Abstract
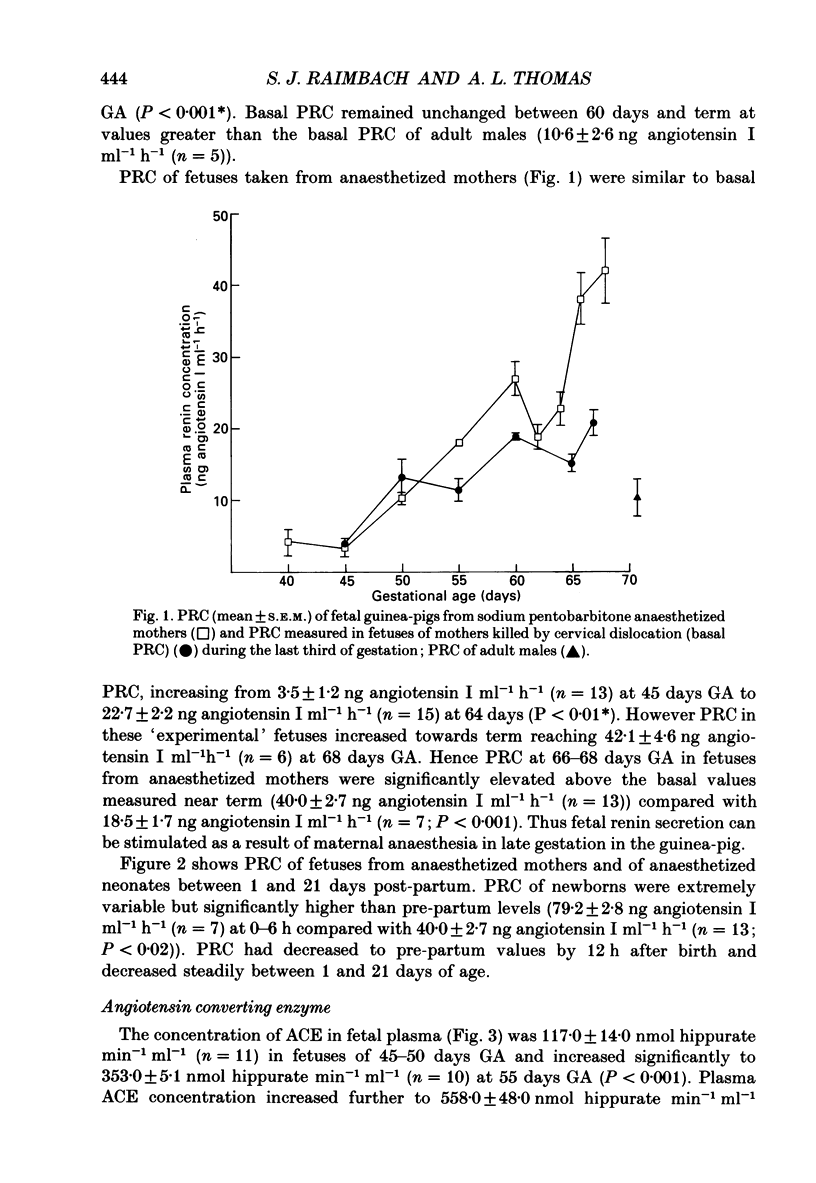
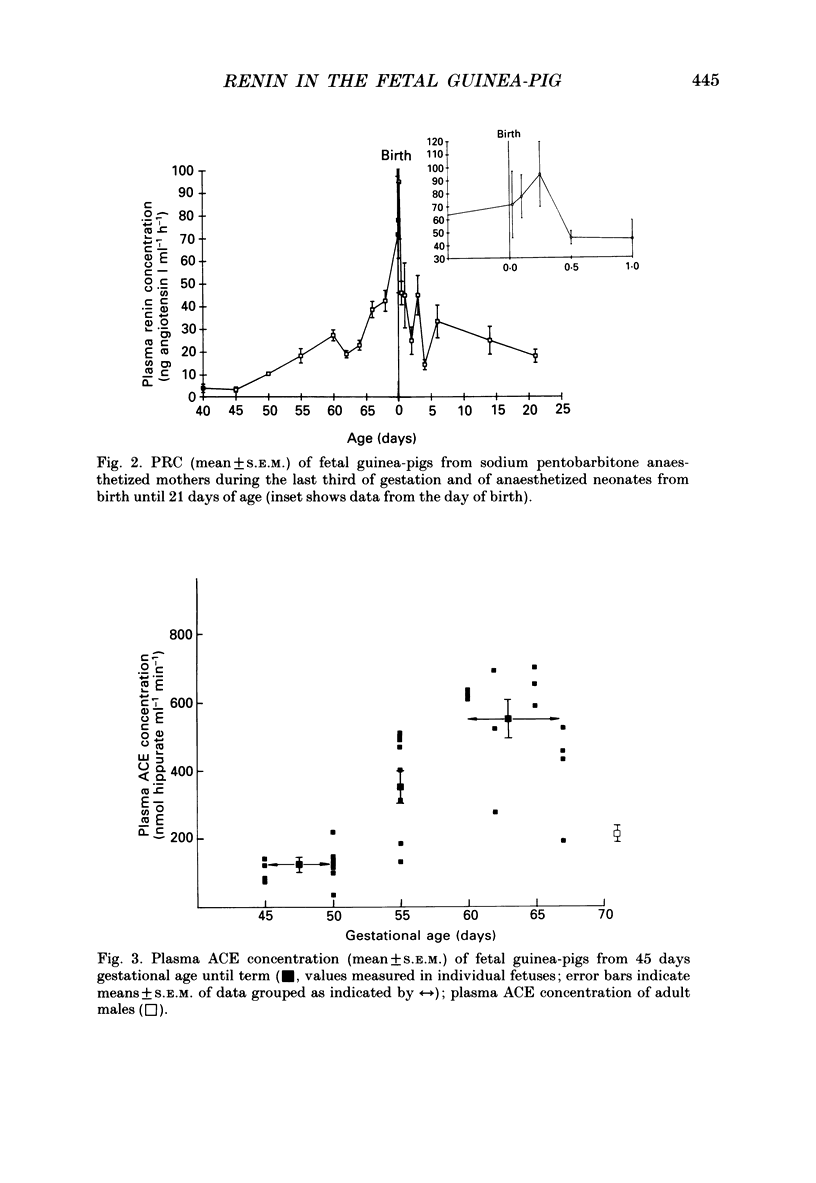
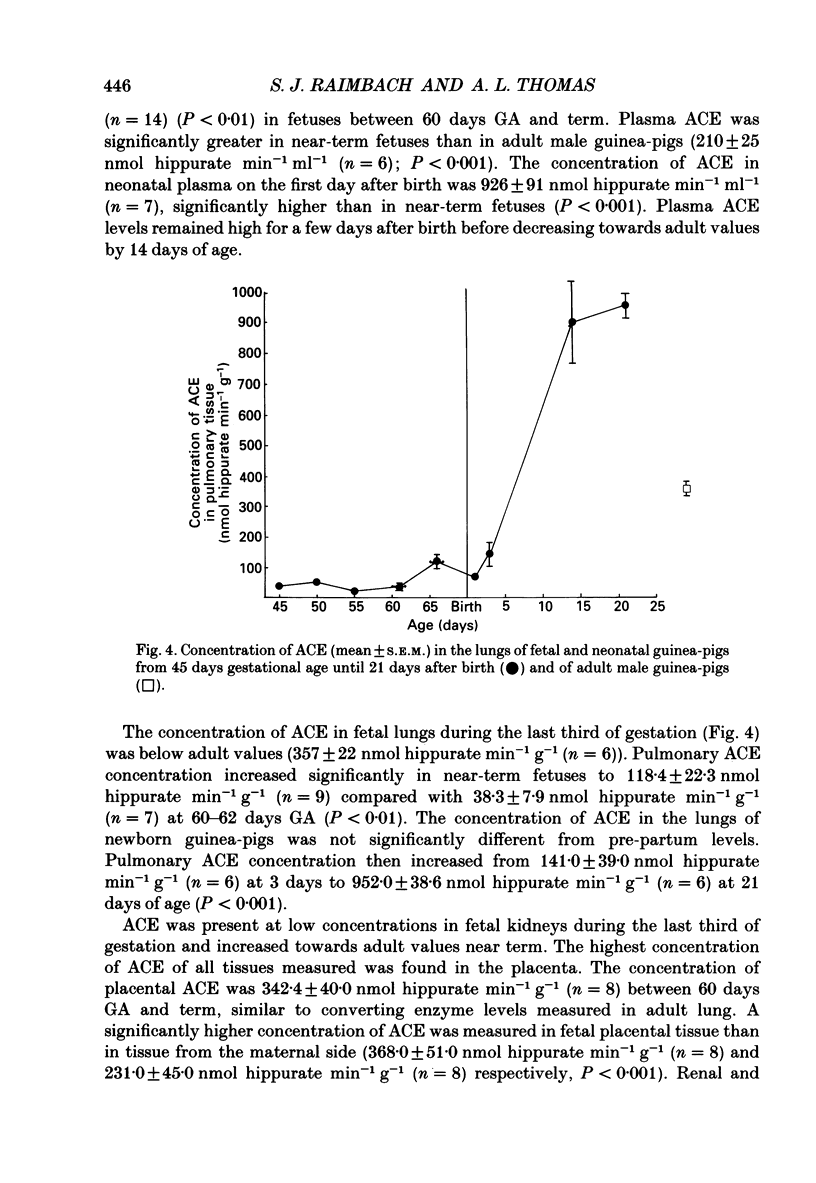
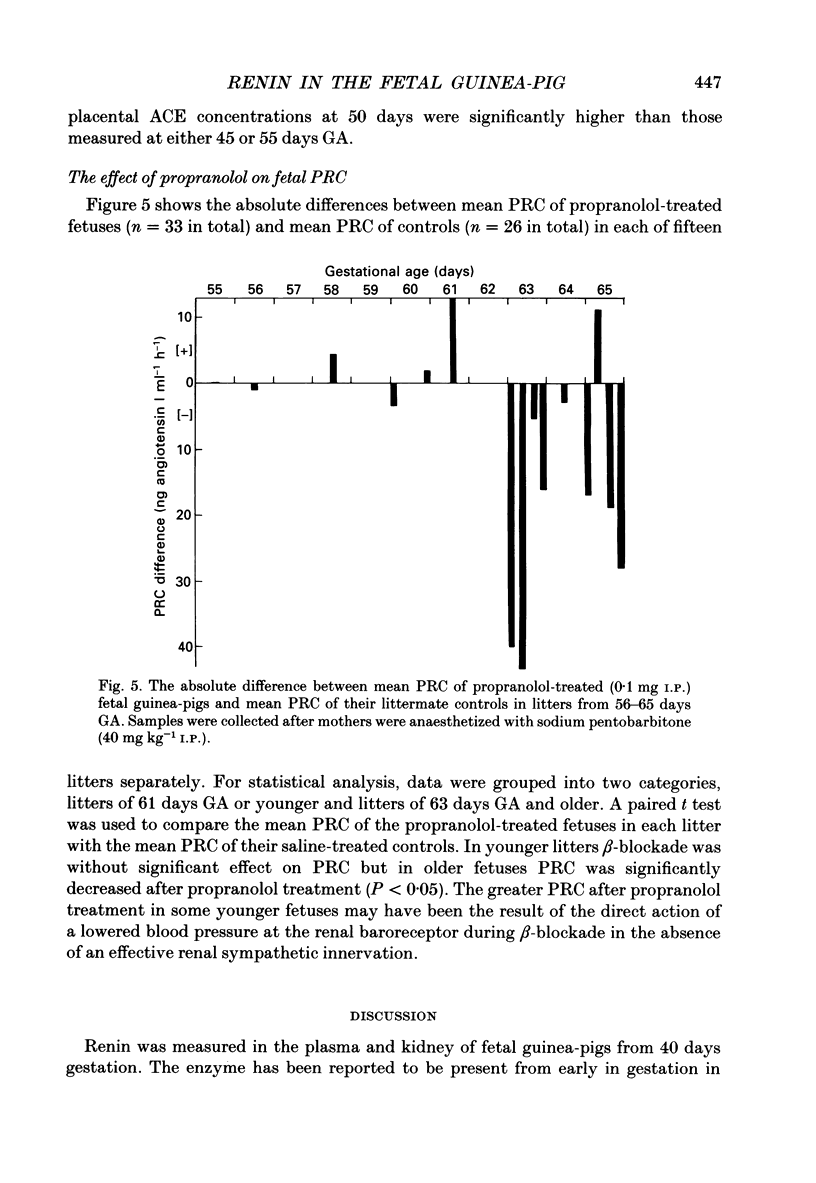
1. Plasma renin concentration (PRC) and plasma and pulmonary angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) concentration were measured in fetal and neonatal guinea-pigs from 45 days gestational age (GA) until 21 days post-partum. 2. Fetal PRC increased towards term to reach values greater than those measured in normal adult males. Pentobarbitone anaesthesia of the mother resulted in significant elevation of fetal PRC after 66 days GA but not before this time. 3. PRC were very high in the newborn guinea-pig, decreased rapidly during the first 24 h after birth and then more gradually, to reach approximately adult values by day 21. 4. Fetal plasma ACE concentration increased towards term to reach values greater than those measured in adult males and decreased subsequently. 5. Pulmonary ACE concentrations were very low throughout gestation but increased considerably between days 3 and 14 post-partum. Low concentrations of ACE were measured in other fetal tissues but placental concentrations were relatively high. 6. Propranolol (0.1 mg I.P.) or saline was administered (under halothane-nitrous oxide anaesthesia) to fetuses of litters of various GA from 55 days to term. Fetal PRC were measured 3 h later. Propranolol treatment resulted in significantly lower fetal PRC than saline treatment in litters aged 63 days to term but not in younger litters. 7. These data indicate that the renin-angiotensin system is functional in the fetal guinea-pig during the last third of gestation. Fetal plasma renin concentrations near term are greater than those measured in normal adult males. This may, in part, reflect an increased influence of the fetal sympathetic nervous system.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailie M. D., Derkx F. H., Schalekamp M. A. Release of active and inactive renin by the pig kidney during development. Dev Pharmacol Ther. 1980;1(1):47–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton Pipkin F., Kirkpatrick S. M., Lumbers E. R., Mott J. C. Renin and angiotensin-like levels in foetal, new-born and adult sheep. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(3):575–588. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell P. R., Seegal B. C., Hsu K. C., Das M., Soffer R. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme: vascular endothelial localization. Science. 1976 Mar 12;191(4231):1050–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.175444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver J. G., Mott J. C. Plasma renin, (Na+) and (K+) in immature foetal lambs with indwelling catheters. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(2):73P–75P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKER S. E., HELLER H. The mechanism of water diuresis in adult and newborn guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1951 Jan;112(1-2):149–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Champlain J., Malmfors T., Olson L., Sachs C. Ontogenesis of peripheral adrenergic neurons in the rat: pre- and postnatal observations. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Oct;80(2):276–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhall U., Cowen T., Haven A. J., Burnstock G. Perivascular noradrenergic and peptide-containing nerves show different patterns of changes during development and ageing in the guinea-pig. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1986 Jun;16(2):109–126. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(86)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon M. J., Gillin M. E., Ryness J. M., de Swiet M. Plasma renin activity and aldosterone concentration in the human newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Jul;51(7):537–540. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.7.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadeed A., Siegel S. R. Plasma renin activity after birth and in the early newborn period. Am J Perinatol. 1984 Jul;1(4):285–287. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1000022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst P. L., Lovell-Smith C. J. Optimized assay for serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity. Clin Chem. 1981 Dec;27(12):2048–2052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelínek J., Hackenthal R., Hilgenfeldt U., Schaechtelin G., Hackenthal E. The renin-angiotensin system in the perinatal period in rats. J Dev Physiol. 1986 Feb;8(1):33–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Roebuck M. M. The development of the pituitary-adrenal axis in the guinea pig. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1980 May;94(1):107–116. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0940107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokubu T., Ueda E., Nishimura K., Yoshida N. Angiotensin I converting enzyme activity in pulmonary tissue of fetal and newborn rabbits. Experientia. 1977 Sep 15;33(9):1137–1138. doi: 10.1007/BF01922286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotchen T. A., Strickland A. L., Rice T. W., Walters D. R. A study of the renin-angiotensin system in newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1972 Jun;80(6):938–946. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumbers E. R., Stevens A. D. The effects of frusemide, saralasin and hypotension on fetal plasma renin activity and on fetal renal function. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:479–490. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn F. A., Lloyd C. J., Kachel C., Funder J. W. Induction by glucocorticoids of angiotensin converting enzyme production from bovine endothelial cells in culture and rat lung in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):684–692. doi: 10.1172/JCI110663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlet-Benichou C., Pegorier M., Muffat-Joly M., Augeron C. Functional and morphologic patterns of renal maturation in the developing guinea pig. Am J Physiol. 1981 Dec;241(6):F618–F624. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.6.F618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott J. C. The kidneys and arterial pressure in immature and adult rabbits. J Physiol. 1969 May;202(1):25–44. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott J. C. The place of the renin-angiotensin system before and after birth. Br Med Bull. 1975 Jan;31(1):44–50. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Saar N. Some evidence for the maturity of peripheral adrenergic nerves in new-born guinea-pigs. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1975 Jun;53(3):215–222. doi: 10.1038/icb.1975.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes G. K., Fleischman A. R., Catt K. J., Chez R. A. Plasma renin activity in sheep pregnancy after fetal or maternal nephrectomy. Biol Neonate. 1977;31(3-4):208–212. doi: 10.1159/000240961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernollet M. G., Devynck M. A., Macdonald G. J., Meyer P. Plasma renin activity and adrenal angiotensin II receptors in fetal, newborn, adult and pregnant rabbits. Biol Neonate. 1979;36(3-4):119–127. doi: 10.1159/000241216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards H. K., Lush D. J., Noble A. R., Munday K. A. Inactive renin in rabbit plasma: effect of frusemide. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Apr;60(4):393–398. doi: 10.1042/cs0600393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard J. E., Gomez R. A., Meernik J. G., Kuehl W. D., VanOrden D. Role of angiotensin II on the adrenal and vascular responses to hemorrhage during development in fetal lambs. Circ Res. 1982 May;50(5):645–650. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.5.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard J. E., Weismann D. N., Gomez R. A., Ayres N. A., Lawton W. J., VanOrden D. E. Renal and adrenal responses to converting-enzyme inhibition in fetal and newborn life. Am J Physiol. 1983 Feb;244(2):R249–R256. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.244.2.R249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph A. M., Heymann M. A. Circulatory changes during growth in the fetal lamb. Circ Res. 1970 Mar;26(3):289–299. doi: 10.1161/01.res.26.3.