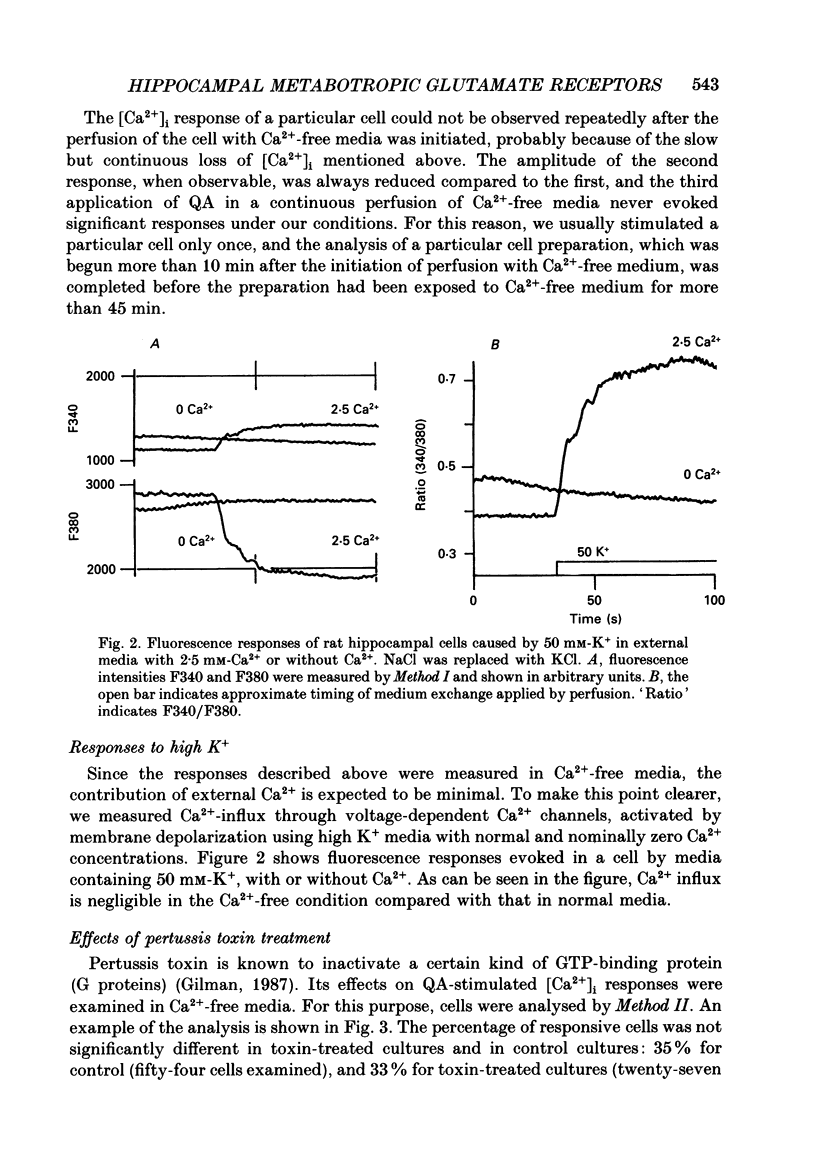



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ascher P., Nowak L. The role of divalent cations in the N-methyl-D-aspartate responses of mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:247–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
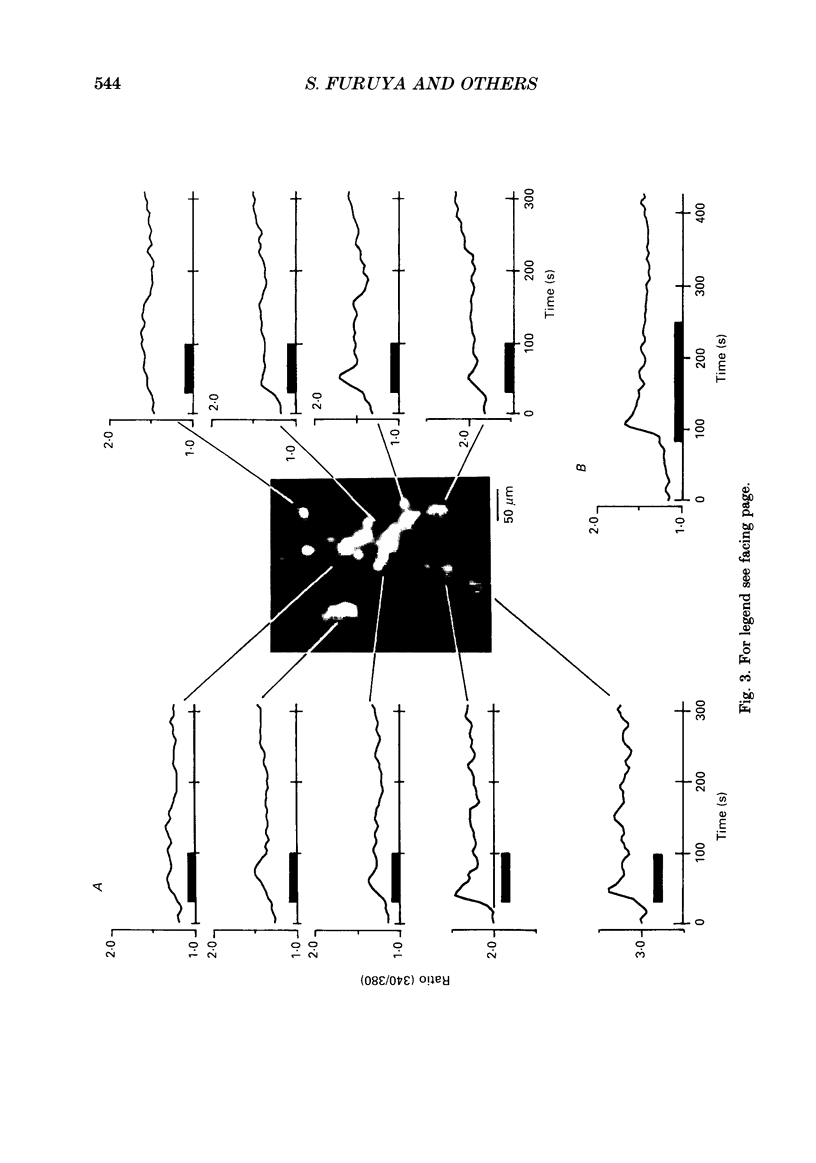
- Banker G. A., Cowan W. M. Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res. 1977 May 13;126(3):397–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90594-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottenstein J. E., Sato G. H. Growth of a rat neuroblastoma cell line in serum-free supplemented medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):514–517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito I., Okada D., Sugiyama H. Pertussis toxin suppresses long-term potentiation of hippocampal mossy fiber synapses. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jul 19;90(1-2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90808-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo Y., Ogura A. Glutamate-induced increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration in isolated hippocampal neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep;89(1):191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch G., Larson J., Kelso S., Barrionuevo G., Schottler F. Intracellular injections of EGTA block induction of hippocampal long-term potentiation. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):719–721. doi: 10.1038/305719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Smith S. J., Barker J. L. NMDA-receptor activation increases cytoplasmic calcium concentration in cultured spinal cord neurones. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):519–522. doi: 10.1038/321519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Kauer J. A., Zucker R. S., Nicoll R. A. Postsynaptic calcium is sufficient for potentiation of hippocampal synaptic transmission. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):81–84. doi: 10.1126/science.2845577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., MacDermott A. B., Westbrook G. L., Smith S. J., Barker J. L. Agonist- and voltage-gated calcium entry in cultured mouse spinal cord neurons under voltage clamp measured using arsenazo III. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3230–3244. