Abstract
1. During operative aorto-femoral vascular reconstructions on sixteen patients, the sympathetic chain was stimulated electrically between the L2 and L4 ganglia while blood flow was monitored by laser doppler flowmeters from the skin on the sole of the foot and the ankle and by an electromagnetic flowmeter from the deep femoral artery. Epidural anaesthesia to at least the T6 level was used which excluded reflex effects. 2. Stimulation (10 Hz) at 1-12 mA current strengths for 30 s evoked both reductions and increases of blood flow in glabrous and hairy skin. Initial short-lasting flow increases (durations 9-19 s) followed by sustained decreases were common: sometimes there were sustained flow increases at low and decreases at high current strengths. 3. In the deep femoral artery (supplying predominantly muscle) only flow reductions were evoked. 4. The results provide evidence for sympathetically mediated vasodilatation in the skin of the human foot whereas leg muscles may be supplied by vasoconstrictor nerves only.
Full text
PDF


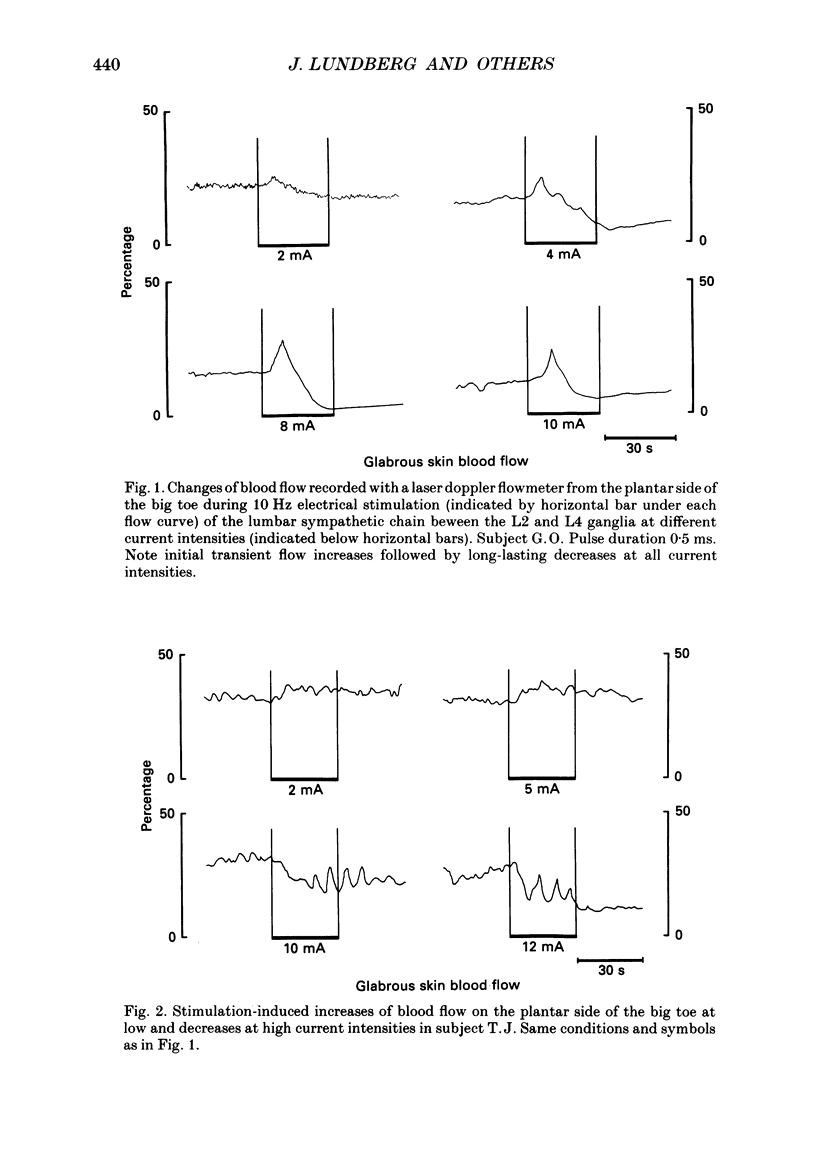
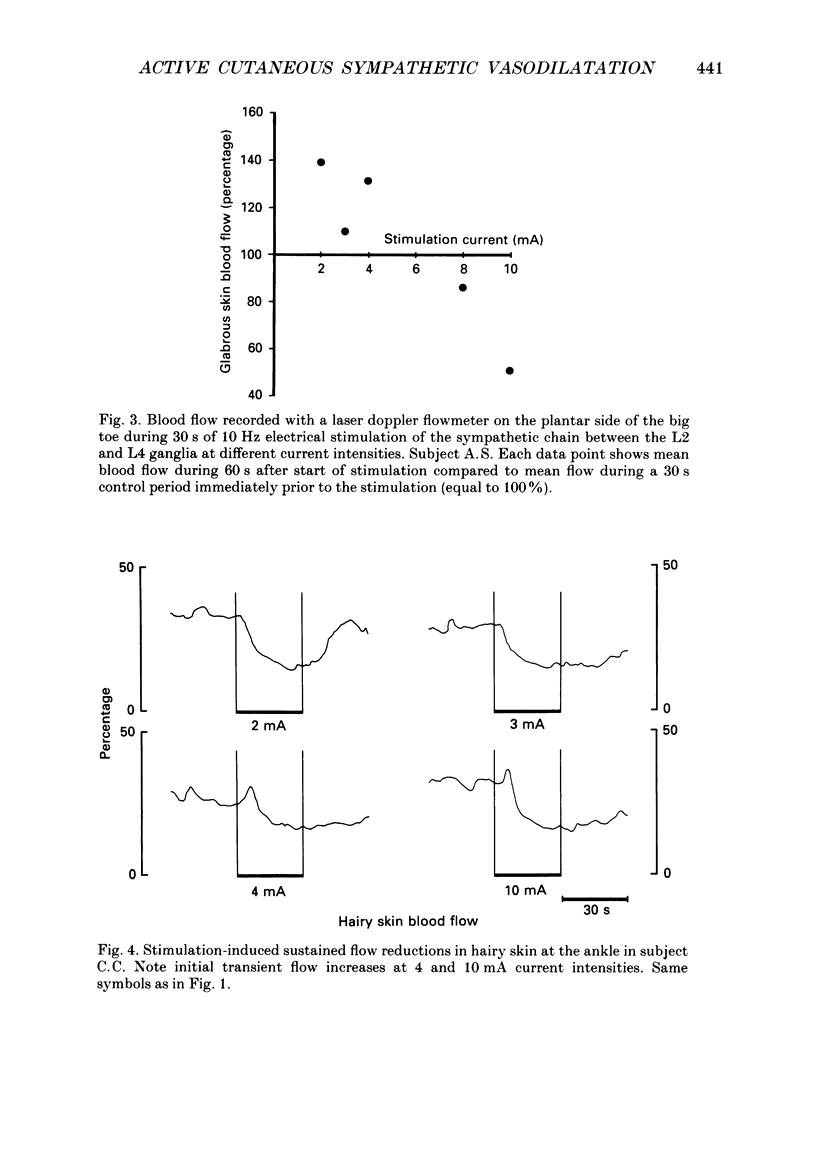
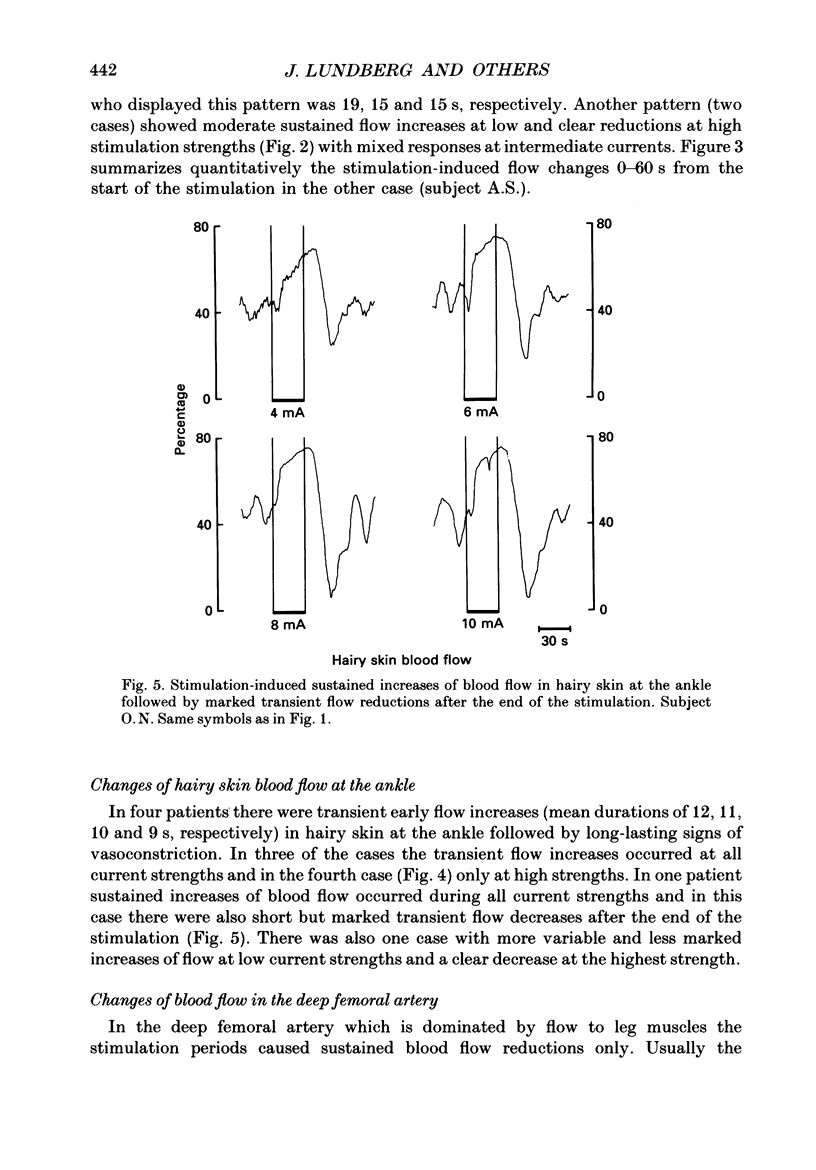
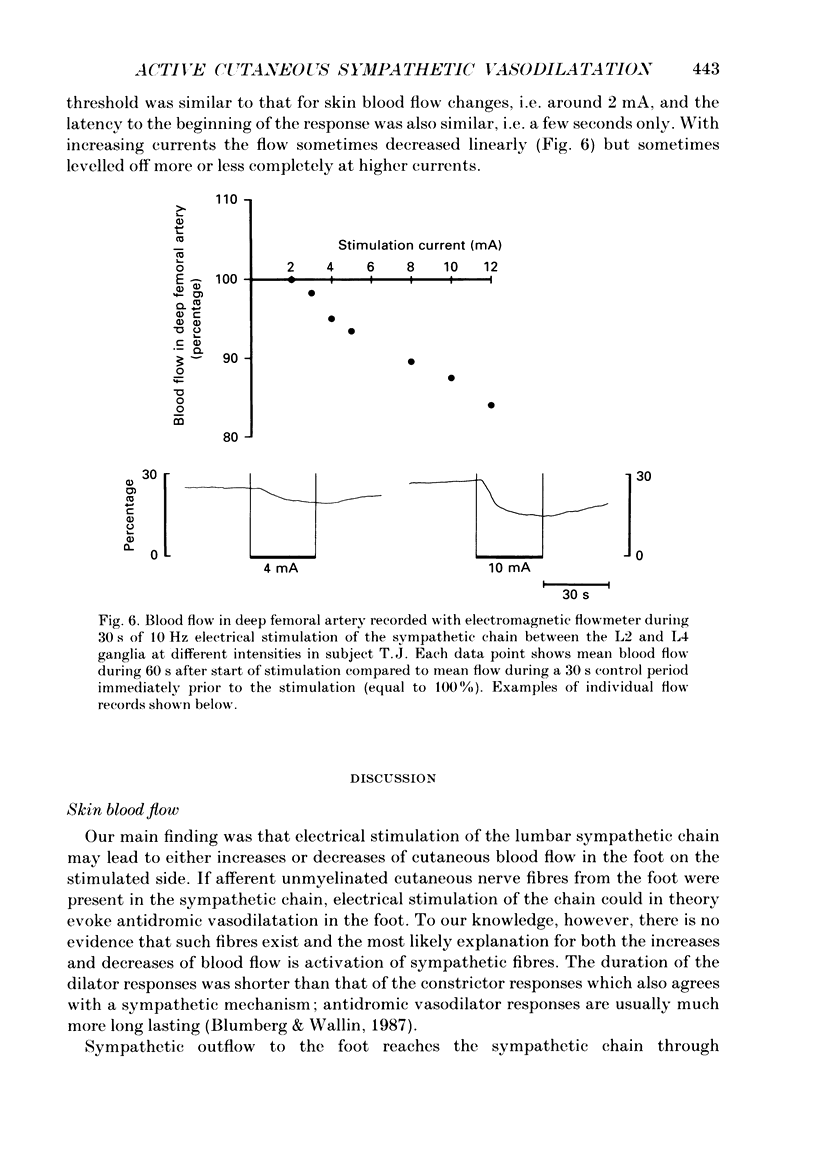



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAIR D. A., GLOVER W. E., GREENFIELD A. D., RODDIE I. C. Excitation of cholinergic vasodilator nerves to human skeletal muscles during emotional stress. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:633–647. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bini G., Hagbarth K. E., Hynninen P., Wallin B. G. Thermoregulatory and rhythm-generating mechanisms governing the sudomotor and vasoconstrictor outflow in human cutaneous nerves. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:537–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. A., Glover W. E., Roddie I. C. Vasomotor fibres to skin in the upper arm, calf and thigh. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153(2):232–238. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg H., Wallin B. G. Direct evidence of neurally mediated vasodilatation in hairy skin of the human foot. J Physiol. 1987 Jan;382:105–121. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton B., Carmichael E. A., Stürup G. Vaso-constriction following deep inspiration. J Physiol. 1936 Jan 15;86(1):83–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius W., Hagbarth K. E., Hongell A., Wallin B. G. Manoeuvres affecting sympathetic outflow in human skin nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Feb;84(2):177–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagius J., Wallin B. G. Sympathetic reflex latencies and conduction velocities in normal man. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Sep;47(3):433–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASKELL P. Are there sympathetic vasodilator nerves to the vessels of the hands. J Physiol. 1956 Mar 28;131(3):647–656. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLENHOFEN K., HILDEBRANDT G. Psychische Einflüsse auf die Muskeldurchblutung. Pflugers Arch. 1957;263(6):637–646. doi: 10.1007/BF00362852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagbarth K. E., Hallin R. G., Hongell A., Torebjörk H. E., Wallin B. G. General characteristics of sympathetic activity in human skin nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Feb;84(2):164–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway G. A., Jr, Watkins D. W. Laser Doppler measurement of cutaneous blood flow. J Invest Dermatol. 1977 Sep;69(3):306–309. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12507665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. M., Taylor W. F., Shepherd A. P., Park M. K. Laser-Doppler measurement of skin blood flow: comparison with plethysmography. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Mar;56(3):798–803. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.3.798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G. E., Tenland T., Oberg P. A. Evaluation of a laser Doppler flowmeter for measurement of tissue blood flow. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1980 Oct;27(10):597–604. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1980.326582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normell L. A. Distribution of impaired cutaneous vasomotor and sudomotor function in paraplegic man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1974;138:25–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberle J., Elam M., Karlsson T., Wallin B. G. Temperature-dependent interaction between vasoconstrictor and vasodilator mechanisms in human skin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Apr;132(4):459–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODDIE I. C., SHEPHERD J. T., WHELAN R. F. The contribution of constrictor and dilator nerves to the skin vasodilatation during body heating. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):489–497. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnoff S. J., Simeone F. A. VASODILATOR FIBERS IN THE HUMAN SKIN. J Clin Invest. 1947 May;26(3):453–459. doi: 10.1172/JCI101829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjernberg L., Blumberg H., Wallin B. G. Sympathetic activity in man after spinal cord injury. Outflow to muscle below the lesion. Brain. 1986 Aug;109(Pt 4):695–715. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.4.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. G., König U. Changes of skin nerve sympathetic activity during induction of general anaesthesia with thiopentone in man. Brain Res. 1976 Feb 13;103(1):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90698-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. G., Stjernberg L. Sympathetic activity in man after spinal cord injury. Outflow to skin below the lesion. Brain. 1984 Mar;107(Pt 1):183–198. doi: 10.1093/brain/107.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


