Abstract
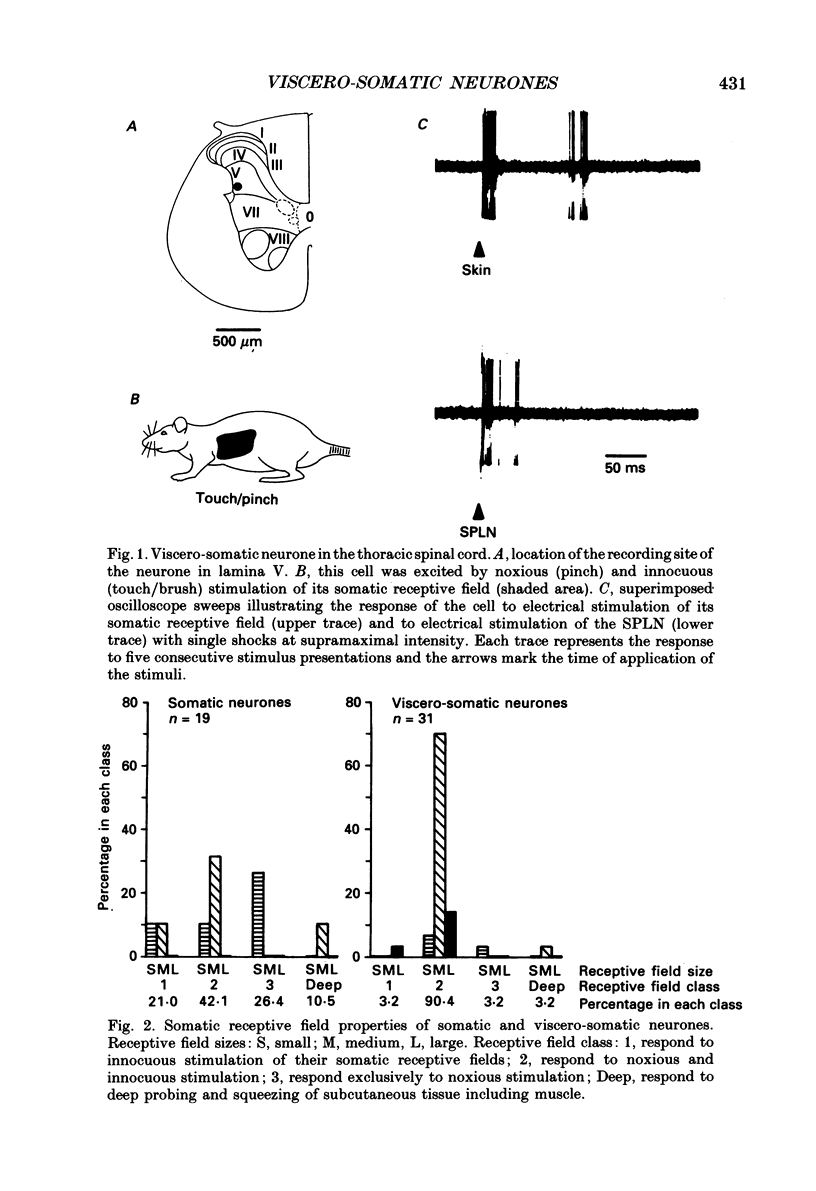
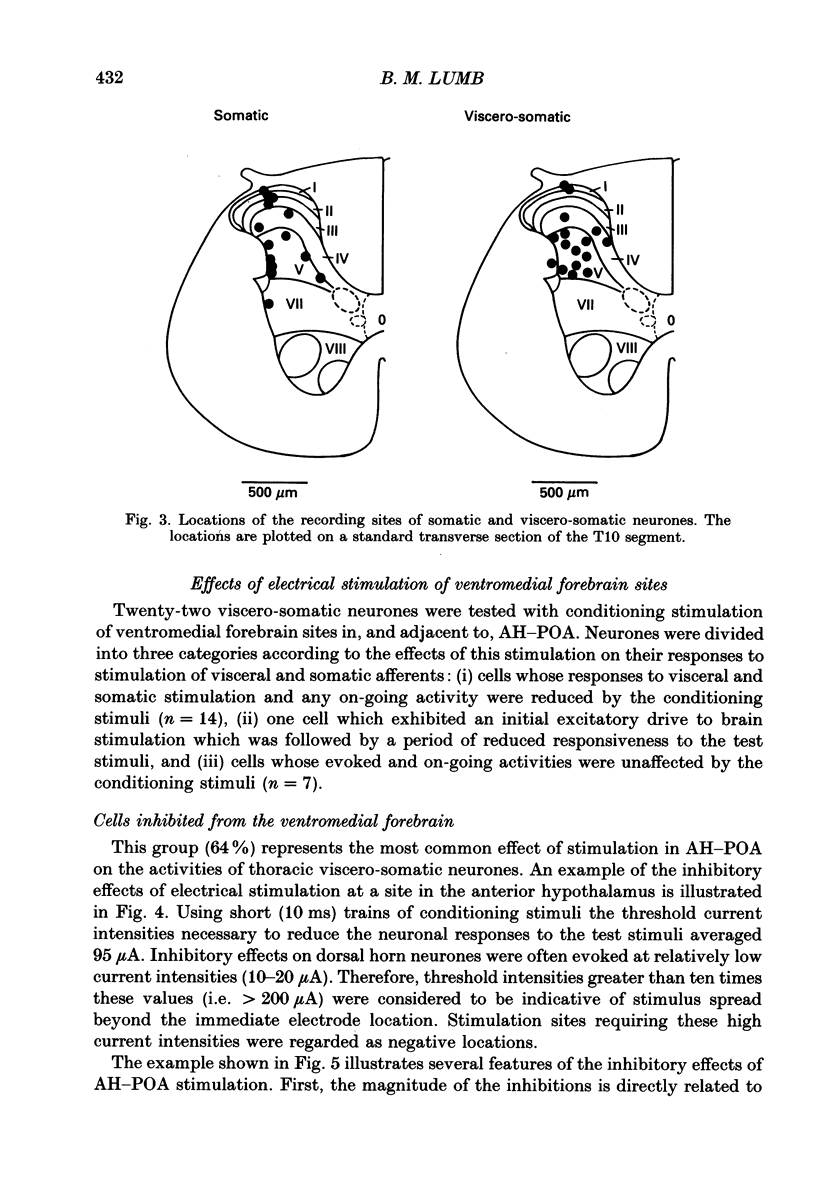
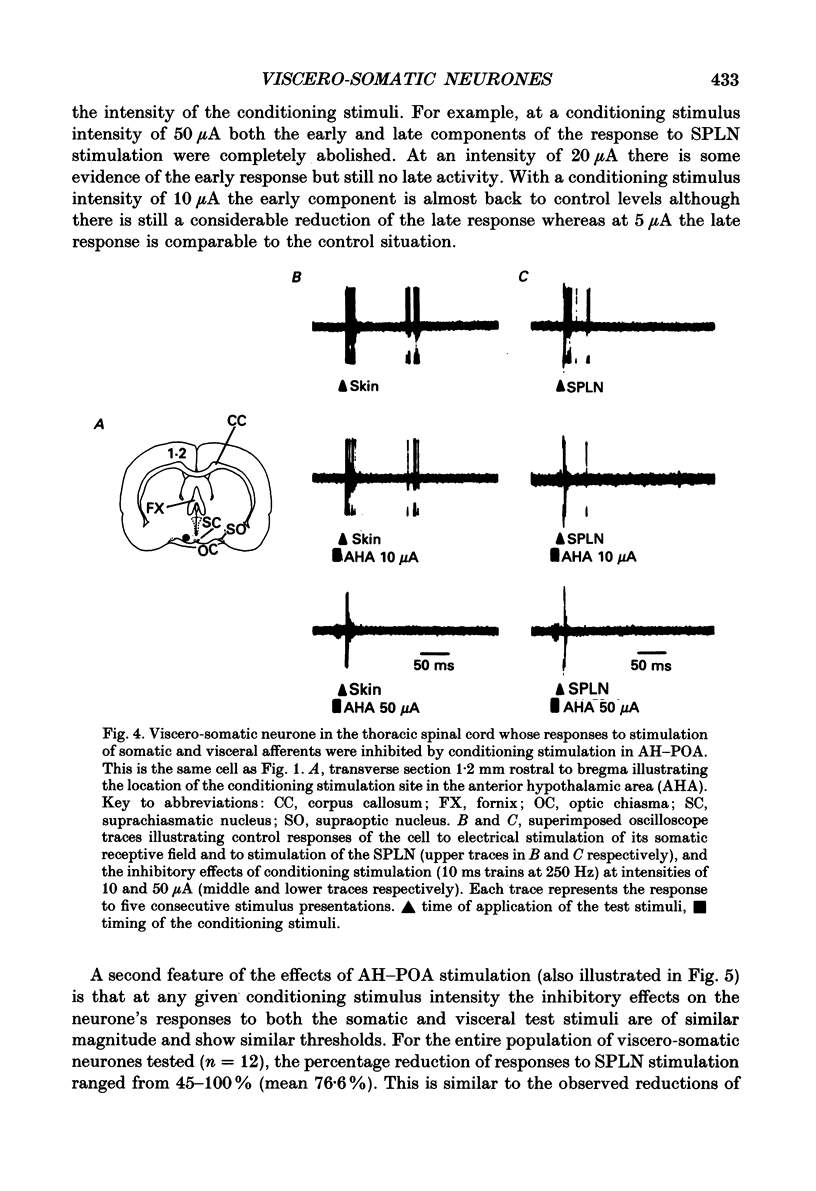
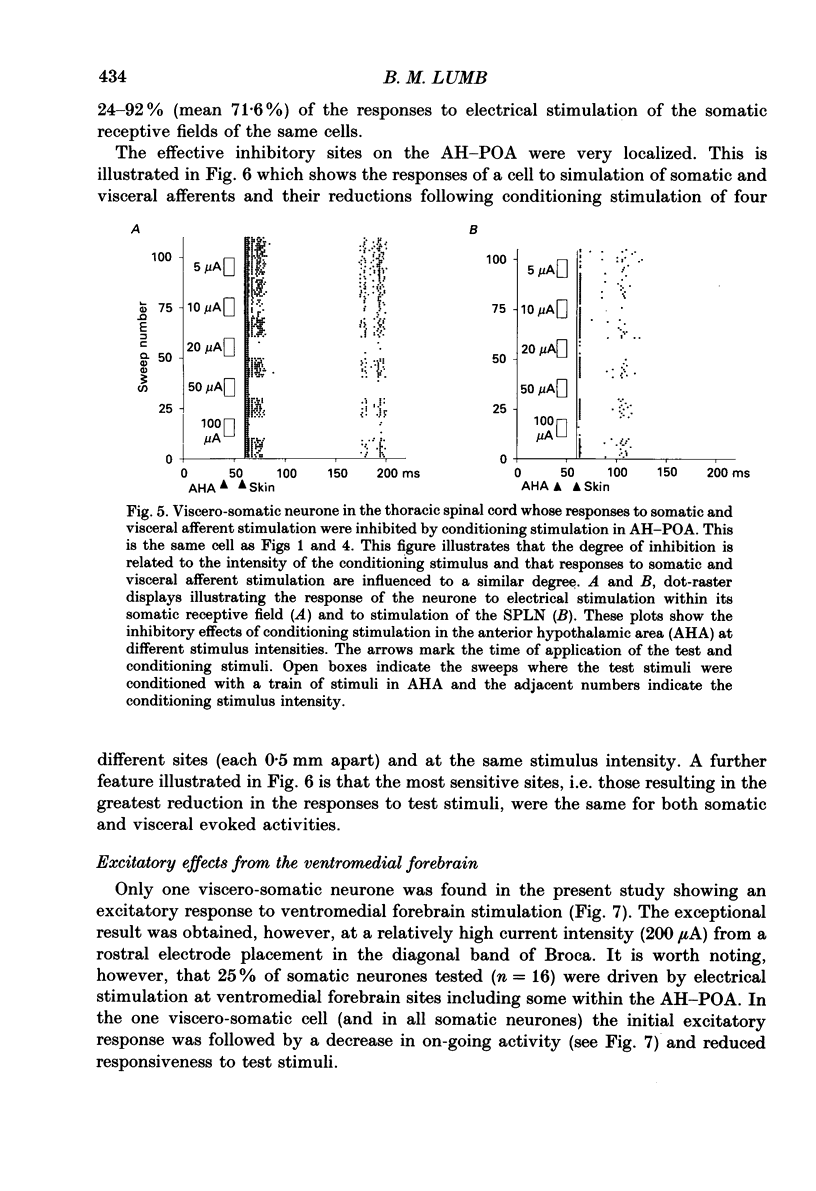
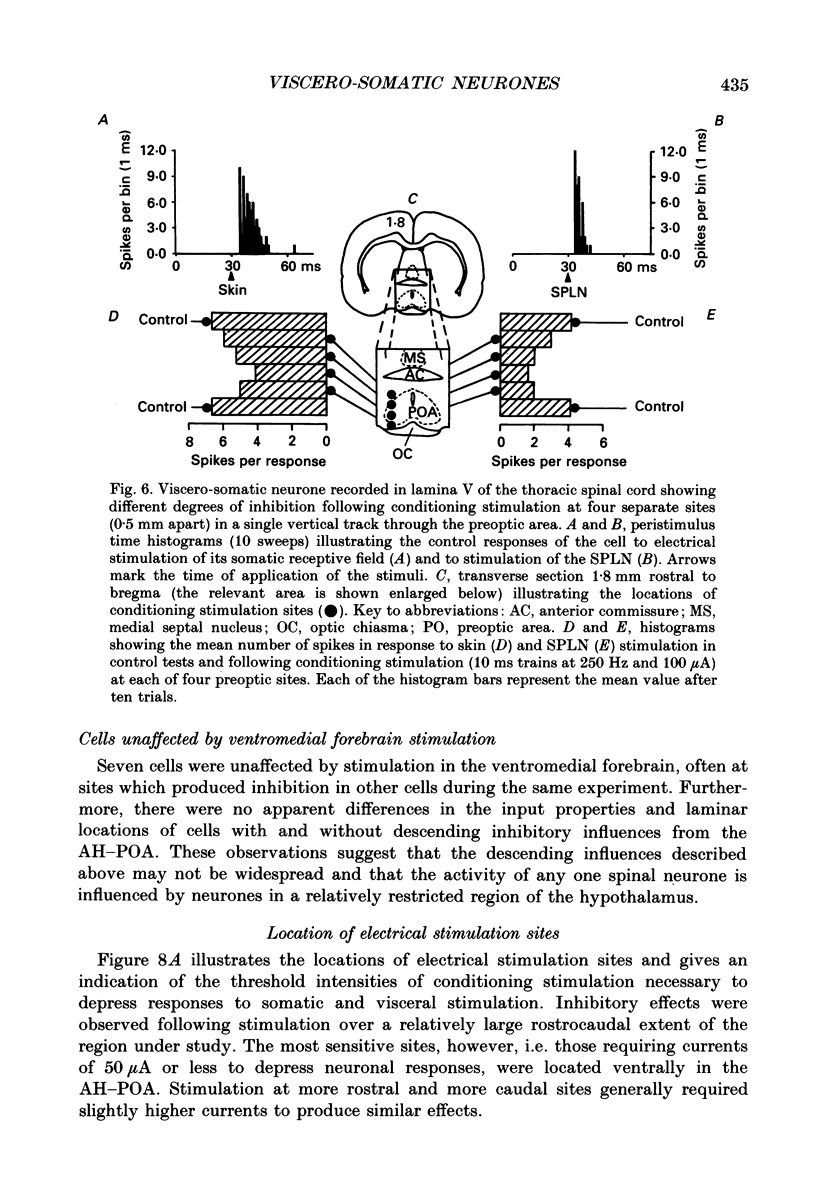
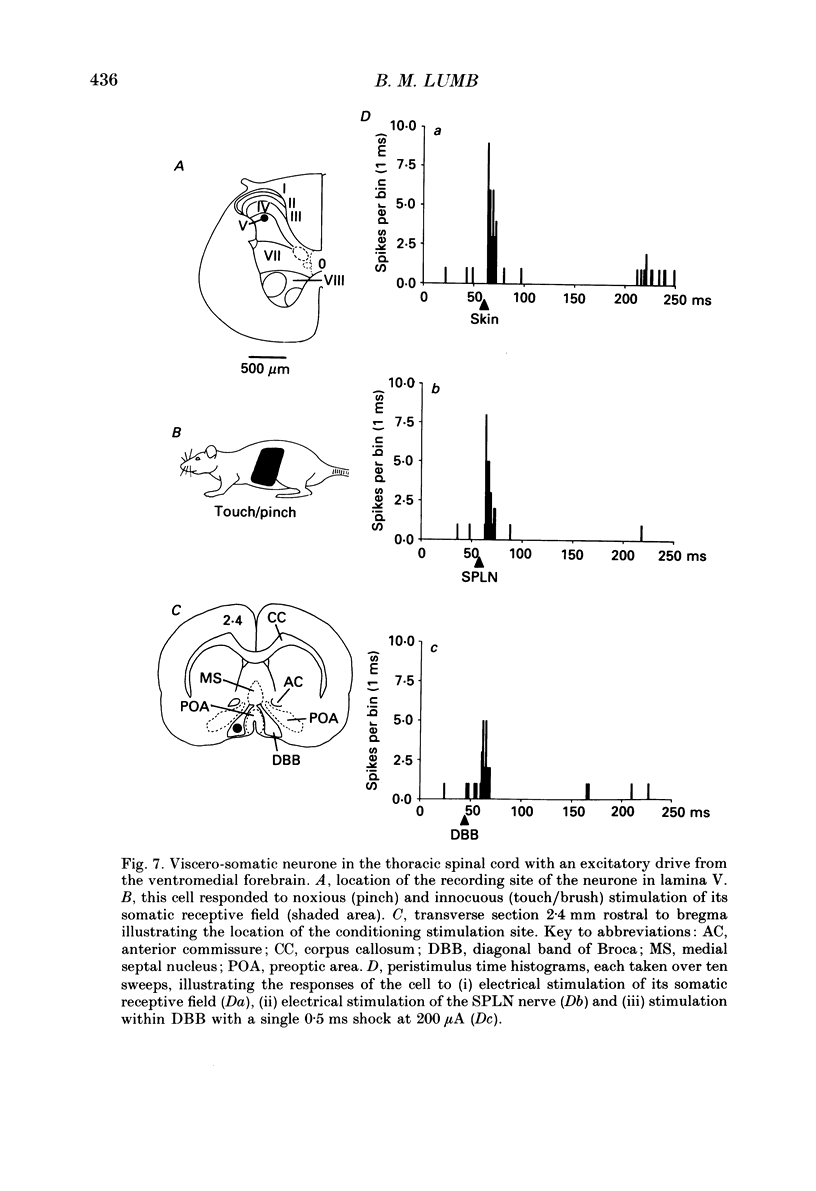
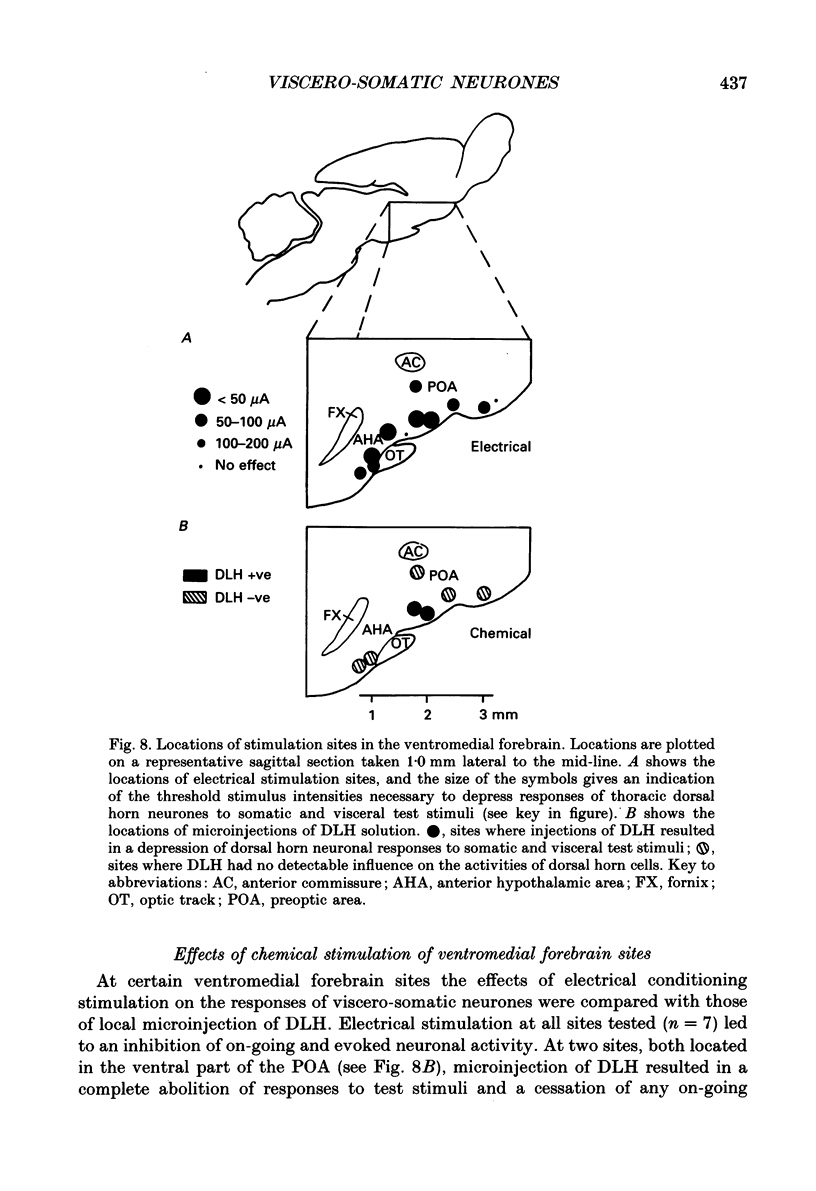
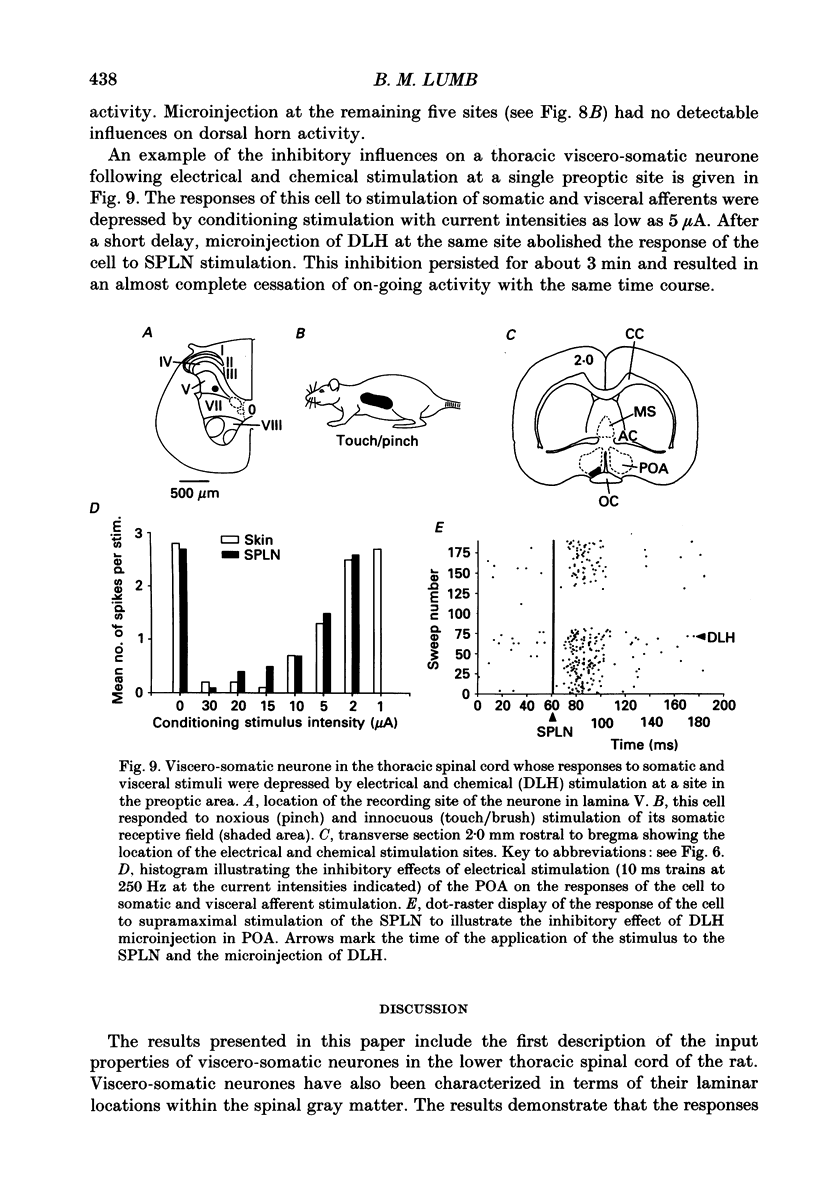
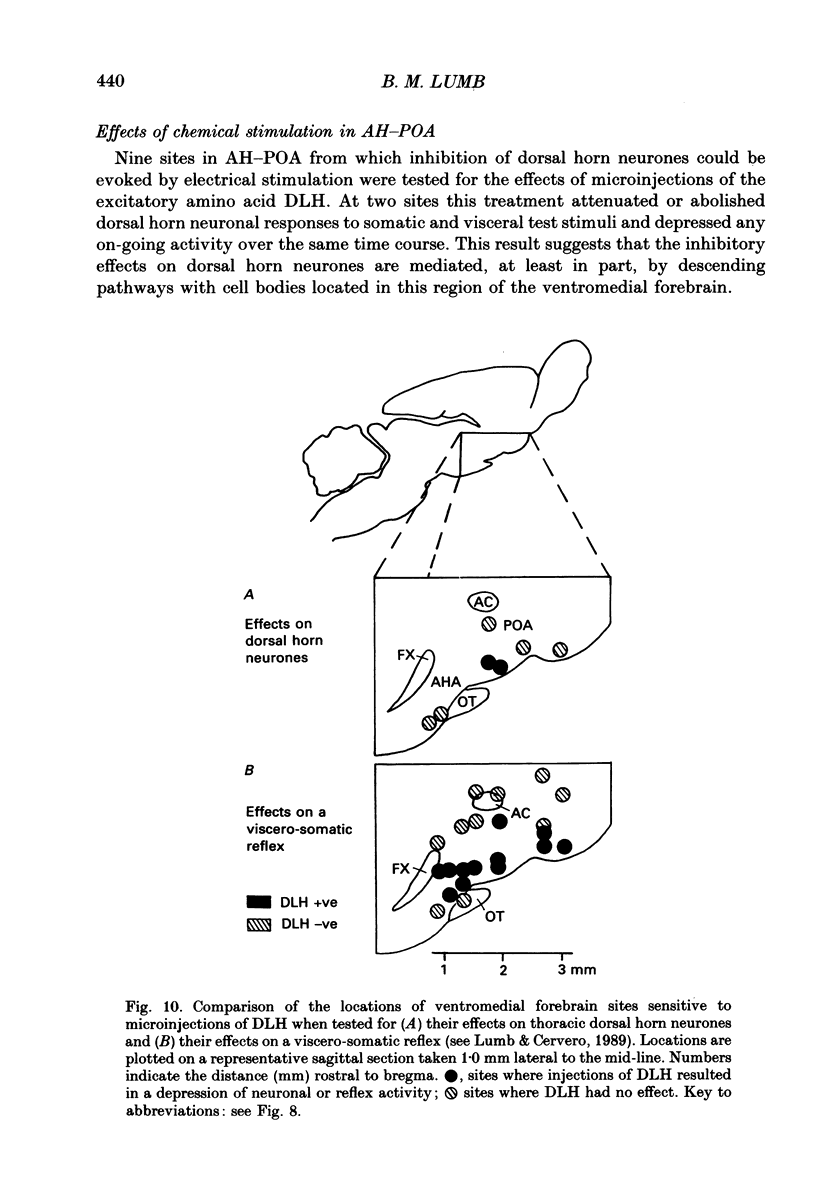
1. Single unit electrical activity has been recorded from thirty-four viscero-somatic neurones in the dorsal horn of the lower thoracic spinal cord (T9-T11) of chloralose-anaesthetized rats. All neurones were driven by natural and/or electrical stimulation within their somatic receptive fields and gave excitatory responses to electrical stimulation of the ipsilateral splanchnic nerve. Descending influences on these neurones were tested by electrical and chemical (microinjections of DL-homocysteic acid) stimulation of sites in the rostral hypothalamus. 2. The electrical activity of most viscero-somatic neurones (64%) was inhibited by electrical stimulation at sites throughout the anterior hypothalamus-preoptic region. In any one cell, responses to stimulation of visceral and somatic afferent fibres were inhibited to the same extent and any on-going activity was also depressed. Only one cell was driven by the conditioning stimulus and the electrical activity of the remaining cells (n = 7) was unaffected. 