Abstract
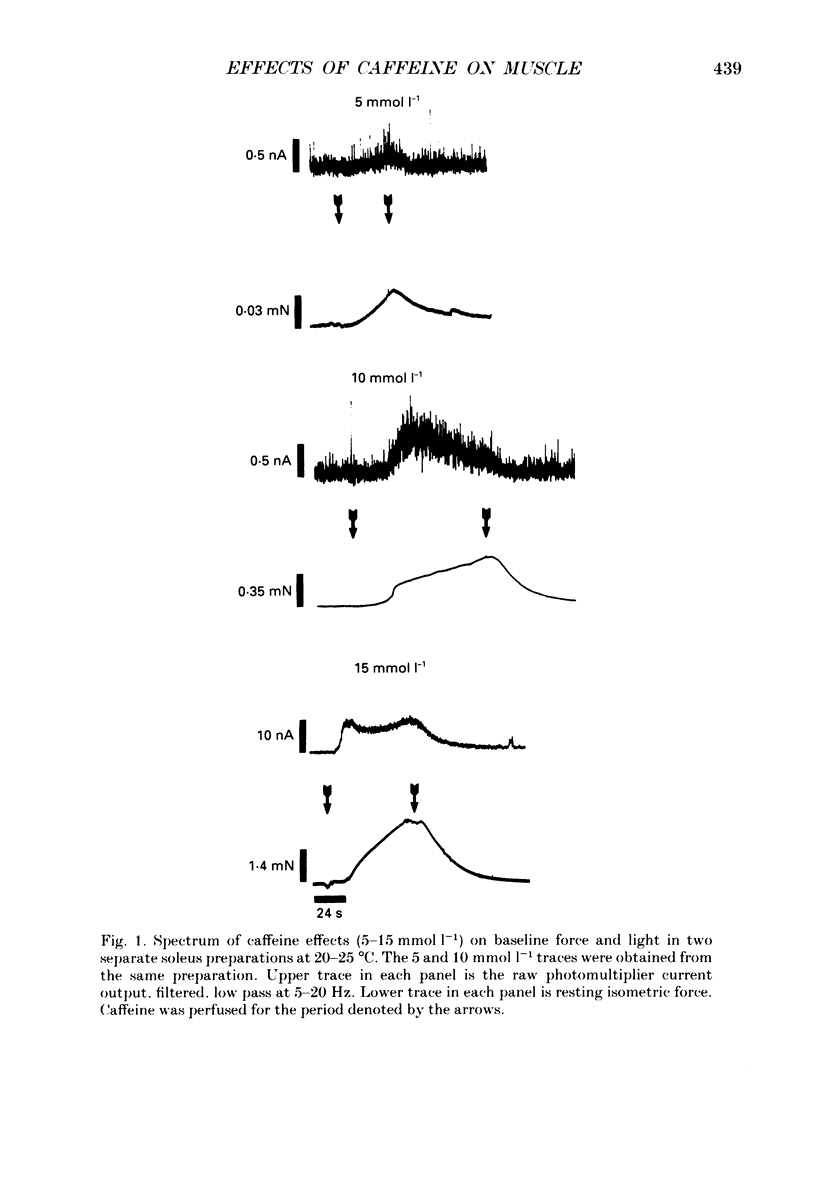
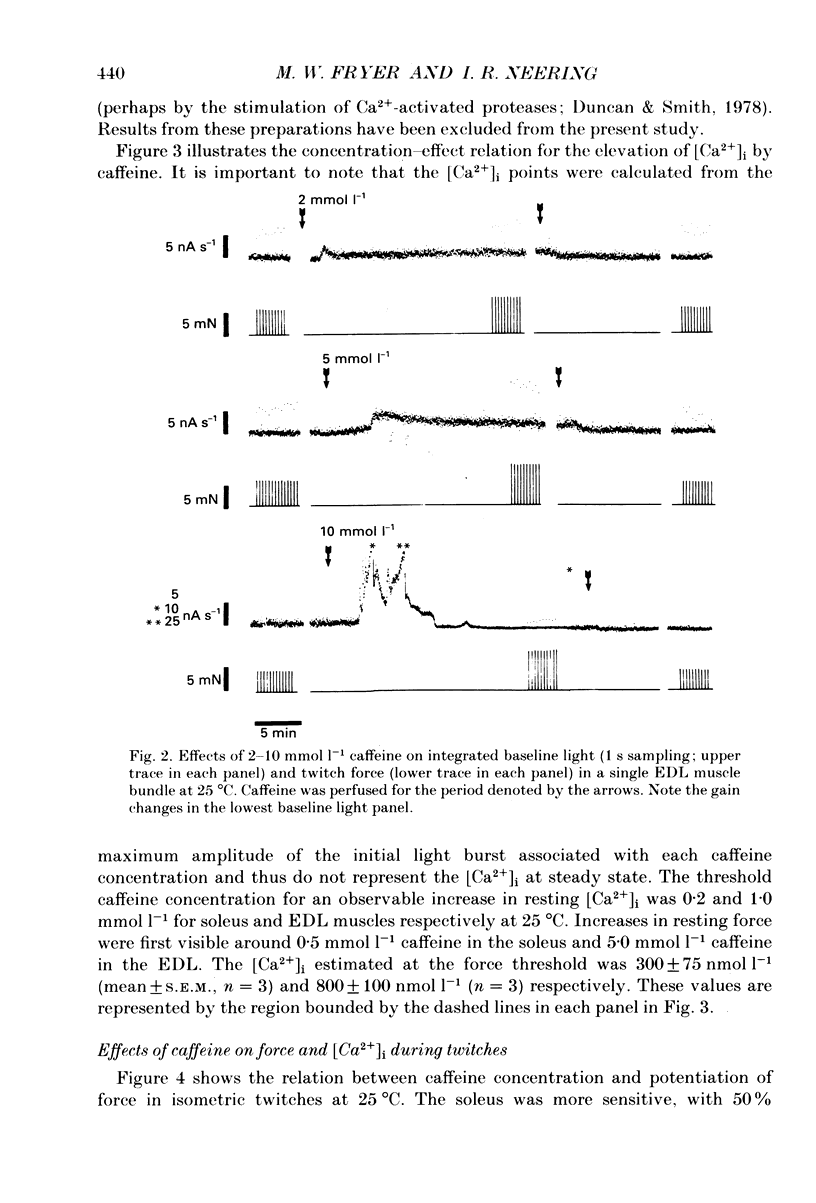
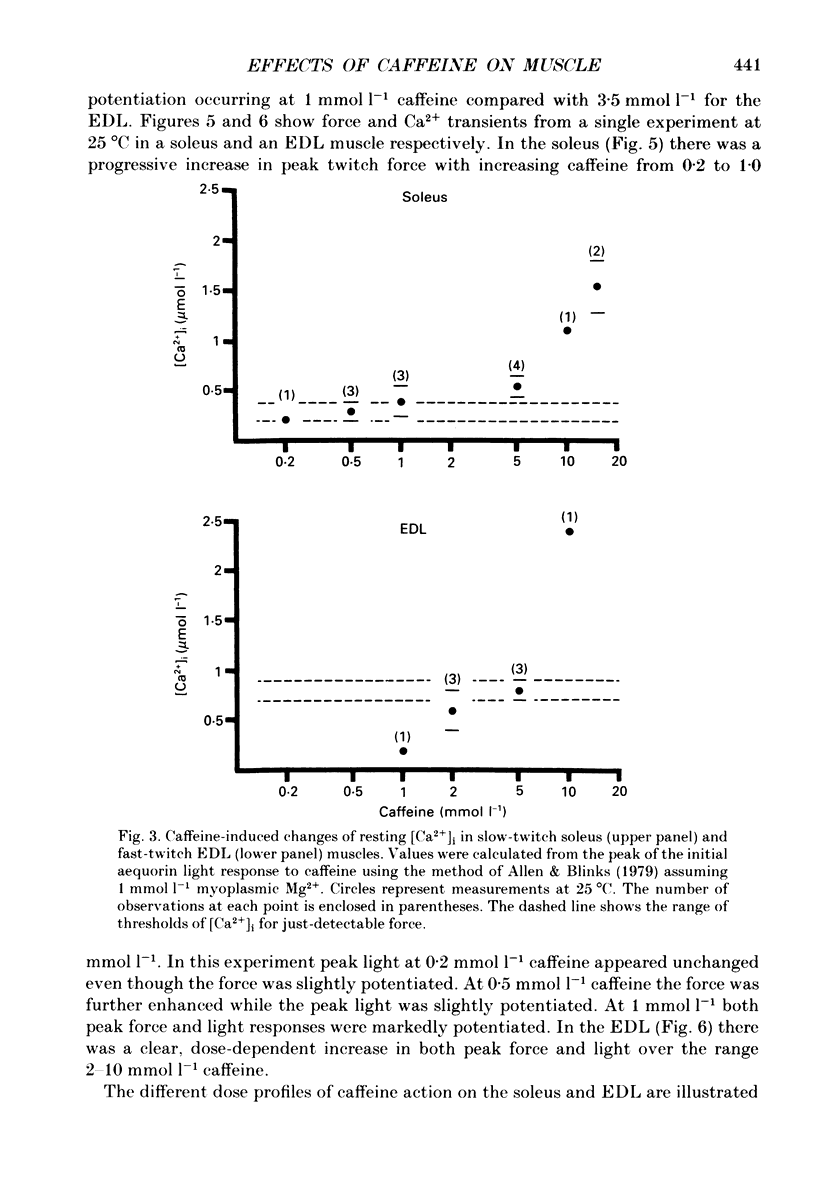
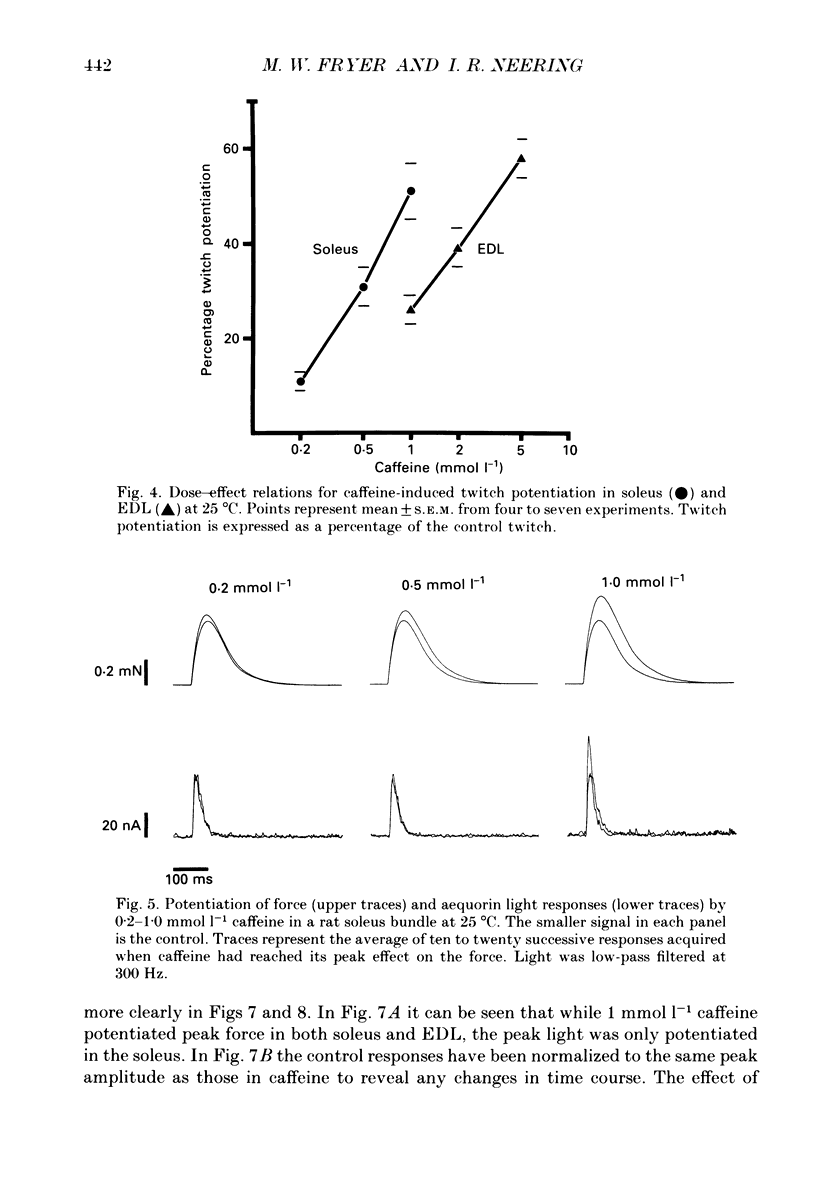
1. The effects of caffeine (0.2-20 mmol l-1) have been examined on calcium transients (measured with aequorin) and isometric force in intact bundles of fibres from soleus (slow-twitch) and extensor digitorum longus (EDL; fast-twitch) muscles of the rat. 2. At 25 degrees C, threshold caffeine concentration for an observable increase in resting [Ca2+]i was 0.2 and 1.0 mmol l-1 for soleus and EDL muscles respectively. Increases in resting force were first detectable at about 0.5 mmol l-1 caffeine for soleus muscles and 5.0 mmol l-1 caffeine for EDL muscles and occurred in the range 0.2-0.4 mumol l-1 [Ca2+]i for soleus and 0.7-0.9 mumol l-1 for EDL. 3. Caffeine potentiated the twitch responses of soleus and EDL in a dose-related manner. The soleus was more sensitive in this respect, with 50% potentiation occurring at 1 mmol l-1 caffeine compared with 3.5 mmol l-1 for the EDL. Concentrations of caffeine below 2 mmol l-1 potentiated Ca2+ transients associated with twitches in both soleus and EDL muscles with no apparent change in the decay rate constant. 4. High concentrations of caffeine (greater than 2 mmol l-1) further potentiated peak Ca2+ in the EDL but depressed it in the soleus. The rate of decay of the Ca2+ transient in high caffeine was significantly prolonged in the soleus but remained unaffected in the EDL. 5. The phosphodiesterase inhibitor, 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX) had little effect on force or [Ca2+]i at concentrations known to significantly increase intracellular cyclic AMP levels. 6. The Ca2+ transient during fused tetani was characterized by an initial peak, a decline to a plateau level and sometimes a gradual rise towards the end of the stimulus train. Peak [Ca2+]i during normal tetani ranged between 1.1 and 2.4 mumol l-1 in the soleus and 1.9 and 4.0 mumol l-1 in the EDL. 7. Caffeine potentiated both force and [Ca2+]i during tetanus. Since the increase of the Ca2+ transient was significantly greater than potentiation of force, it is likely that saturation of myofilaments occurs. The primary effect of caffeine on the Ca2+ transient was an elevation of the plateau phase. 