Abstract
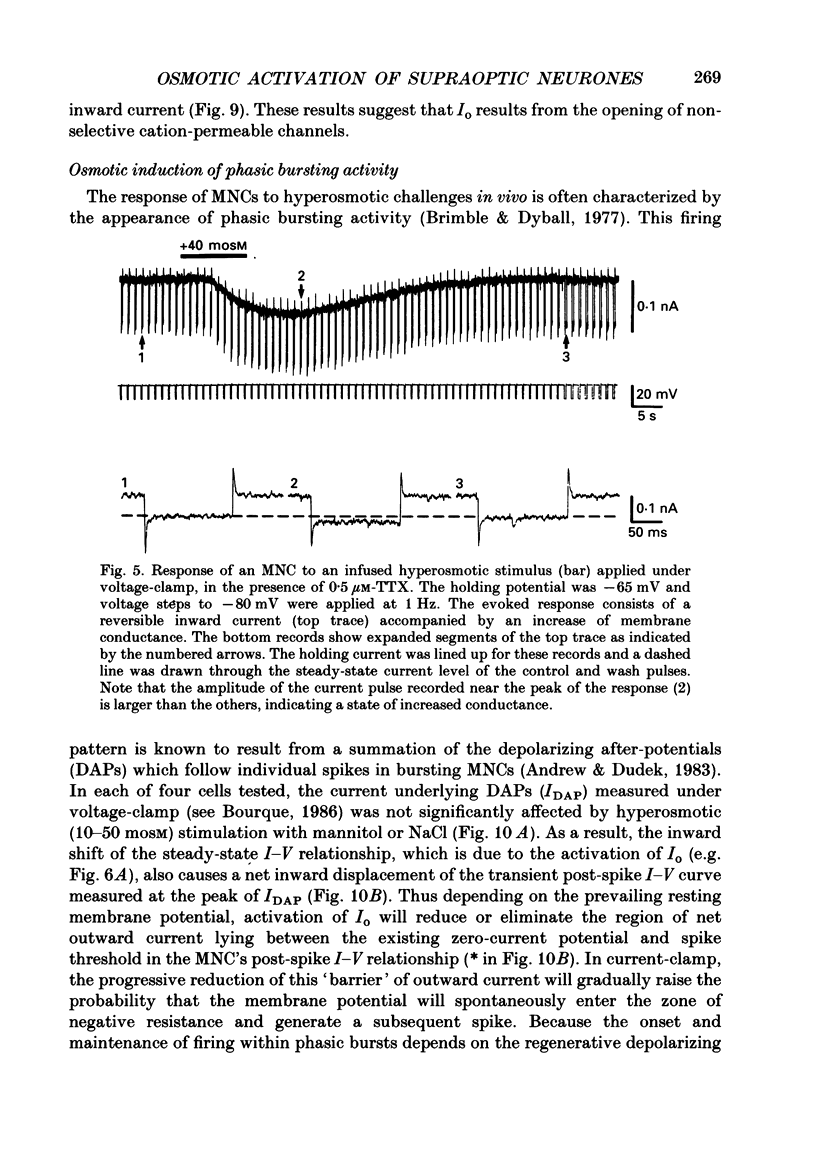
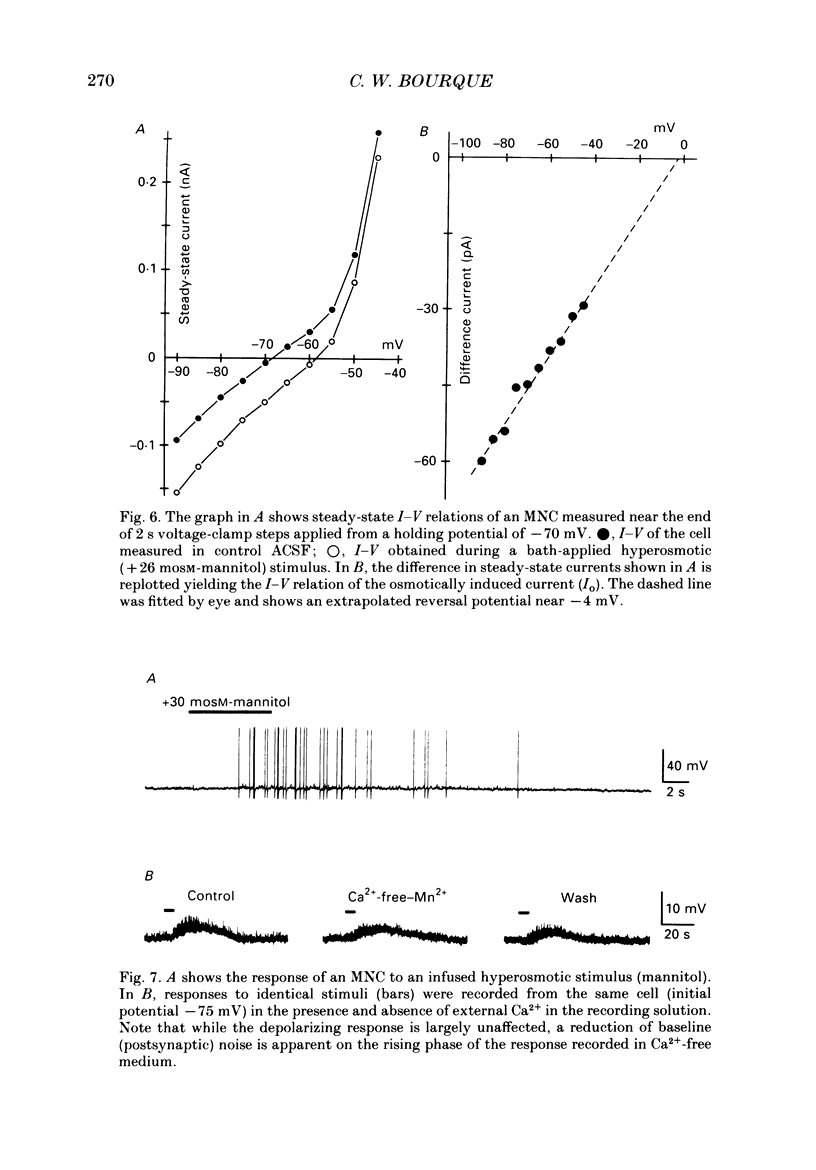
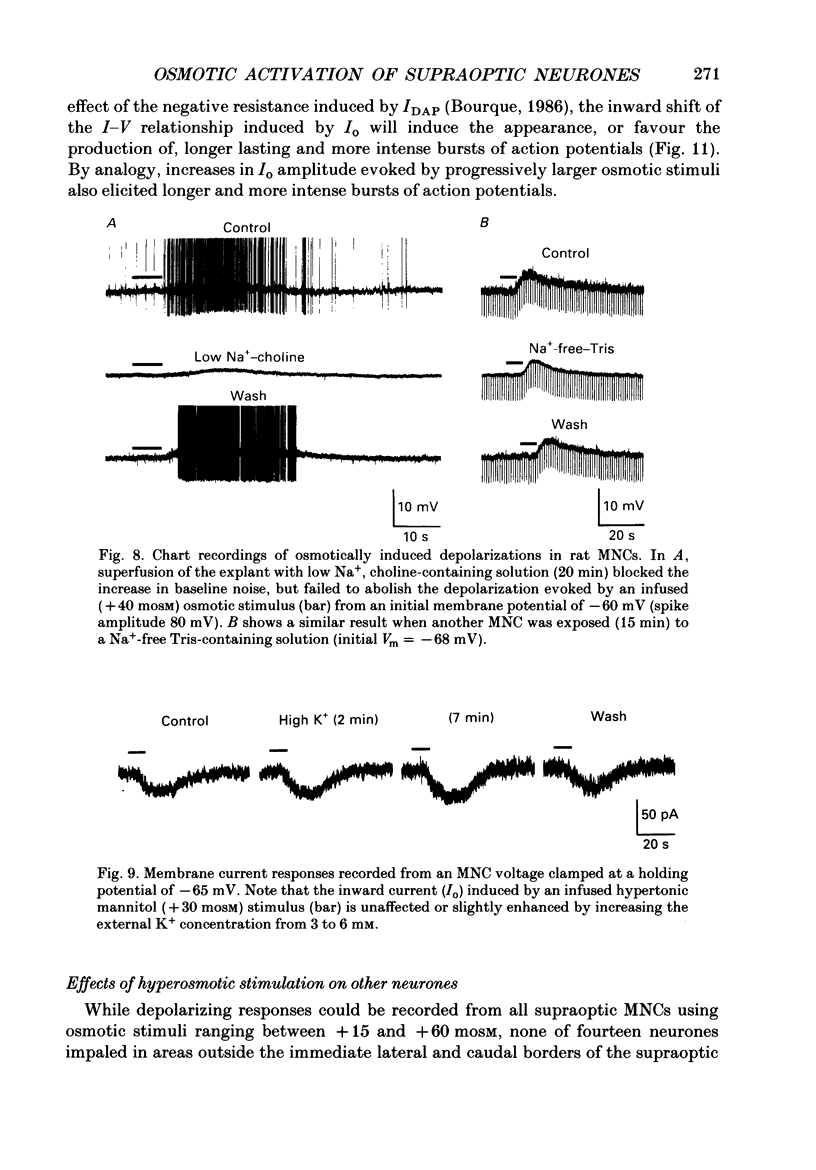
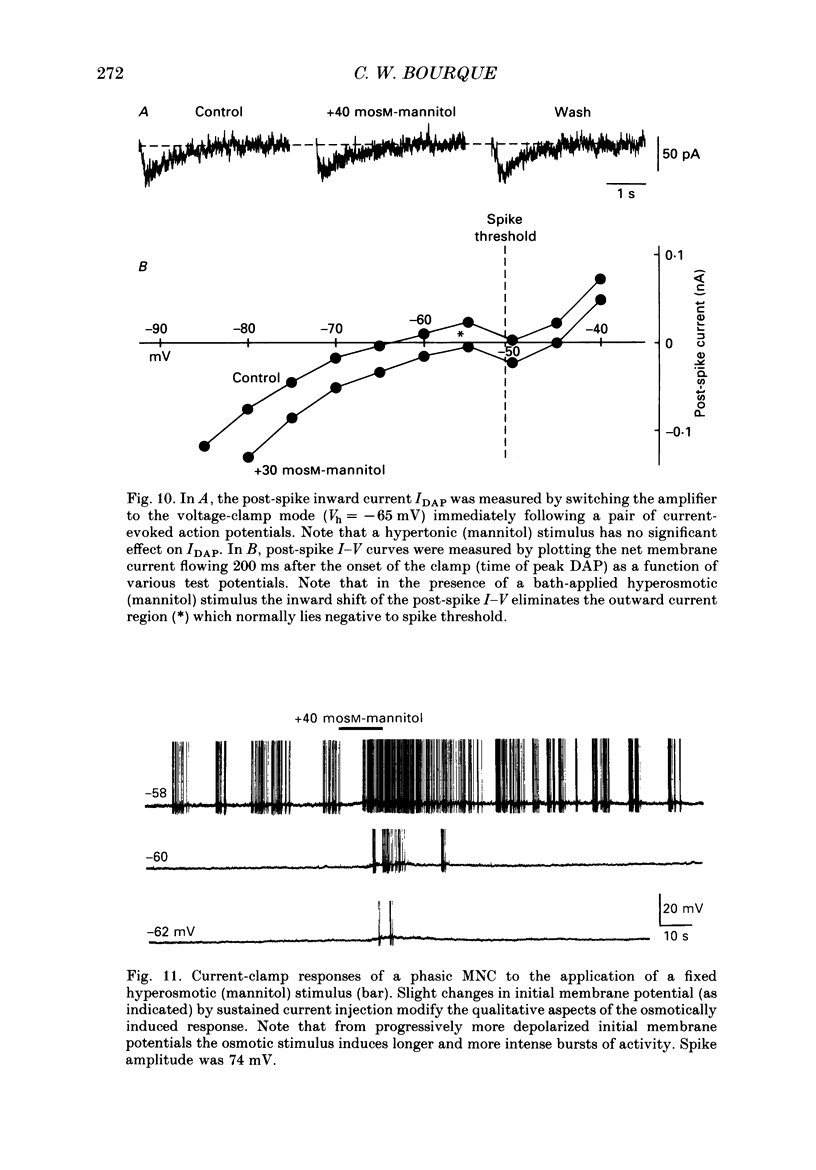
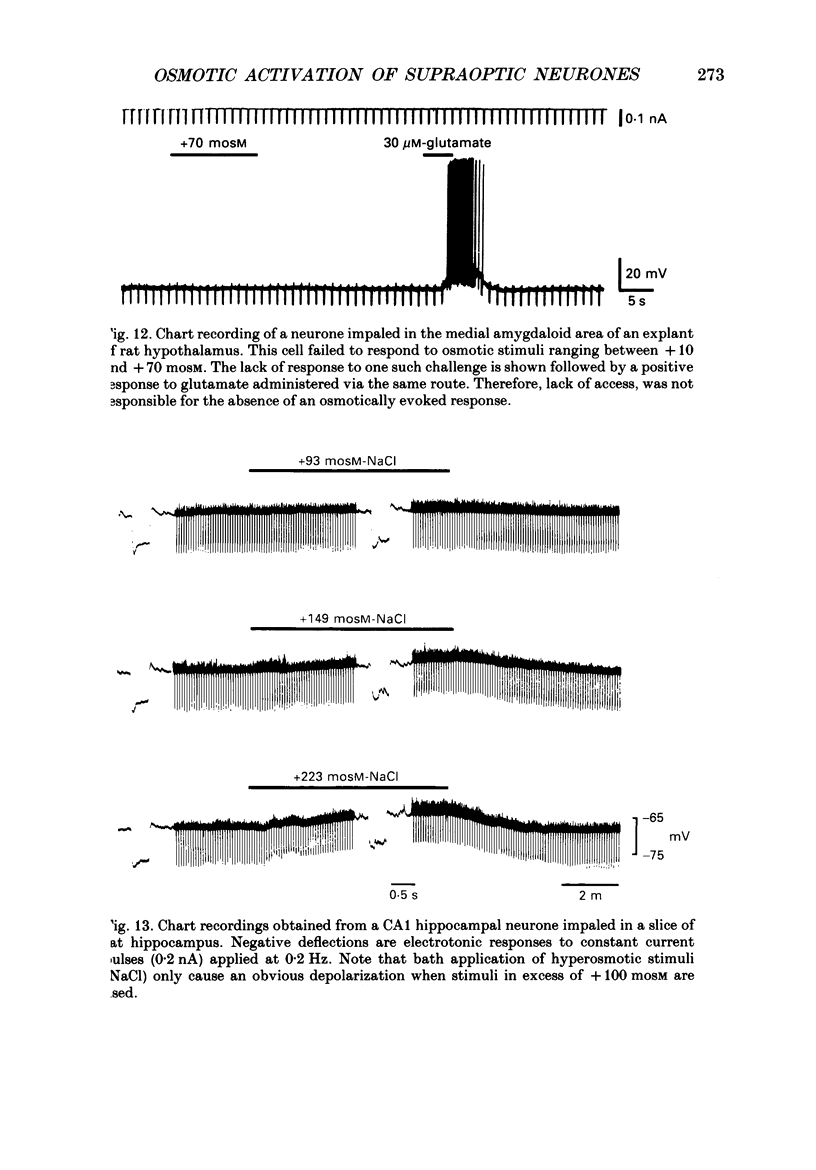
1. Magnocellular neurosecretory cells (MNCs) were impaled in the supraoptic nucleus of rat hypothalamic explants maintained in vitro. Current- and voltage-clamp analysis of the osmotically induced response was performed at 34 degrees C. 2. Addition of mannitol or NaCl to cause a rise in fluid osmolarity (greater than +6 mosM) caused a membrane depolarization whose amplitude increased when elicited from more hyperpolarized levels. Changes in temperature (34-28 degrees C), addition of TTX, or superfusion with Na(+)-free or Ca2(+)-free solutions did not block the osmotically induced depolarization. In control solutions the