3. At certain hypothalamic sites the effects of electrical conditioning stimulation on the responses of viscero-somatic neurones were compared with those of local microinjection of DL-homocysteic acid. Electrical stimulation at all sites tested (n = 7) led to an inhibition of on-going and evoked neuronal activity. At two hypothalamic sites, both located in the ventral part of the preoptic area, microinjection of DL-homocysteic acid resulted in a complete abolition of the responses to the test stimuli and in a cessation of any on-going activity. Microinjection of DL-homocysteic acid at the remaining five sites had no detectable influences on dorsal horn activity. 4. The results of this study include the first description of input properties of viscero-somatic neurones in the lower thoracic spinal cord of the rat. In addition, these results demonstrate that transmission of visceral and somatic information through these neurones can be modulated by pathways that originate in the anterior hypothalamus-preoptic region of the ventromedial forebrain.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammons W. S., Blair R. W., Foreman R. D. Raphe magnus inhibition of primate T1-T4 spinothalamic cells with cardiopulmonary visceral input. Pain. 1984 Nov;20(3):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(84)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besson J. M., Chaouch A. Peripheral and spinal mechanisms of nociception. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jan;67(1):67–186. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein R., Cliffer K. D., Giesler G. J., Jr Direct somatosensory projections from the spinal cord to the hypothalamus and telencephalon. J Neurosci. 1987 Dec;7(12):4159–4164. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-12-04159.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstens E., MacKinnon J. D., Guinan M. J. Inhibition of spinal dorsal horn neuronal responses to noxious skin heating by medial preoptic and septal stimulation in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Oct;48(4):981–989. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.4.