Abstract
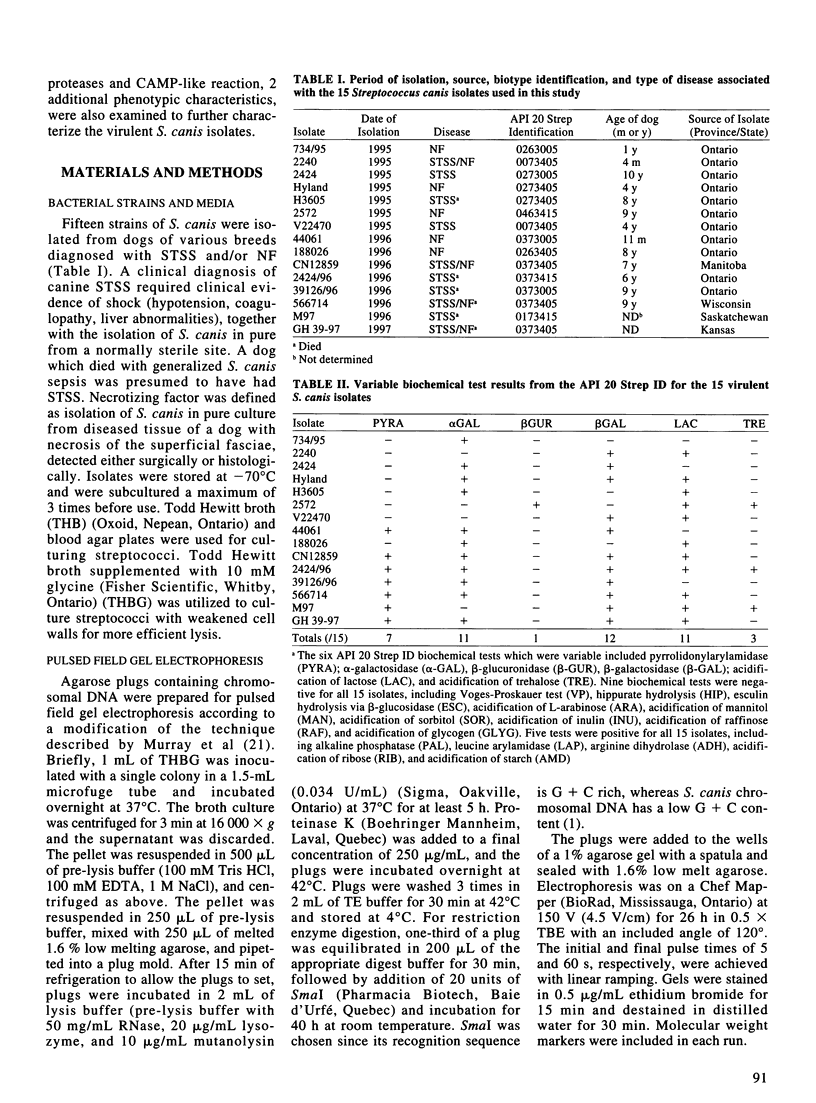
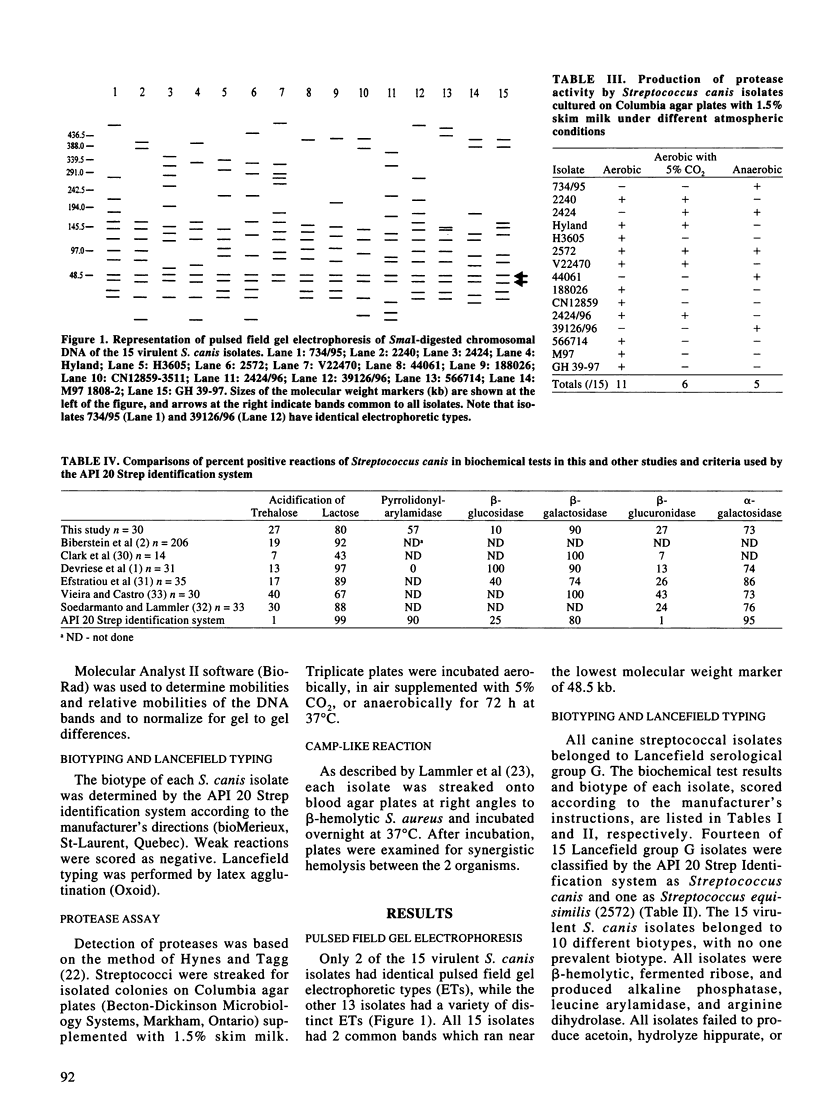
The emergence of streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS) and necrotizing fasciitis (NF) in dogs caused by Streptococcus canis has been reported by our laboratory. Since clonal expansion is thought to be partially responsible for the spread of invasive strains of Streptococcus pyogenes in humans, the relatedness of 15 isolates of S. canis from canine STSS and/or NF was examined using pulsed field gel electrophoresis and biotyping; production of proteases and of a CAMP-like reaction were also examined. Only 2 of the 15 STSS and/or NF isolates were clonally related, suggesting that the emergence of canine STSS/NF is not the result of clonal expansion of one or more highly virulent strains of S. canis. All of the isolates produced proteases and demonstrated a CAMP-like reaction, which appear to be additional characteristics of S. canis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bert F., Branger C., Lambert-Zechovsky N. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis is more discriminating than multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis for typing pyogenic streptococci. Curr Microbiol. 1997 Apr;34(4):226–229. doi: 10.1007/s002849900173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bert F., Picard B., Branger C., Lambert-Zechovsky N. Analysis of genetic relationships among strains of groups A, C and G streptococci by random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. J Med Microbiol. 1996 Oct;45(4):278–284. doi: 10.1099/00222615-45-4-278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberstein E. L., Brown C., Smith T. Serogroups and biotypes among beta-hemolytic streptococci of canine origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):558–561. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.558-561.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaussee M. S., Liu J., Stevens D. L., Ferretti J. J. Genetic and phenotypic diversity among isolates of Streptococcus pyogenes from invasive infections. J Infect Dis. 1996 Apr;173(4):901–908. doi: 10.1093/infdis/173.4.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Berrafati J. F., Janda J. M., Bottone E. J. Biotyping and exoenzyme profiling as an aid in the differentiation of human from bovine group G streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):706–710. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.706-710.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone L. A., Woodard D. R., Schlievert P. M., Tomory G. S. Clinical and bacteriologic observations of a toxic shock-like syndrome due to Streptococcus pyogenes. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):146–149. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corning B. F., Murphy J. C., Fox J. G. Group G streptococcal lymphadenitis in rats. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2720–2723. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2720-2723.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling C. L. Standardization and evaluation of the CAMP reaction for the prompt, presumptive identification of Streptococcus agalactiae (Lancefield group B) in clinical material. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Feb;1(2):171–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.2.171-174.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J., Brown J. E., Rosendal S. Association of the RTX proteins of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae with hemolytic, CAMP, and neutrophil-cytotoxic activities. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):2139–2142. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.2139-2142.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiou A., Colman G., Hahn G., Timoney J. F., Boeufgras J. M., Monget D. Biochemical differences among human and animal streptococci of Lancefield group C or group G. J Med Microbiol. 1994 Aug;41(2):145–148. doi: 10.1099/00222615-41-2-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gürtürk K., Lämmler C. Purification and partial characterization of a cohaemolysin (CAMP-factor) produced by Streptococcus canis. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1990 Sep;2(2):97–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb03506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoge C. W., Schwartz B., Talkington D. F., Breiman R. F., MacNeill E. M., Englender S. J. The changing epidemiology of invasive group A streptococcal infections and the emergence of streptococcal toxic shock-like syndrome. A retrospective population-based study. JAMA. 1993 Jan 20;269(3):384–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglauer F., Kunstýr I., Mörstedt R., Farouq H., Wullenweber M., Damsch S. Streptococcus canis arthritis in a cat breeding colony. J Exp Anim Sci. 1991;34(2):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang M., Babiuk L. A., Potter A. A. Cloning, sequencing and expression of the CAMP factor gene of Streptococcus uberis. Microb Pathog. 1996 May;20(5):297–307. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1996.0028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens D., Sterzik B., Fehrenbach F. J. Unspecific binding of group B streptococcal cocytolysin (CAMP factor) to immunoglobulins and its possible role in pathogenicity. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):720–732. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiska D. L., Thiede B., Caracciolo J., Jordan M., Johnson D., Kaplan E. L., Gruninger R. P., Lohr J. A., Gilligan P. H., Denny F. W., Jr Invasive group A streptococcal infections in North Carolina: epidemiology, clinical features, and genetic and serotype analysis of causative organisms. J Infect Dis. 1997 Oct;176(4):992–1000. doi: 10.1086/516540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. W., Prescott J. F., Mathews K. A., Betschel S. D., Yager J. A., Guru V., DeWinter L., Low D. E. Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome in dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1996 Oct 15;209(8):1421–1426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Singh K. V., Heath J. D., Sharma B. R., Weinstock G. M. Comparison of genomic DNAs of different enterococcal isolates using restriction endonucleases with infrequent recognition sites. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2059–2063. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2059-2063.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Hauser A. R., Kim M. H., Schlievert P. M., Nelson K., Selander R. K. Streptococcus pyogenes causing toxic-shock-like syndrome and other invasive diseases: clonal diversity and pyrogenic exotoxin expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2668–2672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Kapur V., Szeto J., Pan X., Swanson D. S., Martin D. R. Genetic diversity and relationships among Streptococcus pyogenes strains expressing serotype M1 protein: recent intercontinental spread of a subclone causing episodes of invasive disease. Infect Immun. 1995 Mar;63(3):994–1003. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.3.994-1003.