Abstract
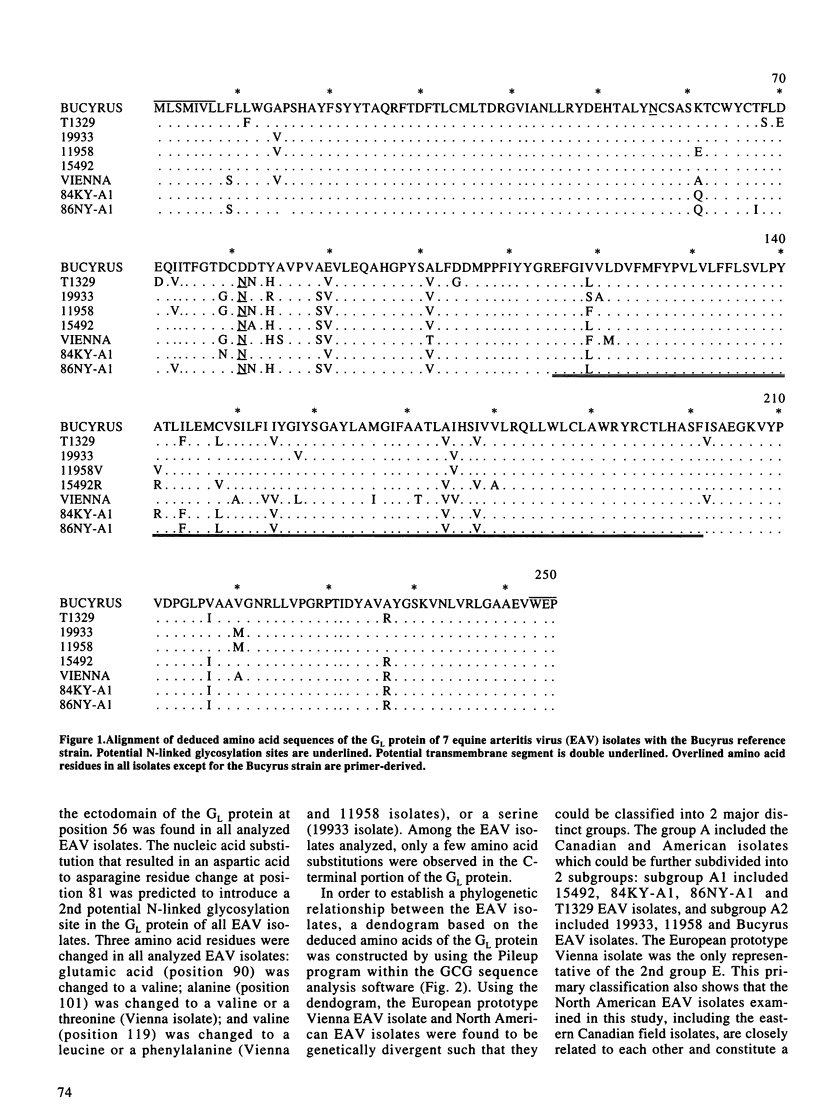
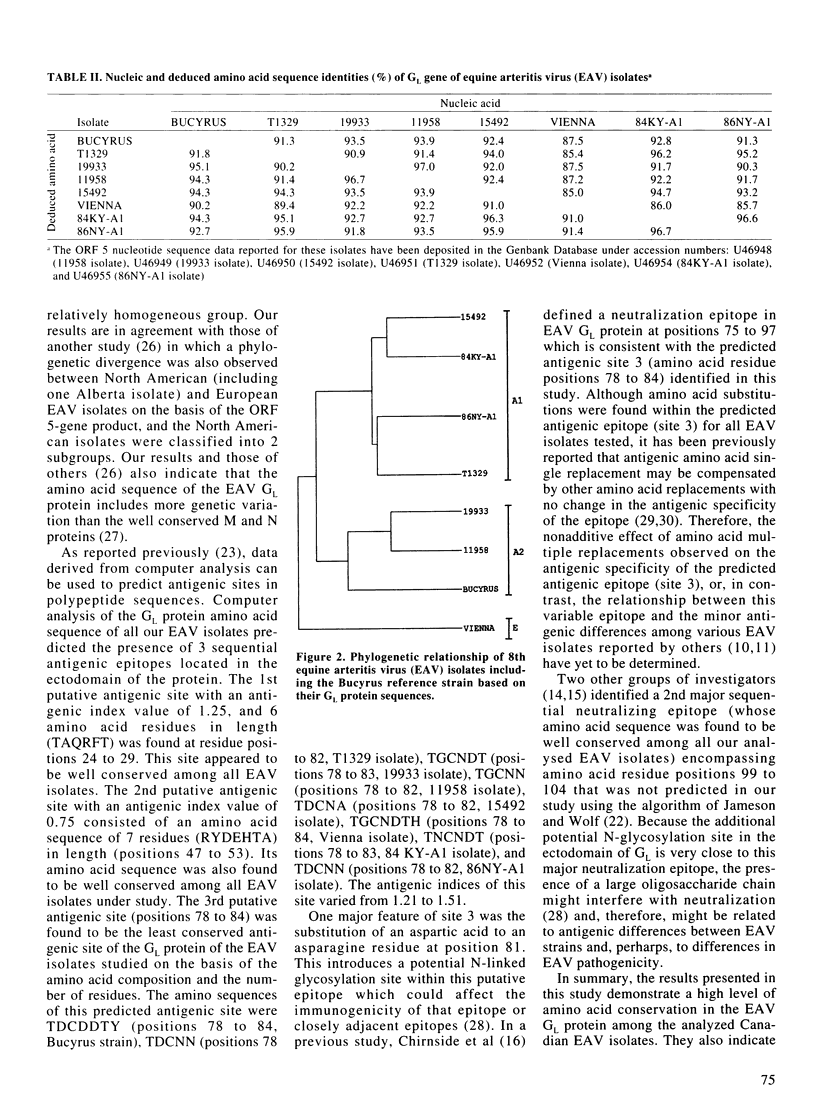
The genetic variation in equine arteritis virus (EAV) GL protein encoding gene was investigated. Nucleic and deduced amino acid sequences from 7 different EAV isolates, including 4 eastern Canadian field isolates, were compared with those of the Bucyrus reference strain. Nucleotide sequence identities between these isolates and the Bucyrus reference strain ranged from 87.5% (Vienna isolate) to 93.9% (11958 isolate). Amino acid identities with the Bucyrus reference strain varied from 90.2% (Vienna isolate) to 95.1% (19933 isolate). A 2nd potential N-linked glycosylation site was found at position 81 in the GL protein of all EAV isolates. Three amino acid substitutions at residue position 90 (Glu-->Val), position 101 (Ala-->Val or Thr), and position 119 (Val-->Leu, Phe or Ser) were also found in all EAV isolates. Phylogenetic analysis showed that the North American EAV isolates, including the Canadian isolates, and the European prototype Vienna isolate could be classified in 2 distinct groups. Three putative sequential antigenic sites were predicted in EAV GL protein. The 1st antigenic site (TAQRFT) was located at positions 24 to 29, and the 2nd antigenic site (RYDEHTA) at positions 47 to 53. The 3rd antigenic site was predicted to be located at positions 78 to 84 and showed the less conserved amino acid sequence.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANS J. T., DOLL E. R., KNAPPENBERGER R. E. An outbreak of abortion caused by the equine arteritis virus. Cornell Vet. 1957 Jan;47(1):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasuriya U. B., Maclachlan N. J., De Vries A. A., Rossitto P. V., Rottier P. J. Identification of a neutralization site in the major envelope glycoprotein (GL) of equine arteritis virus. Virology. 1995 Mar 10;207(2):518–527. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasuriya U. B., Rossitto P. V., DeMaula C. D., MacLachlan N. J. A 29K envelope glycoprotein of equine arteritis virus expresses neutralization determinants recognized by murine monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1993 Nov;74(Pt 11):2525–2529. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-11-2525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasuriya U. B., Timoney P. J., McCollum W. H., MacLachlan N. J. Phylogenetic analysis of open reading frame 5 of field isolates of equine arteritis virus and identification of conserved and nonconserved regions in the GL envelope glycoprotein. Virology. 1995 Dec 20;214(2):690–697. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.0087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker Y. Computer prediction of antigenic and topogenic domains in HSV-1 and HSV-2 glycoprotein B (gB). Virus Genes. 