Abstract
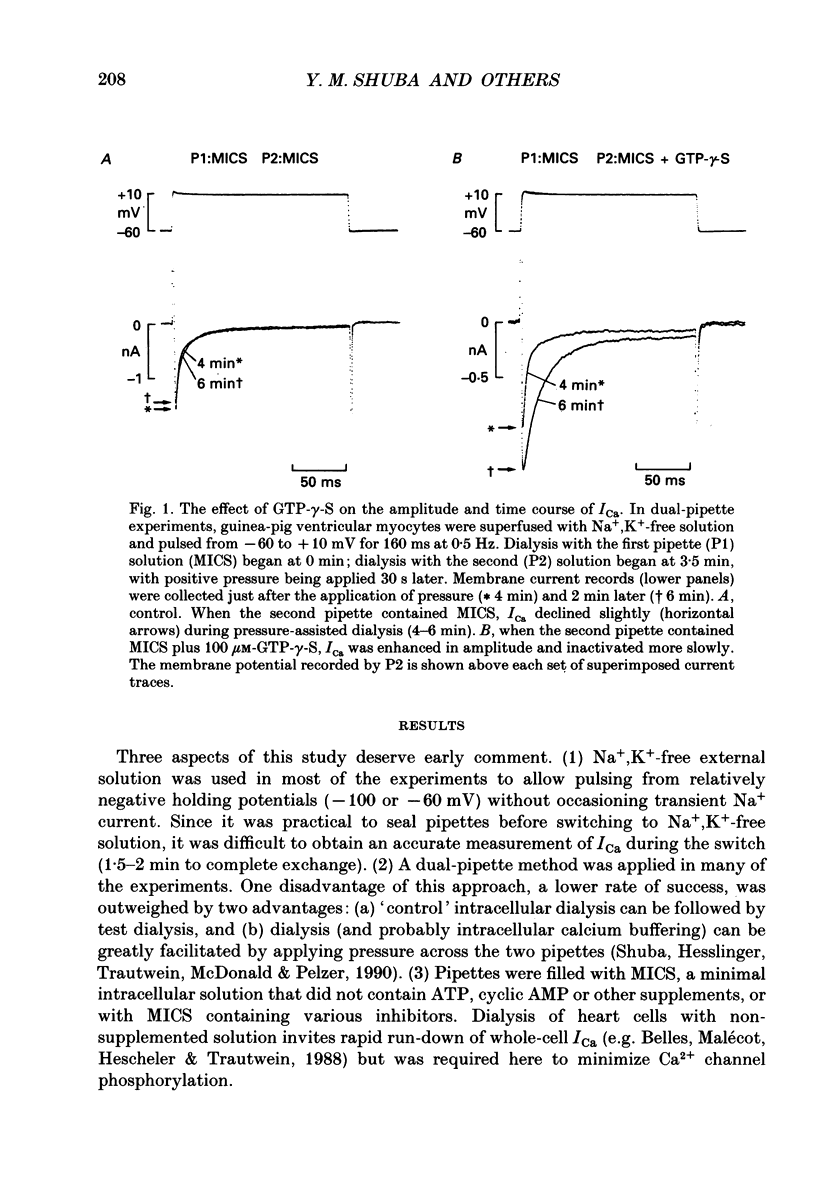
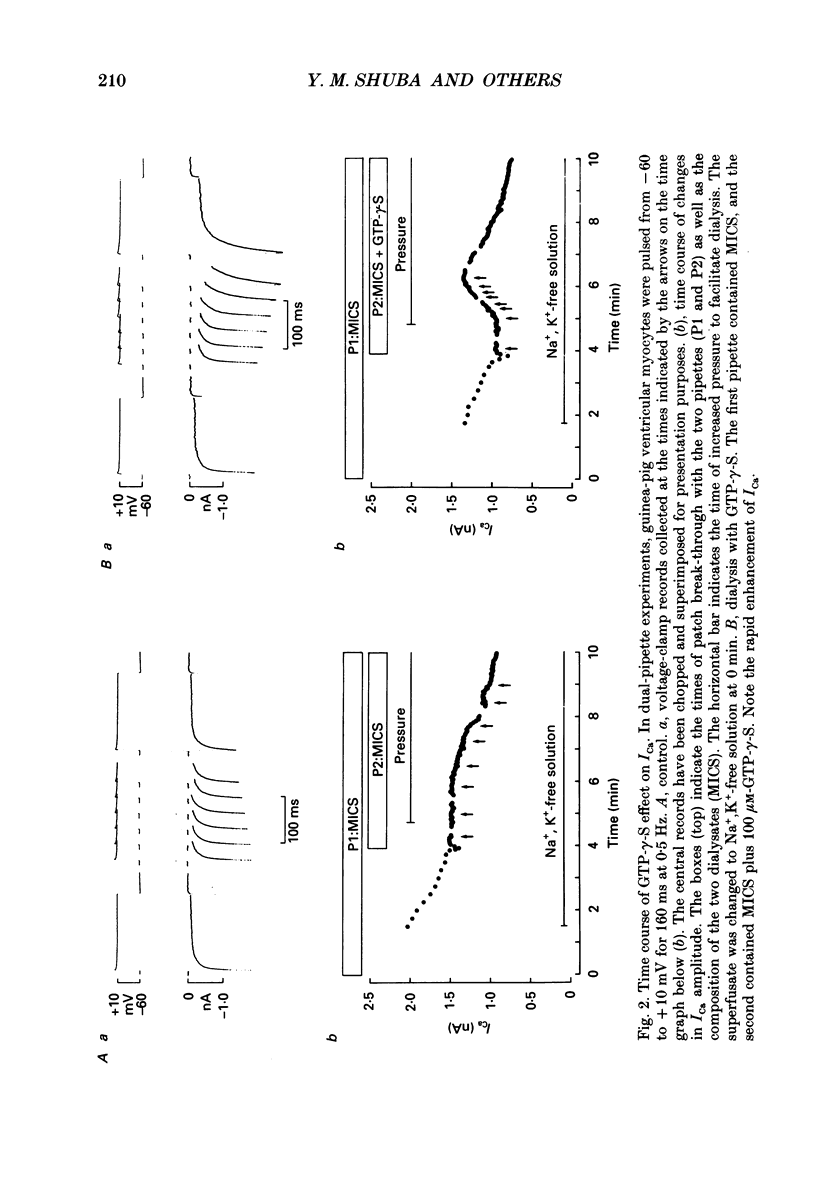
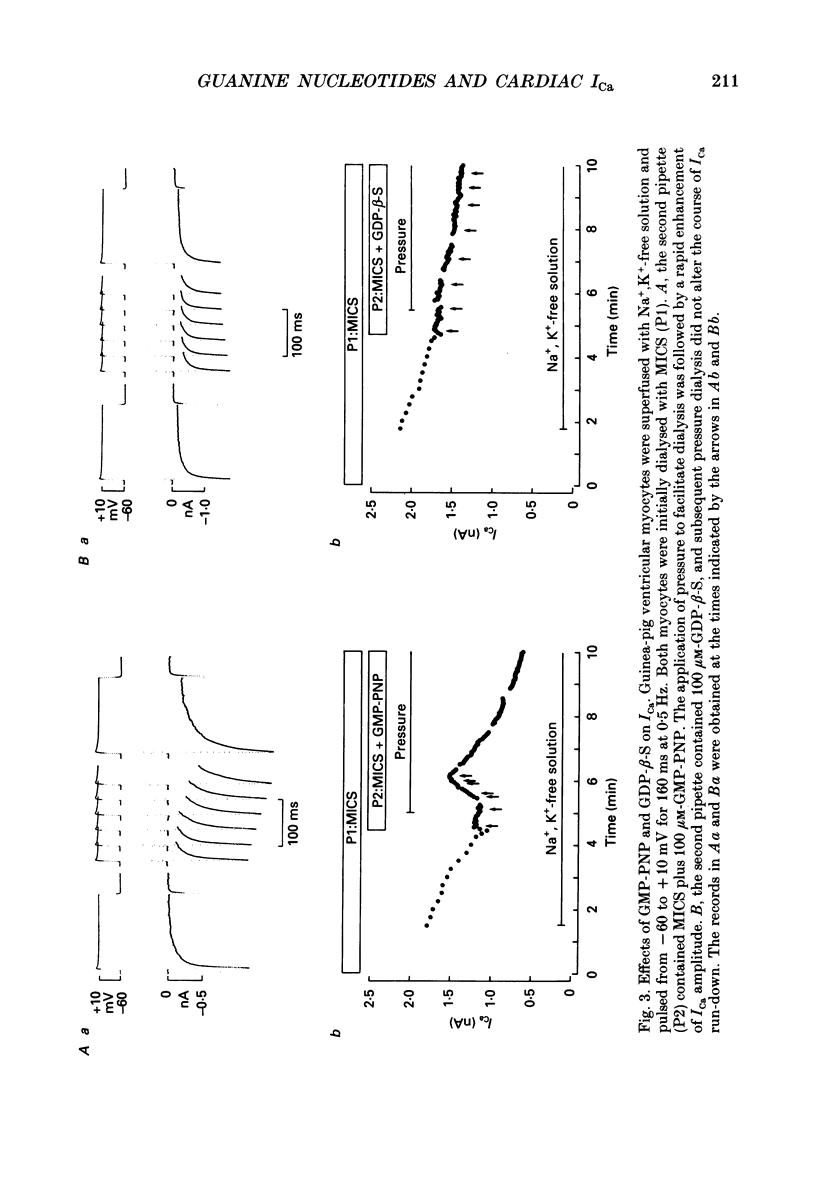
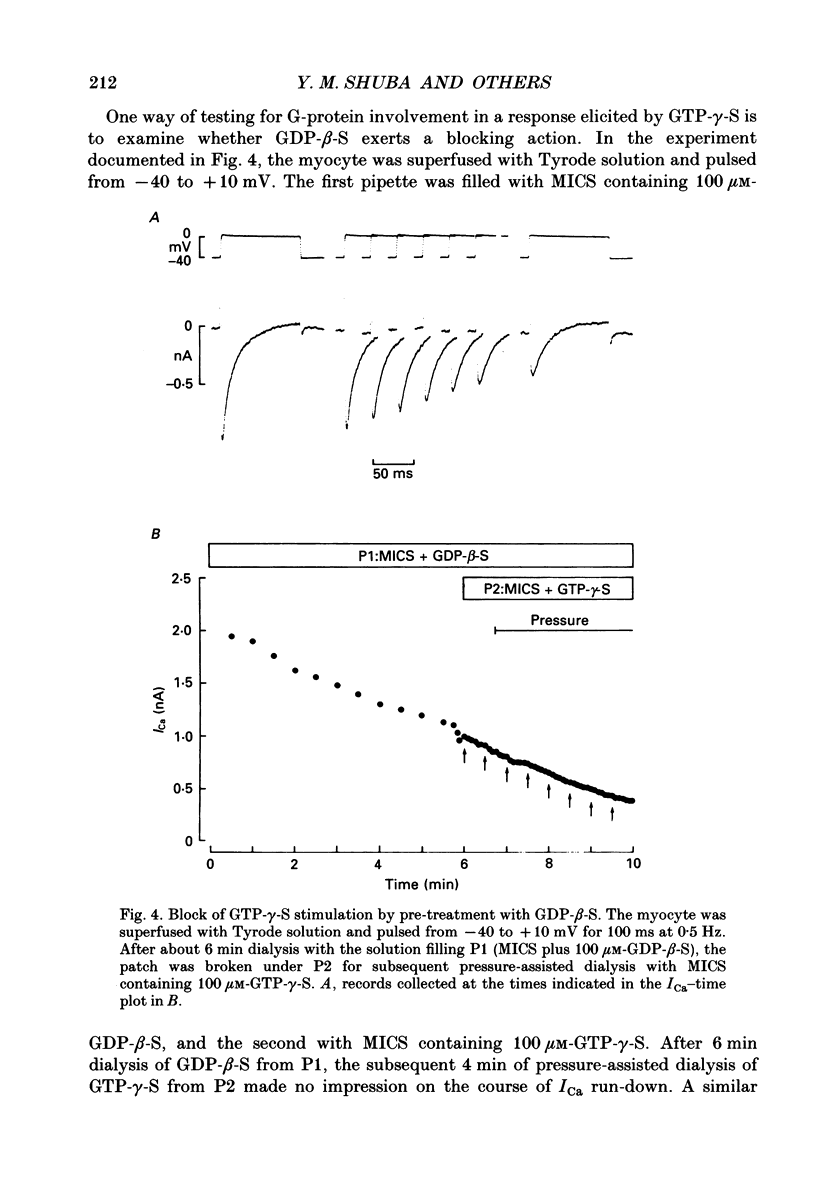
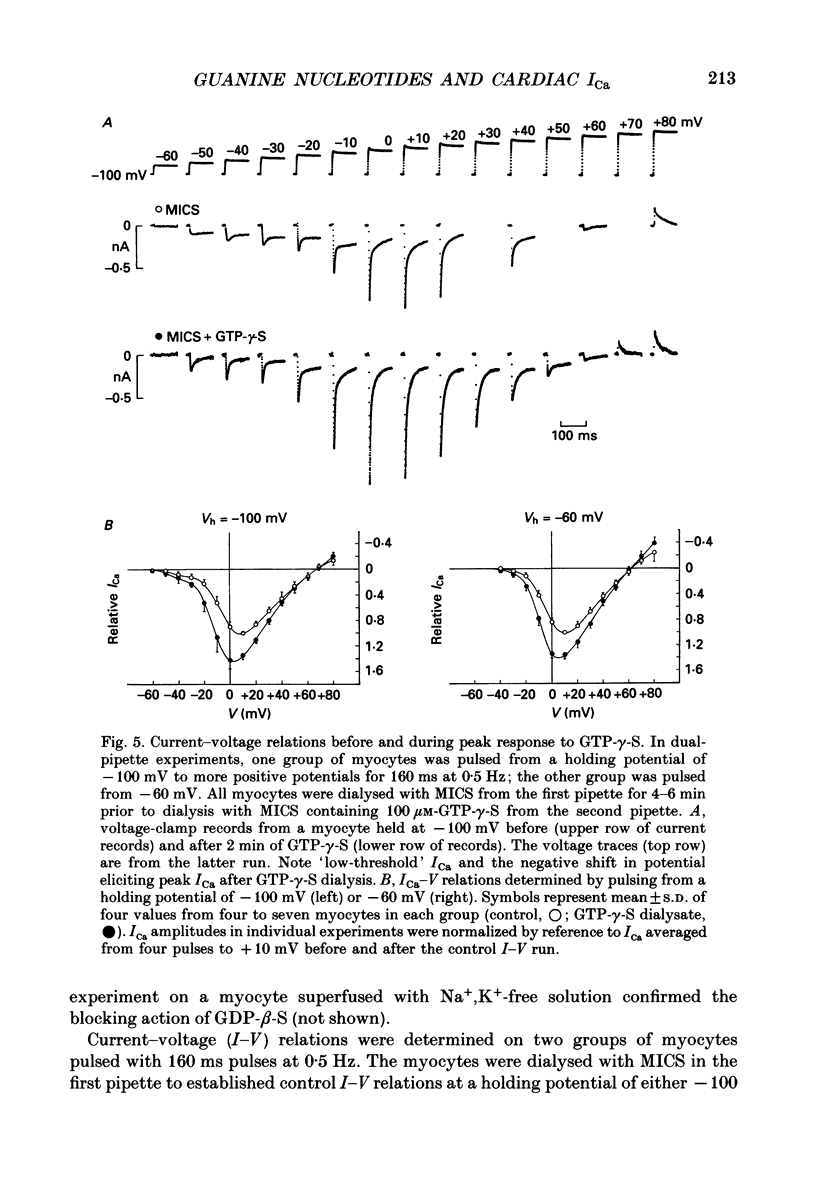
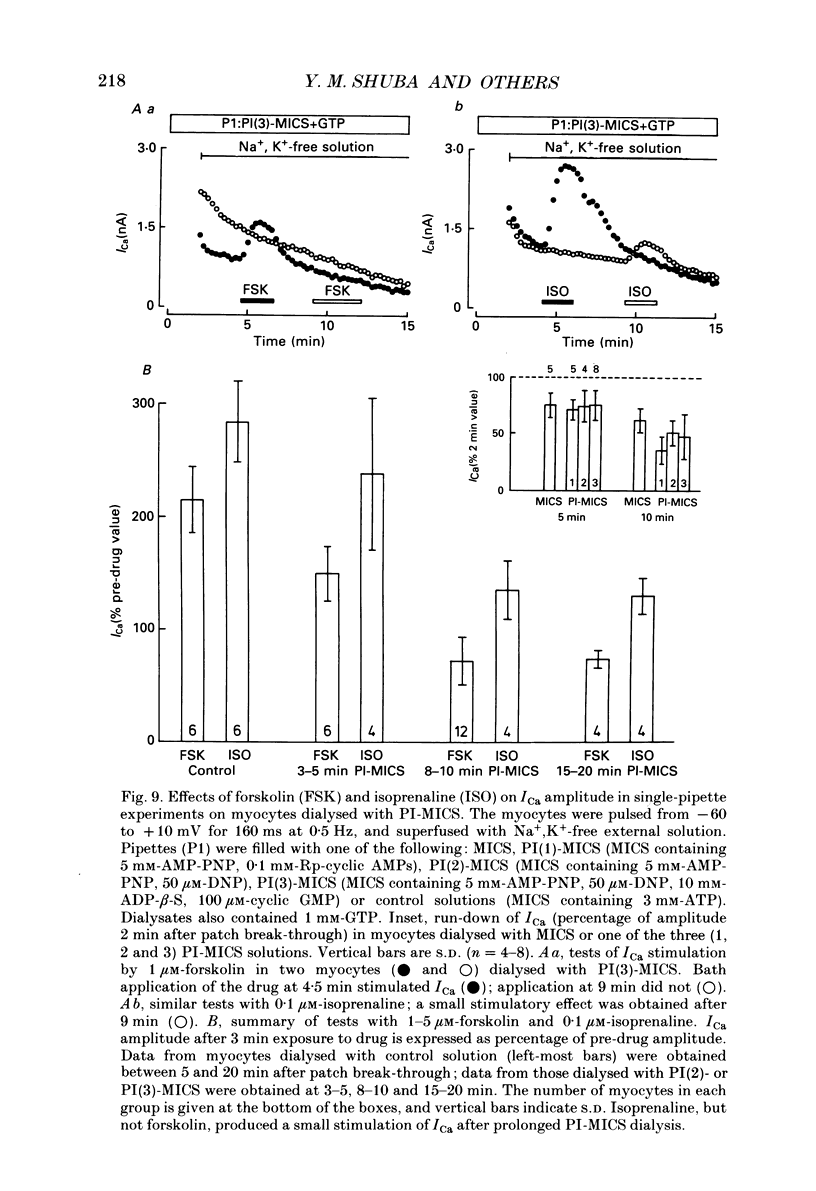
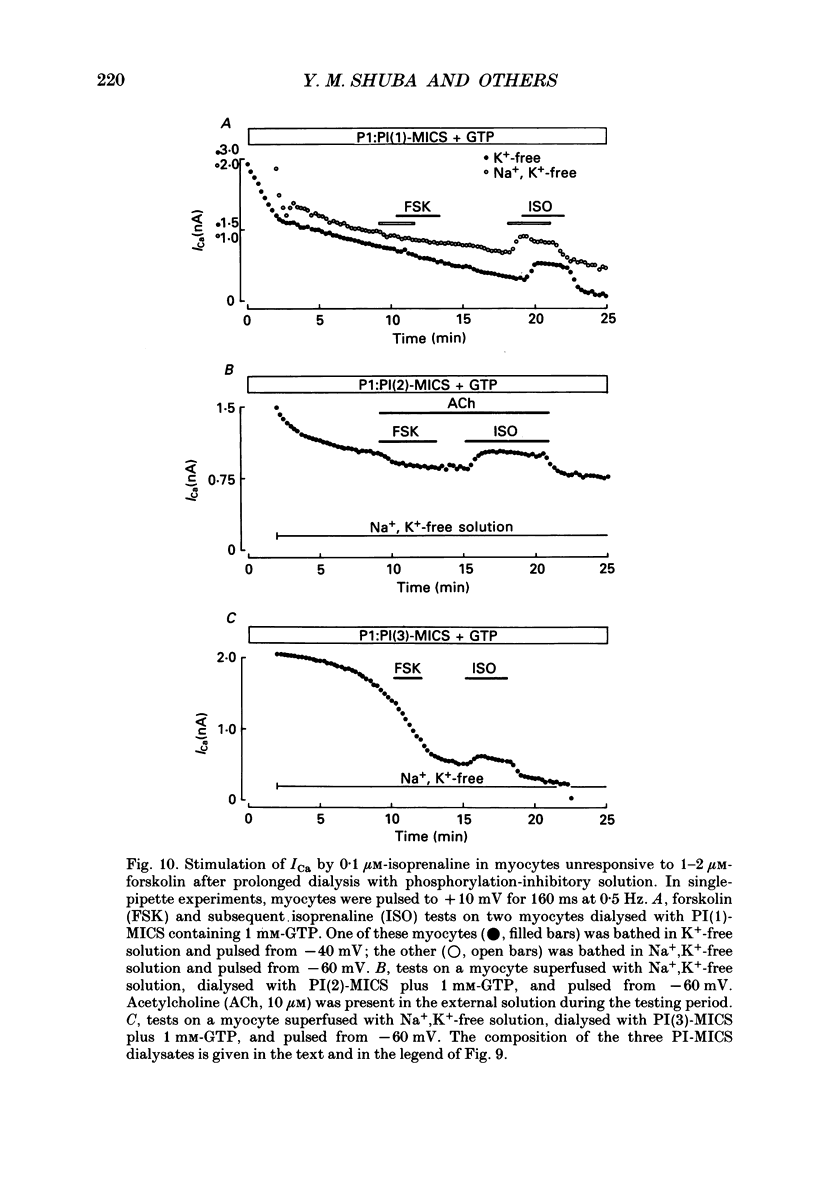
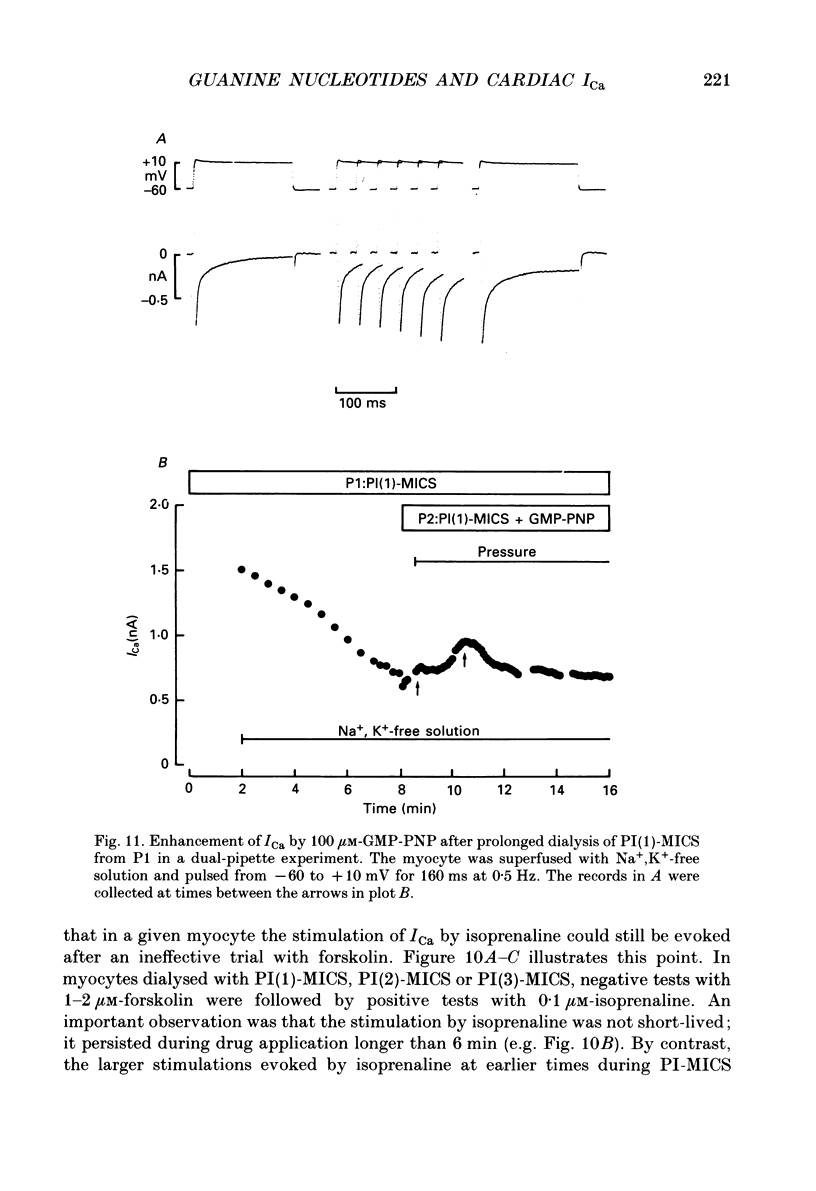
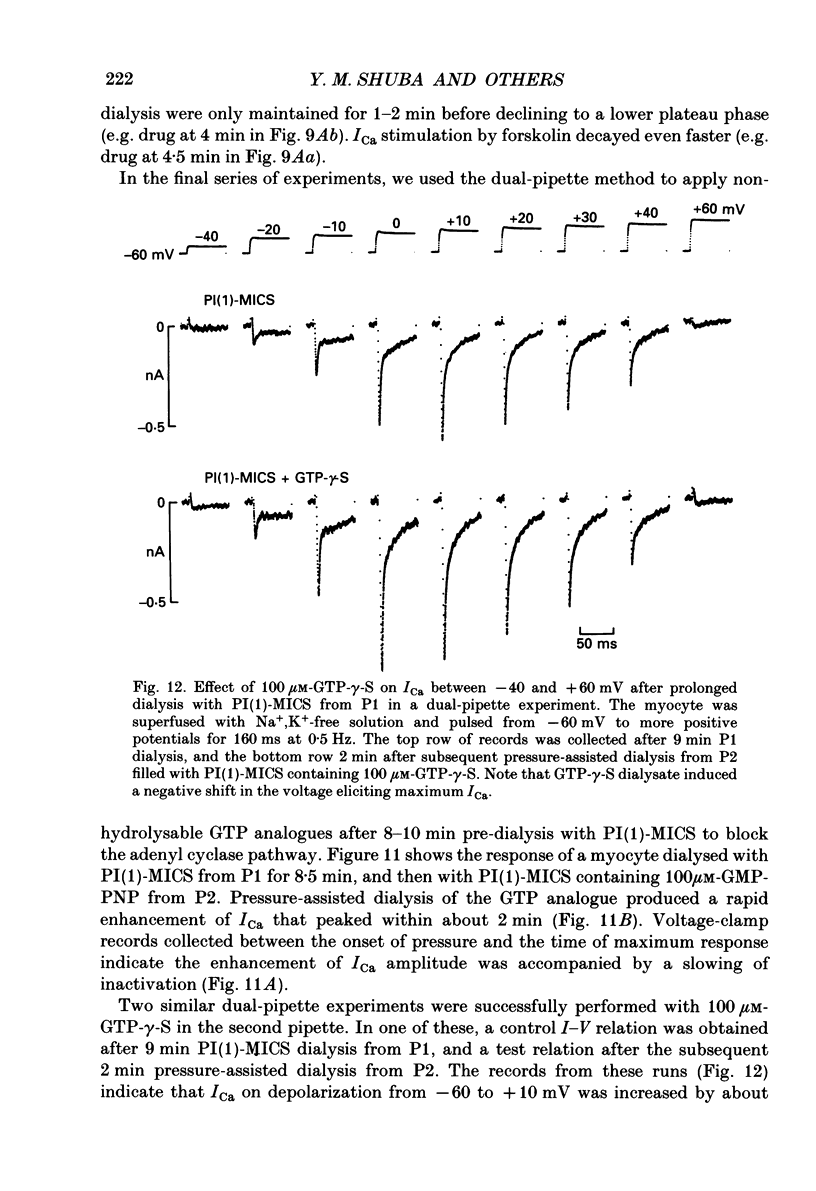
1. Whole-cell calcium current (ICa) was recorded in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes superfused with Na+,K(+)-free solution and dialysed with a substrate-free solution (minimum intracellular solution, MICS). A dual tight-seal pipette method was often used to permit pressure-enhanced dialysis of a test solution after a given pre-dialysis. 2. In dual-pipette experiments, test dialysates contained 100 mM-GTP-gamma-S (guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate] or 100 microM-GMP-PNP (guanyl-5'-imidodiphosphate). These non-hydrolysable analogues of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) enhanced ICa amplitude (+ 10 mV) by 20-40%. Dialysates containing 100 microM-GTP or GDP-beta-S (guanosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate] were ineffective, and pre-dialysis with GDP-beta-S blocked stimulation by GTP-gamma-S. 3. Non-hydrolysable GTP analogues slowed the inactivation of ICa and shifted the voltage eliciting maximum ICa by 5-10 mV in the negative direction. 