Abstract
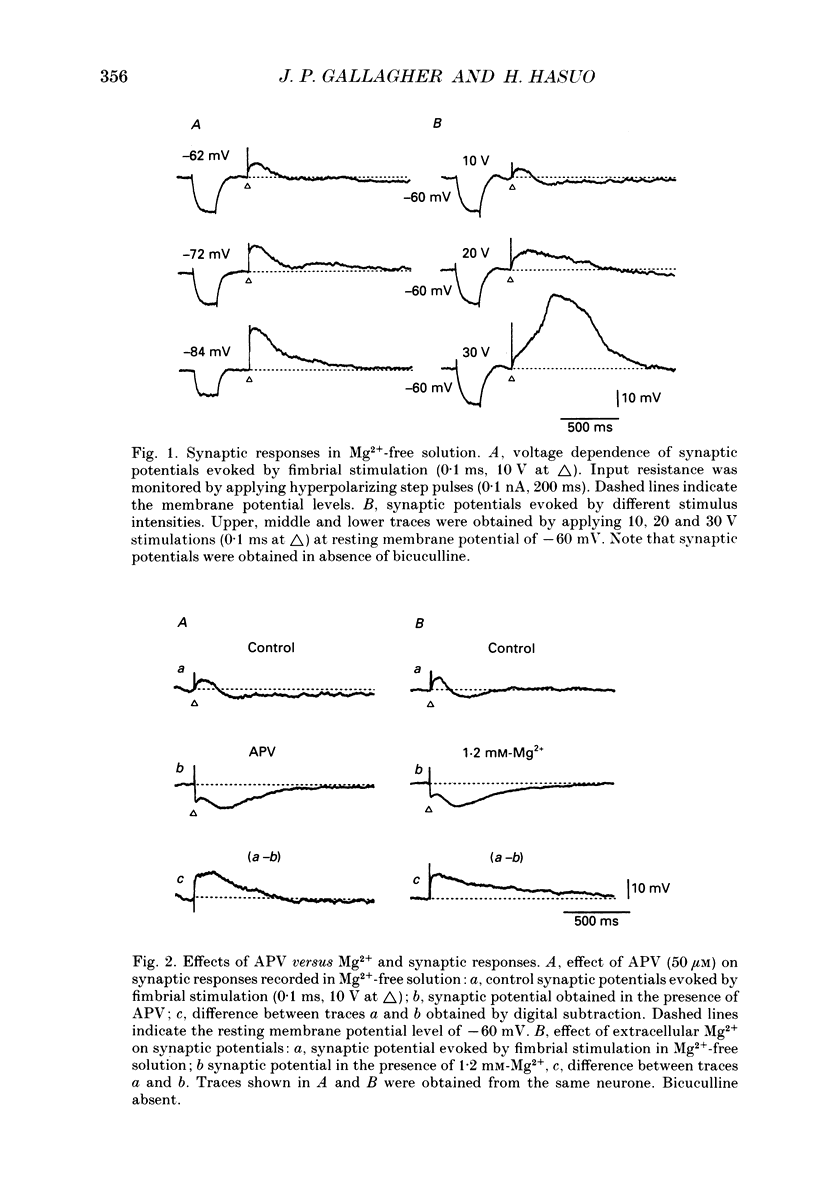
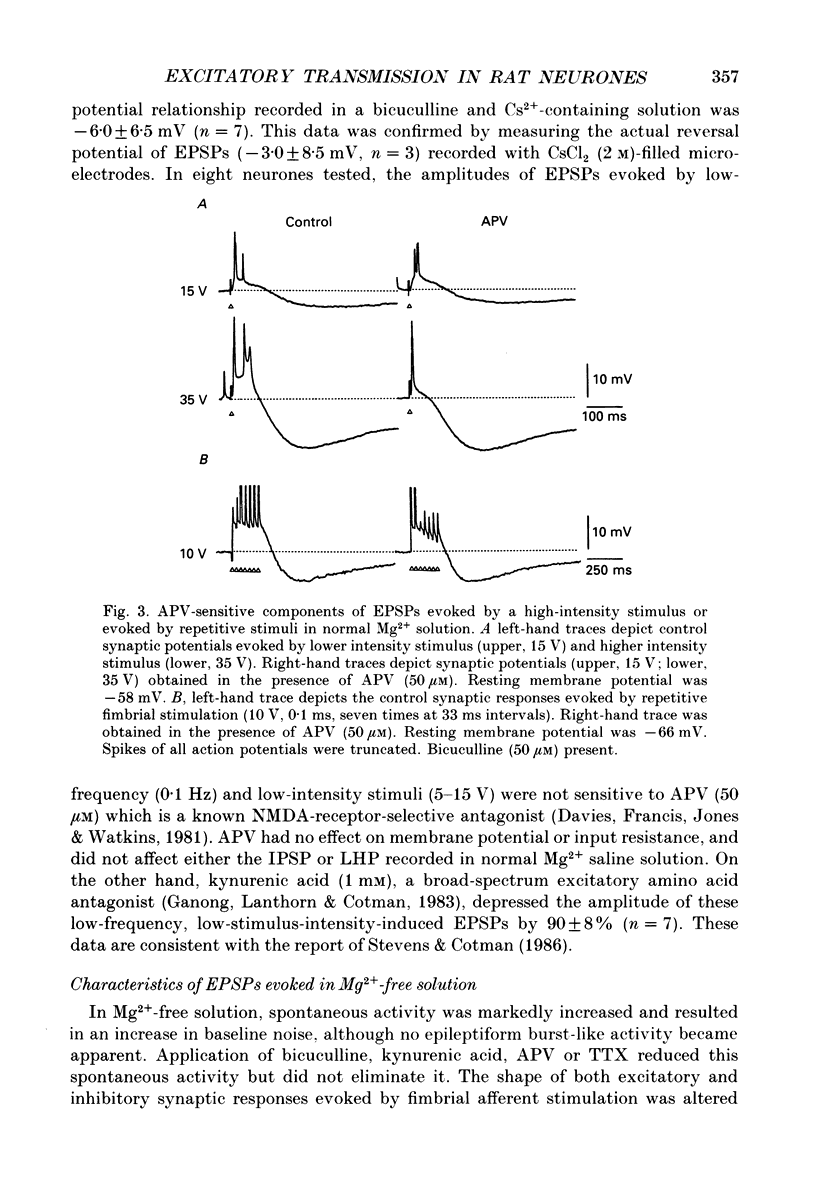
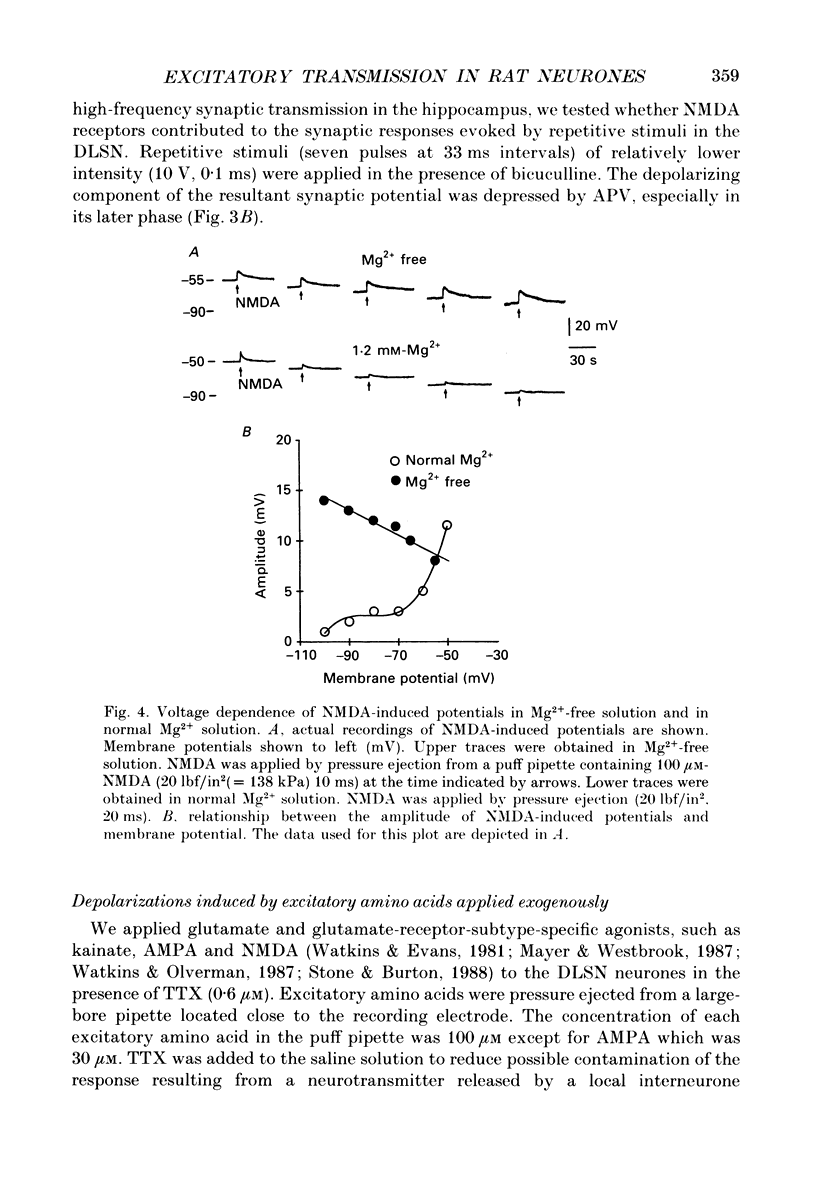
1. Intracellular recordings were made from rat dorsolateral septal nucleus (DLSN) neurones in vitro. We investigated depolarizations resulting from pressure application of excitatory amino acids and compared these to synaptically evoked excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs). 2. EPSPs evoked by focal fimbrial afferent stimulation in saline with 30-50 microM-bicuculline and 1.2 mM-Mg2+ yielded a linear amplitude-voltage relationship: their reversal potential was -3 mV. These EPSPs exhibited little sensitivity to 2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoate (APV), an N-methyl-D-aspartate(NMDA)-receptor-specific antagonist, but were markedly depressed by kynurenic acid, a broad-spectrum excitatory amino acid antagonist. 3. In Mg2(+)-free solution, the amplitude and the duration of EPSPs were increased markedly masking the following inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) and the late hyperpolarizing potential (LHP). These facilitated and broadened EPSPs were sensitive to APV or Mg2+. The APV or Mg2(+)-sensitive component of the EPSP obtained by digital subtraction suggests a slower time course for the NMDA-receptor-mediated EPSP compared to the non-NMDA-receptor-mediated EPSP. On the other hand, in normal Mg2+ solution an EPSP evoked by either a single strong stimulus or by repetitive stimuli had APV-sensitive components. 4. The depolarizing potentials induced by pressure application of glutamate, kainate, alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate (AMPA), quisqualate or NMDA were compared. The amplitude-voltage relationship of depolarizations induced by NMDA obtained in a normal Mg2+ solution was non-linear, but approached linearity when the same responses were recorded in a Mg2(+)-free solution. Depolarizations induced by kainate, AMPA and quisqualate were linear in their amplitude-voltage relationship in the presence or absence of Mg2+. APV blocked NMDA-induced depolarizations specifically, while kynurenic acid blocked all the depolarizations induced by NMDA, quisqualate, or kainate. 5. Our data demonstrate the existence of NMDA-receptor-mediated synaptic potentials in the rat DLSN, the characteristics of which are similar to those in other central nervous system regions.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P., Blackstad T. W., Lömo T. Location and identification of excitatory synapses on hippocampal pyramidal cells. Exp Brain Res. 1966;1(3):236–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00234344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Bregestovski P., Nowak L. N-methyl-D-aspartate-activated channels of mouse central neurones in magnesium-free solutions. