Abstract
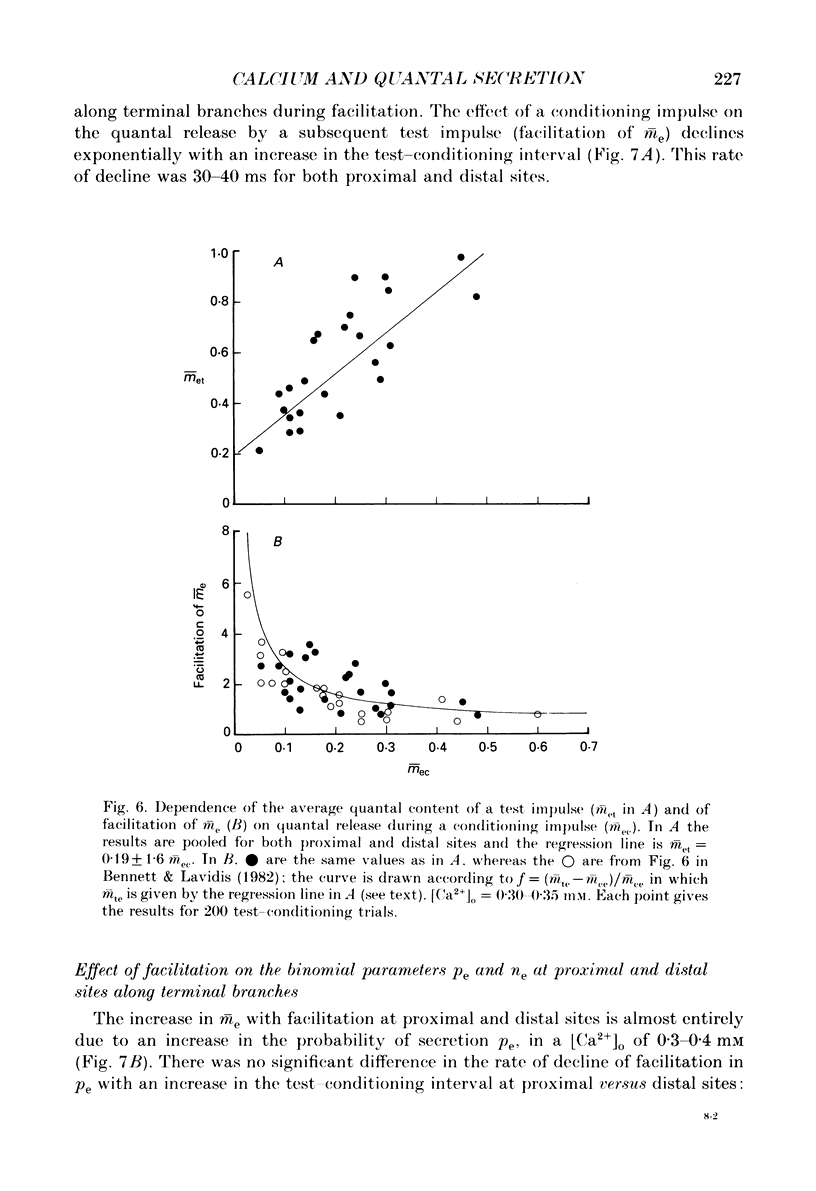
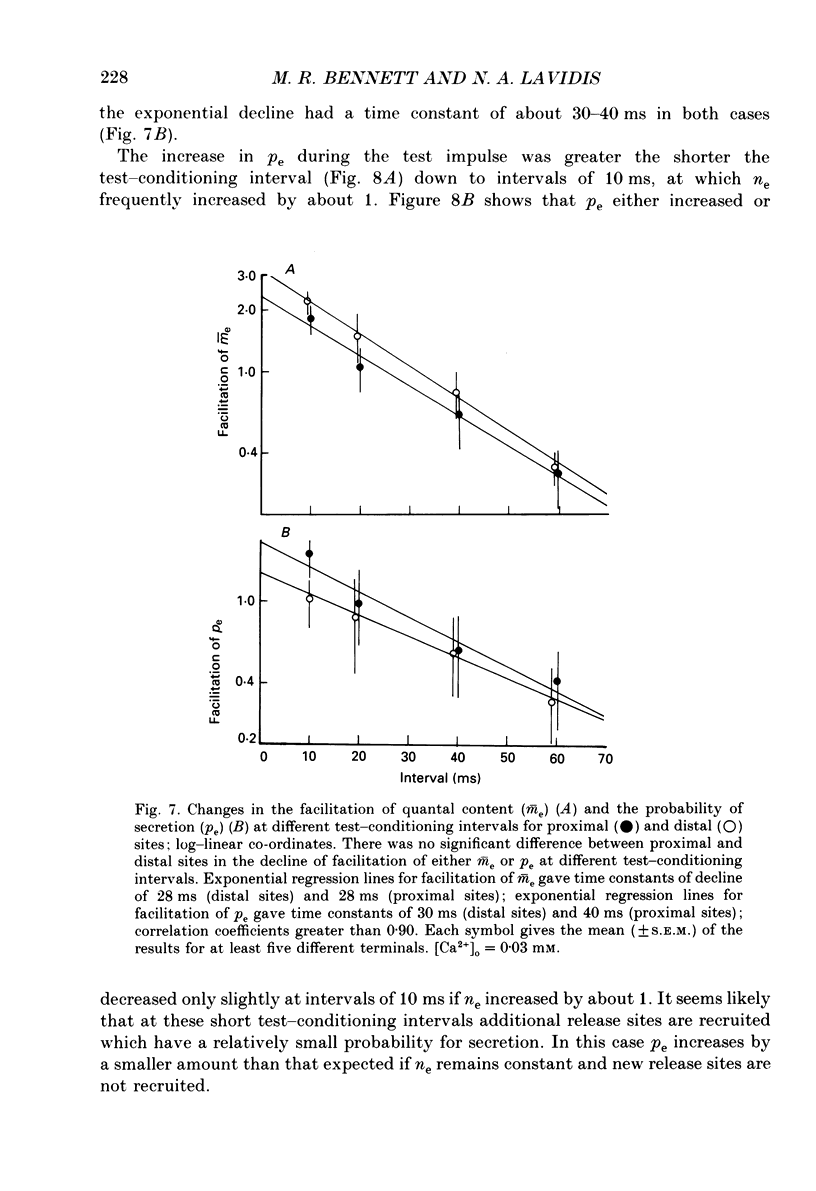
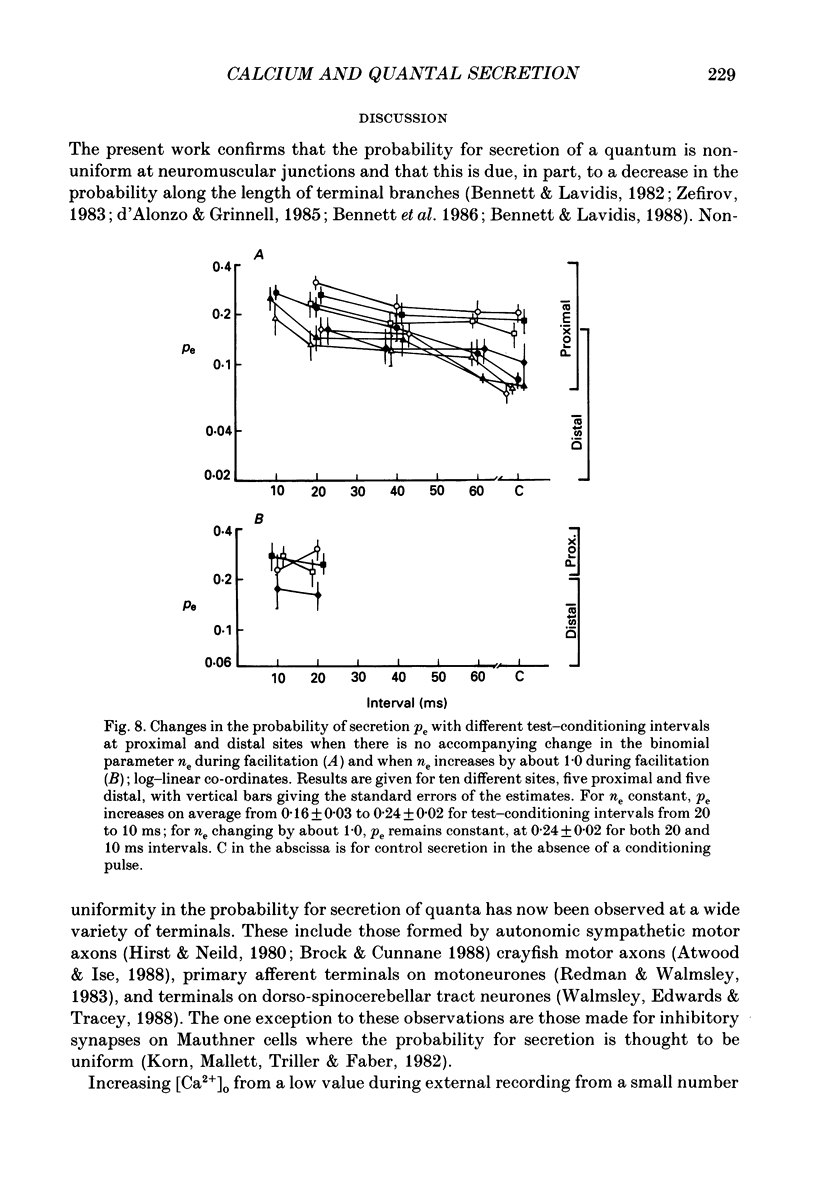
1. The number of quanta secreted from visualized release sites along terminal branches at toad (Bufo marinus) neuromuscular junctions in different extracellular concentrations of calcium ions. [Ca2+]o, and during facilitation was determined. Terminal branches were visualized by prior staining with the fluorescent dye, 3-3 diethyloxardicarbocyanine iodide (DiOC2(5)). 2. Increasing [Ca2+]o between 0.25 and 0.4 mM gave a similar proportional increase in the mean quantal content of the end-plate potential recorded with an extracellular electrode (me) at all sites along terminal branches. Thus the length constant for the experimental decline in me along terminal branches (the quantal length constant) remained constant with an increase in [Ca2+]o. The increase in m with [Ca2+]o followed a fourth power relation at both proximal and distal release sites. 3. The increase in me with [Ca2+]o was almost entirely due to an increase in the binomial probability for secretion, pe, which increased as the third to fourth power of [Ca2+]o. However, at higher [Ca2+]o there was an increasing tendency for the binomial parameter ne to increase. It is shown that when ne increases by about 1 there is very little change in pe, suggesting that the new release site recruited at high [Ca2+]o has a relatively low probability for secretion. 4. Test impulses gave a similar proportional increase in me following a conditioning impulse at all sites along terminal branches. The quantal length constant remained constant for both conditioning and test values of me. The increase in me for the test impulse increased linearly with an increase in me for the conditioning impulse at all release sites. 5. Facilitation of me declined exponentially with an increase in the test-conditioning interval. The time constant for this decline (30-40 ms) was similar at both proximal and distal release sites. Changes in facilitation of me were almost entirely due to changes in pe except at very short test-conditioning intervals of about 10 ms. At these intervals ne frequently increased by about 1 and there was very little change in pe. Again, this suggests that additional release sites recruited at short intervals have relatively low probability for secretion. 6. The results indicate that relatively low probability release sites exist in close juxtaposition to relatively high probability release sites which themselves decline in probability along the length of terminal branches.