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cechetto D. F., Saper C. B. Neurochemical organization of the hypothalamic projection to the spinal cord in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jun 22;272(4):579–604. doi: 10.1002/cne.902720410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervero F., Tattersall J. E. Somatic and visceral sensory integration in the thoracic spinal cord. Prog Brain Res. 1986;67:189–205. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62763-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman C. D., Ammons W. S., Foreman R. D. Raphe magnus inhibition of feline T1-T4 spinoreticular tract cell responses to visceral and somatic inputs. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Mar;53(3):773–785. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.3.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba T., Murata Y. Afferent and efferent connections of the medial preoptic area in the rat: a WGA-HRP study. Brain Res Bull. 1985 Mar;14(3):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(85)90091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad L. C., Pfaff D. W. Efferents from medial basal forebrain and hypothalamus in the rat. I. An autoradiographic study of the medial preoptic area. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Sep 15;169(2):185–219. doi: 10.1002/cne.901690205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWNMAN C. B. Skeletal muscle reflexes of splanchnic and intercostal nerve origin in acute spinal and decerebrate cats. J Neurophysiol. 1955 May;18(3):217–235. doi: 10.1152/jn.1955.18.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman R. D., Blair R. W., Ammons W. S. Neural mechanisms of cardiac pain. Prog Brain Res. 1986;67:227–243. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62765-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelsema A. J., Roe M. J., Calaresu F. R. Neurally mediated cardiovascular responses to stimulation of cell bodies in the hypothalamus of the rat. Brain Res. 1989 Mar 13;482(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90543-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giesler G. J., Jr, Liebeskind J. C. Inhibition of visceral pain by electrical stimulation of the periaqueductal gray matter. Pain. 1976 Mar;2(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(76)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holstege G. Some anatomical observations on the projections from the hypothalamus to brainstem and spinal cord: an HRP and autoradiographic tracing study in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jun 