4. ICa enhancement by GTP analogues was attributed to the activation of three GTP-binding regulatory (G) proteins (Gi, Gp and Gs). In single-pipette experiments, the inactivation of Gi by pre-treatment with pertussis toxin did not block enhancement, and a Gp-activating regimen (external acetylcholine-internal GTP) was without effect. Thus, it is probable that the effects of GTP analogues on ICa were primarily mediated by Gs activation. 5. PI-MICS dialysates contained phosphorylation-pathway inhibitors and were used to inhibit Ca2+ channel phosphorylation via the adenyl cyclase pathway. These were deemed effective since forskolin (1-5 microM) doubled ICa during control dialysis but was without effect after 8 min PI-MICS dialysis. However, 0.1 microM-isoprenaline increased ICa by 35% in myocytes totally unresponsive to forskolin, suggesting that beta-adrenergic receptor occupation can stimulate ICa even when the phosphorylation pathway is blocked. 6. After prolonged dialysis of myocytes with PI-MICS, ICa was still enhanced by pressure-assisted dialysis of 100 microM-GTP-gamma-S or GMP-PNP. We conclude that activated Gs has a direct effect on cardiac Ca2+ channels.
Full text
PDF



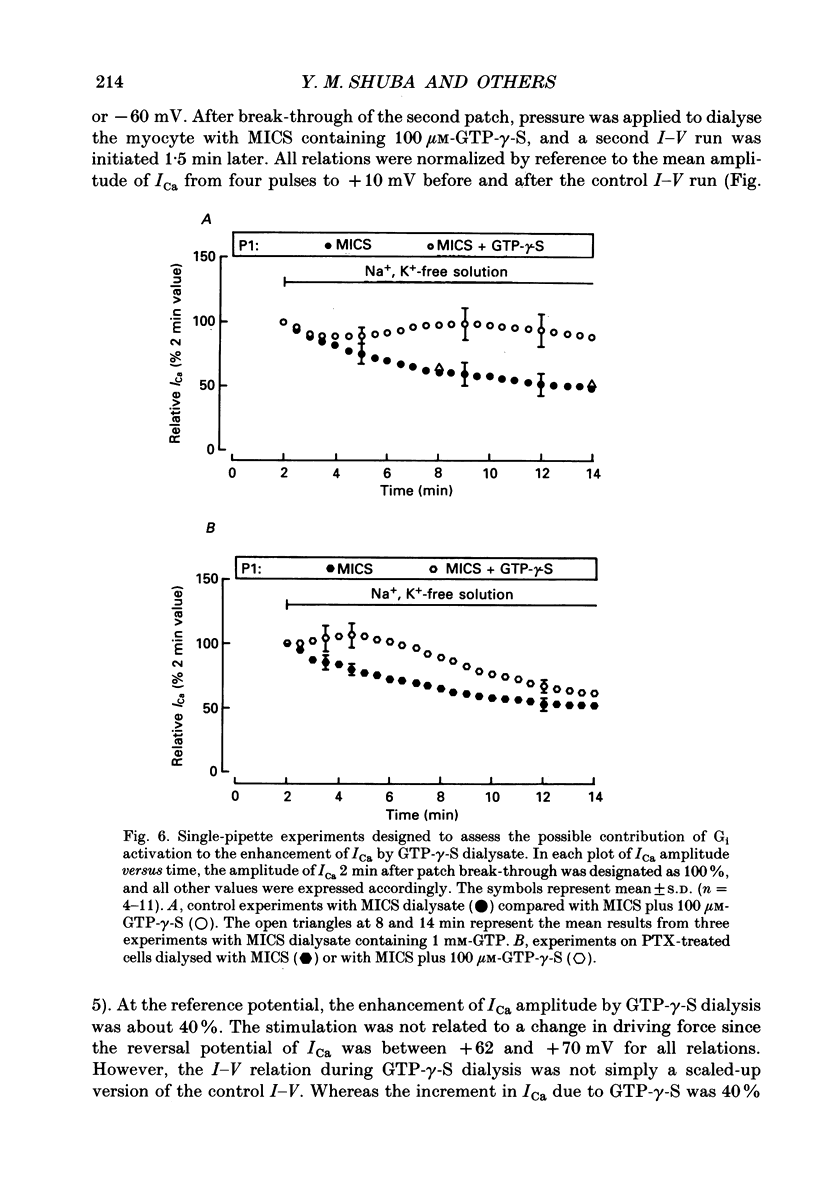








Selected References
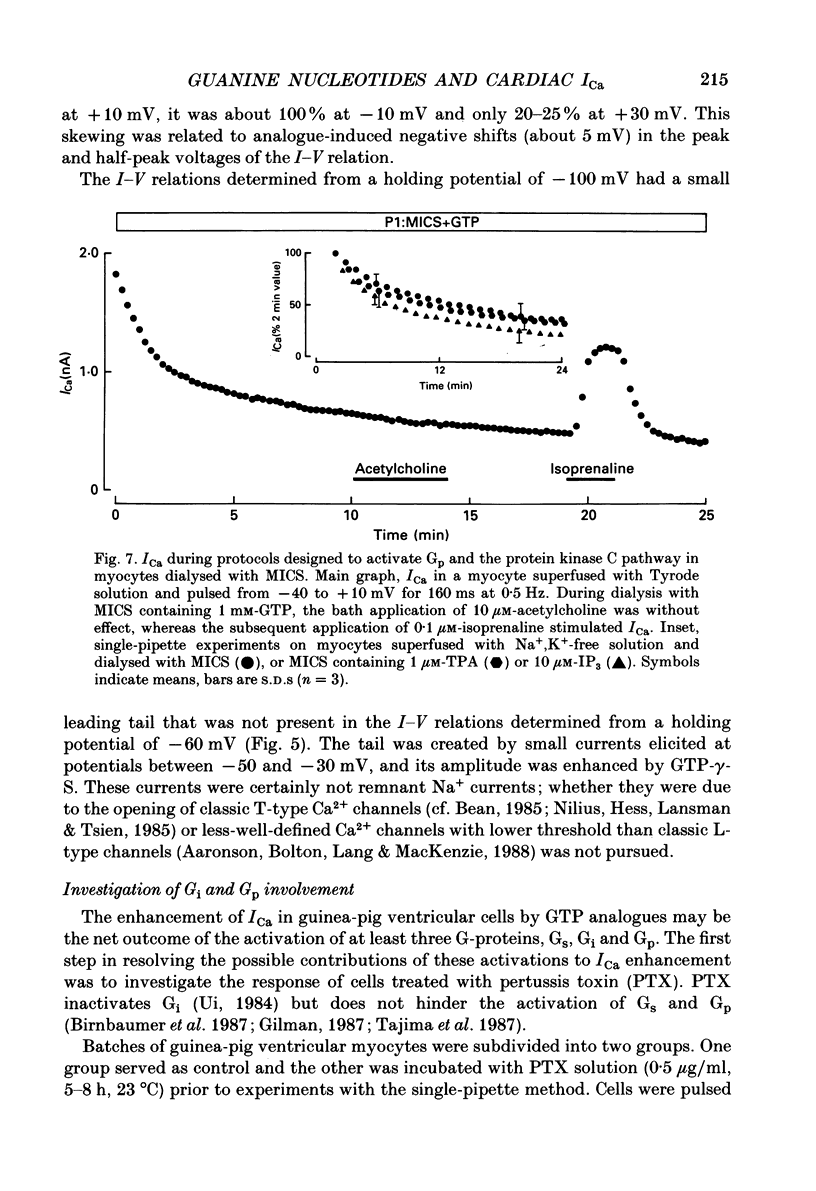
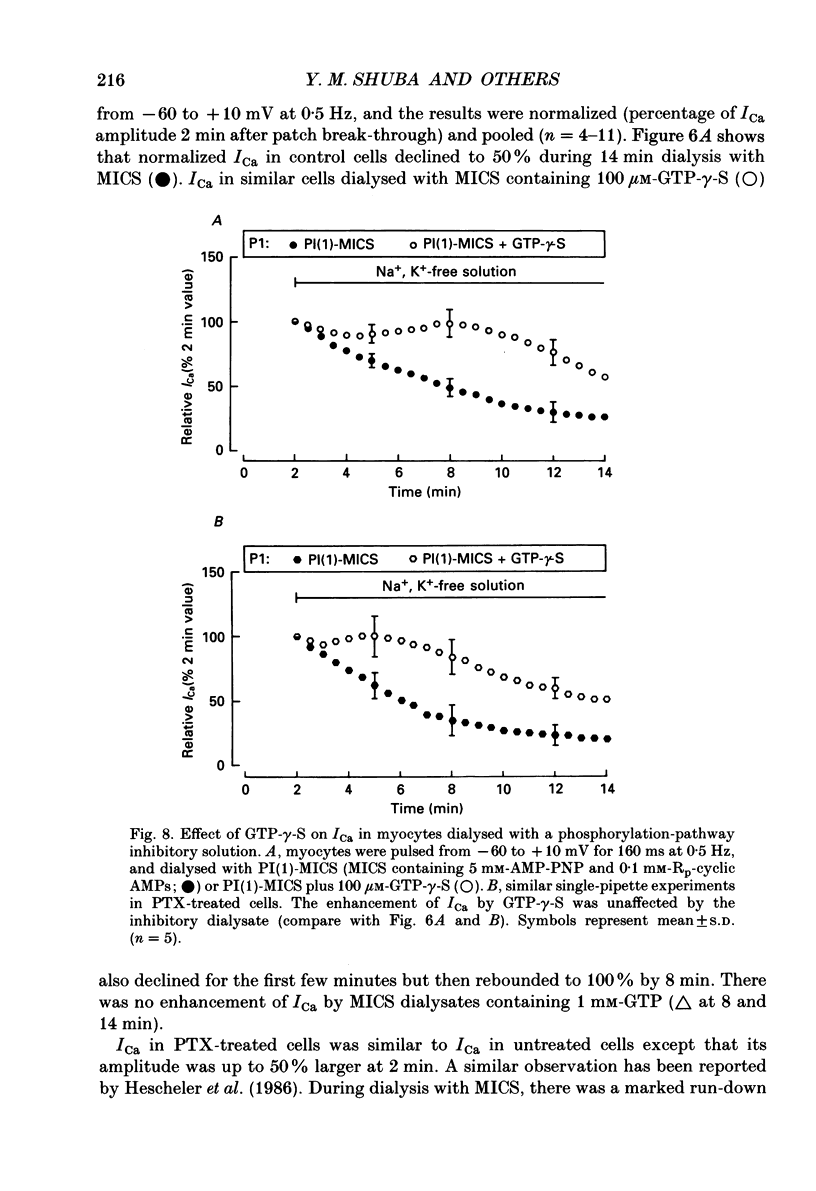
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson P. I., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J., MacKenzie I. Calcium currents in single isolated smooth muscle cells from the rabbit ear artery in normal-calcium and high-barium solutions. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:57–75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Multiple types of calcium channels in heart muscle and neurons. Modulation by drugs and neurotransmitters. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;560:334–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Beta-adrenergic modulation of calcium channels in frog ventricular heart cells. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):371–375. doi: 10.1038/307371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Two kinds of calcium channels in canine atrial cells. Differences in kinetics, selectivity, and pharmacology. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jul;86(1):1–30. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belles B., Malécot C. O., Hescheler J., Trautwein W. "Run-down" of the Ca current during long whole-cell recordings in guinea pig heart cells: role of phosphorylation and intracellular calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Apr;411(4):353–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00587713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and beta-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):538–540. doi: 10.1038/317538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Peper K. Iontophoretic application of acetylcholine: advantages of high resistance micropipettes in connection with an electronic current pump. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Apr 22;348(3):263–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00587417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischmeister R., Shrier A. Interactive effects of isoprenaline, forskolin and acetylcholine on Ca2+ current in frog ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Oct;417:213–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. W., Strawbridge R. A., Watanabe A. M. Muscarinic receptor regulation of cardiac adenylate cyclase activity. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1987 Jan;19(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(87)80544-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockerzi V., Oeken H. J., Hofmann F., Pelzer D., Cavalié A., Trautwein W. Purified dihydropyridine-binding site from skeletal muscle t-tubules is a functional calcium channel. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):66–68. doi: 10.1038/323066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Kameyama M., Trautwein W. On the mechanism of muscarinic inhibition of the cardiac Ca current. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):182–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00580674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Trautwein W. Modification of L-type calcium current by intracellularly applied trypsin in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:259–274. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto Y., Yatani A., Reeves J. P., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Alpha-subunit of Gs directly activates cardiac calcium channels in lipid bilayers. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H722–H728. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Klöckner U. Calcium currents of isolated bovine ventricular myocytes are fast and of large amplitude. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):30–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00584965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. G., Goldstein D., Brown J. H. Guanine nucleotide-dependent inositol trisphosphate formation in chick heart cells. Circ Res. 1988 Feb;62(2):299–305. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama M., Hescheler J., Hofmann F., Trautwein W. Modulation of Ca current during the phosphorylation cycle in the guinea pig heart. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):123–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00580662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama M., Hofmann F., Trautwein W. On the mechanism of beta-adrenergic regulation of the Ca channel in the guinea-pig heart. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Oct;405(3):285–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00582573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A. Effects of calcium and calcium-chelating agents on the inward and outward current in the membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):569–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacerda A. E., Rampe D., Brown A. M. Effects of protein kinase C activators on cardiac Ca2+ channels. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):249–251. doi: 10.1038/335249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan I. B. Phosphorylation of ion channels. J Membr Biol. 1985;87(3):177–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01871217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. F., MacLeod D. P. DNP-induced dissipation of ATP in anoxic ventricular muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(3):583–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T., Pelzer D., Trautwein W. Dual action (stimulation, inhibition) of D600 on contractility and calcium channels in guinea-pig and cat heart cells. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:569–586. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius B., Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. A novel type of cardiac calcium channel in ventricular cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):443–446. doi: 10.1038/316443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelzer D., Pelzer S., McDonald T. F. Properties and regulation of calcium channels in muscle cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1990;114:107–207. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Cassel D. Role of guanine nucleotides in hormonal activation of adenylate cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;14:15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons M. A., Hartzell H. C. Role of phosphodiesterase in regulation of calcium current in isolated cardiac myocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;33(6):664–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong J. A., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W., Kaczmarek L. K. Stimulation of protein kinase C recruits covert calcium channels in Aplysia bag cell neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):714–717. doi: 10.1038/325714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima T., Tsuji Y., Brown J. H., Pappano A. J. Pertussis toxin-insensitive phosphoinositide hydrolysis, membrane depolarization, and positive inotropic effect of carbachol in chick atria. Circ Res. 1987 Sep;61(3):436–445. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.3.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., Van Driel R., Jastorff B., Baraniak J., Stec W. J., De Wit R. J. Competitive cAMP antagonists for cAMP-receptor proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10020–10024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilven J., Coronado R. Opening of dihydropyridine calcium channels in skeletal muscle membranes by inositol trisphosphate. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):587–589. doi: 10.1038/336587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse S., Feramisco J. R., Casnellie J. E., Krebs E. G., Walsh D. A. Studies on the kinetic mechanism of the catalytic subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3693–3701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Wilson C. B. Quantitative and qualitative studies of antibody-induced mesangial cell damage in the rat. Kidney Int. 1987 Oct;32(4):514–525. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Brown A. M. Rapid beta-adrenergic modulation of cardiac calcium channel currents by a fast G protein pathway. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):71–74. doi: 10.1126/science.2544999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Imoto Y., Reeves J. P., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. A G protein directly regulates mammalian cardiac calcium channels. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2446390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Imoto Y., Codina J., Hamilton S. L., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. The stimulatory G protein of adenylyl cyclase, Gs, also stimulates dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Evidence for direct regulation independent of phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase or stimulation by a dihydropyridine agonist. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9887–9895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount R. G. ATP analogs. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:1–56. doi: 10.1002/9780470122884.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



