Abstract
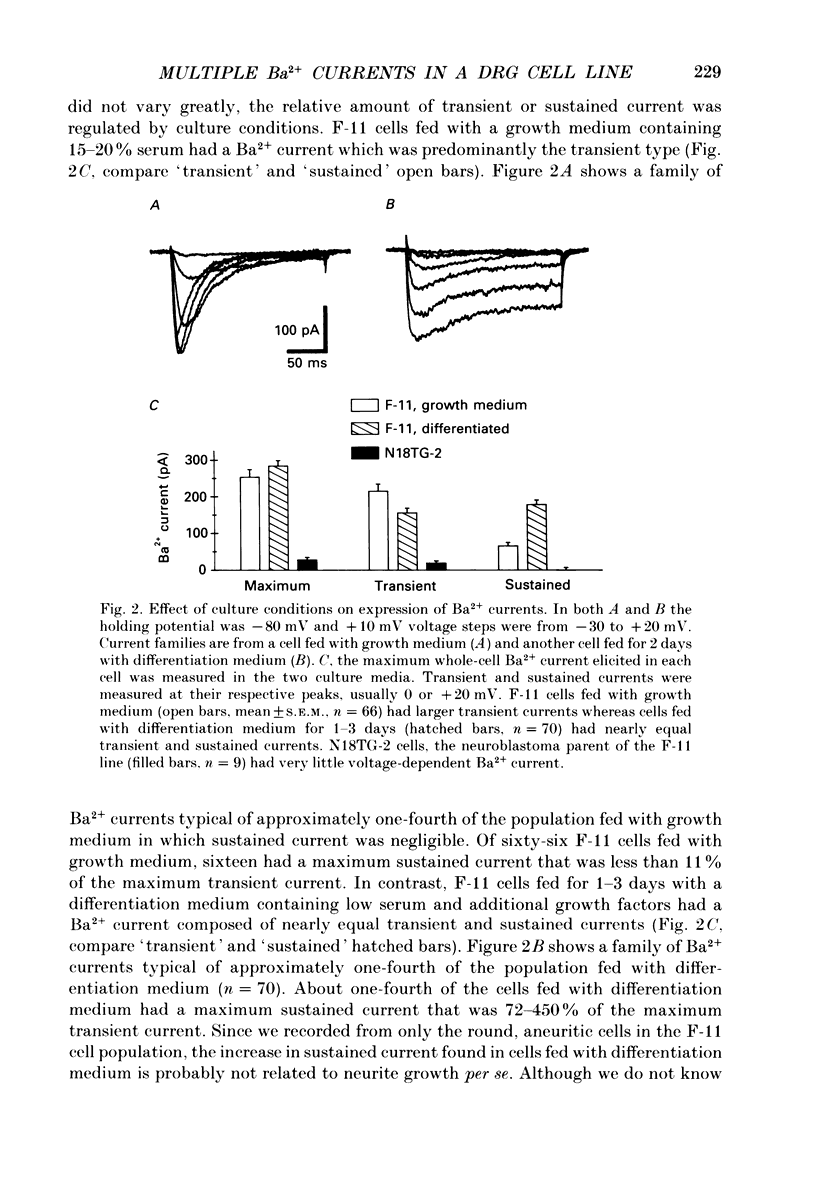
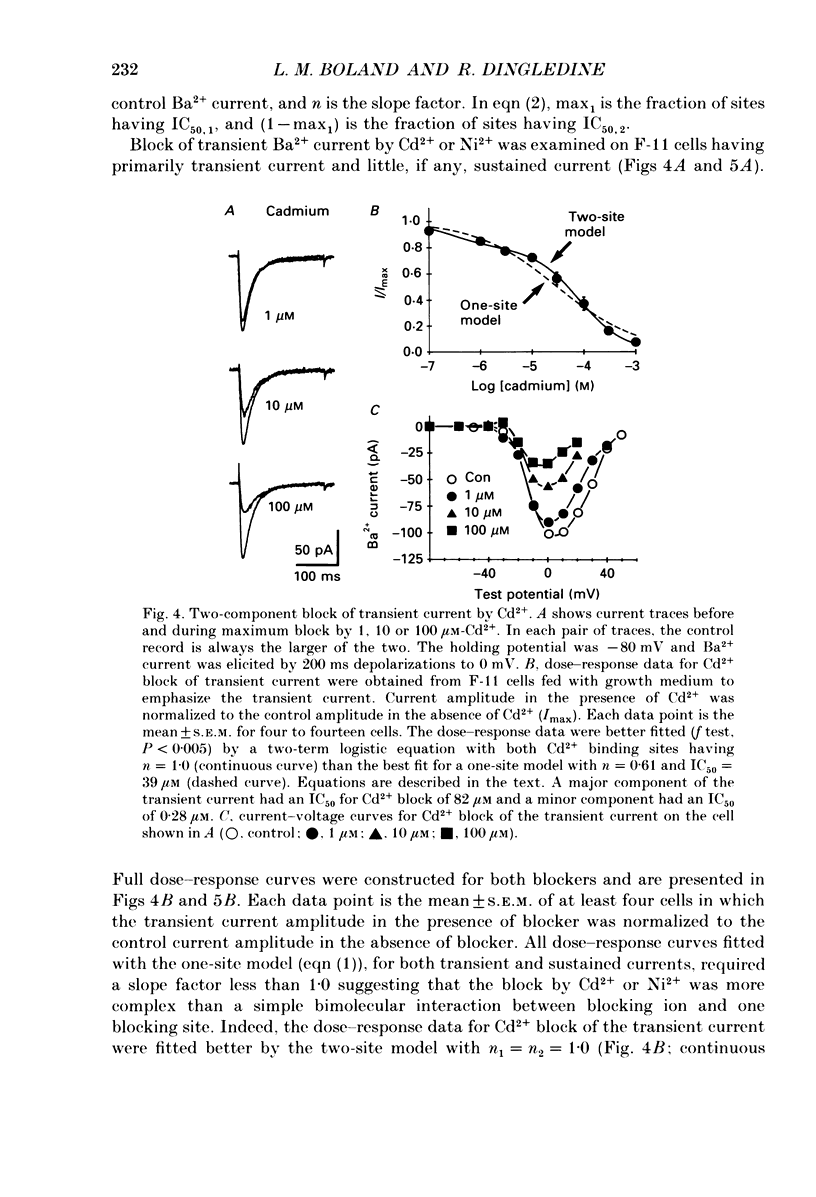
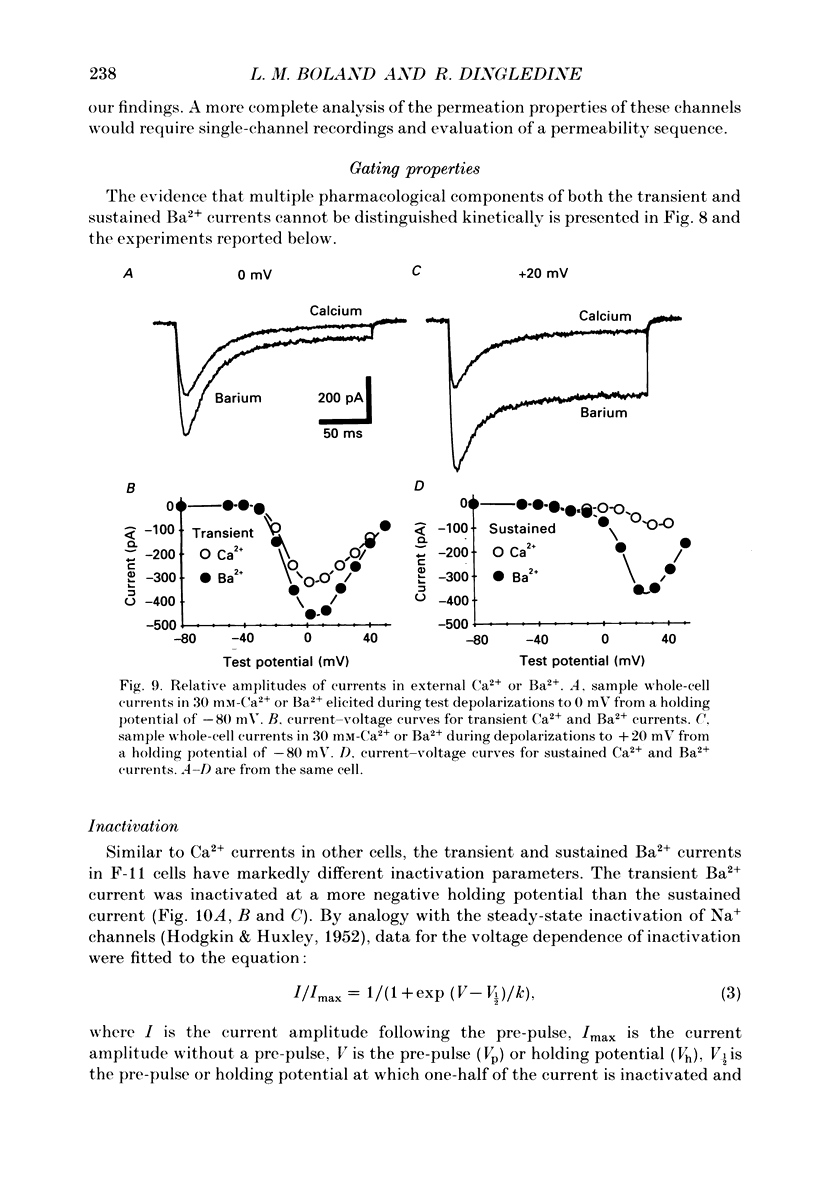
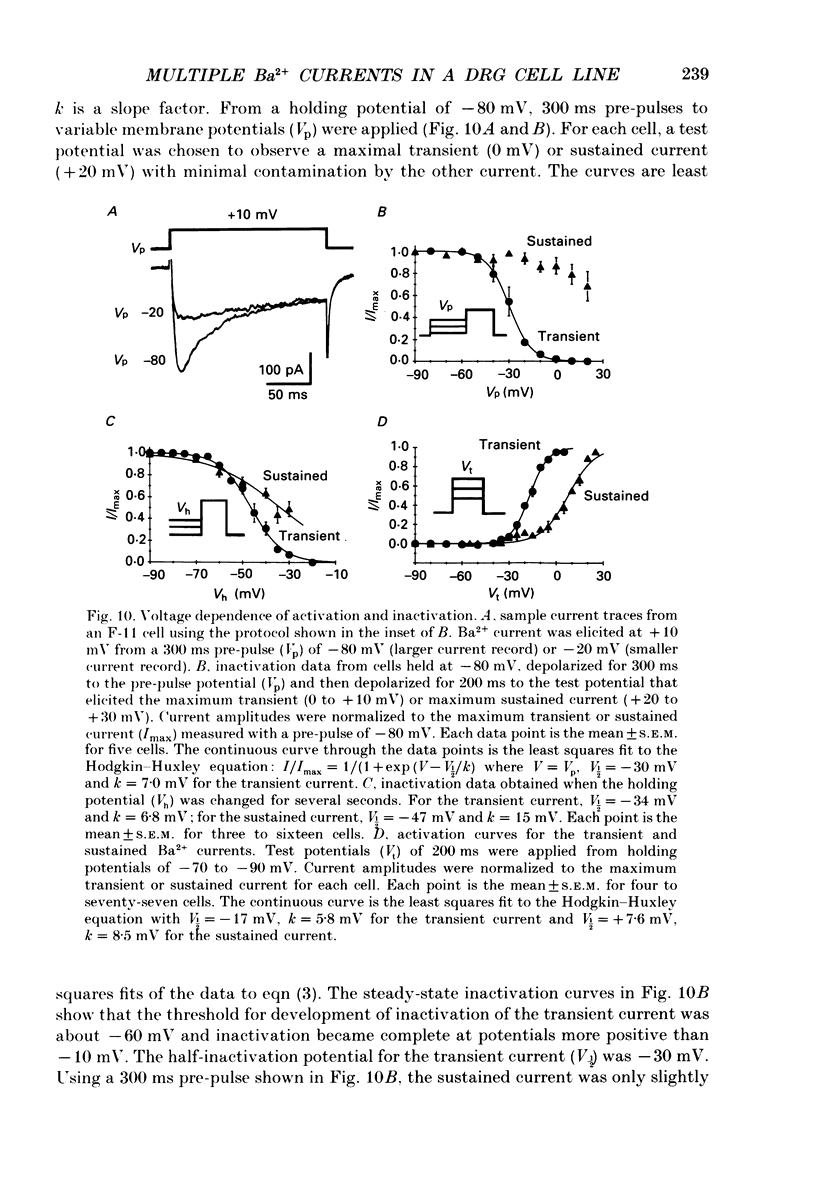
1. Currents through voltage-activated Ca2+ channels in rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) x mouse neuroblastoma hybrid (F-11) cells were studied using the whole-cell patch clamp technique with 30 mM-Ba2+ as charge carrier. Two components of the inward Ba2+ current were distinguished on the basis of voltage dependence and time course. Each component could be further subdivided based on pharmacology. 2. A transient inward current activated at test potentials positive to -40 mV, peaked within 20 ms and then decayed during a 200 ms depolarization. The peak amplitude of the transient current occurred between -10 and +10 mV. With a 300 ms conditioning pulse, half-inactivation of the transient current occurred at -30 mV. A sustained inward current activated at test potentials positive to -30 mV and reached a maximum at +20 to +30 mV. The sustained current showed little voltage-dependent inactivation over 200 ms. The amplitudes of both the transient and sustained currents were increased by perfusing with Ba2+ instead of Ca2+. 3. Most F-11 cells had both the transient and sustained Ba2+ currents although the relative amount of the two currents varied with culture conditions. The transient current was more prominent in cells fed with a 'growth' medium (15-20% serum) whereas the sustained current was increased in cells fed with a 'differentiation' medium (1% serum plus growth factors). F-11 cells can be used to study transient current in relative isolation from sustained Ca2+ current under certain culture conditions. The neuroblastoma parent of the F-11 cell line, N18TG-2 cells, exhibited little or no voltage-dependent Ba2+ current. 4. Brief application of omega-conotoxin fraction GVIA (10 microM) produced a long-lasting block of 81% of the sustained current and 27% of the transient current. 