Abstract
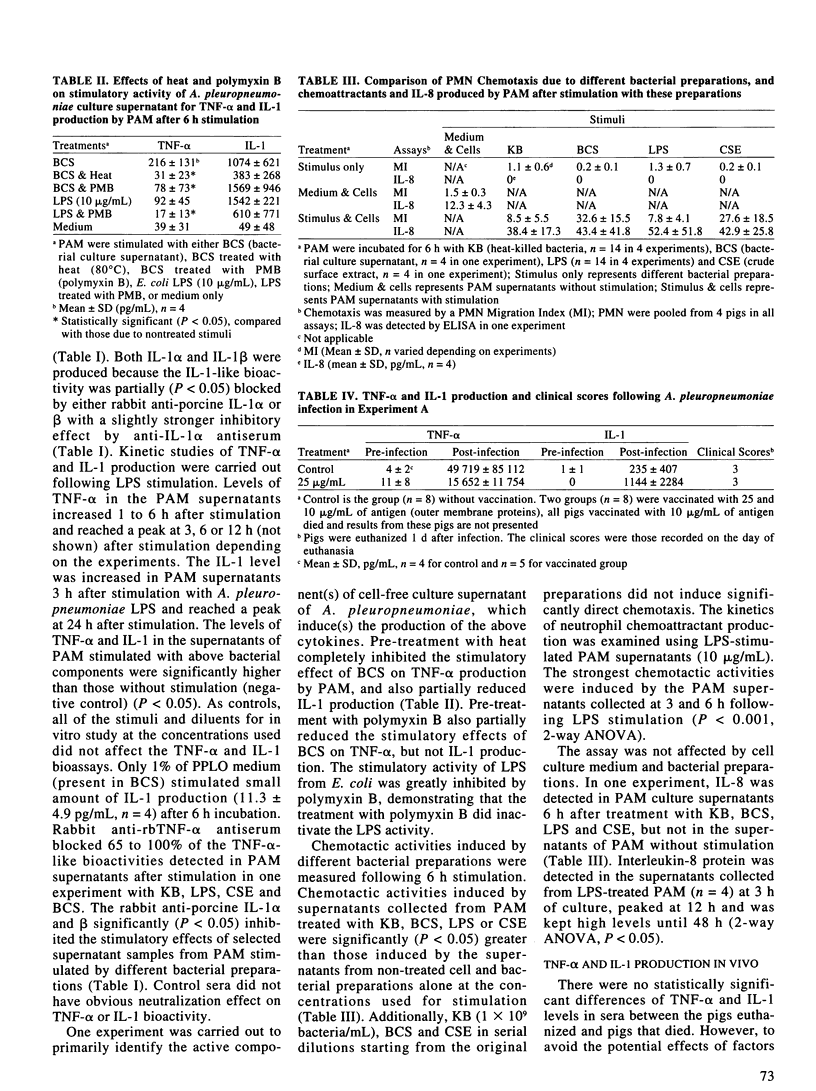
The in vitro production of proinflammatory cytokines after stimulation with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae and the relation of these cytokines in vivo with the disease caused by A. pleuropneumoniae were investigated. Within 24 h, in vitro stimulation by A. pleuropneumoniae (serotype 1) preparations, including killed bacteria, bacterial culture supernatant, lipopolysaccharide, and bacterial extracts, porcine pulmonary alveolar macrophages (PAM) produced significant (P < 0.05) amounts of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) as measured by bioassays. The supernatants containing interleukin-8 from PAM after stimulation by bacterial preparations showed significant neutrophil chemotaxis, while bacterial preparations alone did not. After in vivo infection with A. pleuropneumoniae, the mean levels of TNF-alpha and IL-1 in serum, as measured by bioassays, were elevated 37- to 27836-fold for TNF-alpha and 11- to 5941-fold higher for IL-1 within 4 d post-infection, depending on the treatments, and remained elevated up to Day 7. Both cytokines were also detected in porcine lungs by bioassays and immunocytochemistry. The results indicated that both secreted and surface components of A. pleuropneumoniae can stimulate PAM to produce proinflammatory mediators. Neutrophil chemoattractants rather than bacterial components are the major factor causing acute lung inflammation. The elevation of TNF-alpha and IL-1 in pigs occurred coincident with the onset of acute clinical disease.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baarsch M. J., Scamurra R. W., Burger K., Foss D. L., Maheswaran S. K., Murtaugh M. P. Inflammatory cytokine expression in swine experimentally infected with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1995 Sep;63(9):3587–3594. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.9.3587-3594.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertram T. A. Pathobiology of Acute Pulmonary Lesions in Swine Infected with Haemophilus (Actinobacillus) pleuropneumoniae. Can Vet J. 1988 Jul;29(7):574–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. A., Godson D., Campos M., Sileghem M., Babiuk L. A. Capture immunoassay for ruminant tumor necrosis factor-alpha: comparison with bioassay. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Jan;35(3-4):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(93)90040-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk W., Krammer P. H., Männel D. N. A new assay for interleukin-1 in the presence of interleukin-2. J Immunol Methods. 1987 May 4;99(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick B. W., Osburn B. I., Olander H. J. Isolation and biological characterization of two lipopolysaccharides and a capsular-enriched polysaccharide preparation from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;47(7):1433–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossum C., Wattrang E., Fuxler L., Jensen K. T., Wallgren P. Evaluation of various cytokines (IL-6, IFN-alpha, IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha) as markers for acute bacterial infection in swine--a possible role for serum interleukin-6. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1998 Jul 8;64(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(98)00126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R. L., Redding G. J., Henderson W. R., Truog W. E. Group B streptococcus induces tumor necrosis factor in neonatal piglets. Effect of the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor pentoxifylline on hemodynamics and gas exchange. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Mar;143(3):598–604. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.3.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimåker M., Kragsbjerg P., Forsgren M., Olcén P. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with meningitis of different etiologies: high levels of TNF alpha indicate bacterial meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1993 Apr;167(4):882–889. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.4.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. B., Foster D. C., Mathewes S. L., Osborn S. G., Kuijper J. L., Forstrom J. W., Martin T. R. Molecular cloning of porcine alveolar macrophage-derived neutrophil chemotactic factors I and II; identification of porcine IL-8 and another intercrine-alpha protein. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 3;31(43):10483–10490. doi: 10.1021/bi00158a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Aarden L. A., Thijs L. G. Role of cytokines in sepsis. Adv Immunol. 1997;66:101–195. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60597-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannum C. H., Wilcox C. J., Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Dripps D. J., Heimdal P. L., Armes L. G., Sommer A., Eisenberg S. P., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity of a human interleukin-1 inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):336–340. doi: 10.1038/343336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. B., Nielsen S. E., Berg K. Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J Immunol Methods. 1989 May 12;119(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holobaugh P. A., McChesney D. C. Effect of anticoagulants and heat on the detection of tumor necrosis factor in murine blood. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Dec 31;135(1-2):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90261-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H., Potter A. A., Campos M., Leighton F. A., Willson P. J., Yates W. D. Pathogenesis of porcine Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia: Part I. Effects of surface components of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae in vitro and in vivo. Can J Vet Res. 1998 Apr;62(2):93–101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesmok G., Lindsey C., Duerr M., Fournel M., Emerson T., Jr Efficacy of monoclonal antibody against human recombinant tumor necrosis factor in E. coli-challenged swine. Am J Pathol. 1992 Nov;141(5):1197–1207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Standiford T., Kasahara K., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 (IL-8): the major neutrophil chemotactic factor in the lung. Exp Lung Res. 1991 Jan-Feb;17(1):17–23. doi: 10.3109/01902149109063278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. R., Raugi G., Merritt T. L., Henderson W. R., Jr Relative contribution of leukotriene B4 to the neutrophil chemotactic activity produced by the resident human alveolar macrophage. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1114–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI113168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Manogue K. R., Spriggs D. R., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M., Wilmore D. W. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1481–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Burrowes C. E., Cybulsky M. I., Dinarello C. A. Acute inflammation and a Shwartzman-like reaction induced by interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Synergistic action of the cytokines in the induction of inflammation and microvascular injury. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):463–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A., Ikejima T., Connolly R. J., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 induces a shock-like state in rabbits. Synergism with tumor necrosis factor and the effect of cyclooxygenase inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1162–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI113431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orencole S. F., Dinarello C. A. Characterization of a subclone (D10S) of the D10.G4.1 helper T-cell line which proliferates to attomolar concentrations of interleukin-1 in the absence of mitogens. Cytokine. 1989 Nov;1(1):14–22. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(89)91044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace L. W., Kreeger J. M., Bailey K. L., Turnquist S. E., Fales W. H. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in calves experimentally infected with Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Jan;35(3-4):353–364. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(93)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson K., Larsson I., Hallén Sandgren C. Effects of certain inflammatory mediators on bovine neutrophil migration in vivo and in vitro. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Jul;37(2):99–112. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(93)90058-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin J. A., Sylvester I., Smith S., Yoshimura T., Leonard E. J. Macrophages cultured in vitro release leukotriene B4 and neutrophil attractant/activation protein (interleukin 8) sequentially in response to stimulation with lipopolysaccharide and zymosan. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1556–1564. doi: 10.1172/JCI114875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi-Campos A., Anderson C., Gerlach G. F., Klashinsky S., Potter A. A., Willson P. J. Immunization of pigs against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae with two recombinant protein preparations. Vaccine. 1992;10(8):512–518. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90349-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOPE R. E. PORCINE CONTAGIOUS PLEUROPNEUMONIA. I. EXPERIMENTAL TRANSMISSION, ETIOLOGY, AND PATHOLOGY. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:357–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J., Sarsfield S. J., Townsend Y. Pig interleukin 1. Purification of two immunologically different leukocyte proteins that cause cartilage resorption, lymphocyte activation, and fever. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1208–1222. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibille Y., Reynolds H. Y. Macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils in lung defense and injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Feb;141(2):471–501. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.2.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordillo L. M., Afseth G., Davies G., Babiuk L. A. Effects of recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on bovine peripheral blood and mammary gland neutrophil function in vitro. Can J Vet Res. 1992 Jan;56(1):16–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spagnuolo P. J., Ellner J. J. Comparative stimulation of granulocyte adherence and chemotaxis by bacterial products. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):519–524. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.519-524.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli P. The pathophysiology of tumor necrosis factors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:411–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willson P. J., Rossi-Campos A., Potter A. A. Tissue reaction and immunity in swine immunized with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae vaccines. Can J Vet Res. 1995 Oct;59(4):299–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]