response was consistently accompanied by an increase in the frequency of spontaneous postsynaptic potentials. Thus, osmotic stimuli have a direct effect on MNCs, and they also apparently activate other neurones which are presynaptic to these cells. 3. Under voltage-clamp, hyperosmotic stimuli induced an inward current (Io) accompanied by an increase in membrane conductance. The current was unaffected or slightly enhanced by doubling the external K+ concentration. Io was also characterized by a linear I-V relation (between -100 and -50mV) and an extrapolated reversal potential near -10 mV. Io presumably results from the activation of a voltage-independent and non-selective cationic conductance. 4. Hyperosmotic stimuli did not affect the depolarizing after-current (IDAP) responsible for the production of phasic bursts. However, the inward shift of the post-spike I-V curve caused by Io could reduce or eliminate the region of net outward current which lies negative to spike threshold in silent neurones. Thus in MNCs displaying IDAP, activation of Io by a rise in osmotic pressure can induce or enhance phasic bursting activity. 5. Application of hyperosmotic stimuli sufficient to excite most MNCs (+20 to +80 mosM) did not elicit a response from any of seventeen neurones impaled in areas lateral and caudal to the supraoptic nucleus. Recordings obtained from three CA1 neurones in slices of rat hippocampus revealed that stimuli in excess of +100 mosM are required to evoke appreciable non-specific depolarizations. 6. These studies indicate that the specific endogenous osmosensitivity of MNCs results from the activation of the intrinsic current Io. Furthermore, interactions