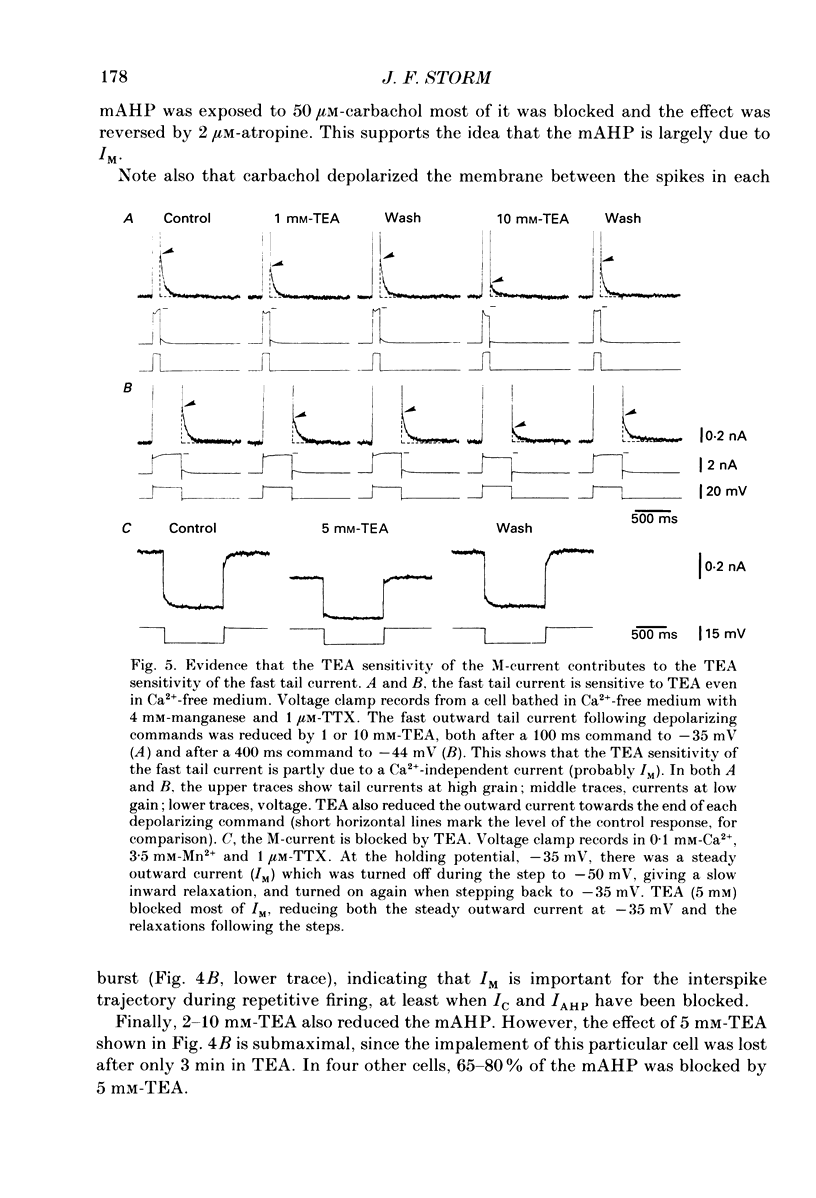