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:207–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Nowak L. Quisqualate- and kainate-activated channels in mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:227–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcar V. J., Johnston G. A. The structural specificity of the high affinity uptake of L-glutamate and L-aspartate by rat brain slices. J Neurochem. 1972 Nov;19(11):2657–2666. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake J. F., Brown M. W., Collingridge G. L. CNQX blocks acidic amino acid induced depolarizations and synaptic components mediated by non-NMDA receptors in rat hippocampal slices. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jun 29;89(2):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90378-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coan E. J., Collingridge G. L. Characterization of an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor component of synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal slices. Neuroscience. 1987 Jul;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Herron C. E., Lester R. A. Frequency-dependent N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:301–312. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. The antagonism of amino acid-induced excitations of rat hippocampal CA1 neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:19–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Howe J. R., Ogden D. C. Noise and single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:189–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Usowicz M. M. Multiple-conductance channels activated by excitatory amino acids in cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):525–528. doi: 10.1038/325525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale N., Grillner S. Dual-component synaptic potentials in the lamprey mediated by excitatory amino acid receptors. J Neurosci. 1986 Sep;6(9):2653–2661. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-09-02653.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale N., Roberts A. Dual-component amino-acid-mediated synaptic potentials: excitatory drive for swimming in Xenopus embryos. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:35–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale N., Roberts A. Excitatory amino acid receptors in Xenopus embryo spinal cord and their role in the activation of swimming. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:527–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. 2-Amino-5-phosphonovalerate (2APV), a potent and selective antagonist of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jan 1;21(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrance J. F., Shimono T., Kitai S. T. Hippocampal inputs to the lateral septal nucleus: patterns of facilitation and inhibition. Brain Res. 1972 Feb 25;37(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90681-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L. Slow excitatory postsynaptic currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured mouse central neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Fagg G. E. Acidic amino acid binding sites in mammalian neuronal membranes: their characteristics and relationship to synaptic receptors. Brain Res. 1984 May;319(2):103–164. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. P., Hasuo H. Bicuculline- and phaclofen-sensitive components of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced hyperpolarizations in rat dorsolateral septal nucleus neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Nov;418:367–377. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong A. H., Lanthorn T. H., Cotman C. W. Kynurenic acid inhibits synaptic and acidic amino acid-induced responses in the rat hippocampus and spinal cord. Brain Res. 1983 Aug 22;273(1):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J. Cellular uptake disguises action of L-glutamate on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. With an appendix: diffusion of transported amino acids into brain slices. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 May;85(1):297–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herron C. E., Lester R. A., Coan E. J., Collingridge G. L. Frequency-dependent involvement of NMDA receptors in the hippocampus: a novel synaptic mechanism. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):265–268. doi: 10.1038/322265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herron C. E., Lester R. A., Coan E. J., Collingridge G. L. Intracellular demonstration of an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor mediated component of synaptic transmission in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Sep 16;60(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joëls M., Urban I. J. Amino acid neurotransmission between fimbria-fornix fibers and neurons in the lateral septum of the rat: a microiontophoretic study. Exp Neurol. 