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreu R., Barrett E. F. Calcium dependence of evoked transmitter release at very low quantal contents at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:79–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwood H. L., Tse F. W. Changes in binomial parameters of quantal release at crustacean motor axon terminals during presynaptic inhibition. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:177–193. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Charlton M. P. Calcium dependence of presynaptic calcium current and post-synaptic response at the squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:619–640. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balnave R. J., Gage P. W. Facilitation of transmitter secretion from toad motor nerve terminals during brief trains of action potentials. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(2):435–451. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T., Pettigrew A. G. The effect of calcium ions on the binomial statistic parameters that control acetylcholine release at preganglionic nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;257(3):597–620. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Jones P., Lavidis N. A. The probability of quantal secretion along visualized terminal branches at amphibian (Bufo marinus) neuromuscular synapses. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:257–274. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Lavidis N. A., Lavidis-Armson F. The probability of quantal secretion at release sites of different length in toad (Bufo marinus) muscle. J Physiol. 1989 Nov;418:235–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Lavidis N. A. Quantal secretion at release sites of nerve terminals in toad (Bufo marinus) muscle during formation of topographical maps. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:567–579. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Lavidis N. A. The effect of calcium ions on the secretion of quanta evoked by an impulse at nerve terminal release sites. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Oct;74(4):429–456. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock J. A., Cunnane T. C. Electrical activity at the sympathetic neuroeffector junction in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:607–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton M. P., Smith S. J., Zucker R. S. Role of presynaptic calcium ions and channels in synaptic facilitation and depression at the squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:173–193. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couteaux R., Pécot-Dechavassine M. Vésicules synaptiques et poches au niveau des "zones actives" de la jonction neuromusculaire. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Dec 21;271(25):2346–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alonzo A. J., Grinnell A. D. Profiles of evoked release along the length of frog motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:235–258. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Localization of active spots within the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):630–649. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera A. A., Grinnell A. D., Wolowske B. Ultrastructural correlates of experimentally altered transmitter release efficacy in frog motor nerve terminals. Neuroscience. 1985 Nov;16(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera A. A., Grinnell A. D., Wolowske B. Ultrastructural correlates of naturally occurring differences in transmitter release efficacy in frog motor nerve terminals. J Neurocytol. 1985 Apr;14(2):193–202. doi: 10.1007/BF01258447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Landis D. M. Functional changes in frog neuromuscular junctions studied with freeze-fracture. J Neurocytol. 1974 Mar;3(1):109–131. doi: 10.1007/BF01111936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Some properties of spontaneous excitatory junction potentials recorded from arterioles of guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:43–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The nature of the antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):434–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. W., Wernig A. The binomial nature of transmitter release at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):757–767. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J. THE LOCALIZATION OF CHOLINESTERASE ACTIVITY IN RAT CARDIAC MUSCLE BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Nov;23:217–232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Estimates of quantal content during 'chemical potentiation' of transmitter release. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Aug 31;205(1160):369–378. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn H., Mallet A., Triller A., Faber D. S. Transmission at a central inhibitory synapse. II. Quantal description of release, with a physical correlate for binomial n. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Sep;48(3):679–707. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.3.