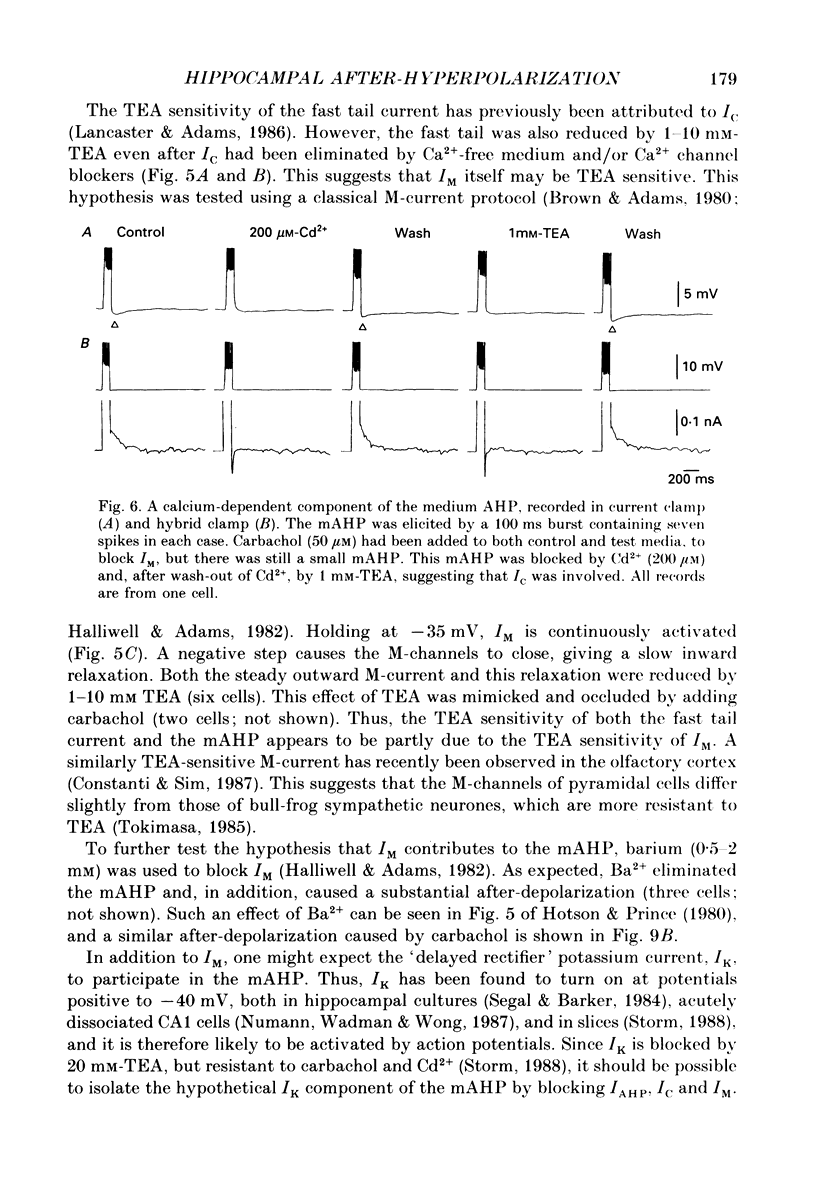