8. Caffeine concentrations below 5 mmol l-1 potentiate twitch and tetanic force in both fast- and slow-twitch mammalian skeletal muscles primarily by increasing both the basal and stimulus-evoked release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELSSON J., THESLEFF S. Activation of the contractile mechanism in striated muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Oct 28;44(1):55–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abercrombie R. F., Roos A. The intracellular pH of frog skeletal muscle: its regulation in hypertonic solutions. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:189–204. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen D. G., Kurihara S. The effects of muscle length on intracellular calcium transients in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:79–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Rüdel R., Taylor S. R. Calcium transients in isolated amphibian skeletal muscle fibres: detection with aequorin. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:291–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Wier W. G., Hess P., Prendergast F. G. Measurement of Ca2+ concentrations in living cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(1-2):1–114. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Allen D. G. Model of calcium movements during activation in the sarcomere of frog skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):913–925. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84238-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R., Heizmann C. W. Calcium-binding protein parvalbumin is associated with fast contracting muscle fibres. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):504–506. doi: 10.1038/297504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connett R. J., Ugol L. M., Hammack M. J., Hays E. T. Twitch potentiation and caffeine contractures in isolated rat soleus muscle. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1983;74(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(83)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delay M., Ribalet B., Vergara J. Caffeine potentiation of calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Jun;375:535–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F., Banyard M. R., Medveczky C. J. Distribution of calcium