1992 Apr;6(2):131–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01703062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer M., Novak Z., Fotedar A., Fraga E., Singh B. Critical role of an amino acid residue in a T cell determinant is due to its interaction with a neighboring non-critical residue. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Sep;20(9):2145–2148. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirnside E. D., Wearing C. M., Binns M. M., Mumford J. A. Comparison of M and N gene sequences distinguishes variation amongst equine arteritis virus isolates. J Gen Virol. 1994 Jun;75(Pt 6):1491–1497. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-6-1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirnside E. D., de Vries A. A., Mumford J. A., Rottier P. J. Equine arteritis virus-neutralizing antibody in the horse is induced by a determinant on the large envelope glycoprotein GL. J Gen Virol. 1995 Aug;76(Pt 8):1989–1998. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-8-1989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deregt D., de Vries A. A., Raamsman M. J., Elmgren L. D., Rottier P. J. Monoclonal antibodies to equine arteritis virus proteins identify the GL protein as a target for virus neutralization. J Gen Virol. 1994 Sep;75(Pt 9):2439–2444. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-9-2439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigen M. The origin of genetic information: viruses as models. Gene. 1993 Dec 15;135(1-2):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A., Goldman A. Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:321–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga Y., Matsumura T., Sugiura T., Wada R., Imagawa H., Kanemaru T., Kamada M. Use of the serum neutralisation test for equine viral arteritis with different virus strains. Vet Rec. 1994 May 28;134(22):574–576. doi: 10.1136/vr.134.22.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga Y., McCollum W. H. Complement-fixation reactions in equine viral arteritis. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Dec;38(12):2043–2046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser A. L., de Vries A. A., Dubovi E. J. Comparison of equine arteritis virus isolates using neutralizing monoclonal antibodies and identification of sequence changes in GL associated with neutralization resistance. J Gen Virol. 1995 Sep;76(Pt 9):2223–2233. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-9-2223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigera P. R., Mathieu M. E., Wagner R. R. Effect of glycosylation on the conformational epitopes of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus (New Jersey serotype). Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90002-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson B. A., Wolf H. The antigenic index: a novel algorithm for predicting antigenic determinants. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):181–186. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mateu M. G., Andreu D., Carreño C., Roig X., Cairó J. J., Camarero J. A., Giralt E., Domingo E. Non-additive effects of multiple amino acid substitutions on antigen-antibody recognition. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1385–1389. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. W., McCollum W. H., Timoney P. J., Klingeborn B. W., Hyllseth B., Golnik W., Erasmus B. Genomic variability among globally distributed isolates of equine arteritis virus. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Sep;32(2):101–115. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90099-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revision of the taxonomy of the Coronavirus, Torovirus and Arterivirus genera. Arch Virol. 1994;135(1-2):227–237. doi: 10.1007/BF01309782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijder E. J., Wassenaar A. L., Spaan W. J. Proteolytic processing of the replicase ORF1a protein of equine arteritis virus. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5755–5764. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5755-5764.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Laurent G., Morin G., Archambault D. Detection of equine arteritis virus following amplification of structural and nonstructural viral genes by reverse transcription-PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Mar;32(3):658–665. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.3.658-665.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. H., Strauss E. G. Evolution of RNA viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:657–683. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries A. A., Chirnside E. D., Horzinek M. C., Rottier P. J. Structural proteins of equine arteritis virus. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6294–6303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6294-6303.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Boon J. A., Snijder E. J., Chirnside E. D., de Vries A. A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Equine arteritis virus is not a togavirus but belongs to the coronaviruslike superfamily. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2910–2920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2910-2920.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