1;260(1):98–126. doi: 10.1002/cne.902600109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoya Y. The distribution of spinal projection neurons in the hypothalamus of the rat, studied with the HRP method. Exp Brain Res. 1980;40(1):79–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00236665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson G., Lisander B., Martinson J. Hypothalamic control of adrenergic outflow to the stomach in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Jan-Feb;75(1):176–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bars D., Dickenson A. H., Besson J. M. Diffuse noxious inhibitory controls (DNIC). II. Lack of effect on non-convergent neurones, supraspinal involvement and theoretical implications. Pain. 1979 Jun;6(3):305–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(79)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisander B., Delbro D. Hypothalamic stimulation counteracts sympathetically mediated gastrointestinal inhibition in chloralose-anaesthetised cats. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 Aug;20(2):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumb B. M., Cervero F. Modulation of a viscerosomatic reflex by electrical and chemical stimulation of hypothalamic structures in the rat. Brain Res. 1989 Oct 23;500(1-2):400–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumb B. M., Morrison J. F. Electrophysiological evidence for an excitatory projection from ventromedial forebrain structures on to raphe- and reticulo-spinal neurones in the rat. Brain Res. 1986 Aug 13;380(1):162–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokha S. S., Goldsmith G. E., Hellon R. F., Puri R. Hypothalamic control of nocireceptive and other neurons in the marginal layer of the dorsal horn of the medulla (trigeminal nucleus caudalis) in the rat. Exp Brain Res. 1987;65(2):427–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00236316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhuber W. L., Sandoz P. A., Fryscak T. The central projections of primary afferent neurons of greater splanchnic and intercostal nerves in the rat. A horseradish peroxidase study. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1986;174(1):123–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00318344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleson T. D., Kirkpatrick D. B., Goodman S. J. Elevation of pain threshold to tooth shock by brain stimulation in primates. Brain Res. 1980 Jul 21;194(1):79–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert A., Yaksh T. Sites of morphine induced analgesia in the primate brain: relation to pain pathways. Brain Res. 1974 Nov 8;80(1):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90731-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pottoff P., Valentino D., Lal H. Attenuation of morphine analgesia by lesions of the preoptic forebrain region in the rat. Life Sci. 1979 Jan 29;24(5):421–423. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda H., Ikenoue K., Yokota T. Periaqueductal gray inhibition of viscerointercostal and galvanic skin reflexes. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 26;369(1-2):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90516-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall J. E., Cervero F., Lumb B. M. Viscerosomatic neurons in the lower thoracic spinal cord of the cat: excitations and inhibitions evoked by splanchnic and somatic nerve volleys and by stimulation of brain stem nuclei. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Nov;56(5):1411–1423. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.56.5.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


