Abstract
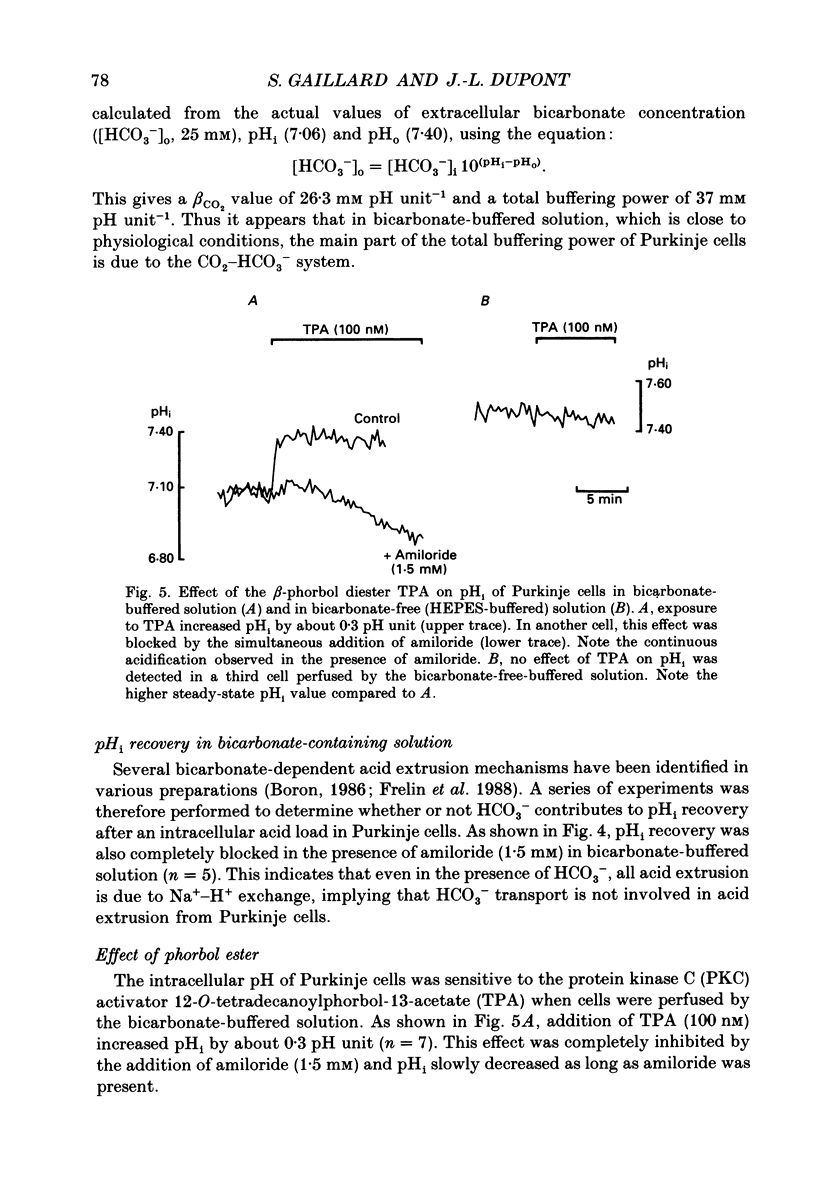
1. Intracellular pH (pHi) was measured in single rat cerebellar Purkinje cells maintained in primary culture using microspectrofluorescence analysis of the intracellularly trapped pH-sensitive dye 2',7'-bis-(2-carboxyethyl)-5 (and -6)-carboxyfluorescein (BCECF). 2. The ratio of the fluorescence signals measured at 530 nm in response to an alternating excitation at 450 and 490 nm was calibrated using the K(+)-H+ ionophore nigericin. This calibration gave a steady-state pHi of 7.06 +/- 0.02 (S.E.M., n = 17) when cells were perfused by a 5% CO2-25 mM-HCO3(-)-buffered solution at an external pH of 7.40 at 37 degrees C. 3. Replacement of external chloride with gluconate in the presence of bicarbonate induced a cytoplasmic alkalinization of about 0.3 pH unit. This alkalinization was independent of external sodium and was greatly reduced by 0.5 mM-DIDS, indicating the presence of a chloride-bicarbonate exchange. 4. In bicarbonate-free (HEPES-buffered) solution the steady-state pHi was 7.37 +/- 0.02 (n = 19), significantly higher than in bicarbonate-buffered solution. Recovery from an intracellular acid load brought about by the ammonium chloride pre-pulse technique was blocked by the removal of external sodium or the addition of 1.5 mM-amiloride, indicating the presence of a sodium-hydrogen exchange. 5. In bicarbonate-buffered solution pHi recovery after an acid load was also completely blocked by addition of 1.5 mM-amiloride indicating the absence of a bicarbonate-dependent acid extrusion mechanism. 6. Addition of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA, 100 nM) induced an amiloride-sensitive alkalinization of about 0.3 pH unit in bicarbonate-buffered solution but had no effect in HEPES-buffered solution. This observation suggests that in cultured Purkinje cells the sodium-hydrogen exchanger could be activated through a protein kinase C pathway only when pHi is maintained at a low physiological value by the activity of the chloride-bicarbonate exchange.
