Abstract
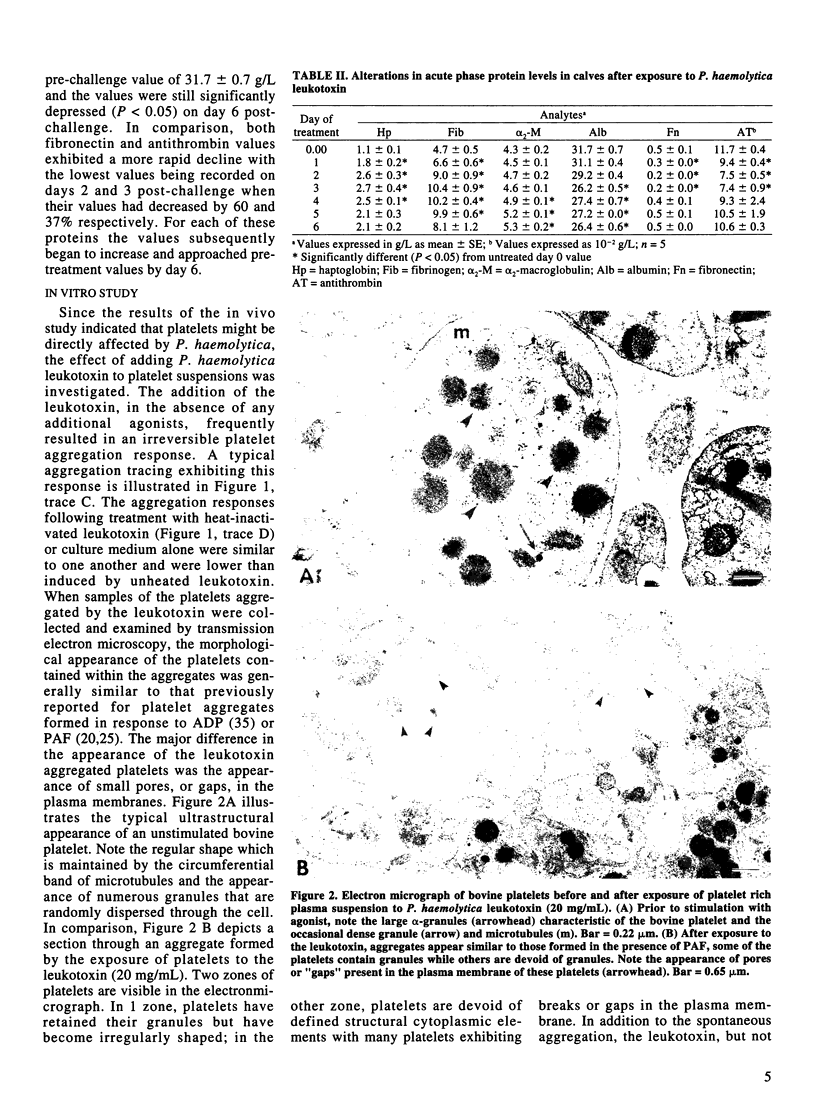
Platelet function was assessed by aggregometry in 10 Holstein calves before and after exposure to Pasteurella haemolytica (biotype A, serotype 1) by intrabronchial challenge. At 24 h after exposure the platelets had become more reactive to stimulation with known platelet agonists such as adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and platelet-activating factor (PAF) and the platelet aggregates that formed were more resistant to disaggregation. The activation of platelets was an early response in the challenged calves as platelet function had returned to pretreatment levels 72 h after exposure to the bacteria while the acute phase reactant proteins, haptoglobin and fibrinogen, were approaching their peak values and alpha 2-macroglobulin levels had also risen significantly (P < 0.05) at this time. The plasma levels of these proteins were still elevated and albumin levels were depressed 6 d post-treatment. At post-mortem all calves exhibited pneumonic tissue damage. When P. haemolytica leukotoxin was added directly to bovine platelet suspensions both spontaneous aggregation and an increase in the aggregation response to ADP and PAF stimulation were observed. The morphological appearance of the platelet aggregates exhibited the typical pattern for bovine platelets with 2 distinct zones of cells being visible within each aggregate. One zone contained platelets in which the cytoplasmic granules were still evident and the other zone contained irregularly shaped platelets devoid of granular content. In the latter zone, discrete gaps, or pores, were evident in the plasma membrane of numerous platelets. This pore formation is characteristic of leukotoxin action and is not observed in ADP or PAF induced aggregates.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adusu T. E., Conlon P. D., Shewen P. E., Black W. D. Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin induces histamine release from bovine pulmonary mast cells. Can J Vet Res. 1994 Jan;58(1):1–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:927–929. doi: 10.1038/194927b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baluyut C. S., Simonson R. R., Bemrick W. J., Maheswaran S. K. Interaction of Pasteurella haemolytica with bovine neutrophils: identification and partial characterization of a cytotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Nov;42(11):1920–1926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. Escherichia coli hemolysin may damage target cell membranes by generating transmembrane pores. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.63-69.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy G. S., Gentry P. A. Characterization of the normal bovine platelet aggregation response. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1989;92(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(89)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breider M. A., Walker R. D., Hopkins F. M., Schultz T. W., Bowersock T. L. Pulmonary lesions induced by Pasteurella haemolytica in neutrophil sufficient and neutrophil deficient calves. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Apr;52(2):205–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breider M. A., Yang Z. Tissue factor expression in bovine endothelial cells induced by Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide and interleukin-1. Vet Pathol. 1994 Jan;31(1):55–60. doi: 10.1177/030098589403100107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Car B. D., Slauson D. O., Suyemoto M. M., Doré M., Neilsen N. R. Expression and kinetics of induced procoagulant activity in bovine pulmonary alveolar macrophages. Exp Lung Res. 1991 Sep-Oct;17(5):939–957. doi: 10.3109/01902149109064327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Car B. D., Suyemoto M. M., Neilsen N. R., Slauson D. O. The role of leukocytes in the pathogenesis of fibrin deposition in bovine acute lung injury. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1191–1198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Renshaw H. W., Martens R. J., Livingston C. W., Jr Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin: chemiluminescent responses of peripheral blood leukocytes from several different mammalian species to leukotoxin- and opsonin-treated living and killed Pasteurella haemolytica and Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jan;47(1):67–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinkenbeard K. D., Mosier D. A., Confer A. W. Transmembrane pore size and role of cell swelling in cytotoxicity caused by Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):420–425. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.420-425.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinkenbeard K. D., Mosier D. A., Timko A. L., Confer A. W. Effects of Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin on cultured bovine lymphoma cells. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Feb;50(2):271–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinkenbeard K. D., Upton M. L. Lysis of bovine platelets by Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1991 Mar;52(3):453–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Clinkenbeard K. D., Mosier D. A. Molecular aspects of virulence of Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Vet Res. 1990 Apr;54 (Suppl):S48–S52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon P., Gervais M., Chaudhari S., Conlon J. Effects of Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxic culture supernatant on bovine neutrophil aggregation. Can J Vet Res. 1992 Jul;56(3):199–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner J. G., Eckersall P. D., Wiseman A., Bain R. K., Douglas T. A. Acute phase response in calves following infection with Pasteurella haemolytica, Ostertagia ostertagi and endotoxin administration. Res Vet Sci. 1989 Sep;47(2):203–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner J. G., Eckersall P. D., Wiseman A., Bain R. K., Douglas T. A. Acute phase response in calves following infection with Pasteurella haemolytica, Ostertagia ostertagi and endotoxin administration. Res Vet Sci. 1989 Sep;47(2):203–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry P. A. The mammalian blood platelet: its role in haemostasis, inflammation and tissue repair. J Comp Pathol. 1992 Oct;107(3):243–270. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(92)90002-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry P. A., Tremblay R. R., Ross M. L. Failure of aspirin to impair bovine platelet function. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jun;50(6):919–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson D. L., Campos M., Attah-Poku S. K., Redmond M. J., Cordeiro D. M., Sethi M. S., Harland R. J., Babiuk L. A. Serum haptoglobin as an indicator of the acute phase response in bovine respiratory disease. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Jun 1;51(3-4):277–292. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(95)05520-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haritani M., Nakazawa M., Oohashi S., Yamada Y., Haziroglu R., Narita M. Immunoperoxidase evaluation of pneumonic lesions induced by Pasteurella haemolytica in calves. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Sep;48(9):1358–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henricks P. A., Binkhorst G. J., Drijver A. A., Nijkamp F. P. Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin enhances production of leukotriene B4 and 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid by bovine polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3238–3243. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3238-3243.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jericho K. W., Langford E. V. Aerosol vaccination of calves with pasteurella haemolytica against experimental respiratory disease. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):287–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A., Maxie M. G., Savan M., Ruhnke H. L., Thomson R. G., Barnum D. A., Geissinger H. D. The pulmonary clearance of Pasteurella haemolytica in calves infected with bovine virus diarrhea or Mycoplasma bovis. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):302–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran S. K., Kannan M. S., Weiss D. J., Reddy K. R., Townsend E. L., Yoo H. S., Lee B. W., Whiteley L. O. Enhancement of neutrophil-mediated injury to bovine pulmonary endothelial cells by Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2618–2625. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2618-2625.