Abstract
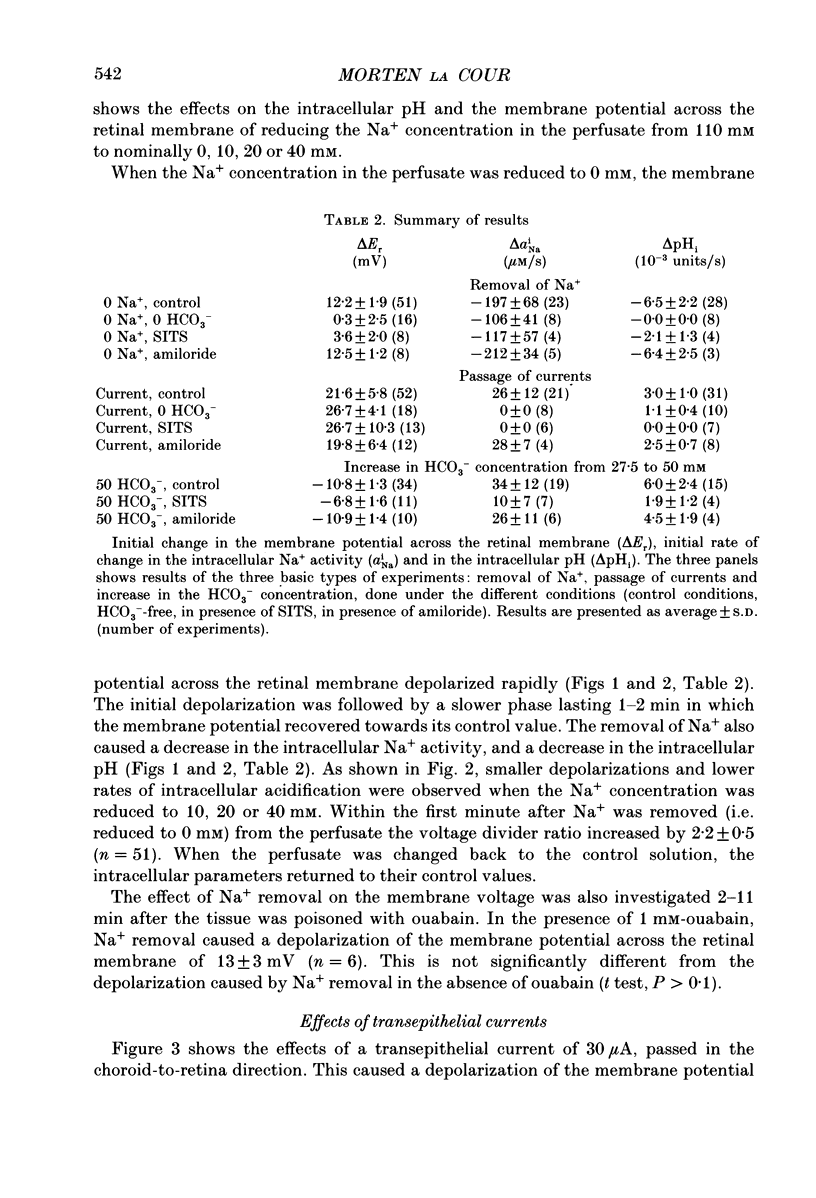
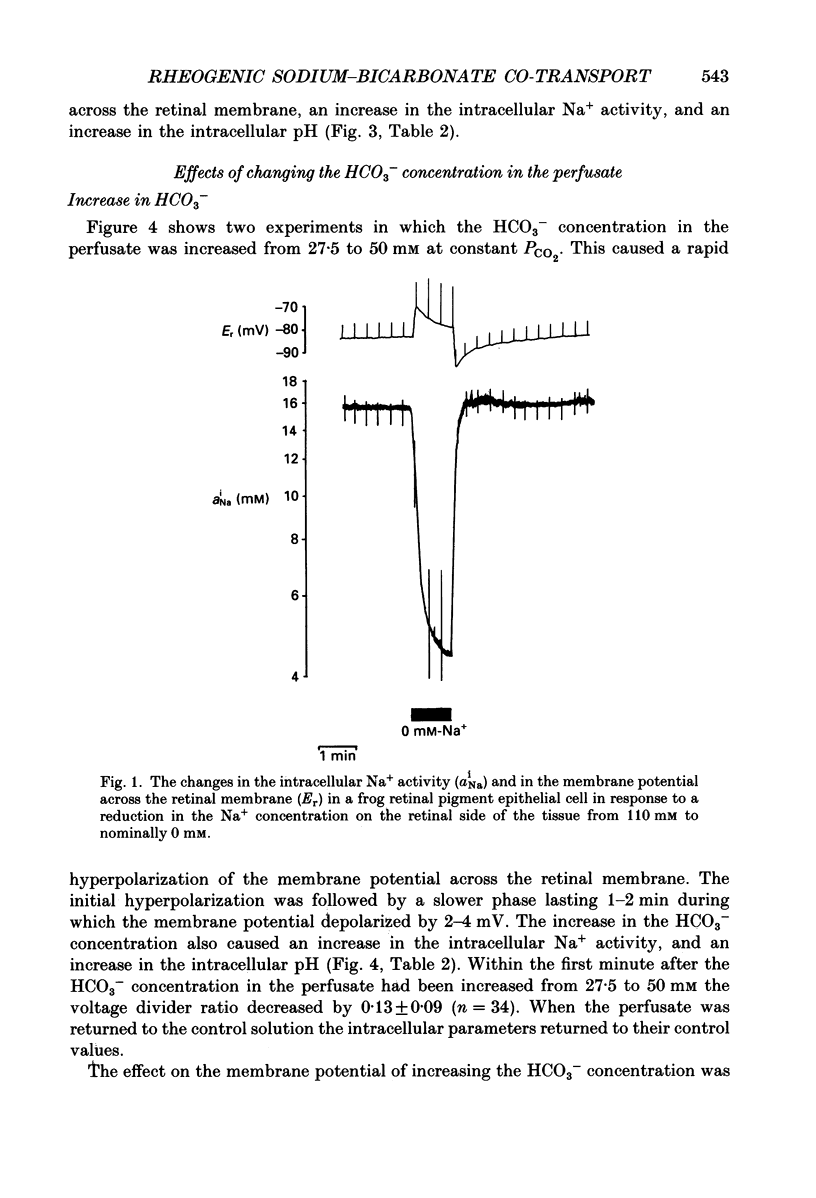
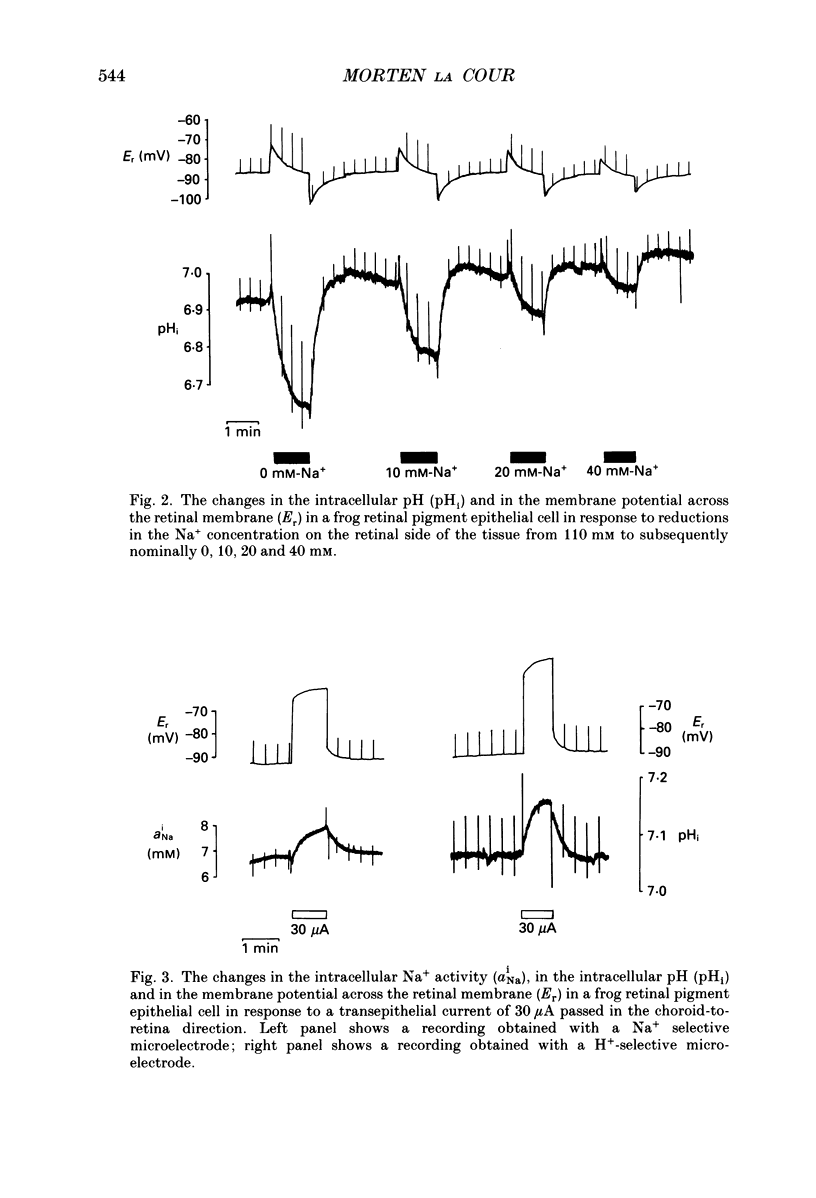
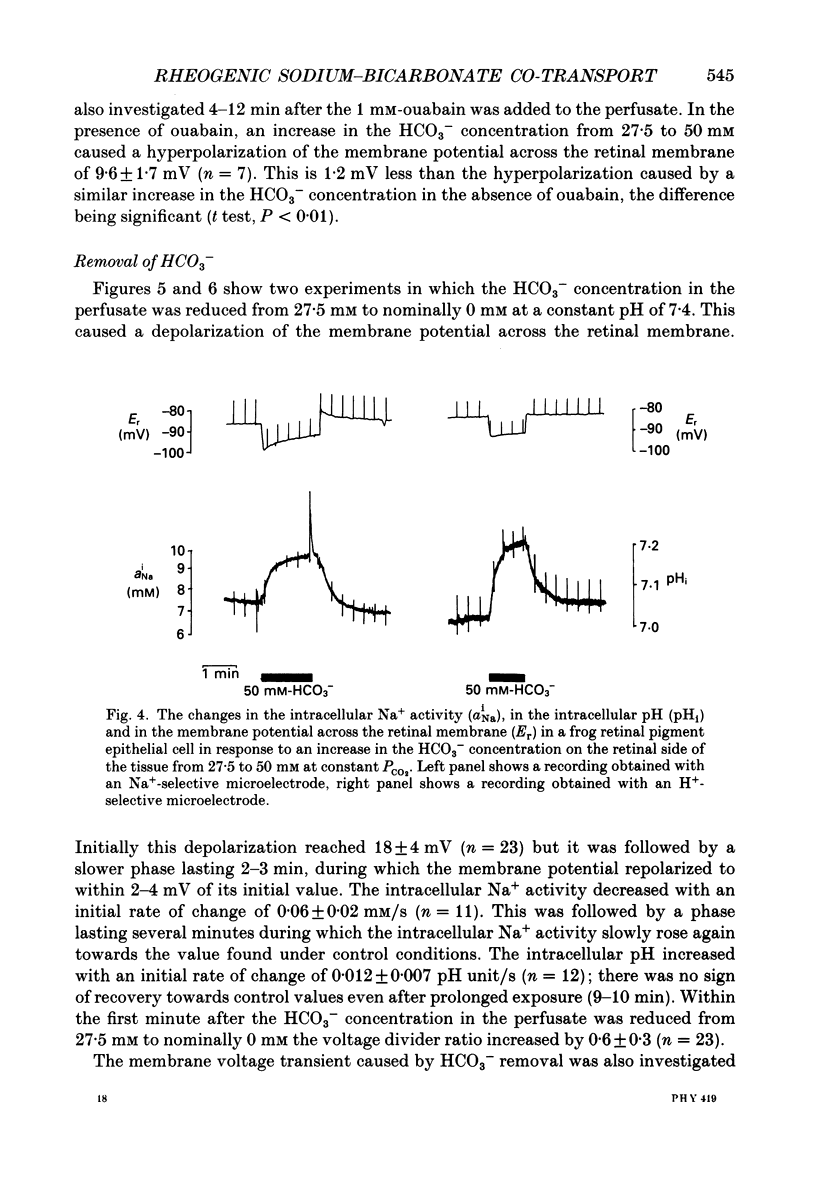
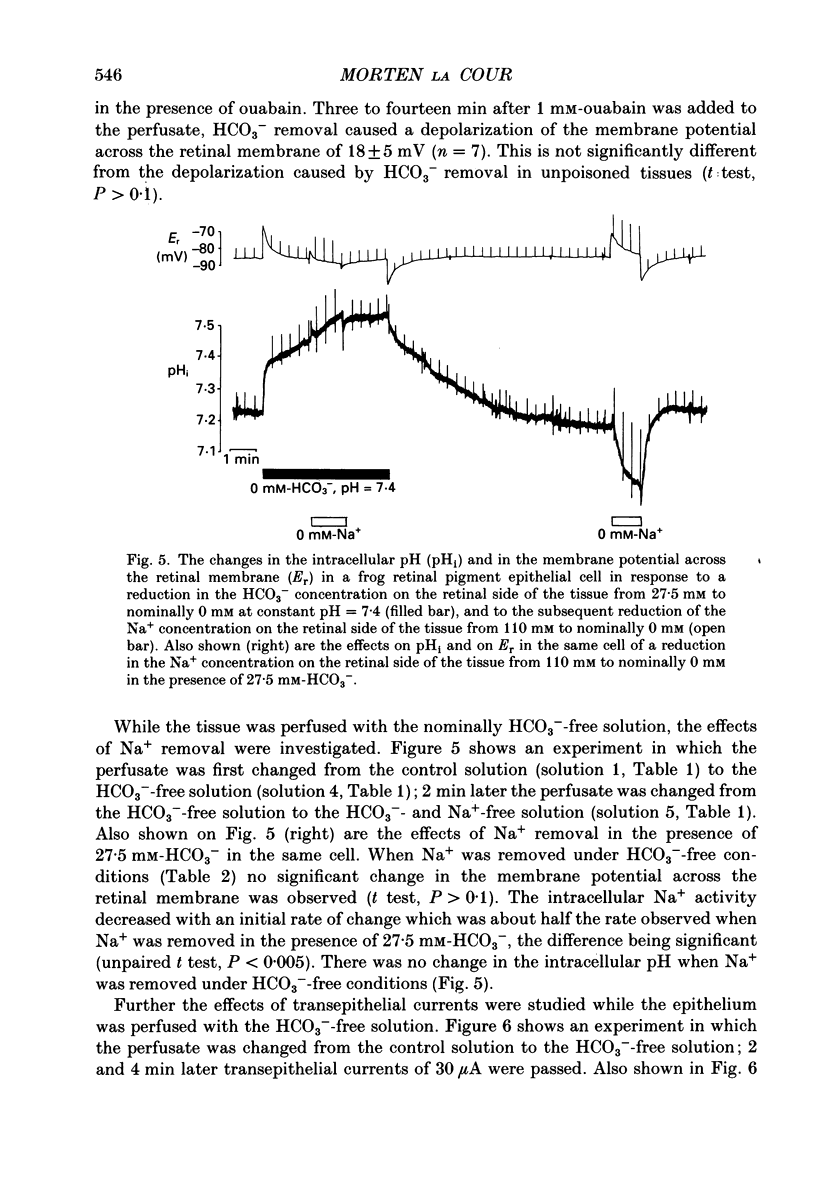
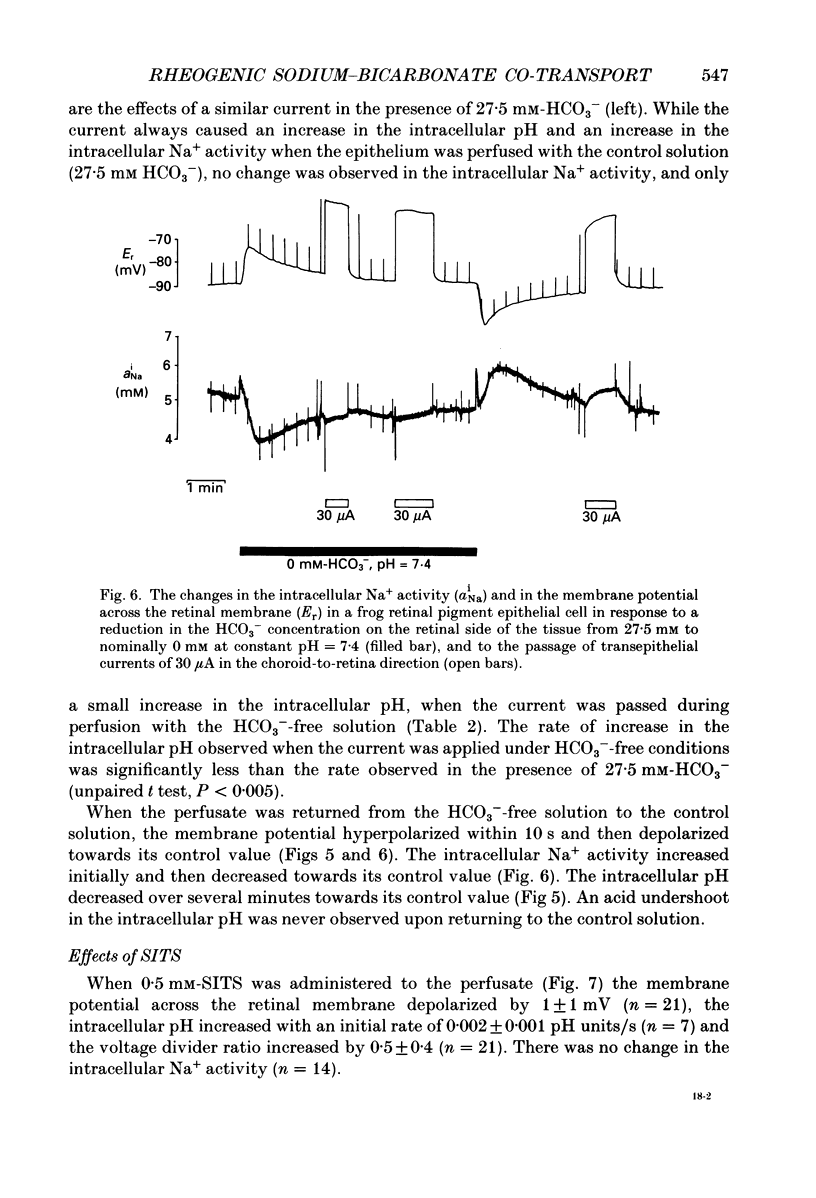
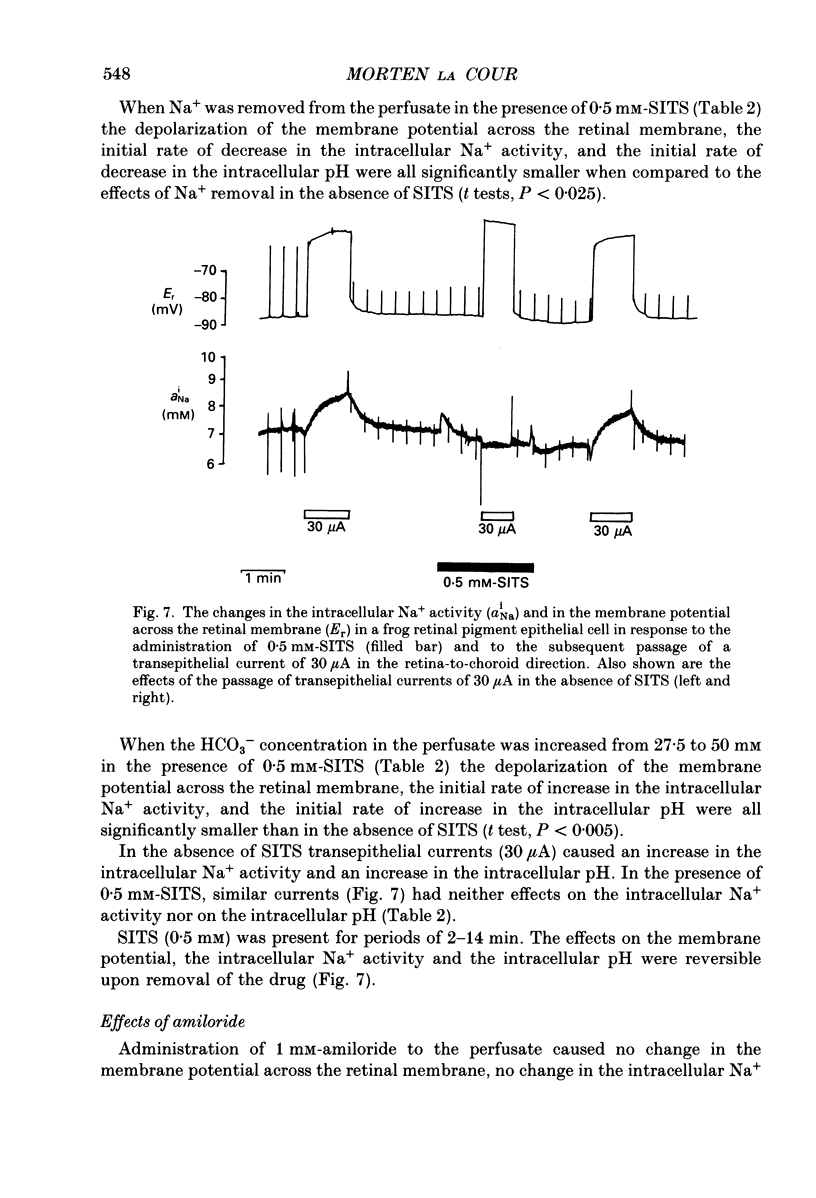
1. Na+ and HCO3- transport across the retinal membrane of the frog retinal pigment epithelium was studied by means of double-barrelled Na(+)- and pH-selective microelectrodes. Transient changes in the intracellular pH and in the intracellular Na+ activity were monitored in response to abrupt changes in the Na+ concentration and in the HCO3- concentration on the retinal side of the epithelium, and in response to transepithelial currents. 2. Removal of Na+ from the retinal side of the epithelium caused a depolarization of the membrane potential across the retinal membrane, a decrease in the intracellular Na+ activity and a