Full text
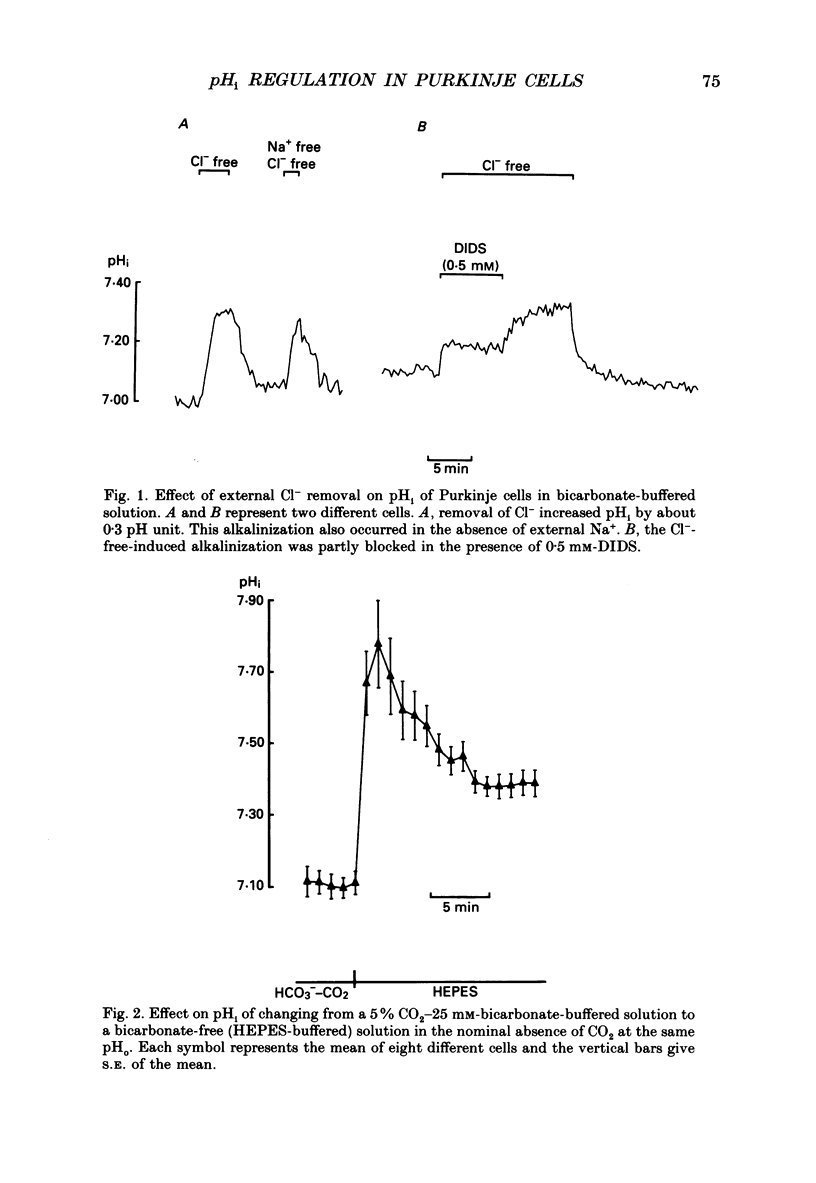
PDF



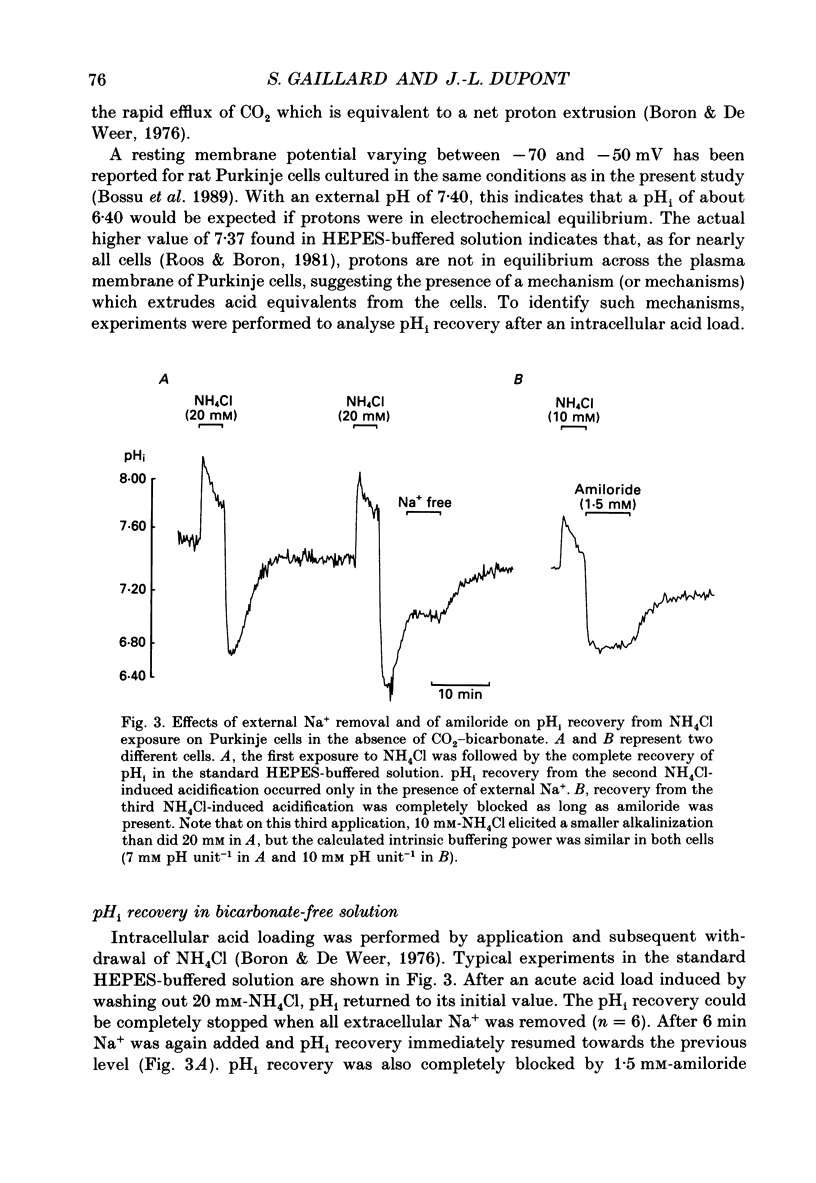
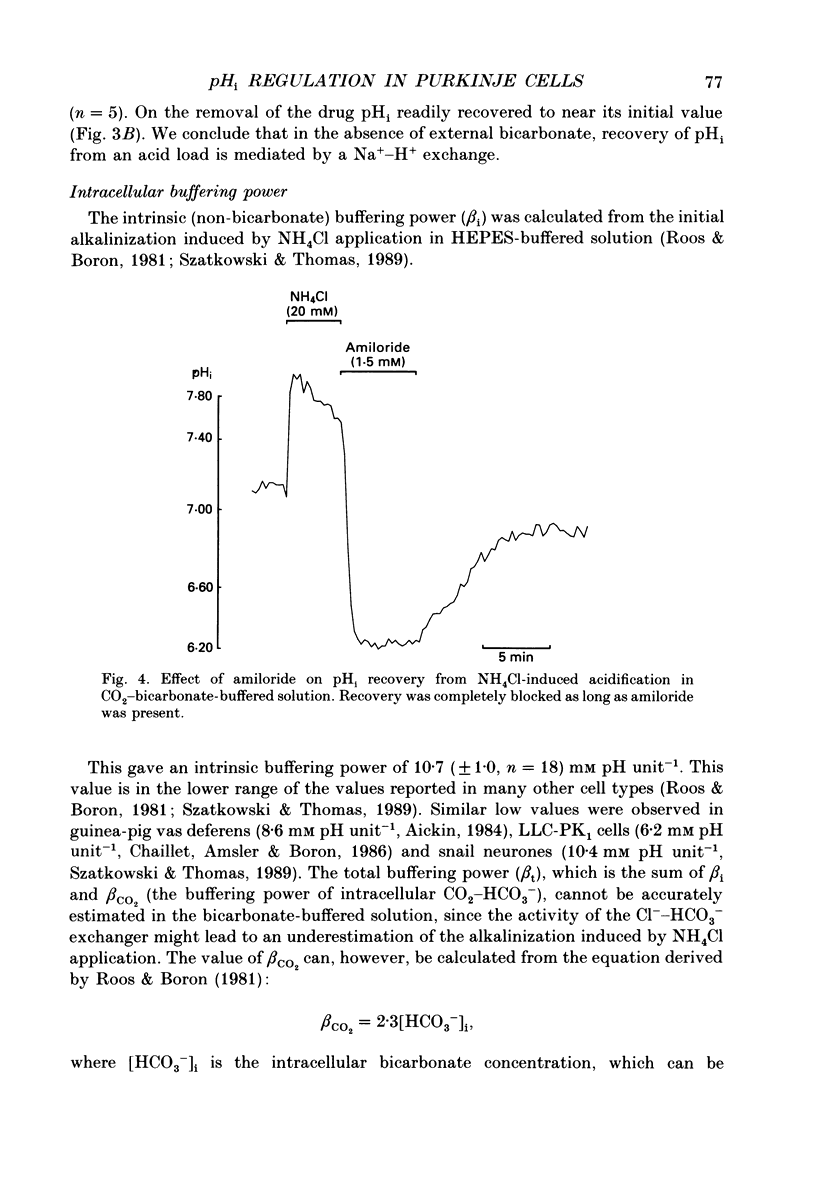





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aickin C. C. Direct measurement of intracellular pH and buffering power in smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:571–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Nee J., Suhm M. A. Modifier role of internal H+ in activating the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):161–163. doi: 10.1038/299161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Hamill O. P., Sakmann B. Mechanism of anion permeation through channels gated by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid in mouse cultured spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:243–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., De Weer P. Intracellular pH transients in squid giant axons caused by CO2, NH3, and metabolic inhibitors. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jan;67(1):91–112. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F. Intracellular pH regulation in epithelial cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:377–388. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.002113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossu J. L., Dupont J. L., Feltz A. Calcium currents in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells maintained in culture. Neuroscience. 1989;30(3):605–617. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busa W. B., Nuccitelli R. Metabolic regulation via intracellular pH. Am J Physiol. 1984 Apr;246(4 Pt 2):R409–R438. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.4.R409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Whiteley B., Zhuang Y. X., Glaser L. Mitogen-independent activation of Na+/H+ exchange in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells: regulation by medium osmolarity. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Feb;122(2):178–186. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaillet J. R., Amsler K., Boron W. F. Optical measurements of intracellular pH in single LLC-PK1 cells: demonstration of Cl-HCO3 exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):522–526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesler M., Chan C. Y. Stimulus-induced extracellular pH transients in the in vitro turtle cerebellum. Neuroscience. 1988 Dec;27(3):941–948. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesler M. Regulation of intracellular pH in reticulospinal neurones of the lamprey, Petromyzon marinus. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:241–261. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepel F., Penit-Soria J. Inward rectification and low threshold calcium conductance in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells. An in vitro study. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:1–23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Schlue W. R. The regulation of intracellular pH by identified glial cells and neurones in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:261–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelin C., Vigne P., Ladoux A., Lazdunski M. The regulation of the intracellular pH in cells from vertebrates. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 16;174(1):3–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rothstein A. Mechanisms of regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01869680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rotin D., Mason M. J. Na+/H+ exchange and growth factor-induced cytosolic pH changes. Role in cellular proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):73–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaila K., Voipio J. Postsynaptic fall in intracellular pH induced by GABA-activated bicarbonate conductance. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):163–165. doi: 10.1038/330163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor R., Jaeger C. B., Llinás R. Electrophysiology of the mammalian cerebellar cortex in organ culture. Neuroscience. 1988 Aug;26(2):493–507. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller S. K., Jentsch T. J., Janicke I., Wiederholt M. Regulation of intracellular pH in cultured bovine retinal pigment epithelial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jan;411(1):47–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00581645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Biddlecome S., Bourke R. S. SITS-inhibitable Cl- transport and Na+-dependent H+ production in primary astroglial cultures. Brain Res. 1979 Sep 7;173(1):111–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konnerth A., Lux H. D., Morad M. Proton-induced transformation of calcium channel in chick dorsal root ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:603–633. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korbmacher C., Helbig H., Stahl F., Wiederholt M. Evidence for Na/H exchange and Cl/HCO3 exchange in A10 vascular smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jul;412(1-2):29–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00583728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kose A., Saito N., Ito H., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y., Tanaka C. Electron microscopic localization of type I protein kinase C in rat Purkinje cells. J Neurosci. 1988 Nov;8(11):4262–4268. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-11-04262.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraig R. P., Ferreira-Filho C. R., Nicholson C. Alkaline and acid transients in cerebellar microenvironment. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Mar;49(3):831–850. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.3.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz I., Golchini K. Na+-independent Cl(-)-HCO-3- exchange in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Role in intracellular pH regulation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4516–4520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:171–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody W. J., Jr The ionic mechanism of intracellular pH regulation in crayfish neurones. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:293–308. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody W., Jr Effects of intracellular H+ on the electrical properties of excitable cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1984;7:257–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.07.030184.