Abstract
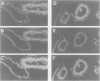
The purpose of this study was to identify organs and cells to which the edema disease verotoxin (VT2e) could bind in pigs. Frozen 4-5 microns thick sections of organs usually affected in edema disease (colon, spinal cord, cerebellum and eyelid) and organs not usually affected (liver, ileum) from two 5- to 6-week-old weaned pigs were permeabilized with acetone, then exposed to VT2e. Unbound VT2e was removed by washing and bound VT2e was detected by immunohistochemistry. In the eyelid, double-label immunofluorescence was used to identify the cells to which VT2e bound. VT2e was shown to bind to all six organs that were examined. The toxin bound to arteries in all organs, to veins in all organs except the liver, and to enterocytes in the ileal crypts. Double labelling of eyelid with monoclonal antibodies specific for von Willebrand factor or alpha-smooth actin and VT2e showed that the toxin bound to endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. The binding of VT2e to endothelium is consistent with findings for other verotoxins but binding to vascular smooth muscle has not been reported for other verotoxins. It is concluded that i) factors other than the presence of receptors for VT2e influence the development of lesions in edema disease, and ii) smooth muscle necrosis, which is characteristic of the vascular lesions in edema disease, may be due to a direct action of toxin on smooth muscle cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd B., Tyrrell G., Maloney M., Gyles C., Brunton J., Lingwood C. Alteration of the glycolipid binding specificity of the pig edema toxin from globotetraosyl to globotriaosyl ceramide alters in vivo tissue targetting and results in a verotoxin 1-like disease in pigs. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1745–1753. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiklid K., Olsnes S. Interaction of Shigella shigae cytotoxin with receptors on sensitive and insensitive cells. J Recept Res. 1980;1(2):199–213. doi: 10.3109/10799898009044098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke S., Harmsen D., Caprioli A., Pierard D., Wieler L. H., Karch H. Clonal relatedness of Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli O101 strains of human and porcine origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Dec;33(12):3174–3178. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.12.3174-3178.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard B. K., Jones M. A., Turner A. A., Lewis D. E., Marcus D. M. Interferon-gamma alters expression of endothelial cell-surface glycosphingolipids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 May 15;279(1):122–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90471-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard B. K., Thurmon L. T., Marcus D. M. Association of glycosphingolipids with intermediate filaments of mesenchymal, epithelial, glial, and muscle cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;21(4):255–271. doi: 10.1002/cm.970210402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Escherichia coli cytotoxins and enterotoxins. Can J Microbiol. 1992 Jul;38(7):734–746. doi: 10.1139/m92-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz M., Clausen H., Nudelman E., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea. XI. Isolation of a shigella toxin-binding glycolipid from rabbit jejunum and HeLa cells and its identification as globotriaosylceramide. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye S. A., Louise C. B., Boyd B., Lingwood C. A., Obrig T. G. Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: interleukin-1 beta enhancement of Shiga toxin cytotoxicity toward human vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3886–3891. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3886-3891.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Jacewicz M., Acheson D. W., Donohue-Rolfe A., Kane A. V., McCluer R. H. Globotriaosylceramide, Gb3, is an alternative functional receptor for Shiga-like toxin 2e. Infect Immun. 1995 Mar;63(3):1138–1141. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.3.1138-1141.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz H. J., Bergeland M. E., Barnes D. M. Pathologic changes in edema disease of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1969 May;30(5):791–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linggood M. A., Thompson J. M. Verotoxin production among porcine strains of Escherichia coli and its association with oedema disease. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Dec;24(4):359–362. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-4-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A. Verotoxin-binding in human renal sections. Nephron. 1994;66(1):21–28. doi: 10.1159/000187761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louise C. B., Obrig T. G. Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: combined cytotoxic effects of shiga toxin and lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin) on human vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1536–1543. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1536-1543.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louise C. B., Obrig T. G. Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic-uremic syndrome: combined cytotoxic effects of Shiga toxin, interleukin-1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor alpha on human vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4173–4179. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4173-4179.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod D. L., Gyles C. L. Purification and characterization of an Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin II variant. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1232–1239. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1232-1239.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod D. L., Gyles C. L., Wilcock B. P. Reproduction of edema disease of swine with purified Shiga-like toxin-II variant. Vet Pathol. 1991 Jan;28(1):66–73. doi: 10.1177/030098589102800109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methiyapun S., Pohlenz J. F., Bertschinger H. U. Ultrastructure of the intestinal mucosa in pigs experimentally inoculated with an edema disease-producing strain of Escherichia coli (0139:K12:H1). Vet Pathol. 1984 Sep;21(5):516–520. doi: 10.1177/030098588402100511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L. Haemolytic-uraemic syndrome: basic science. Lancet. 1994 Feb 12;343(8894):393–397. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobassaleh M., Donohue-Rolfe A., Jacewicz M., Grand R. J., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea: evidence for a developmentally regulated glycolipid receptor for shigella toxin involved in the fluid secretory response of rabbit small intestine. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):1023–1031. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pudymaitis A., Lingwood C. A. Susceptibility to verotoxin as a function of the cell cycle. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Mar;150(3):632–639. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. E., Rotman T. A., Jay V., Smith C. R., Becker L. E., Petric M., Olivieri N. F., Karmali M. A. Experimental verocytotoxemia in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4154–4167. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4154-4167.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. A., Hurley R. M., Lingwood C., Matsell D. G. Escherichia coli verotoxin binding to human paediatric glomerular mesangial cells. Pediatr Nephrol. 1995 Dec;9(6):700–704. doi: 10.1007/BF00868715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel J. E., Perera L. P., Ward S., O'Brien A. D., Ginsburg V., Krivan H. C. Comparison of the glycolipid receptor specificities of Shiga-like toxin type II and Shiga-like toxin type II variants. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):611–618. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.611-618.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonderwoerd M., Clarke R. C., van Dreumel A. A., Rawluk S. A. Colitis in calves: natural and experimental infection with a verotoxin-producing strain of Escherichia coli O111:NM. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Oct;52(4):484–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., Burris J. A., Owens J. W., Gordon V. M., Wadolkowski E. A., O'Brien A. D., Samuel J. E. Comparison of the relative toxicities of Shiga-like toxins type I and type II for mice. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3392–3402. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3392-3402.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., Ramegowda B., Samuel J. E. Purified Shiga-like toxins induce expression of proinflammatory cytokines from murine peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1994 Nov;62(11):5085–5094. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.11.5085-5094.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., Samuel J. E., Perera L. P., Sharefkin J. B., O'Brien A. D. Evaluation of the role of Shiga and Shiga-like toxins in mediating direct damage to human vascular endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):344–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell T. E., Lingwood C. A., Gyles C. L. Interaction of verotoxin 2e with pig intestine. Infect Immun. 1996 May;64(5):1714–1719. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.5.1714-1719.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell T., Cohen A., Lingwood C. A. Induction of verotoxin sensitivity in receptor-deficient cell lines using the receptor glycolipid globotriosylceramide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7898–7901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoja C., Corna D., Farina C., Sacchi G., Lingwood C., Doyle M. P., Padhye V. V., Abbate M., Remuzzi G. Verotoxin glycolipid receptors determine the localization of microangiopathic process in rabbits given verotoxin-1. J Lab Clin Med. 1992 Aug;120(2):229–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Kar N. C., Monnens L. A., Karmali M. A., van Hinsbergh V. W. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 induce expression of the verocytotoxin receptor globotriaosylceramide on human endothelial cells: implications for the pathogenesis of the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood. 1992 Dec 1;80(11):2755–2764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]