Abstract
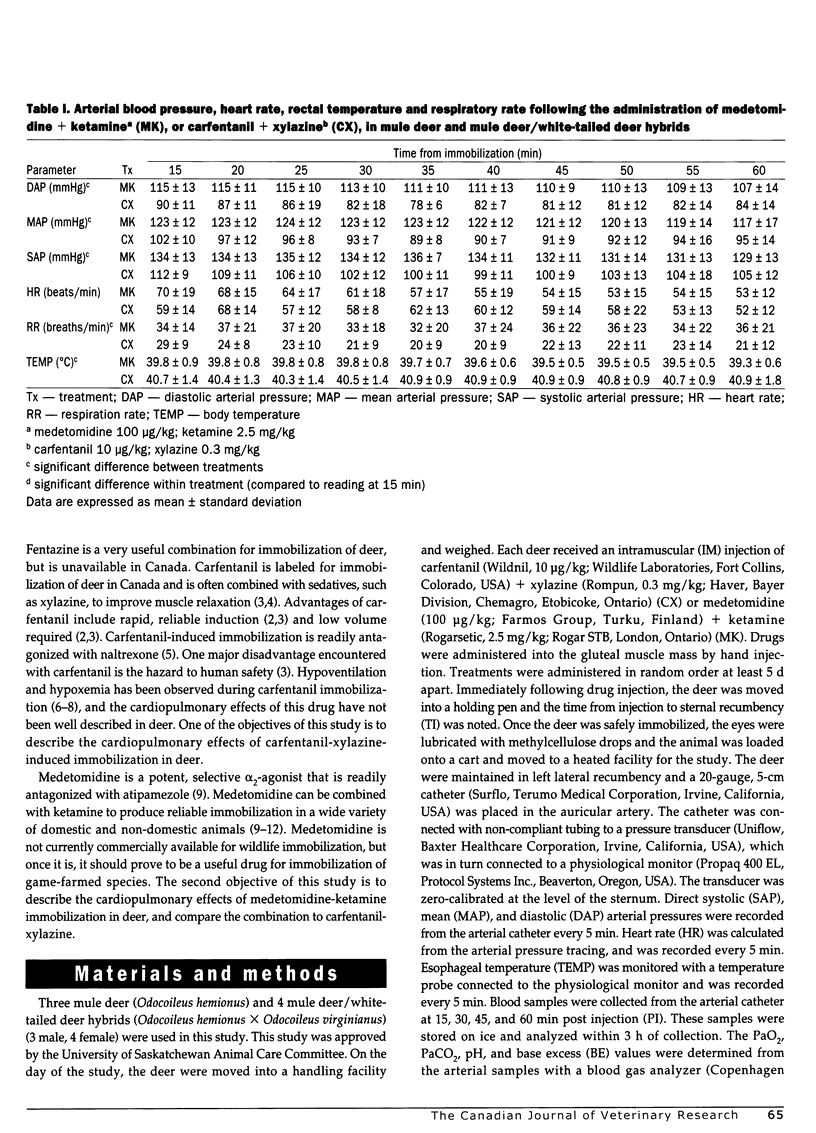
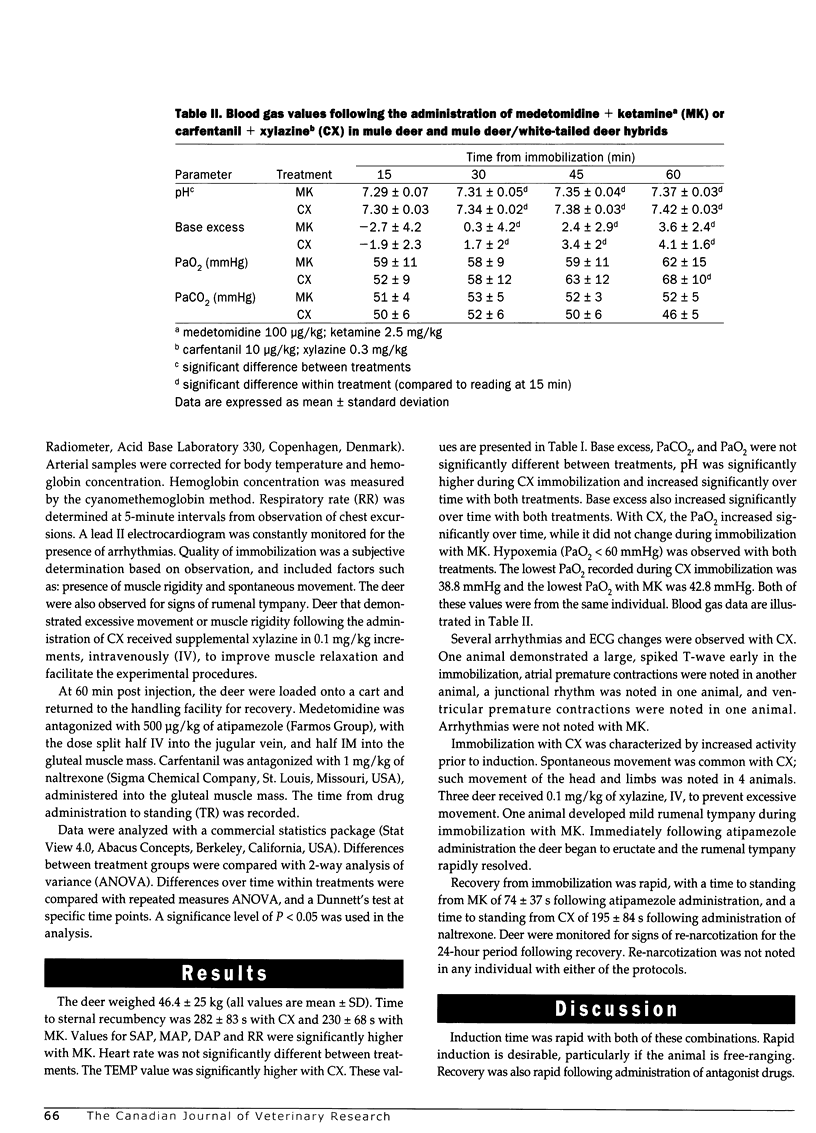
Three mule deer and 4 mule deer/white-tailed deer hybrids were immobilized in a crossover study with carfentanil (10 microg/kg) + xylazine (0.3 mg/kg) (CX), and medetomidine (100 microg/kg) + ketamine (2.5 mg/kg) (MK). The deer were maintained in left lateral recumbency for 1 h with each combination. Deer were immobilized with MK in 230+/-68 s (mean +/- SD) and with CX in 282+/-83 seconds. Systolic, mean and diastolic arterial pressure were significantly higher with MK. Heart rate, PaO2, PaCO2, pH, and base excess were not significantly different between treatments. Base excess and pH increased significantly over time with both treatments. Both treatments produced hypoventilation (PaCO2 > 50 mm Hg) and hypoxemia (PaO2 < 60 mm Hg). PaO2 increased significantly over time with CX. Body temperature was significantly (P<0.05) higher with CX compared to MK. Ventricular premature contractions, atrial premature contractions, and a junctional escape rhythm were noted during CX immobilization. No arrhythmias were noted during MK immobilization. Quality of immobilization was superior with MK, with no observed movement present for the 60 min of immobilization. Movement of the head and limbs occurred in 4 animals immobilized with CX. The major complication observed with both of these treatments was hypoxemia, and supplemental inspired oxygen is recommended during immobilization. Hyperthermia can further complicate immobilization with CX, reinforcing the need for supplemental oxygen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chioléro R., Flatt J. P., Revelly J. P., Jéquier E. Effects of catecholamines on oxygen consumption and oxygen delivery in critically ill patients. Chest. 1991 Dec;100(6):1676–1684. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.6.1676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hikasa Y., Takase K., Emi S., Ogasawara S. Antagonistic effects of alpha-adrenoceptor blocking agents on reticuloruminal hypomotility induced by xylazine in cattle. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Oct;52(4):411–415. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreeger T. J., Del Giudice G. D., Seal U. S., Karns P. D. Immobilization of white-tailed deer with xylazine hydrochloride and ketamine hydrochloride and antagonism by tolazoline hydrochloride. J Wildl Dis. 1986 Jul;22(3):407–412. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-22.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher J., Citino S. B., Dawson R., Jr Effects of a carfentanil-xylazine combination on cardiopulmonary function and plasma catecholamine concentrations in female bongo antelopes. Am J Vet Res. 1997 Feb;58(2):157–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal U. S., Schmitt S. M., Peterson R. O. Carfentanil and xylazine for immobilization of moose (Alces alces) on Isle Royale. J Wildl Dis. 1985 Jan;21(1):48–51. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-21.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio O. M., Bloor B. C., Kim C. Cardiovascular effects of a ketamine-medetomidine combination that produces deep sedation in Yucatan mini swine. Lab Anim Sci. 1992 Dec;42(6):582–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio O., Palmu L. Cardiovascular and respiratory effects of medetomidine in dogs and influence of anticholinergics. Acta Vet Scand. 1989;30(4):401–408. doi: 10.1186/BF03548016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. S., Bush M., Montali R. J. Deaths from exertional myopathy at the National Zoological Park from 1975 to 1985. J Wildl Dis. 1987 Jul;23(3):454–462. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-23.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