1984 Apr;84(1):126–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(84)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joëls M., Urban I. J. Electrophysiological and pharmacological evidence in favor of amino acid neurotransmission in fimbria-fornix fibers innervating the lateral septal complex of rats. Exp Brain Res. 1984;54(3):455–462. doi: 10.1007/BF00235471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. W., Dingledine R. Requirement for glycine in activation of NMDA-receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):835–837. doi: 10.1126/science.2841759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H., Miller J. J. The hippocampal control of neuronal discharges in the septum of the rat. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(3):607–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):729–749. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingai R., Ebina Y. Some properties of membrane current fluctuations induced by kainate, quisqualate, and NMDA in cultured septal neurons of rat. Brain Res. 1988 May 10;448(1):198–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. R., Cotman C. W. Excitatory amino acid antagonists depress transmission in hippocampal projections to the lateral septum. Brain Res. 1986 Sep 24;382(2):437–440. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. R., Gallagher J. P., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Further studies on the action of baclofen on neurons of the dorsolateral septal nucleus of the rat, in vitro. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 9;358(1-2):360–363. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90984-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. R., Gallagher J. P., Shinnick-Gallagher P. In vitro studies of the role of gamma-aminobutyric acid in inhibition in the lateral septum of the rat. Synapse. 1987;1(2):184–190. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. R., Gallagher J. P., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Intracellular recordings from rat dorsolateral septal neurons, in vitro. Brain Res. 1984 Jul 9;305(2):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90441-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Burton N. R. NMDA receptors and ligands in the vertebrate CNS. Prog Neurobiol. 1988;30(4):333–368. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(88)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Sawchenko P. E., Cowan W. M. Evidence that the commissural, associational and septal projections of the regio inferior of the hippocampus arise from the same neurons. Brain Res. 1980 Sep 15;197(1):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90446-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


