Abstract
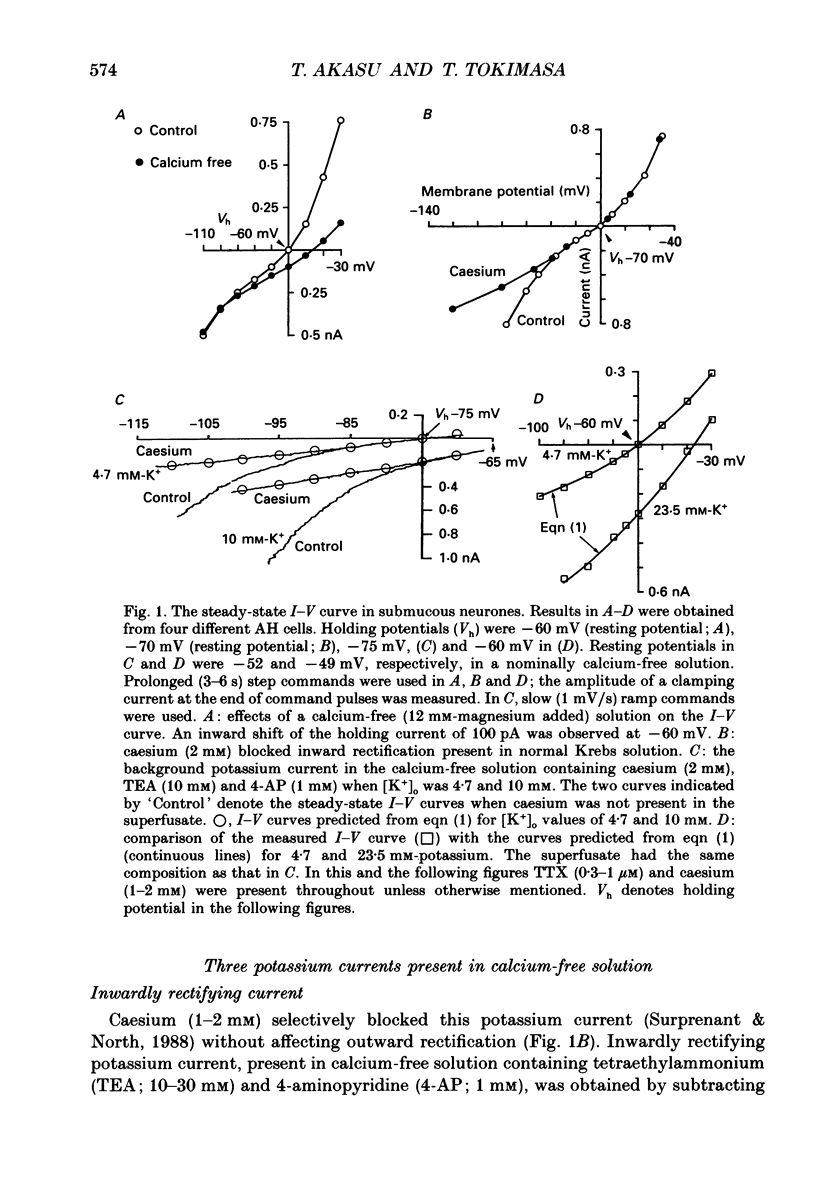
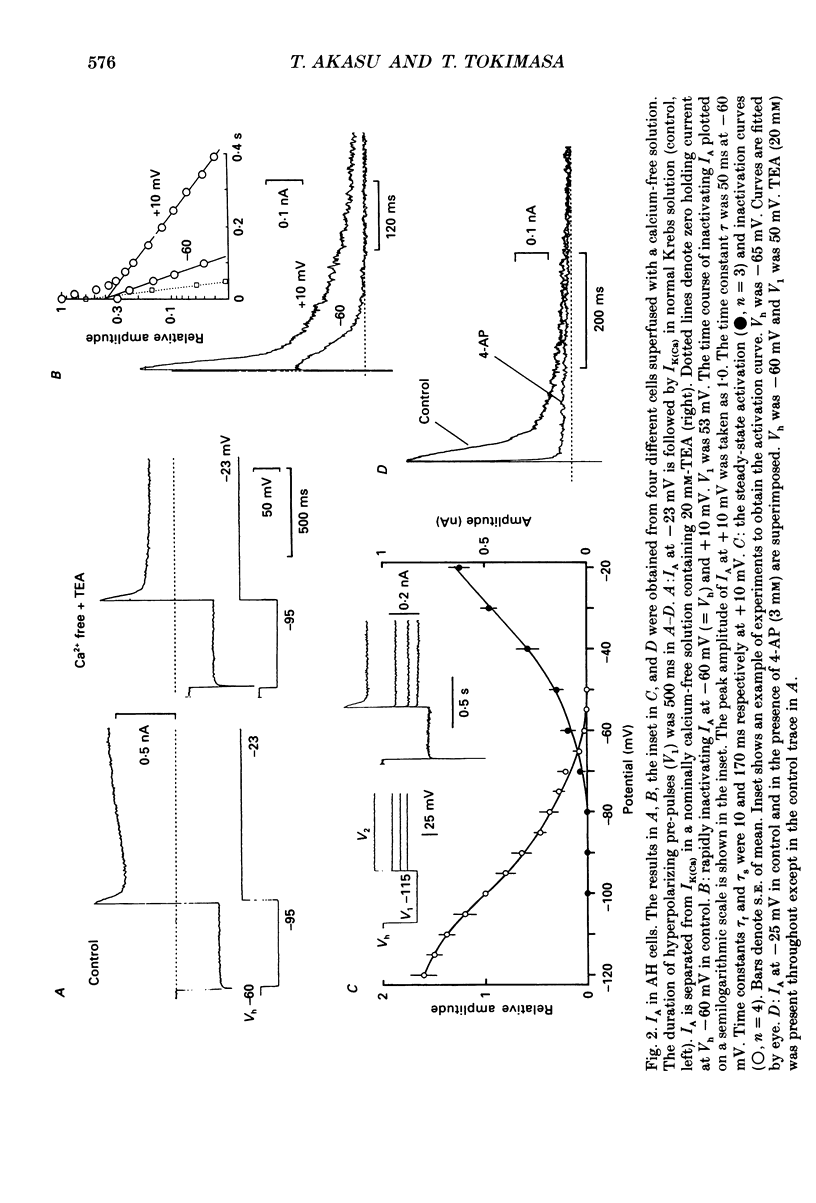
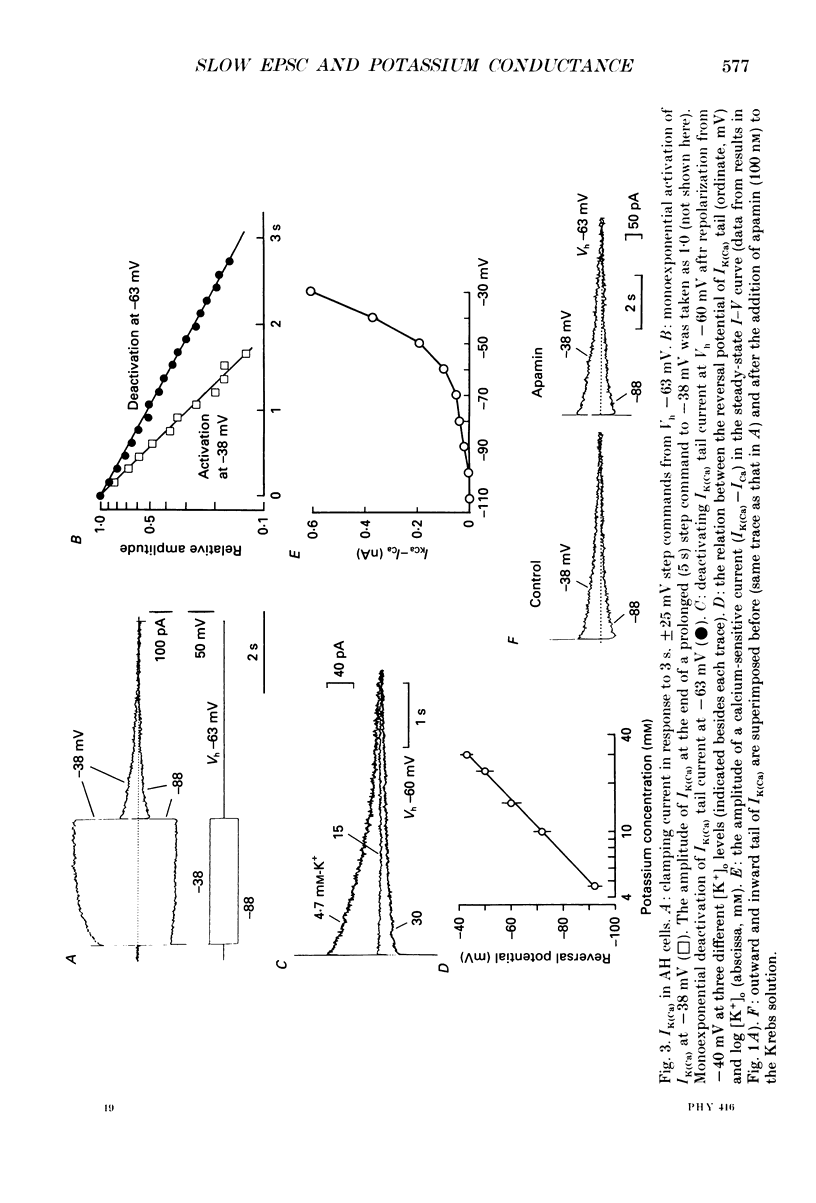
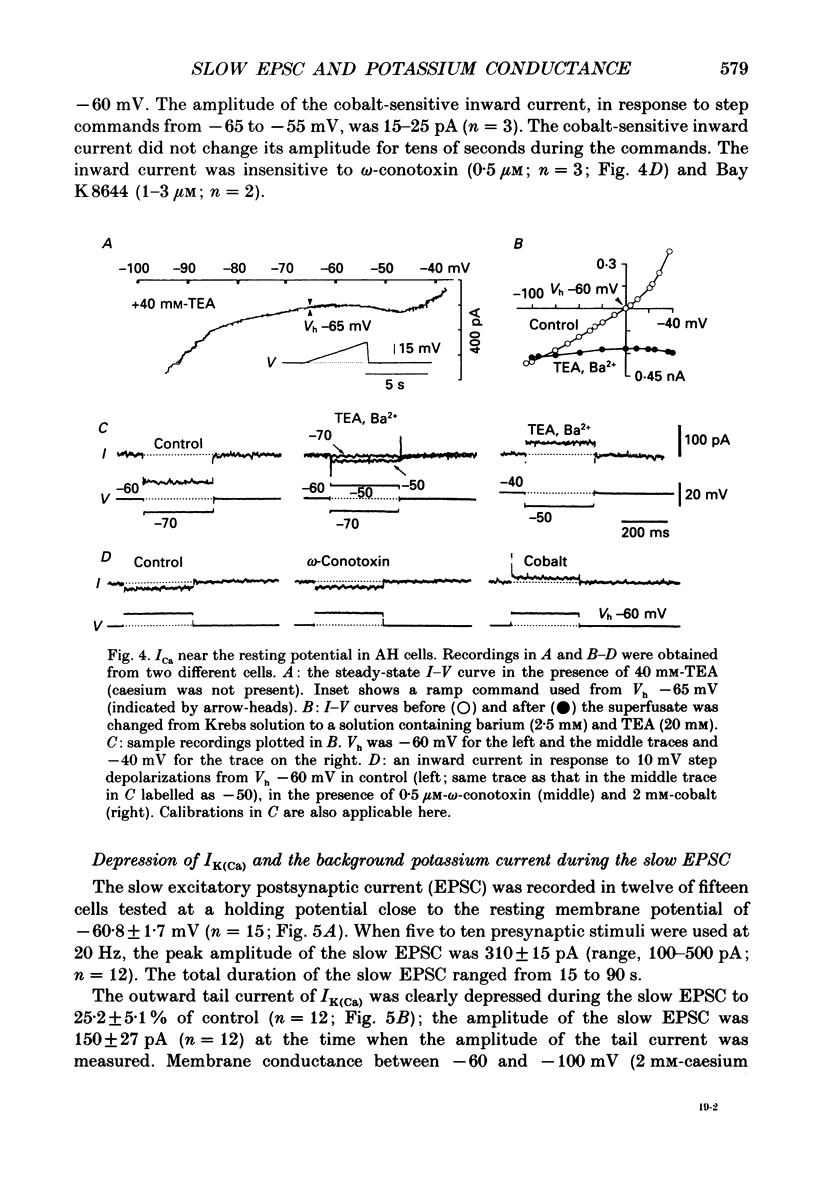
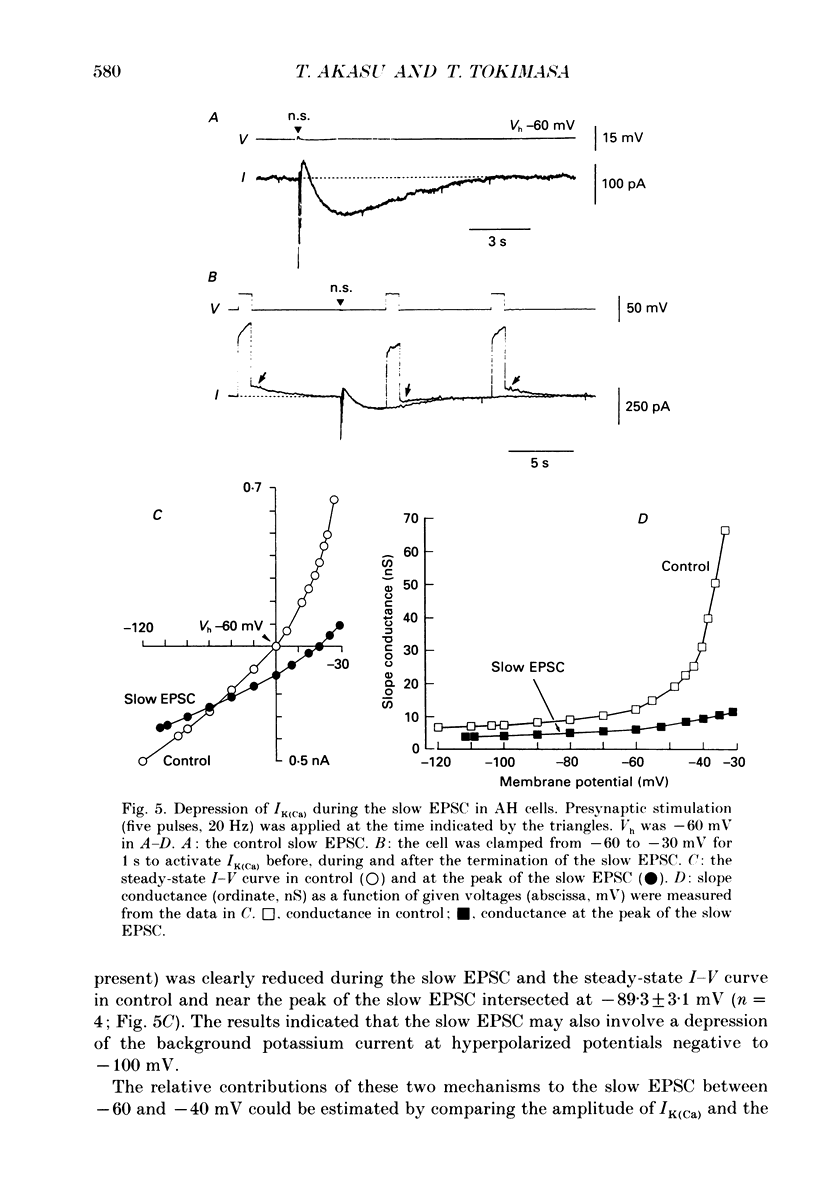
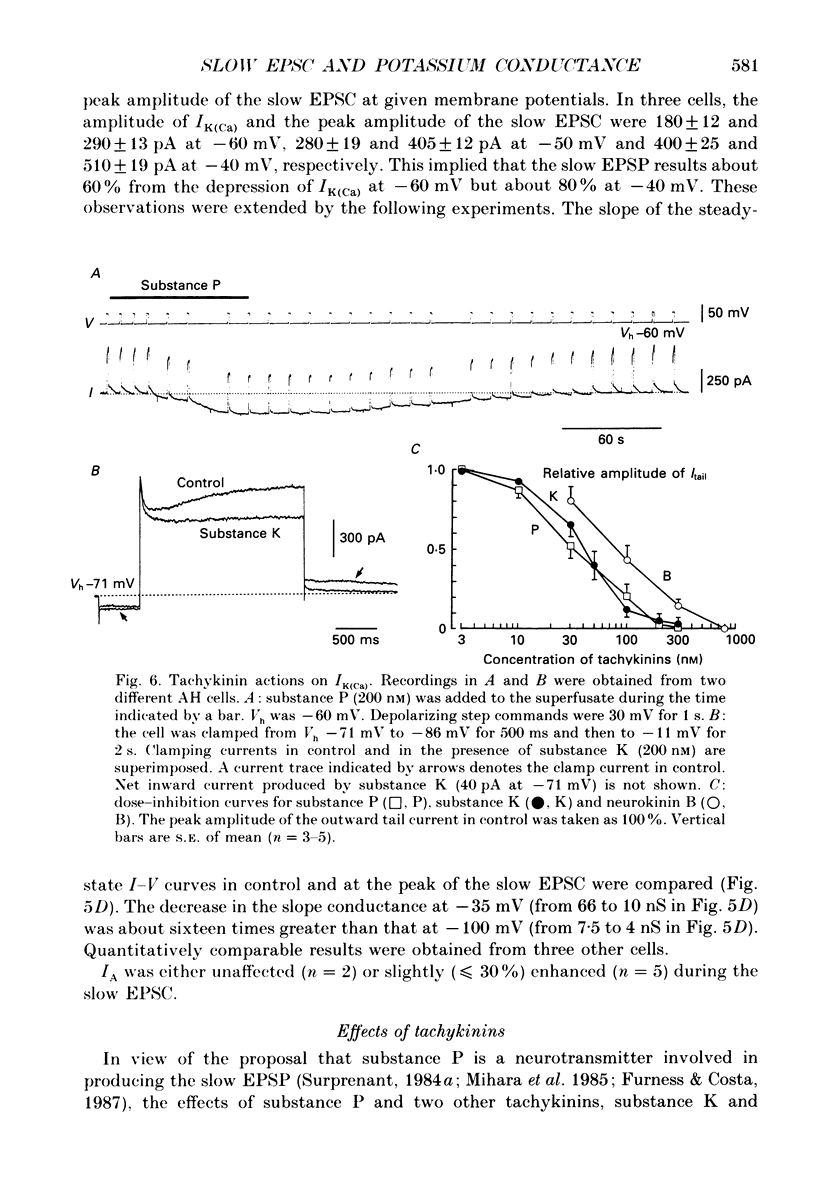
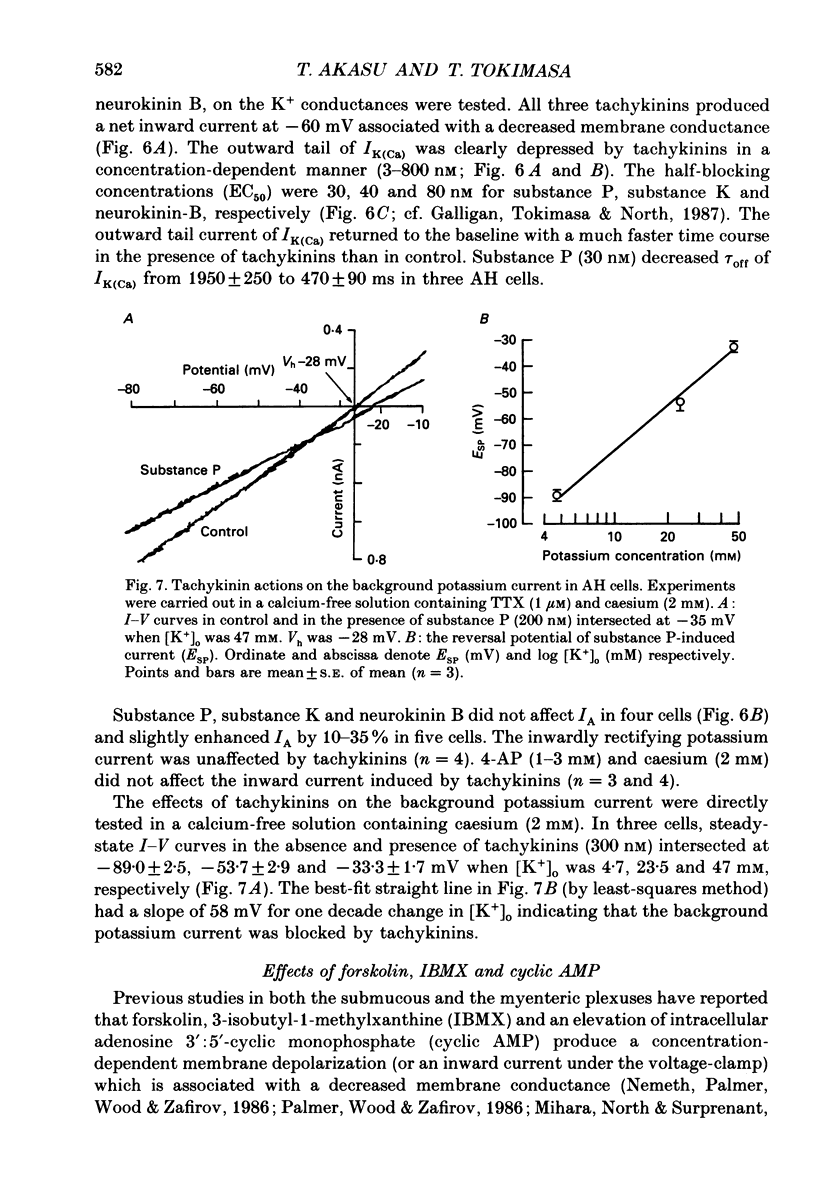
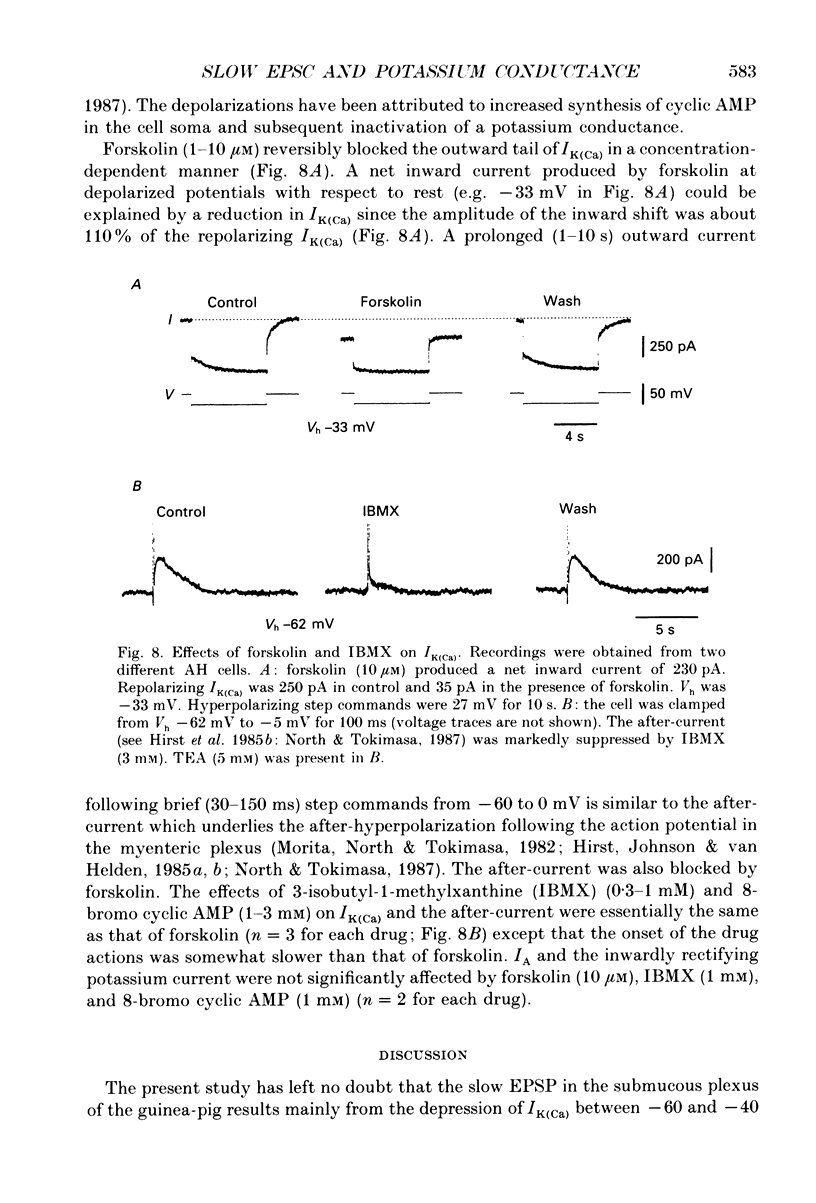
1. Intracellular recordings were made from submucous neurones of the guinea-pig caecum. In most experiments, membrane currents were measured using a single-electrode voltage clamp. 2. A potassium current dependent on calcium influx occurred at rest (approximately equal to 200 pA at -60 mV). The amplitude of the current was increased up to 1 nA at -35 mV and decreased to zero at -100 mV; when fully activated the current did not show any inactivation. An inward calcium current, of 15-25 pA in amplitude near -60 mV and insensitive to omega-conotoxin (0.5 microM), probably activated the potassium current. 