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. M., Gould R. J., Oster-Granite M. L., Gearhart J. D., Snyder S. H. Phorbol ester receptors: autoradiographic identification in the developing rat. Science. 1983 Dec 2;222(4627):1036–1038. doi: 10.1126/science.6316499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord E. P., Brown S. E., Crandall E. D. Cl-/HCO3- exchange modulates intracellular pH in rat type II alveolar epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5599–5606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso A. M., Tsien R. Y., Demarest J. R., Machen T. E. Na-H and Cl-HCO3 exchange in rabbit oxyntic cells using fluorescence microscopy. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):C30–C36. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.1.C30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redhead C. R. Ionic regulation of intracellular pH in rat calvarial osteoblasts. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:455–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlue W. R., Thomas R. C. A dual mechanism for intracellular pH regulation by leech neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:327–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szatkowski M. S., Thomas R. C. The intrinsic intracellular H+ buffering power of snail neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:89–101. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C., Meech R. W. Hydrogen ion currents and intracellular pH in depolarized voltage-clamped snail neurones. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):826–828. doi: 10.1038/299826a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. The role of bicarbonate, chloride and sodium ions in the regulation of intracellular pH in snail neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):317–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne P., Breittmayer J. P., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. Dual control of the intracellular pH in aortic smooth muscle cells by a cAMP-sensitive HCO3-/Cl- antiporter and a protein kinase C-sensitive Na+/H+ antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18023–18029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