ATPase in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of fast- and slow-twitch muscles determined with monoclonal antibodies. J Membr Biol. 1987;99(2):79–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01871228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. J., Smith J. L. The action of caffeine in promoting ultrastructural damage in frog skeletal muscle fibres. Evidence for the involvement of the calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;305(2):159–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00508287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eusebi F., Miledi R., Takahashi T. Calcium transients in mammalian muscles. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):560–561. doi: 10.1038/284560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairhurst A. S. A ryanodine-caffeine-sensitive membrane fraction of skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1974 Nov;227(5):1124–1131. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.5.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryer M. W., Neering I. R. Relationship between intracellular calcium concentration and relaxation of rat fast and slow muscles. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Feb 28;64(2):231–235. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryer M. W., Neering I. R., Stephenson D. G. Effects of 2,3-butanedione monoxime on the contractile activation properties of fast- and slow-twitch rat muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:53–75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs F. Inhibition of sarcotubular calcium transport by caffeine: species and temperature dependence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 8;172(3):566–570. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iaizzo P. A., Klein W., Lehmann-Horn F. Fura-2 detected myoplasmic calcium and its correlation with contracture force in skeletal muscle from normal and malignant hyperthermia susceptible pigs. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jun;411(6):648–653. doi: 10.1007/BF00580861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson A., Hinkes M. J., Taylor S. R. Contracture and twitch potentiation of fast and slow muscles of the rat at 20 and 37 C. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jan;218(1):33–41. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Kurihara S. Effects of caffeine on intracellular calcium concentrations in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:269–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Kurihara S., Sakai T. Change in intracellular calcium ion concentration induced by caffeine and rapid cooling in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1985 Aug;365:131–146. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Szücs G. Effect of caffeine on intramembrane charge movement and calcium transients in cut skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:559–578. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer G. L., Wells J. N. Xanthines and skeletal muscle: lack of relationship between phosphodiesterase inhibition and increased twitch tension in rat diaphragms. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;17(1):73–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberer E., Pette D. Immunochemical quantification of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase, of calsequestrin and of parvalbumin in rabbit skeletal muscles of defined fiber composition. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 2;156(3):489–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. R., Wanek L. A., Taylor S. R. Skeletal muscle: length-dependent effects of potentiating agents. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.6974399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Oetliker H. The action of caffeine on the activation of the contractile mechanism in straited muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):51–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney R. N., Neering I. R. The measurement of changes in intracellular free calcium during action potentials in mammalian neurones. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Mar;13(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Zhu P. H. Calcium transients evoked by action potentials in frog twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:655–679. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Blinks J. R. Intracellular Ca2+ transients in the cat papillary muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Apr;60(4):524–528. doi: 10.1139/y82-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagala M. K. Effect of length and caffeine on isometric tetanus relaxation of frog sartorius muscles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 10;591(1):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDOW A., TAYLOR S. R., ISAASON A., SEGUIN J. J. ELECTROCHEMICAL COUPLING IN POTENTIATION OF MUSCULAR CONTRACTION. Science. 1964 Feb 7;143(3606):577–579. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3606.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson M. M., Coelho H. S., Reuben J. P. Caffeine inhibition of calcium accumulation by the sarcoplasmic reticulum in mammalian skinned fibers. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(3):219–230. doi: 10.1007/BF01870128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Williams D. A. Calcium-activated force responses in fast- and slow-twitch skinned muscle fibres of the rat at different temperatures. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:281–302. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. W. Ca2+ dependence of stimulated 45Ca efflux in skinned muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Apr;77(4):419–443. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.4.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su J. Y., Hasselbach W. Caffeine-induced calcium release from isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum of rabbit skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Jan;400(1):14–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00670530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Herz R. The relationship between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Nov;52(5):750–759. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.5.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt I. R., Stephenson D. G. Effects of caffeine on Ca-activated force production in skinned cardiac and skeletal muscle fibres of the rat. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Aug;398(3):210–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00657153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka T., Somlyo A. P. Calcium and magnesium contents and volume of the terminal cisternae in caffeine-treated skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):558–568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