3. Step depolarizations from potentials negative to -80 mV evoked a transient (less than or equal to 200 ms at -40 mV) potassium current which was blocked by 4-aminopyridine (1-3 mM). Hyperpolarizing commands to potentials negative to -87 mV evoked an inwardly rectifying potassium current which was selectively blocked by caesium (1-2 mM). The residual cell current between -100 and -40 mV in calcium-free solution containing tetraethylammonium (20 mM), caesium (2 mM) and 4-amino-pyridine (3 mM) conformed to constant field assumptions. This current was called a background potassium current. 4. Decrease in membrane conductance during the slow excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) was due predominantly (greater than or equal to 90%) to a reduction in the calcium-activated potassium current at -35 mV, but due almost exclusively to a reduction in the background potassium current at potentials more negative than -100 mV. The relative contribution of the two currents to the slow EPSC was entirely dependent on the relative contribution of the currents to the membrane conductance at given potentials. 5. The transient potassium current was unaffected or slightly enhanced during the slow EPSC. The inwardly rectifying potassium current was unaffected during the slow EPSC. 6. Three tachykinins (substance P, substance K and neurokinin B; 3-800 nM), forskolin (1-30 microM), 8-bromoadenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate (8-bromo cyclic AMP; 1-3 mM), 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (0.3-1 mM) mimicked the conductance changes during the slow EPSC in a concentration-dependent manner. 7. It is concluded that the slow excitatory synaptic potential in the submucous plexus, presumably mediated by peptidergic transmitters, results from an inactivation of two distinct potassium currents, at least one of which is controlled by intracellular calcium ions.