decrease in the intracellular pH. 3. An increase in the HCO3- concentration on the retinal side of the epithelium from 27.5 to 50 mM caused a hyperpolarization of the membrane potential across the retinal membrane, an increase in the intracellular Na+ activity and an increase in the intracellular pH. 4. Passage of a transepithelial current of 30 microA in the choroid-to-retina direction caused an increase in the intracellular Na+ activity and an increase in the intracellular pH. 5. The data are interpreted as evidence for rheogenic co-transport of Na+, HCO3- across the retinal membrane of the frog retinal pigment epithelium. 6. The transient changes described under 2, 3 and 4 above were blocked by 0.5 mM-4-acetamido-4'-isothiocyanostilbene-2.2'-disulphonic acid (SITS). The Na(+)- HCO3- co-transport was not inhibited by 1 mM-amiloride.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpern R. J. Mechanism of basolateral membrane H+/OH-/HCO-3 transport in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. A sodium-coupled electrogenic process. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Nov;86(5):613–636. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.5.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besharse J. C., Dunis D. A. Rod photoreceptor disc shedding in eye cups: relationship to bicarbonate and amino acids. Exp Eye Res. 1983 Apr;36(4):567–579. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(83)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biagi B. A. Effects of the anion transport inhibitor, SITS, on the proximal straight tubule of the rabbit perfused in vitro. J Membr Biol. 1985;88(1):25–31. doi: 10.1007/BF01871210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biagi B. A., Sohtell M. Electrophysiology of basolateral bicarbonate transport in the rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 2):F267–F272. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.2.F267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Basolateral HCO3- transport. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):53–94. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curci S., Debellis L., Frömter E. Evidence for rheogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransport in the basolateral membrane of oxyntic cells of frog gastric fundus. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(5):497–504. doi: 10.1007/BF00585075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes B. A., Adorante J. S., Miller S. S., Lin H. Apical electrogenic NaHCO3 cotransport. A mechanism for HCO3 absorption across the retinal pigment epithelium. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jul;94(1):125–150. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Keller S. K., Koch M., Wiederholt M. Evidence for coupled transport of bicarbonate and sodium in cultured bovine corneal endothelial cells. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(3):189–204. doi: 10.1007/BF01868713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Koch M., Bleckmann H., Wiederholt M. Effect of bicarbonate, pH, methazolamide and stilbenes on the intracellular potentials of cultured bovine corneal endothelial cells. J Membr Biol. 1984;78(2):103–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01869198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Matthes H., Keller S. K., Wiederholt M. Electrical properties of sodium bicarbonate symport in kidney epithelial cells (BSC-1). Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 2):F954–F968. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.6.F954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Schill B. S., Schwartz P., Matthes H., Keller S. K., Wiederholt M. Kidney epithelial cells of monkey origin (BSC-1) express a sodium bicarbonate cotransport. Characterization by 22Na+ flux measurements. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15554–15560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller S. K., Jentsch T. J., Janicke I., Wiederholt M. Regulation of intracellular pH in cultured bovine retinal pigment epithelial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jan;411(1):47–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00581645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes A. G., Siebens A. W., Giebisch G., Boron W. F. Electrogenic Na/HCO3 cotransport across basolateral membrane of isolated perfused Necturus proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 2):F340–F350. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.2.F340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlue W. R., Deitmer J. W. Ionic mechanisms of intracellular pH regulation in the nervous system. Ciba Found Symp. 1988;139:47–69. doi: 10.1002/9780470513699.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Experimental displacement of intracellular pH and the mechanism of its subsequent recovery. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:3P–22P. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitomi K., Burckhardt B. C., Frömter E. Rheogenic sodium-bicarbonate cotransport in the peritubular cell membrane of rat renal proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):360–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00595689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- la Cour M., Lund-Andersen H., Zeuthen T. Potassium transport of the frog retinal pigment epithelium: autoregulation of potassium activity in the subretinal space. J Physiol. 1986 Jun;375:461–479. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