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran S. K., Weiss D. J., Kannan M. S., Townsend E. L., Reddy K. R., Whiteley L. O., Srikumaran S. Effects of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 leukotoxin on bovine neutrophils: degranulation and generation of oxygen-derived free radicals. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Jun;33(1-2):51–68. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(92)90034-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamo W., Fröman G., Sundås A., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin, fibrinogen and type II collagen to streptococci isolated from bovine mastitis. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jun;2(6):417–424. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Lumsden J. H. The relationship of hematology and serum chemistry parameters to treatment for respiratory disease and weight gain in Ontario feedlot calves. Can J Vet Res. 1987 Oct;51(4):499–505. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers K. M., Hopkins G., Holmsen H., Benson K., Prieur D. J. Ultrastructure of resting and activated storage pool deficient platelets from animals with the Chédiak-Higashi syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1982 Mar;106(3):364–377. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panciera R. J., Corstvet R. E. Bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: model for Pasteurella haemolytica- and Pasteurella multocida-induced pneumonia in cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Dec;45(12):2532–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L. Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv Immunol. 1983;34:141–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Cytotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica acting on bovine leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.91-94.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slocombe R. F., Malark J., Ingersoll R., Derksen F. J., Robinson N. E. Importance of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of acute pneumonic pasteurellosis in calves. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Nov;46(11):2253–2258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and characterization of genes encoding the secretion function of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):916–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.916-928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. D., Hopkins F. M., Schultz T. W., McCracken M. D., Moore R. N. Changes in leukocyte populations in pulmonary lavage fluids of calves after inhalation of Pasteurella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Dec;46(12):2429–2433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley L. O., Maheswaran S. K., Weiss D. J., Ames T. R. Alterations in pulmonary morphology and peripheral coagulation profiles caused by intratracheal inoculation of live and ultraviolet light-killed Pasteurella haemolytica A1 in calves. Vet Pathol. 1991 Jul;28(4):275–285. doi: 10.1177/030098589102800403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley L. O., Maheswaran S. K., Weiss D. J., Ames T. R., Kannan M. S. Pasteurella haemolytica A1 and bovine respiratory disease: pathogenesis. J Vet Intern Med. 1992 Jan-Feb;6(1):11–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-1676.1992.tb00980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley L. O., Maheswaran S. K., Weiss D. J., Ames T. R. Morphological and morphometrical analysis of the acute response of the bovine alveolar wall to Pasteurella haemolytica A1-derived endotoxin and leucotoxin. J Comp Pathol. 1991 Jan;104(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9975(08)80085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie B. N., Markham R. J., Shewen P. E. Response of calves to lung challenge exposure with Pasteurella haemolytica after parenteral or pulmonary immunization. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Nov;41(11):1773–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittum T. E., Young C. R., Stanker L. H., Griffin D. D., Perino L. J., Littledike E. T. Haptoglobin response to clinical respiratory tract disease in feedlot cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1996 May;57(5):646–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Gentry P. A. Hemostatic profile of bovine ovarian follicular fluid. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1995 May;73(5):624–629. doi: 10.1139/y95-079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