5. The transient and sustained Ba2+ currents in F-11 cells were reversibly blocked by brief exposure to Cd2+ or Ni2+. Block of the sustained current was evident with 100 nM-Cd2+ whereas the threshold concentration for Ni2+ block was 1 microM. Cd2+ and Ni2+ were equipotent blockers of the transient current. Dose-response curves for Cd2+ and Ni2+ block of both sustained and transient currents had shallow slopes suggesting that the block was more complex than a simple bimolecular interaction between blocker and one blocking site. Dose-response curves were fitted by a model that included two binding sites for each divalent blocker.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossu J. L., Feltz A., Thomann J. M. Depolarization elicits two distinct calcium currents in vertebrate sensory neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Apr;403(4):360–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00589247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. J., McCarthy R. T. Nimodipine block of calcium channels in rat anterior pituitary cells. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:195–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewald D. A., Pang I. H., Sternweis P. C., Miller R. J. Differential G protein-mediated coupling of neurotransmitter receptors to Ca2+ channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons in vitro. Neuron. 1989 Feb;2(2):1185–1193. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedulova S. A., Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S. Two types of calcium channels in the somatic membrane of new-born rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forscher P., Oxford G. S. Modulation of calcium channels by norepinephrine in internally dialyzed avian sensory neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1985 May;85(5):743–763. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.5.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Single-channel recordings of three types of calcium channels in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:173–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francel P. C., Harris K., Smith M., Fishman M. C., Dawson G., Miller R. J. Neurochemical characteristics of a novel dorsal root ganglion X neuroblastoma hybrid cell line, F-11. J Neurochem. 