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03230.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Permeation and block of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor channels by divalent cations in mouse cultured central neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:501–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. N., Miller R. J. A glutamate receptor regulates Ca2+ mobilization in hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Meek J. L., Iadarola M. J., Chuang D. M., Roth B. L., Costa E. Coupling of inositol phospholipid metabolism with excitatory amino acid recognition sites in rat hippocampus. J Neurochem. 1986 Jan;46(1):40–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12922.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Wroblewski J. T., Fadda E., Costa E. Pertussis toxin inhibits signal transduction at a specific metabolotropic glutamate receptor in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. Neuropharmacology. 1988 Jun;27(6):551–556. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori H. Mechanical stimulation and Fura-2 fluorescence in the hair bundle of dissociated hair cells of the chick. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:115–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. N., Stone T. W. An iontophoretic investigation of the actions of convulsant kynurenines and their interaction with the endogenous excitant quinolinic acid. Brain Res. 1982 Sep 9;247(1):184–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Récasens M., Sassetti I., Nourigat A., Sladeczek F., Bockaert J. Characterization of subtypes of excitatory amino acid receptors involved in the stimulation of inositol phosphate synthesis in rat brain synaptoneurosomes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 2;141(1):87–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90413-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Pin J. P., Récasens M., Bockaert J., Weiss S. Glutamate stimulates inositol phosphate formation in striatal neurones. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):717–719. doi: 10.1038/317717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Ito I., Hirono C. A new type of glutamate receptor linked to inositol phospholipid metabolism. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):531–533. doi: 10.1038/325531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]