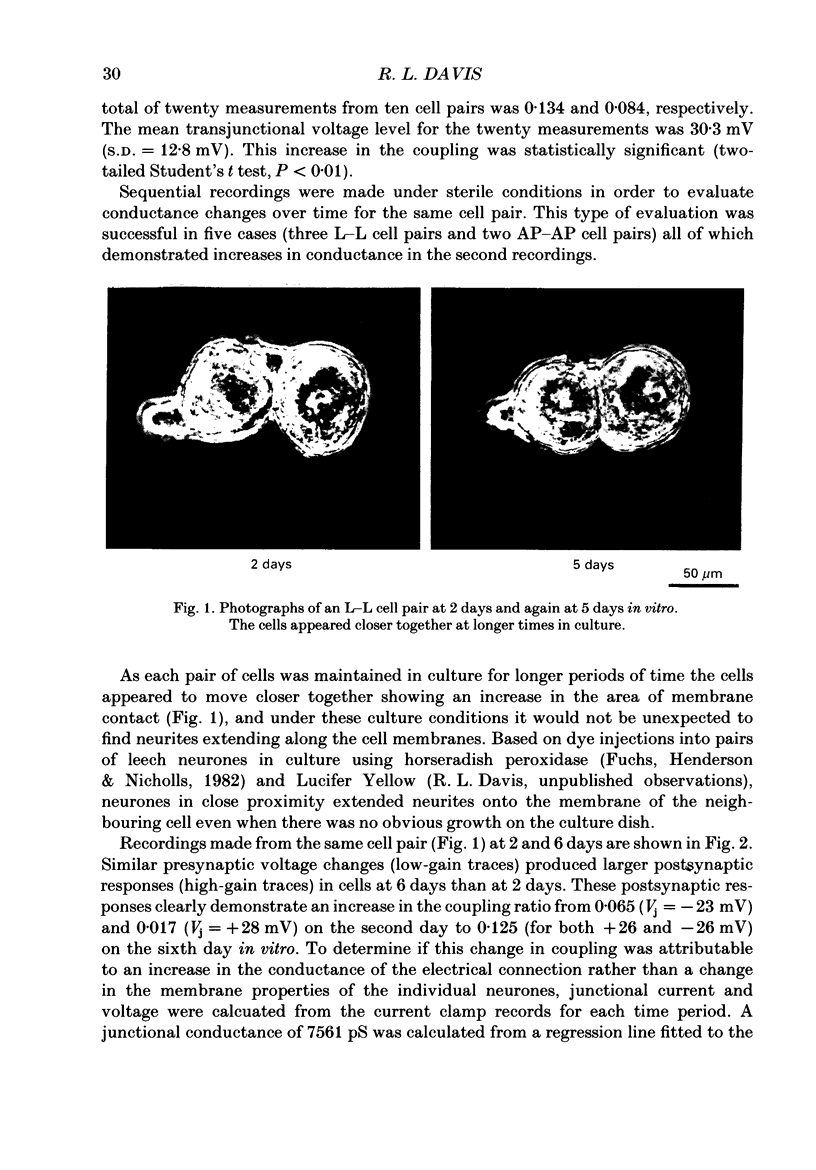
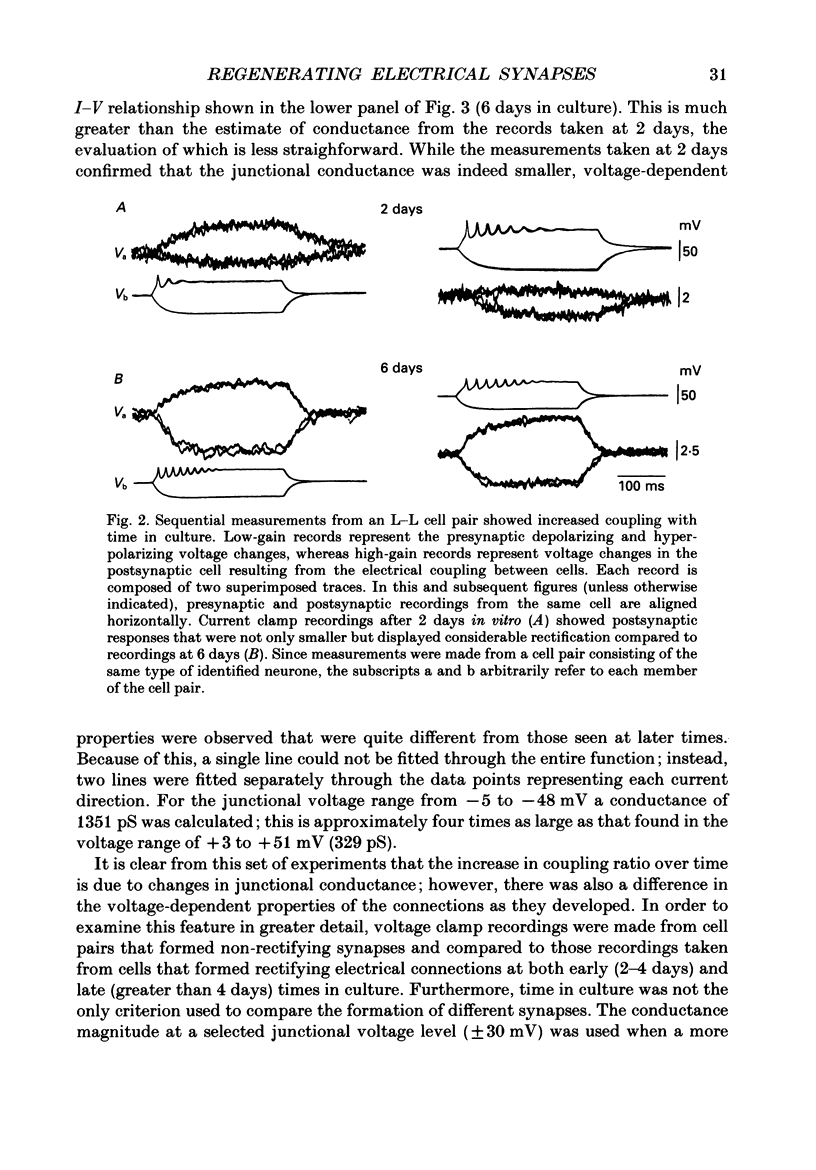
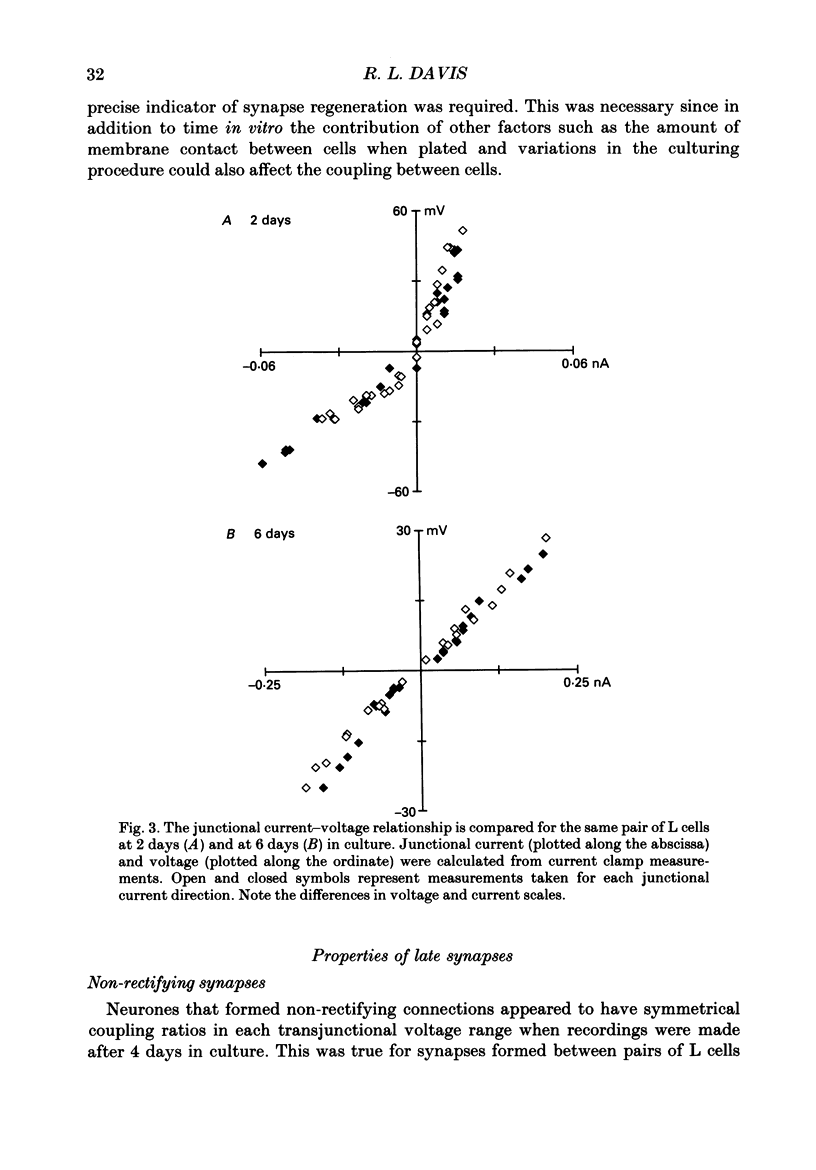
Abstract
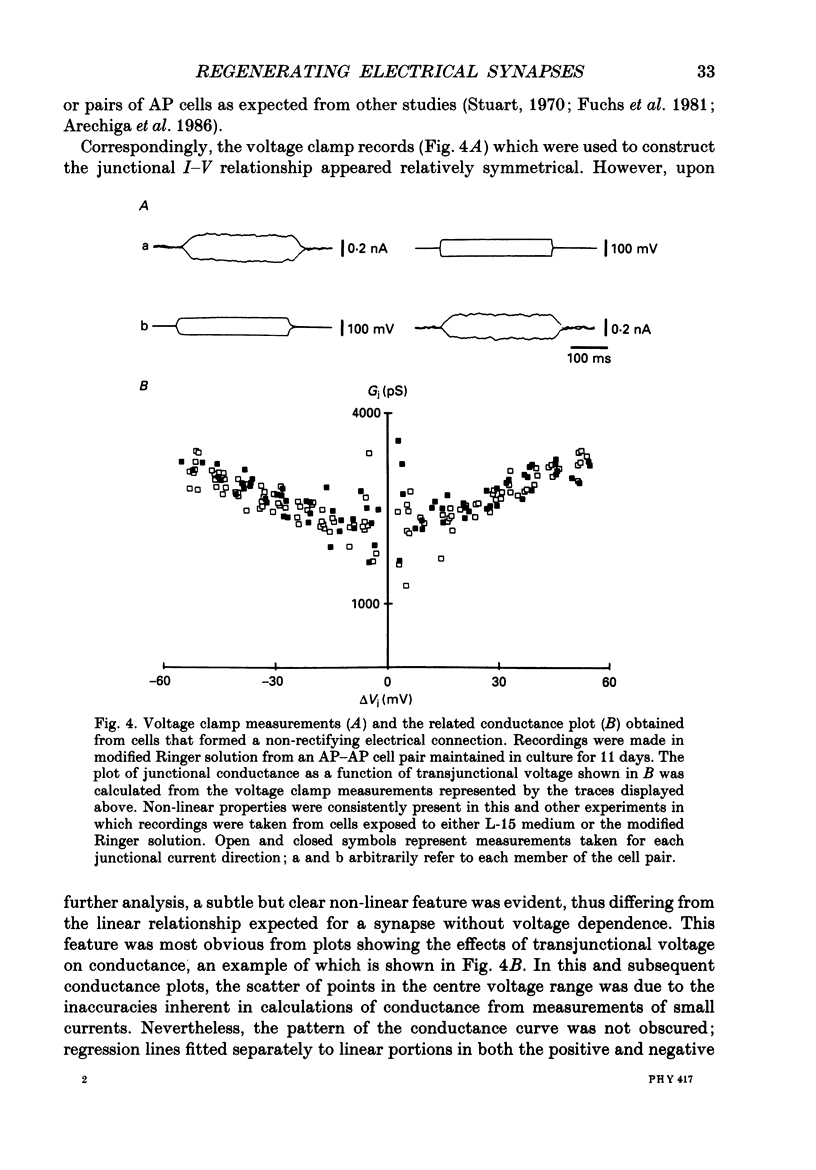
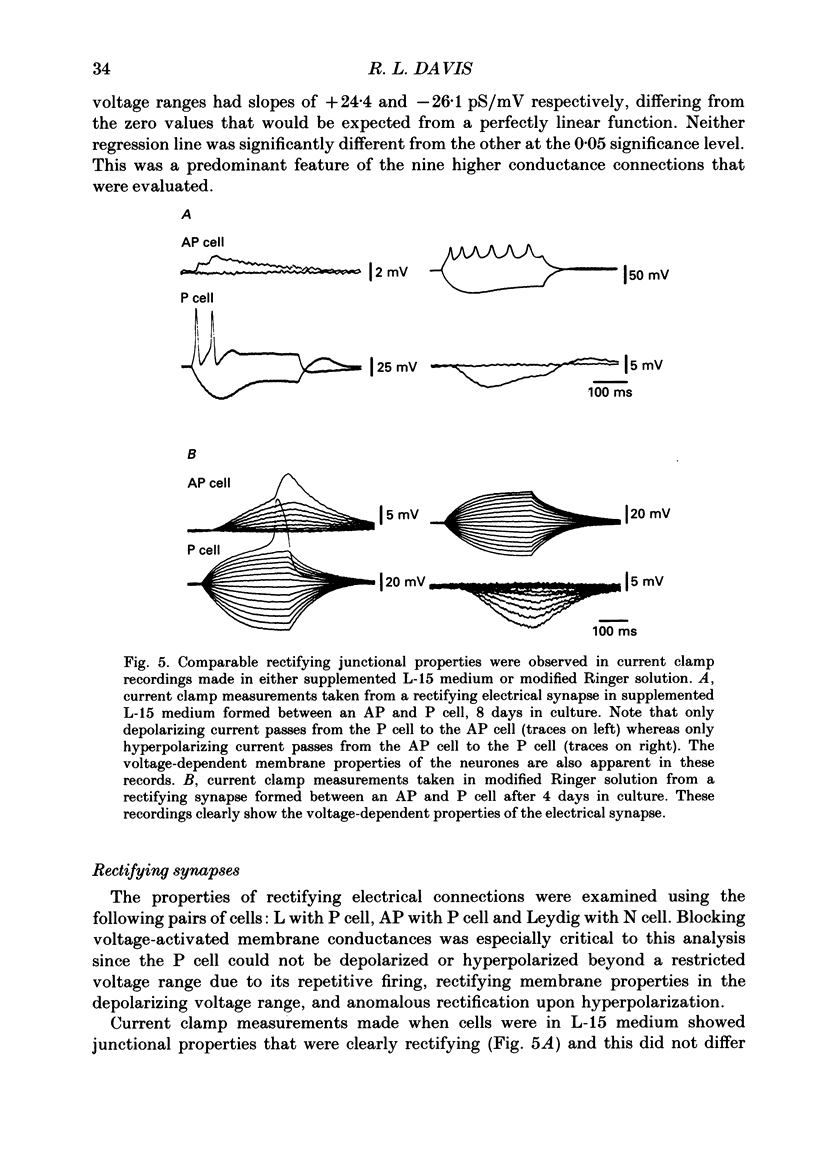
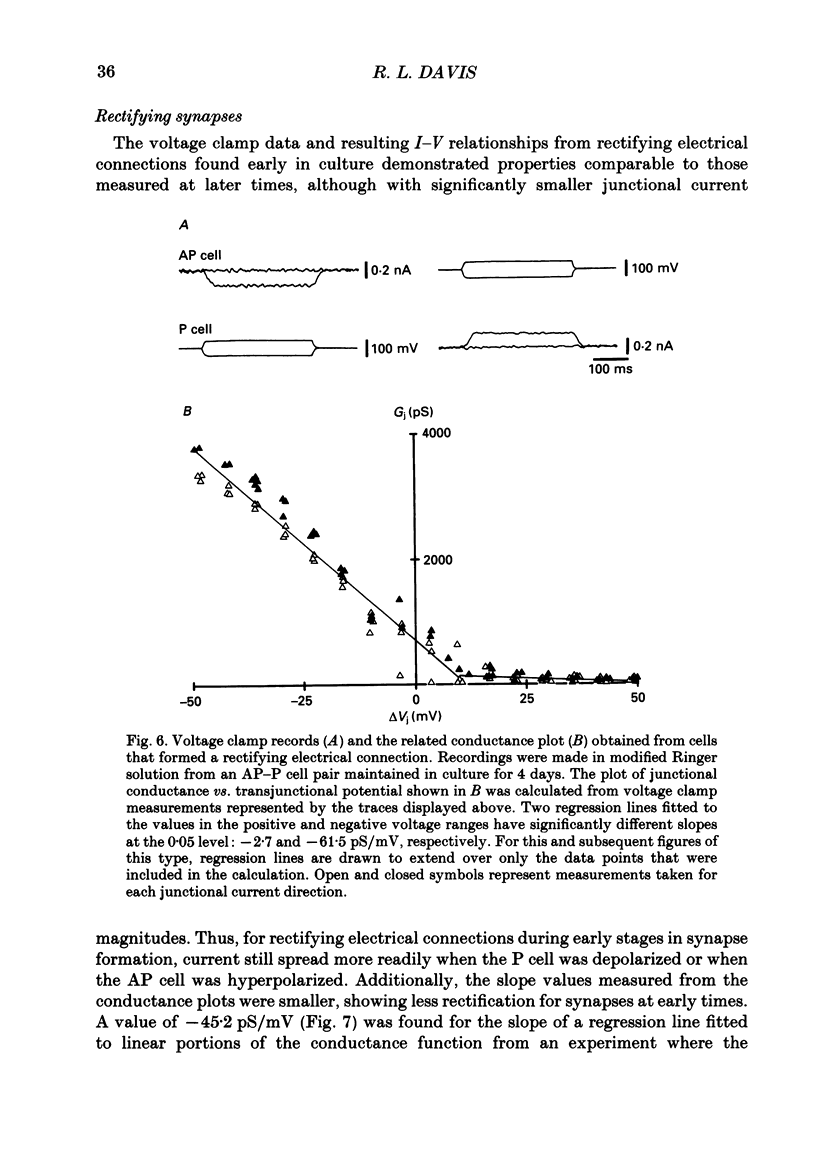
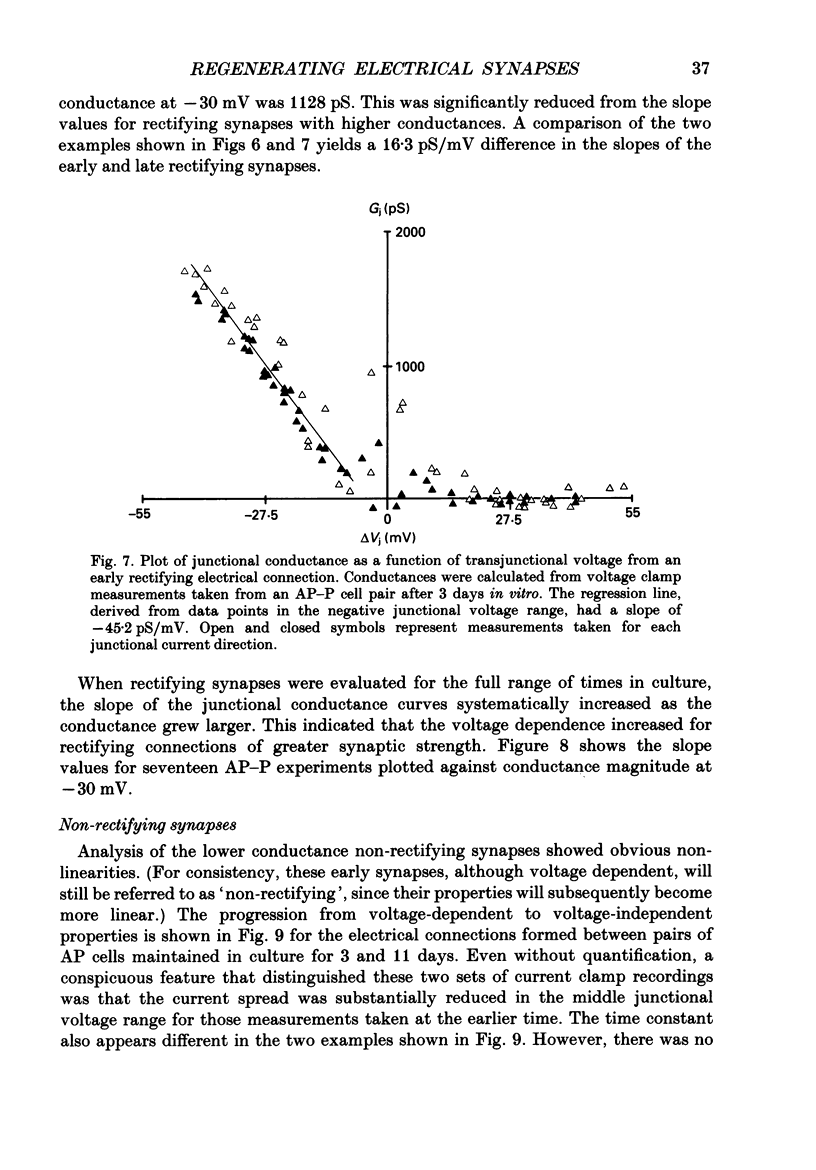
1. The voltage-dependent properties of rectifying and non-rectifying electrical synapses formed between identified leech neurones were quantified during their regeneration in vitro. 2. Junctional conductance increased with time in culture. This was evaluated by making comparisons between cell pairs maintained in vitro for differing amounts of time, as well as by taking repeated measurements from a single cell pair at different time intervals. 3. Non-rectifying electrical synapses were formed between certain identified neurones of the same type. Thus, Leydig cells cultured with Leydig cells established non-rectifying electrical connections, as did Retzius cells, longitudinal motoneurones (L cells) and anterior pagoda (AP) cells, each paired with its own cell type. 4. Rectifying synapses developed when sensory neurones (P cells or N cells) were paired with the other neurones mentioned above that form non-rectifying connections between themselves. The cell combinations examined were L cell-P cell. Leydig cell-N cell, and AP cell-P cell. The direction of current flow across these