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Mathews K., Gyles C. L., Matsumiya L., Miller C., Rinkhardt N., Yager J. A., Hylands R. H., Low D. E. Canine streptococcal toxic shock syndrome in Ontario: An emerging disease? Can Vet J. 1995 Aug;36(8):486–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Miller C. W., Mathews K. A., Yager J. A., DeWinter L. Update on canine streptococcal toxic shock syndrome and necrotizing fasciitis. Can Vet J. 1997 Apr;38(4):241–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Single L. A., Martin D. R. Clonal differences within M-types of the group A Streptococcus revealed by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Feb 1;70(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90567-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soedarmanto I., Lämmler C. Comparative studies on streptococci of serological group G isolated from various origins. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1996 Nov;43(9):513–523. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1996.tb00349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Linton D., Desai M., Efstratiou A., George R. Molecular subtyping of prevalent M serotypes of Streptococcus pyogenes causing invasive disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Nov;33(11):2850–2855. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.11.2850-2855.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L. Invasive group A streptococcus infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):2–11. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swindle M. M., Narayan O., Luzarraga M., Bobbie D. L. Contagious streptococcal lymphadenitis in cats. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1980 Nov 1;177(9):829–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapsall J. W., Phillips E. A. Streptococcus pyogenes streptolysin O as a cause of false-positive CAMP reactions. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):534–537. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.534-537.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Arbeit R. D., Goering R. V., Mickelsen P. A., Murray B. E., Persing D. H., Swaminathan B. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Sep;33(9):2233–2239. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.9.2233-2239.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillman P. C., Dodson N. D., Indiveri M. Group G streptococcal epizootic in a closed cat colony. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1057–1060. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1057-1060.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton M., Carter P. E., Morgan M., Edwards G. F., Pennington T. H. Clonal structure of invasive Streptococcus pyogenes in Northern Scotland. Epidemiol Infect. 1995 Oct;115(2):231–241. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800058362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandamme P., Pot B., Falsen E., Kersters K., Devriese L. A. Taxonomic study of lancefield streptococcal groups C, G, and L (Streptococcus dysgalactiae) and proposal of S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis subsp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1996 Jul;46(3):774–781. doi: 10.1099/00207713-46-3-774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira V. V., Castro A. C. Biochemical properties and whole-cell protein profiles of group G streptococci isolated from dogs. J Appl Bacteriol. 1994 Oct;77(4):408–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1994.tb03442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


