Abstract
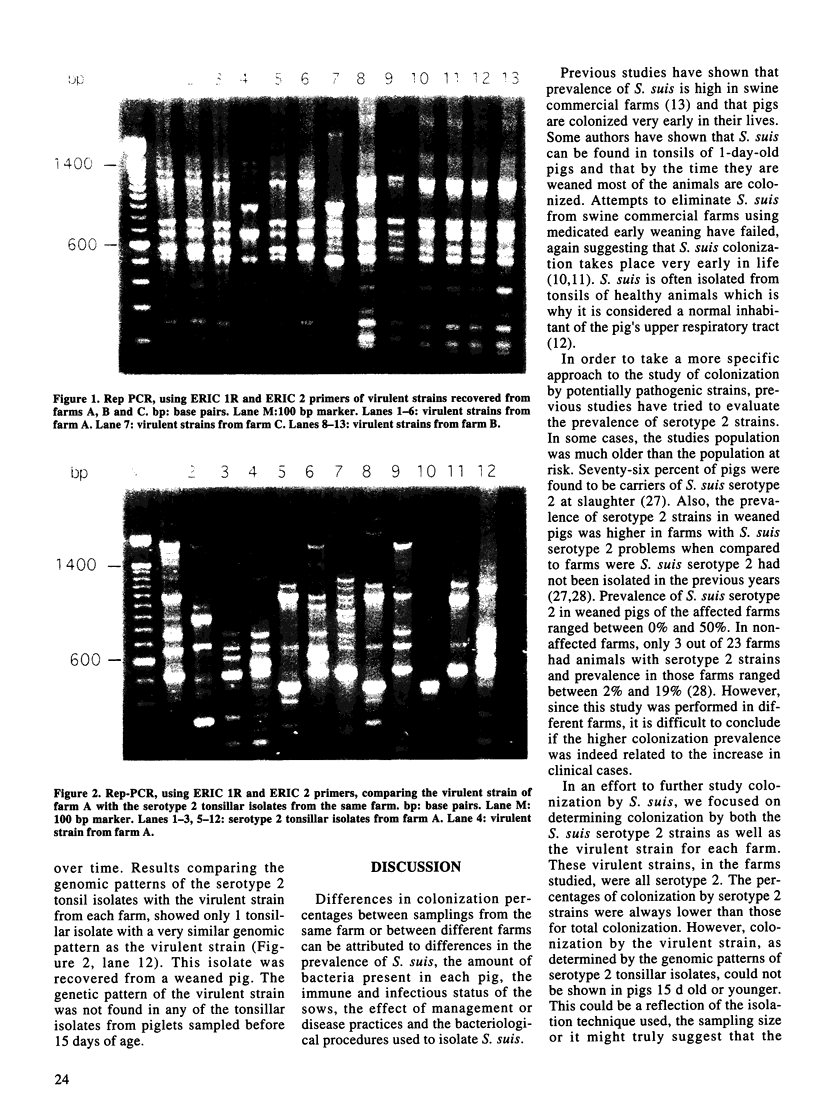
Three swine commercial farms with high mortality rates in nursery pigs due to Streptococcus suis serotype 2 were studied. Brain samples from diseased animals were collected for a period of 6 to 10 mo and used to isolate the strain that was responsible for the mortality (virulent strain) in each farm. Tonsil swabs from piglets at 5, 10 and 15 d were taken to assess both total colonization and colonization by the virulent strain. The effect of sow vaccination against S. suis on colonization was evaluated in 1 of the farms. All suspect tonsil isolates were identified biochemically and then tested against serotype 2. The genomic patterns of serotype 2 isolates were compared to that of the virulent strain using Rep-PCR. Results showed that total colonization by S. suis occurred very early in the pigs' life, with most animals being colonized by weaning age. Prevalence of colonization by serotype 2 strains was much lower than total colonization. After comparing serotype 2 isolates with the virulent strains, only 1 tonsillar isolate had the same genomic pattern as the virulent strain and it belonged to a 4-week-old weaned pig. The genomic pattern of the virulent strain was not found in any tonsillar isolate from 15-day-old or younger pigs. Although limited by sample size, sow vaccination against S. suis increased total colonization at the same time significantly decreasing colonization by serotype 2 strains. Even though most pigs are colonized early in age by S. suis, colonization by the virulent strain is of low prevalence and delayed in time. This could constitute a risk factor for developing the disease later in time, because animals would be colonized when maternal immunity is no longer present, allowing the organism to become systemic.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brisebois L. M., Charlebois R., Higgins R., Nadeau M. Prevalence of Streptococcus suis in four to eight week old clinically healthy piglets. Can J Vet Res. 1990 Jan;54(1):174–177. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. R., Ossowicz C. J. Evaluation of methods used for detecting Streptococcus suis type 2 in tonsils, and investigation of the carrier state in pigs. Res Vet Sci. 1991 Mar;50(2):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0034-5288(91)90104-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Ceyssens K., Hommez J., Kilpper-Bälz R., Schleifer K. H. Characteristics of different Streptococcus suis ecovars and description of a simplified identification method. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Jan;26(1-2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90050-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Hommez J., Pot B., Haesebrouck F. Identification and composition of the streptococcal and enterococcal flora of tonsils, intestines and faeces of pigs. J Appl Bacteriol. 1994 Jul;77(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1994.tb03040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H., Briggs R. E., Loan R. W., Purdy C. W., Zehr E. S. Respiratory tract disease and mucosal colonization by Pasteurella haemolytica in transported cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1996 Sep;57(9):1317–1320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galina L., Collins J. E., Pijoan C. Porcine Streptococcus suis in Minnesota. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1992 Apr;4(2):195–196. doi: 10.1177/104063879200400216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Higgins R., Jacques M., Beaudoin M., Henrichsen J. Characterization of six new capsular types (23 through 28) of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2590–2594. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2590-2594.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Higgins R., Jacques M., Mittal K. R., Henrichsen J. Description of 14 new capsular types of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2633–2636. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2633-2636.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Gottschalk M., Boudreau M., Lebrun A., Henrichsen J. Description of six new capsular types (29-34) of Streptococcus suis. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1995 Jul;7(3):405–406. doi: 10.1177/104063879500700322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A. A., Loeffen P. L., van den Berg A. J., Storm P. K. Identification, purification, and characterization of a thiol-activated hemolysin (suilysin) of Streptococcus suis. Infect Immun. 1994 May;62(5):1742–1748. doi: 10.1093/benz/9780199773787.article.b00034458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford P., Williams A. E., Kroll J. S. Superoxide dismutases of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Streptococcus suis type 2 isolates. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jan 15;61(2-3):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90578-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogollon J. D., Pijoan C., Murtaugh M. P., Collins J. E., Cleary P. P. Identification of epidemic strains of Streptococcus suis by genomic fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):782–787. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.782-787.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogollon J. D., Pijoan C., Murtaugh M. P., Kaplan E. L., Collins J. E., Cleary P. P. Characterization of prototype and clinically defined strains of Streptococcus suis by genomic fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2462–2466. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2462-2466.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau A., Higgins R., Bigras-Poulin M., Nadeau M. Rapid detection of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 in weaned pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Oct;50(10):1667–1671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. A., Robertson I. D., Sanders R. C., Siba P. M., Clegg A., Hampson D. J. The carriage of Streptococcus suis type 2 by pigs in Papua New Guinea. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Feb;110(1):71–78. doi: 10.1017/s095026880005069x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Pedersen K. B., Henrichsen J. Serology of capsulated streptococci pathogenic for pigs: six new serotypes of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):993–996. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.993-996.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto C., Peña J., Suarez P., Imaz M., Castro J. M. Isolation and distribution of Streptococcus suis capsular types from diseased pigs in Spain. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1993 Oct;40(8):544–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1993.tb00175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sihvonen L., Kurl D. N., Salmela P. Infection with Streptococcus suis serotypes 1 and 2 in the same diseased pig. Acta Vet Scand. 1986;27(4):626–628. doi: 10.1186/BF03548143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarradas C., Arenas A., Maldonado A., Luque I., Miranda A., Perea A. Identification of Streptococcus suis isolated from swine: proposal for biochemical parameters. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Feb;32(2):578–580. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.2.578-580.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecht U., Arends J. P., van der Molen E. J., van Leengoed L. A. Differences in virulence between two strains of Streptococcus suis type II after experimentally induced infection of newborn germ-free pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jul;50(7):1037–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecht U., Wisselink H. J., Jellema M. L., Smith H. E. Identification of two proteins associated with virulence of Streptococcus suis type 2. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3156–3162. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3156-3162.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versalovic J., Koeuth T., Lupski J. R. Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6823–6831. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. E., Blakemore W. F., Alexander T. J. A murine model of Streptococcus suis type 2 meningitis in the pig. Res Vet Sci. 1988 Nov;45(3):394–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. E. Relationship between intracellular survival in macrophages and pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis type 2 isolates. Microb Pathog. 1990 Mar;8(3):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90046-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]