rectifying synapses was consistently from the sensory neurone to the other cell in the pair. 5. Non-rectifying connections early in the process of synapse regeneration (1-3 days) showed non-linearities greater than those observed in established non-rectifying synapses. There was a subtle, but clear, voltage dependence even at the later stages of synapse formation (4-18 days). 6. In contrast to non-rectifying connections, rectifying synapses formed between cells at early times in culture showed less voltage dependence than those observed at later times. 7. The marked non-linearities of the non-rectifying connections at early stages in synapse formation along with the reduced voltage dependence of the rectifying connections within the same time period revealed unexpected similarities between the two. At the early stages of synapse formation, the two types of electrical synapse were essentially indistinguishable for one direction of junctional current.
Full text
PDF





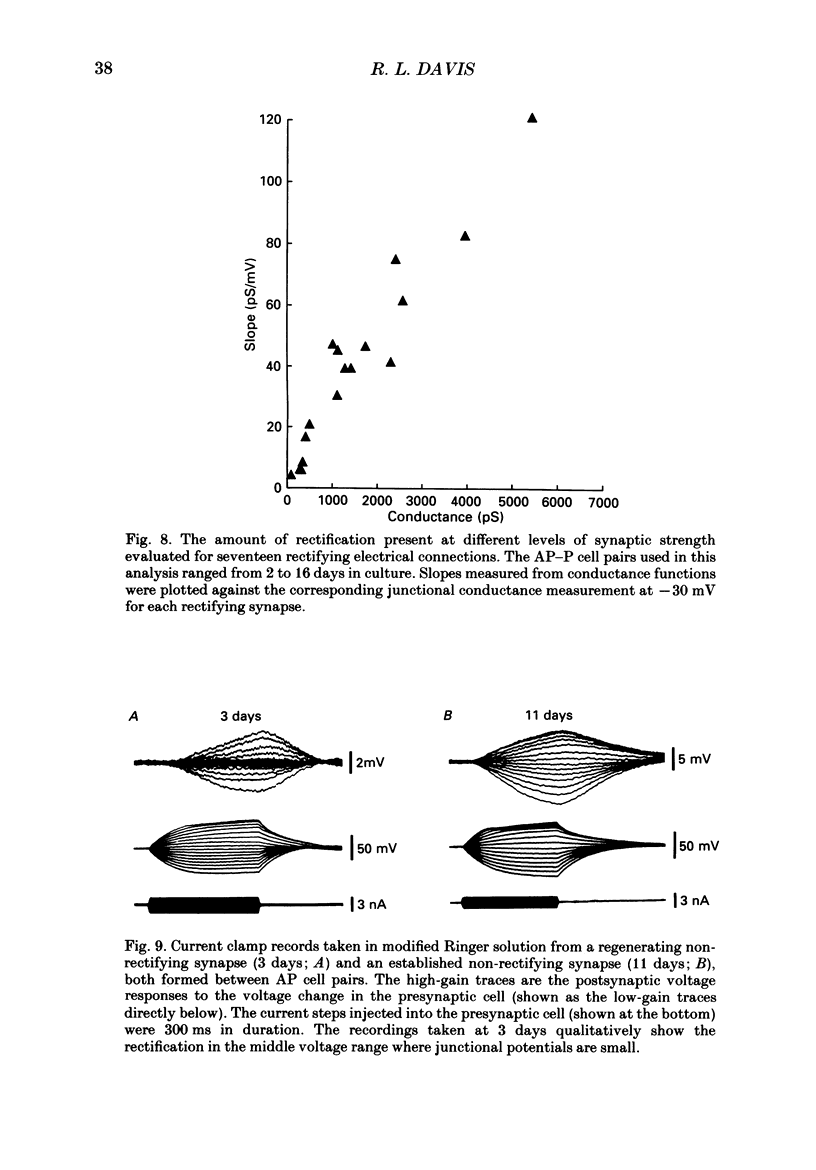
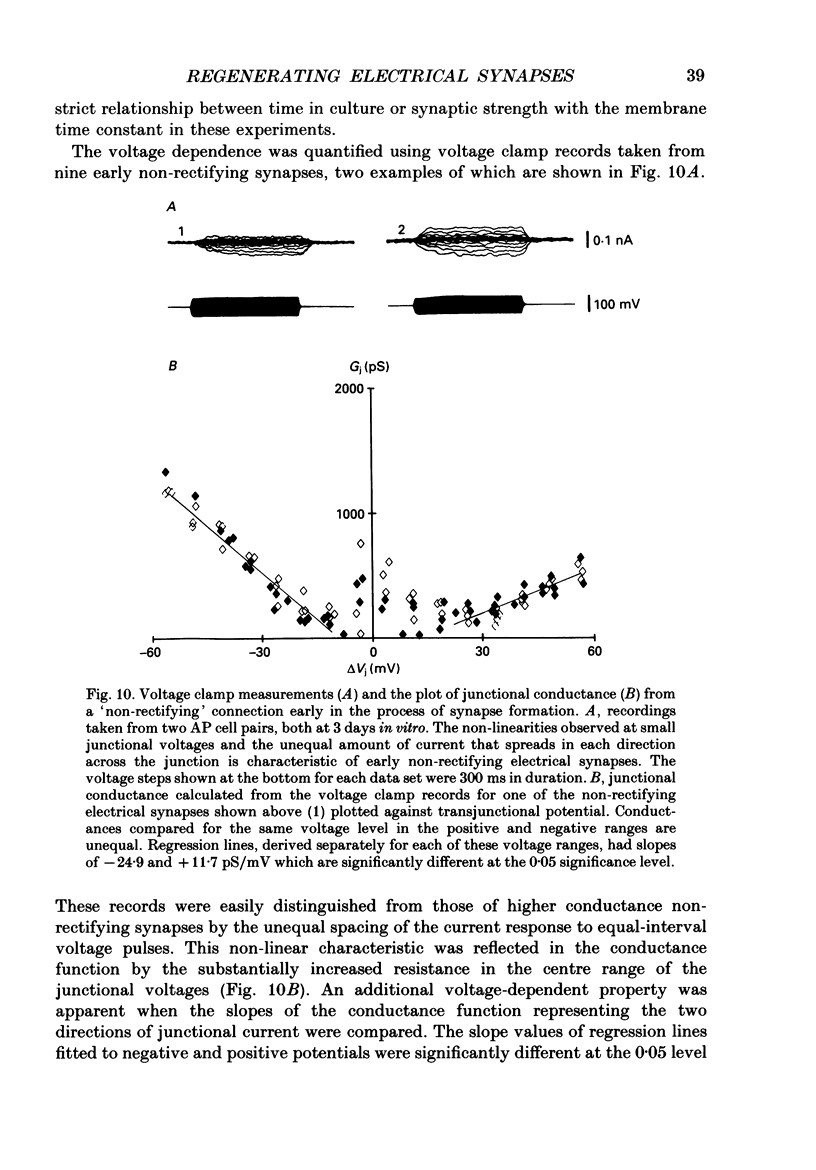
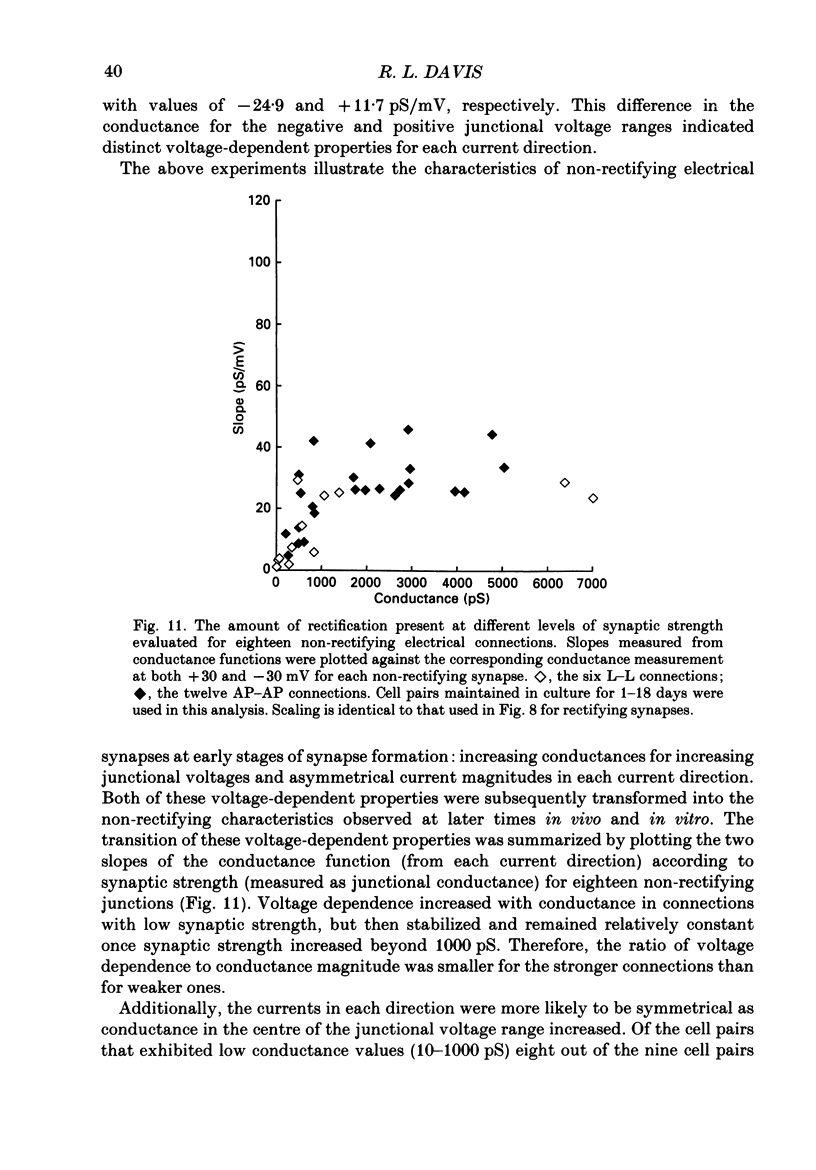
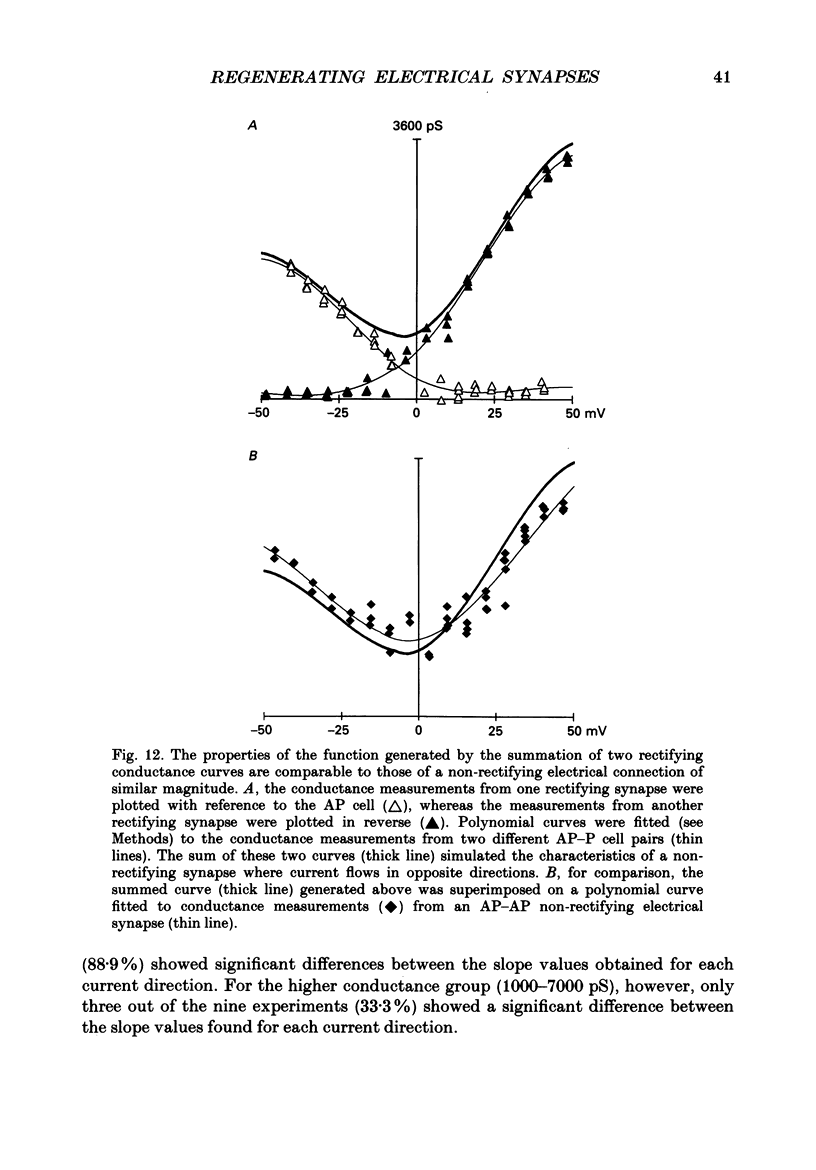





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach A. A., Bennett M. V. A rectifying electrotonic synapse in the central nervous system of a vertebrate. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Feb;53(2):211–237. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azarnia R., Dahl G., Loewenstein W. R. Cell junction and cycle AMP: III. Promotion of junctional membrane permeability and junctional membrane particles in a junction-deficient cell type. J Membr Biol. 1981;63(1-2):133–146. doi: 10.1007/BF01969454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt J. M., Spray D. C. Single-channel events and gating behavior of the cardiac gap junction channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3431–3434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow I., Young S. H. Opening of single gap junction channels during formation of electrical coupling between embryonic muscle cells. Dev Biol. 1987 Aug;122(2):332–337. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mazière A. M., Scheuermann D. W. Increased gap junctional area in the rat liver after administration of dibutyryl cAMP. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;239(3):651–655. doi: 10.1007/BF00219244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel I. D., Drapeau P., Nicholls J. G. Voltage dependence of 5-hydroxytryptamine release at a synapse between identified leech neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:191–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURSHPAN E. J., POTTER D. D. Transmission at the giant motor synapses of the crayfish. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 3;145(2):289–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. A., Henderson L. P., Nicholls J. G. Chemical transmission between individual Retzius and sensory neurones of the leech in culture. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:195–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. A., Nicholls J. G., Ready D. F. Membrane properties and selective connexions of identified leech neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:203–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaume C., Kado R. T., Korn H. Voltage-clamp analysis of a crayfish rectifying synapse. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:91–112. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R., Hammer M., Sheridan J., Revel J. P. Gap junction formation between reaggregated Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4536–4540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinhaus A. L., Prichard J. W. Close relation between TEA responses and Ca-dependent membrane phenomena of four identified leech neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;270(1):181–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinhaus A. L., Prichard J. W. Sodium dependent tetrodotoxin-resistant action potentials in a leech neuron. Brain Res. 1976 Feb 6;102(2):368–373. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90894-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication: the cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):829–913. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R., Kanno Y., Socolar S. J. Quantum jumps of conductance during formation of membrane channels at cell-cell junction. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):133–136. doi: 10.1038/274133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margiotta J. F., Walcott B. Conductance and dye permeability of a rectifying electrical synapse. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):52–55. doi: 10.1038/305052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Trautmann A. Physiological modulation of gap junction permeability. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:993–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Trautmann A. Single-channel currents of an intercellular junction. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):331–335. doi: 10.1038/317331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J. G., Baylor D. A. Specific modalities and receptive fields of sensory neurons in CNS of the leech. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Sep;31(5):740–756. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.5.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obaid A. L., Socolar S. J., Rose B. Cell-to-cell channels with two independently regulated gates in series: analysis of junctional conductance modulation by membrane potential, calcium, and pH. J Membr Biol. 1983;73(1):69–89. doi: 10.1007/BF01870342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ready D. F., Nicholls J. Identified neurones isolated from leech CNS make selective connections in culture. Nature. 1979 Sep 6;281(5726):67–69. doi: 10.1038/281067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose B., Simpson I., Loewenstein W. R. Calcium ion produces graded changes in permeability of membrane channels in cell junction. Nature. 1977 Jun 16;267(5612):625–627. doi: 10.1038/267625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetze S. M., Goodenough D. A. Dye transfer between cells of the embryonic chick lens becomes less sensitive to CO2 treatment with development. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):694–705. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I., Rose B., Loewenstein W. R. Size limit of molecules permeating the junctional membrane channels. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):294–296. doi: 10.1126/science.831276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Physiology and pharmacology of gap junctions. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:281–303. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Harris A. L., Bennett M. V. Equilibrium properties of a voltage-dependent junctional conductance. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jan;77(1):77–93. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Harris A. L., Bennett M. V. Gap junctional conductance is a simple and sensitive function of intracellular pH. Science. 1981 Feb 13;211(4483):712–715. doi: 10.1126/science.6779379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Harris A. L., Bennett M. V. Voltage dependence of junctional conductance in early amphibian embryos. Science. 1979 Apr 27;204(4391):432–434. doi: 10.1126/science.312530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Saez J. C., Brosius D., Bennett M. V., Hertzberg E. L. Isolated liver gap junctions: gating of transjunctional currents is similar to that in intact pairs of rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5494–5497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., White R. L., de Carvalho A. C., Harris A. L., Bennett M. V. Gating of gap junction channels. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):219–230. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84150-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart A. E. Physiological and morphological properties of motoneurones in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):627–646. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turin L., Warner A. Carbon dioxide reversibly abolishes ionic communication between cells of early amphibian embryo. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):56–57. doi: 10.1038/270056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenstra R. D., DeHaan R. L. Measurement of single channel currents from cardiac gap junctions. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):972–974. doi: 10.1126/science.2426781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingart R. Electrical properties of the nexal membrane studied in rat ventricular cell pairs. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:267–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky E. J., Patterson P. H., Willard A. L. Insulin promotes electrical coupling between cultured sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci. 1985 Jul;5(7):1675–1679. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-07-01675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A., Gilula N. B. Functional assembly of gap junction conductance in lipid bilayers: demonstration that the major 27 kd protein forms the junctional channel. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zampighi G. A., Hall J. E., Kreman M. Purified lens junctional protein forms channels in planar lipid films. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8468–8472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]