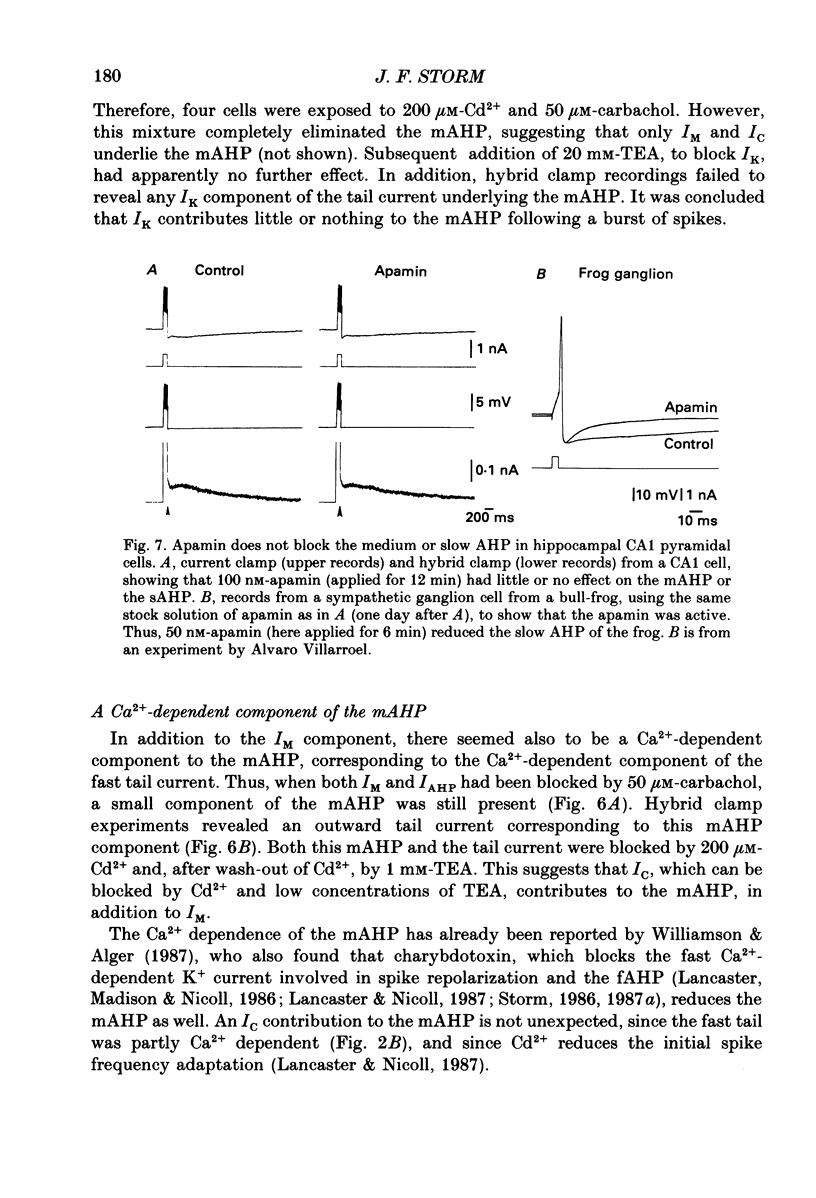
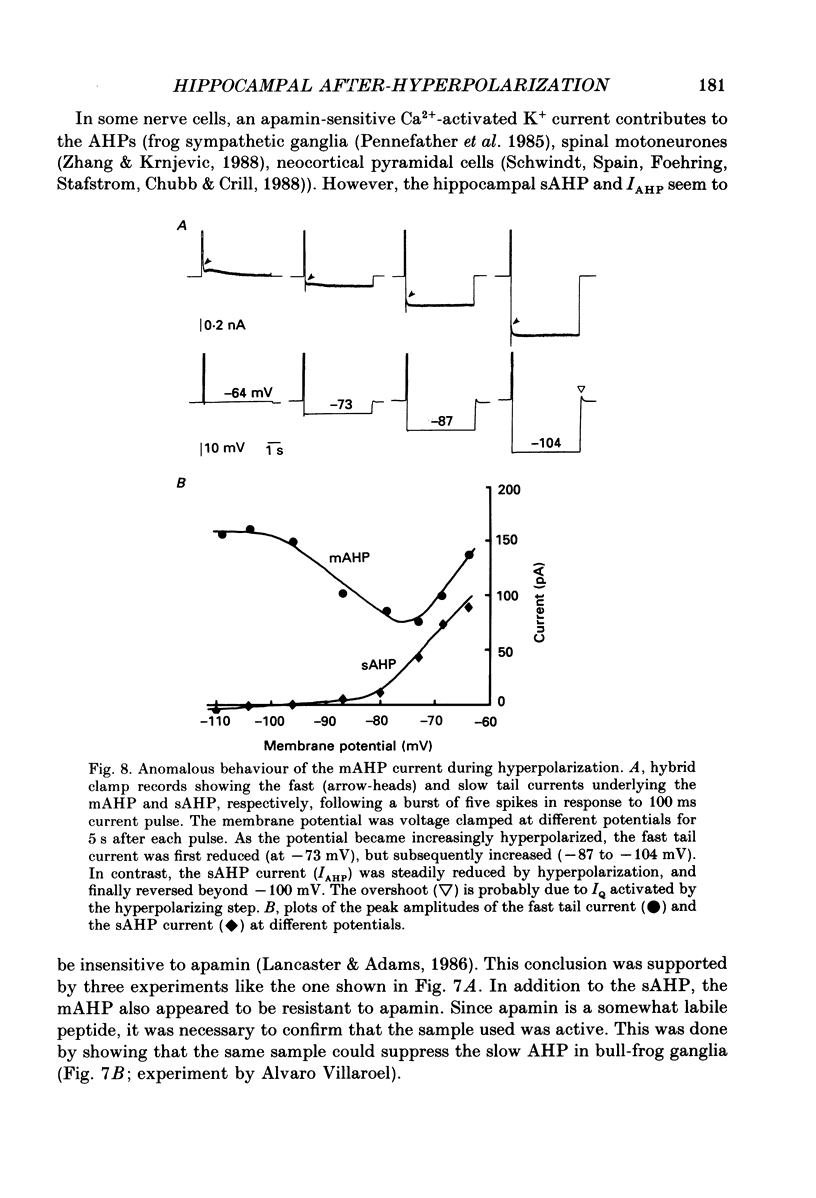