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., McGuinness T. L., Leonard C. S., Sugimori M., Greengard P. Intraterminal injection of synapsin I or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alters neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magrassi L., Purves D., Lichtman J. W. Fluorescent probes that stain living nerve terminals. J Neurosci. 1987 Apr;7(4):1207–1214. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-04-01207.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. M., Heuser J. E. Endocytosis of synaptic vesicle membrane at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):685–698. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman S., Walmsley B. Amplitude fluctuations in synaptic potentials evoked in cat spinal motoneurones at identified group Ia synapses. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:135–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. Estimation of parameters for a model of transmitter release at synapses. Biometrics. 1976 Mar;32(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley B., Edwards F. R., Tracey D. J. Nonuniform release probabilities underlie quantal synaptic transmission at a mammalian excitatory central synapse. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Sep;60(3):889–908. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.60.3.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikami D., Okun L. M. Staining of living presynaptic nerve terminals with selective fluorescent dyes. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):53–56. doi: 10.1038/310053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zefirov A. L. Raspolozhenie i funktsionirovanie tochek osvobozhdeniia mediatora v nervno-myshechnom soedinenii liagushki. Neirofiziologiia. 1985;17(2):152–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zefirov A. L. Sekretsiia mediatora v proksimal'nykh i distal'nykh uchastkakh nervnogo okonchaniia portniazhnoi myshtsy liagushki. Neirofiziologiia. 1983;15(4):362–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S., Fogelson A. L. Relationship between transmitter release and presynaptic calcium influx when calcium enters through discrete channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3032–3036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S., Stockbridge N. Presynaptic calcium diffusion and the time courses of transmitter release and synaptic facilitation at the squid giant synapse. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1263–1269. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01263.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