between Io and IDAP explain how osmotic stimuli can lead to the induction of phasic bursting activity, a response which is known to potentiate the secretion of vasopressin from the neural lobe.
Full text
PDF

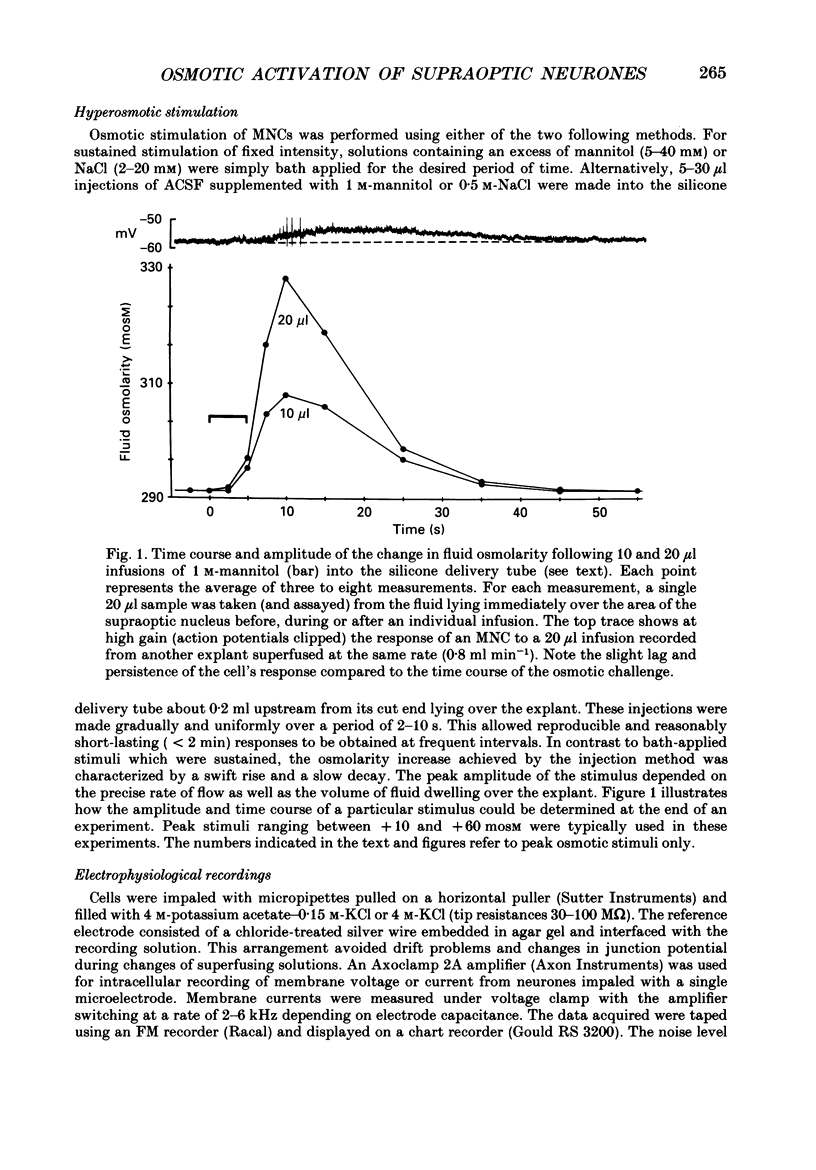
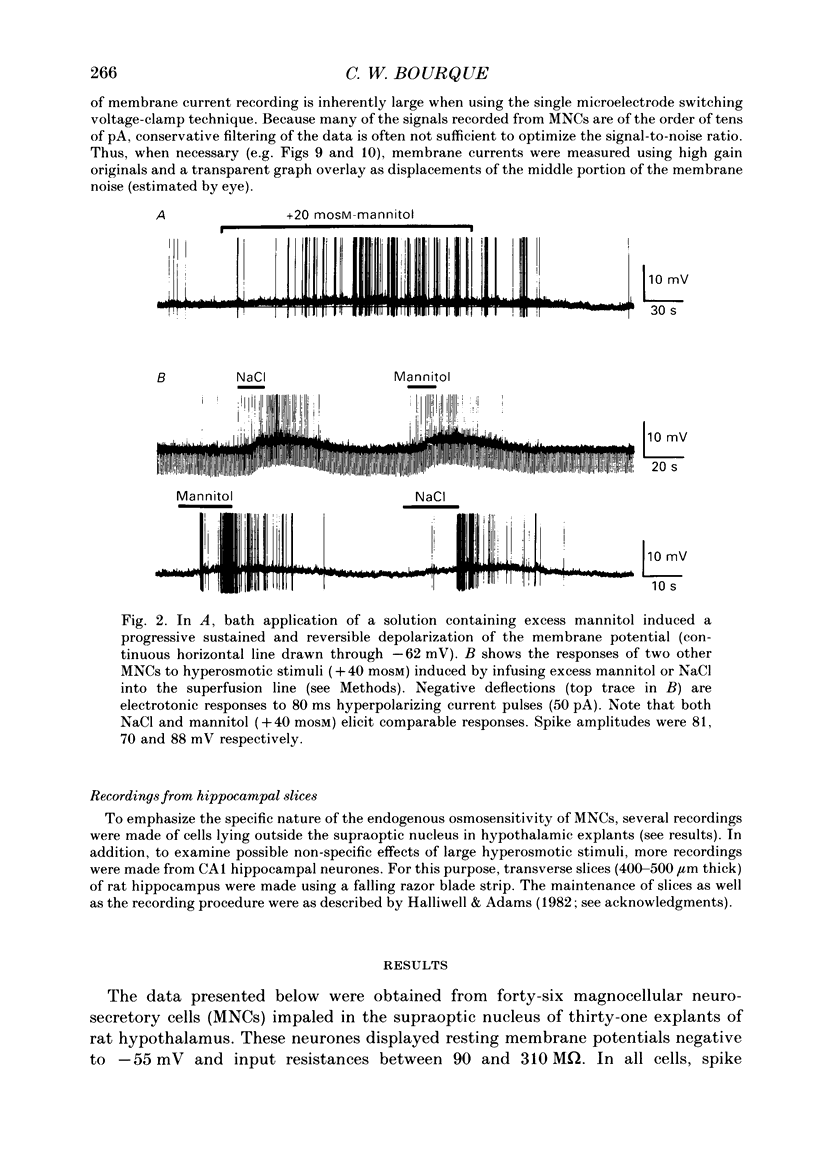
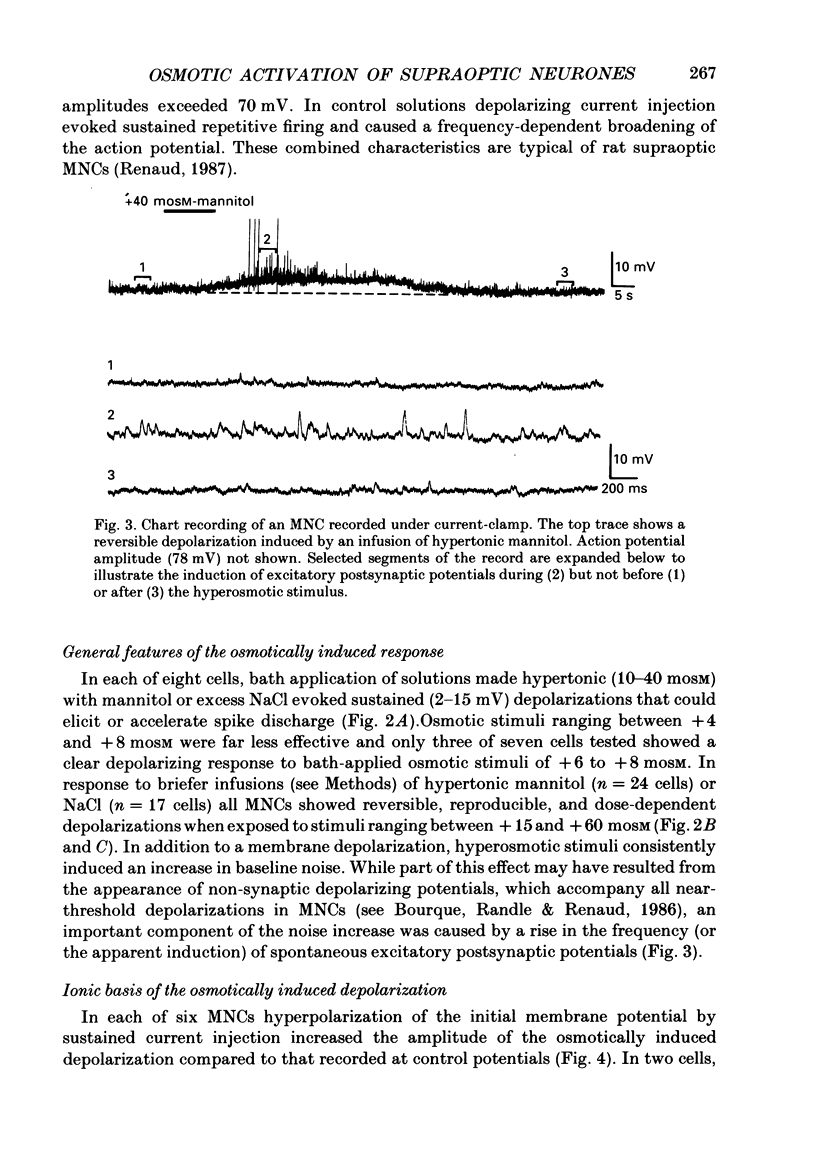
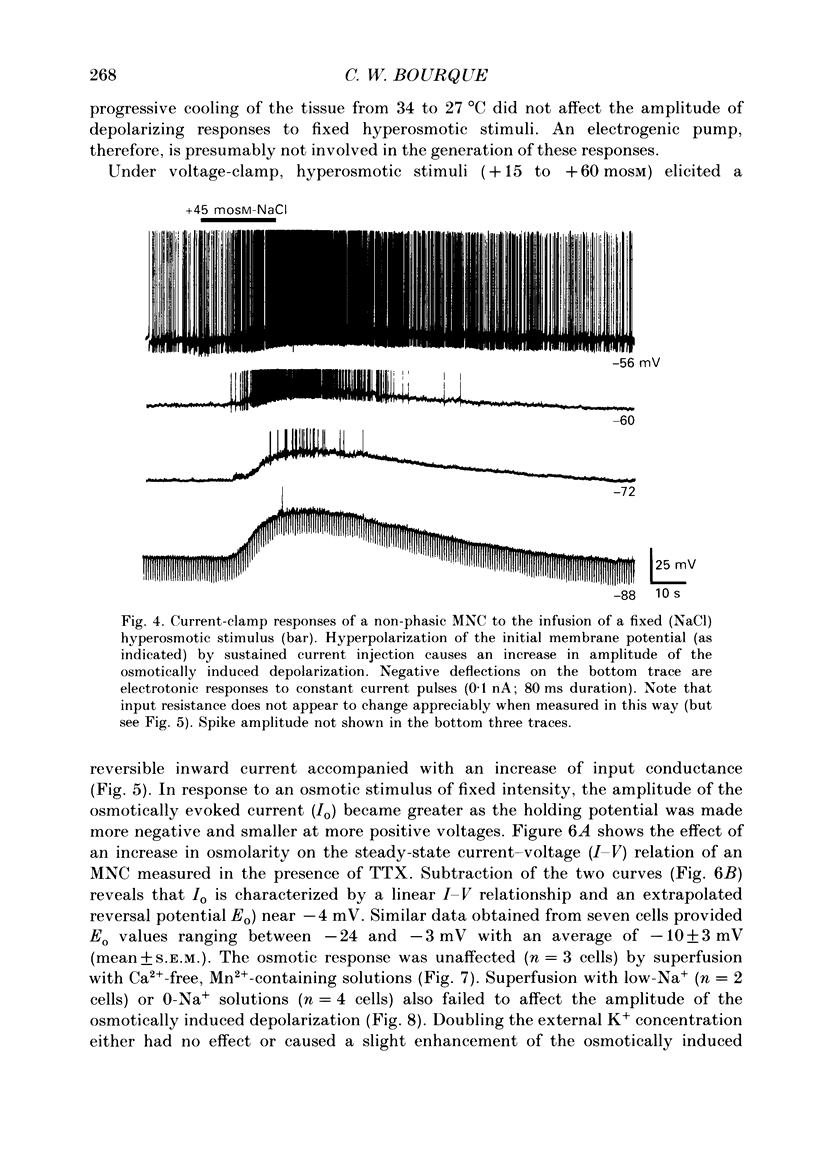




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe H., Ogata N. Ionic mechanism for the osmotically-induced depolarization in neurones of the guinea-pig supraoptic nucleus in vitro. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:157–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew R. D., Dudek F. E. Burst discharge in mammalian neuroendocrine cells involves an intrinsic regenerative mechanism. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1050–1052. doi: 10.1126/science.6879204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R. J., Leng G. Relative efficiency of neural firing patterns for vasopressin release in vitro. Neuroendocrinology. 1981 Nov;33(5):295–299. doi: 10.1159/000123248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W. Calcium-dependent spike after-current induces burst firing in magnocellular neurosecretory cells. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Oct 8;70(2):204–209. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90464-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W., Randle J. C., Renaud L. P. Non-synaptic depolarizing potentials in rat supraoptic neurones recorded in vitro. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:493–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W., Renaud L. P. A perfused in vitro preparation of hypothalamus for electrophysiological studies on neurosecretory neurons. J Neurosci Methods. 1983 Mar;7(3):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(83)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W., Renaud L. P. Activity patterns and osmosensitivity of rat supraoptic neurones in perfused hypothalamic explants. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:631–642. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimble M. J., Dyball R. E. Characterization of the responses of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurones in the supraoptic nucleus to osmotic stimulation. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn F. L., Brennan T. J., Nelson A. E., Robertson G. L. The role of blood osmolality and volume in regulating vasopressin secretion in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3212–3219. doi: 10.1172/JCI107521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton A., Dyball R. E. Phasic firing enhances vasopressin release from the rat neurohypophysis. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):433–440. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer T. M., Adams D. J., Hille B. The permeability of the endplate channel to organic cations in frog muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):469–492. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell J. V., Adams P. R. Voltage-clamp analysis of muscarinic excitation in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 28;250(1):71–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90954-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G., Mason W. T., Dyer R. G. The supraoptic nucleus as an osmoreceptor. Neuroendocrinology. 1982 Jan;34(1):75–82. doi: 10.1159/000123280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G. Rat supraoptic neurones: the effects of locally applied hypertonic saline. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:405–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Wakerley J. B. Electrophysiology of hypothalamic magnocellular neurones secreting oxytocin and vasopressin. Neuroscience. 1982 Apr;7(4):773–808. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita H., Inenaga K., Kawata M., Sano Y. Phasically firing neurons in the supraoptic nucleus of the rat hypothalamus: immunocytochemical and electrophysiological studies. Neurosci Lett. 1983 May 27;37(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90509-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