Abstract
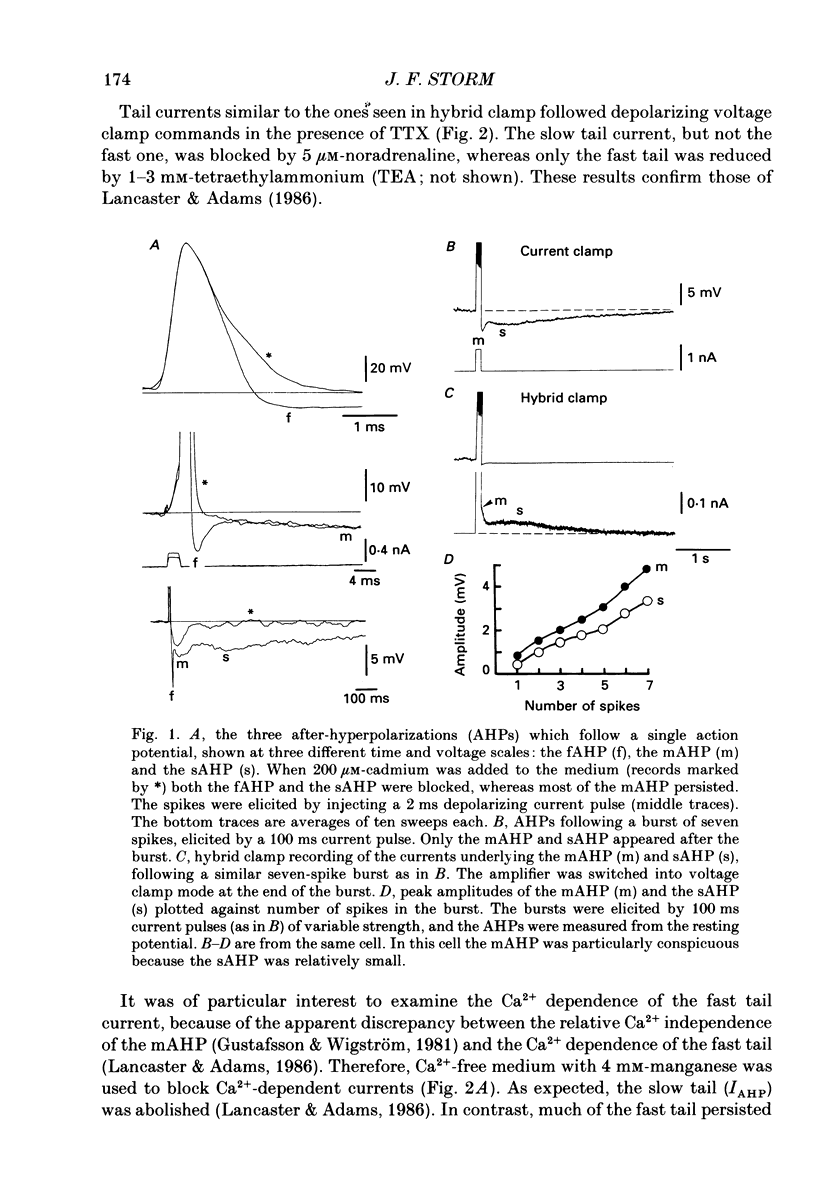