1987 May;48(5):1624–1631. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francel P. C., Miller R. J., Dawson G. Modulation of bradykinin-induced inositol trisphosphate release in a novel neuroblastoma x dorsal root ganglion sensory neuron cell line (F-11). J Neurochem. 1987 May;48(5):1632–1639. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. A., Macdonald R. L. Dynorphin A selectively reduces a large transient (N-type) calcium current of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Calcium channel selectivity for divalent and monovalent cations. Voltage and concentration dependence of single channel current in ventricular heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):538–544. doi: 10.1038/311538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):453–456. doi: 10.1038/309453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirning L. D., Fox A. P., McCleskey E. W., Olivera B. M., Thayer S. A., Miller R. J., Tsien R. W. Dominant role of N-type Ca2+ channels in evoked release of norepinephrine from sympathetic neurons. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):57–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2447647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Dunlap K., Kream R. M. Characterization of the electrically evoked release of substance P from dorsal root ganglion neurons: methods and dihydropyridine sensitivity. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):463–471. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00463.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y. Calcium channels in isolated rat dorsal horn neurones, including labelled spinothalamic and trigeminothalamic cells. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:161–177. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Aosaki T., Fukuda J. Presynaptic Ca-antagonist omega-conotoxin irreversibly blocks N-type Ca-channels in chick sensory neurons. Neurosci Res. 1987 Feb;4(3):228–235. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(87)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Shuba YaM, Savchenko A. N. Three types of calcium channels in the membrane of mouse sensory neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jun;411(6):661–669. doi: 10.1007/BF00580863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansman J. B., Hess P., Tsien R. W. Blockade of current through single calcium channels by Cd2+, Mg2+, and Ca2+. Voltage and concentration dependence of calcium entry into the pore. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):321–347. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of calcium channel blockade by verapamil, D600, diltiazem and nitrendipine in single dialysed heart cells. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):790–794. doi: 10.1038/302790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleskey E. W., Almers W. The Ca channel in skeletal muscle is a large pore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7149–7153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleskey E. W., Fox A. P., Feldman D. H., Cruz L. J., Olivera B. M., Tsien R. W., Yoshikami D. Omega-conotoxin: direct and persistent blockade of specific types of calcium channels in neurons but not muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4327–4331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky H. J., Ransnas L. A. Fitting curves to data using nonlinear regression: a practical and nonmathematical review. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):365–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T., Tsunoo A., Yoshii M. Characterization of two types of calcium channels in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:231–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perney T. M., Hirning L. D., Leeman S. E., Miller R. J. Multiple calcium channels mediate neurotransmitter release from peripheral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6656–6659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platika D., Boulos M. H., Baizer L., Fishman M. C. Neuronal traits of clonal cell lines derived by fusion of dorsal root ganglia neurons with neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3499–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Logothetis D. E., Hess P. Elementary properties and pharmacological sensitivities of calcium channels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rane S. G., Holz G. G., 4th, Dunlap K. Dihydropyridine inhibition of neuronal calcium current and substance P release. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Aug;409(4-5):361–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00583789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Hess P., Tsien R. W. Cardiac calcium channels in planar lipid bilayers. L-type channels and calcium-permeable channels open at negative membrane potentials. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):27–54. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simasko S. M., Weiland G. A., Oswald R. E. Pharmacological characterization of two calcium currents in GH3 cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 1):E328–E336. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.3.E328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swandulla D., Armstrong C. M. Fast-deactivating calcium channels in chick sensory neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):197–218. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Hess P., McCleskey E. W., Rosenberg R. L. Calcium channels: mechanisms of selectivity, permeation, and block. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:265–290. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland G. A., Oswald R. E. The mechanism of binding of dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers to rat brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8456–8464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Participation of calcium spikes during intrinsic burst firing in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1978 Dec 29;159(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90544-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