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:537–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Sim J. A. Calcium-dependent potassium conductance in guinea-pig olfactory cortex neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:173–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galligan J. J., North R. A., Tokimasa T. Muscarinic agonists and potassium currents in guinea-pig myenteric neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan;96(1):193–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galligan J. J., Tokimasa T., North R. A. Effects of three mammalian tachykinins on single enteric neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Nov 23;82(2):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafe P., Mayer C. J., Wood J. D. Synaptic modulation of calcium-dependent potassium conductance in myenteric neurones in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:235–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Johnson S. M., van Helden D. F. The calcium current in a myenteric neurone of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:297–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Johnson S. M., van Helden D. F. The slow calcium-dependent potassium current in a myenteric neurone of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:315–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., McKirdy H. C. Synaptic potentials recorded from neurones of the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):369–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., Katayama Y., Nishi S. Slow postsynaptic potentials in neurones of submucous plexus of guinea-pig caecum and their mimicry by noradrenaline and various peptides. Neuroscience. 1985 Dec;16(4):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., North R. A., Surprenant A. Somatostatin increases an inwardly rectifying potassium conductance in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:335–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A., Tokimasa T. The calcium-activated potassium conductance in guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:341–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth P. R., Palmer J. M., Wood J. D., Zafirov D. H. Effects of forskolin on electrical behaviour of myenteric neurones in guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:439–450. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Surprenant A. Inhibitory synaptic potentials resulting from alpha 2-adrenoceptor activation in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:17–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Depression of calcium-dependent potassium conductance of guinea-pig myenteric neurones by muscarinic agonists. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:253–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Persistent calcium-sensitive potassium current and the resting properties of guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:333–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. M., Wood J. D., Zafirov D. H. Elevation of adenosine 3',5'-phosphate mimics slow synaptic excitation in myenteric neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:451–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennefather P., Lancaster B., Adams P. R., Nicoll R. A. Two distinct Ca-dependent K currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3040–3044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., North R. A. Mechanism of synaptic inhibition by noradrenaline acting at alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jun 22;234(1274):85–114. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. Slow excitatory synaptic potentials recorded from neurones of guinea-pig submucous plexus. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:343–361. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. Two types of neurones lacking synaptic input in the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:363–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Minota S., Kuba K., Koyano K., Abe T. Differential effects of apamin on Ca2+-dependent K+ currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Sep 12;69(3):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90485-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi H., Hirai K., Katayama Y. Measurement of the intracellular calcium concentration in guinea-pig myenteric neurons by using fura-2. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 7;451(1-2):371–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90787-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokimasa T., Akasu T. Histamine H2 receptor mediates postsynaptic excitation and presynaptic inhibition in submucous plexus neurons of the guinea-pig. Neuroscience. 1989;28(3):735–744. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokimasa T., Ariyoshi M., Akasu T. Mianserin blocks alpha 2 adrenoceptors in submucous neurones of the guinea-pig caecum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 10;143(2):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90539-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