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel S. R., Fisher D. A. Ontogeny of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the fetal and newborn lamb. Pediatr Res. 1980 Feb;14(2):99–102. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198002000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalcup S. A., Lipset J. S., Woan J. M., Leuenberger P., Mellins R. B. Inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme activity in cultured endothelial cells by hypoxia. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):966–976. doi: 10.1172/JCI109397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Sulyok E., Németh M., Tényi I., Csaba I. F., Thurzó V., Hadnagy J. The possible role of prostaglandins in the hyperfunction of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the newborn. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1979 Mar;86(3):205–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1979.tb10594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symonds E. M., Furler I. Plasma renin levels in the normal and anephric fetus at birth. Biol Neonate. 1973;23(1):133–138. doi: 10.1159/000240594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetlow H. J., Broughton Pipkin F. Studies on the effect of mode of delivery on the renin-angiotensin system in mother and fetus at term. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1983 Mar;90(3):220–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1983.tb08612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace K. B., Bailie M. D., Hook J. B. Angiotensin-converting enzyme in developing lung and kidney. Am J Physiol. 1978 Mar;234(3):R141–R145. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1978.234.3.R141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigger H. J., Stalcup S. A. Distribution and development of angiotensin converting enzyme in the fetal and newborn rabbit. An immunofluorescence study. Lab Invest. 1978 May;38(5):581–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