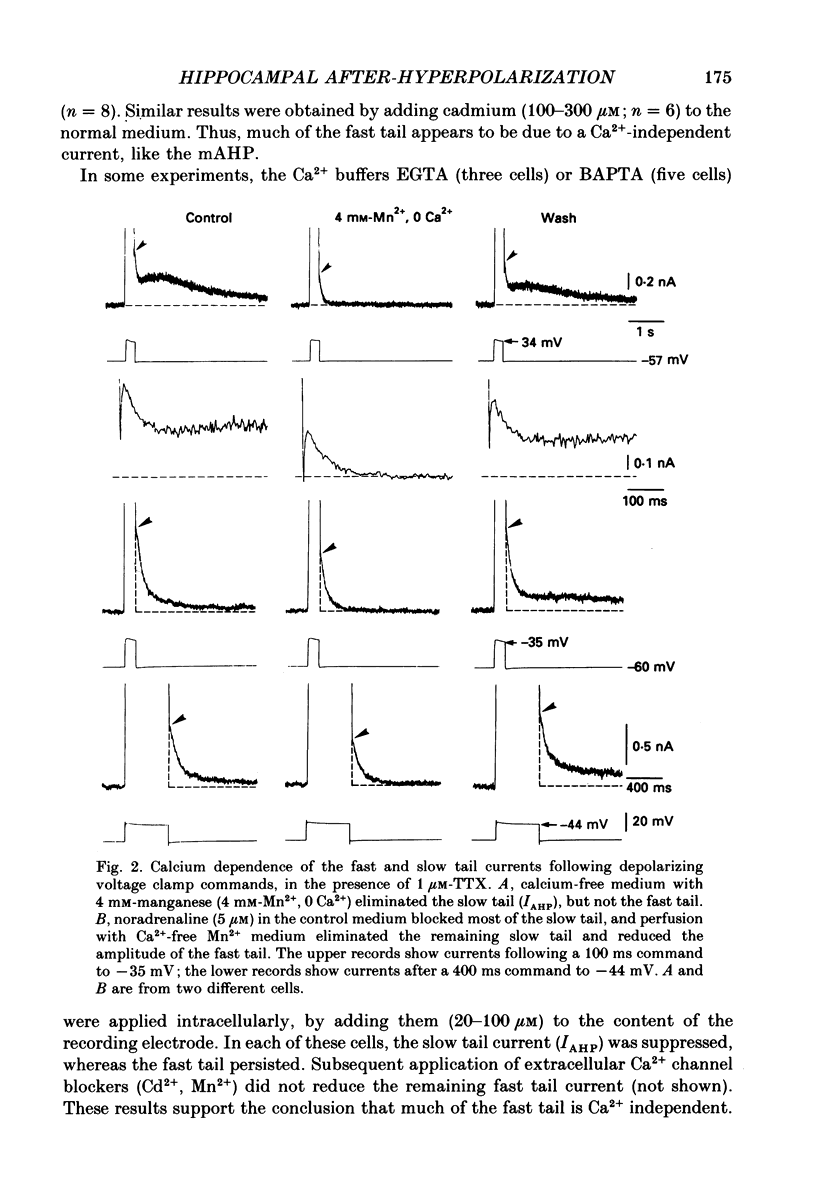
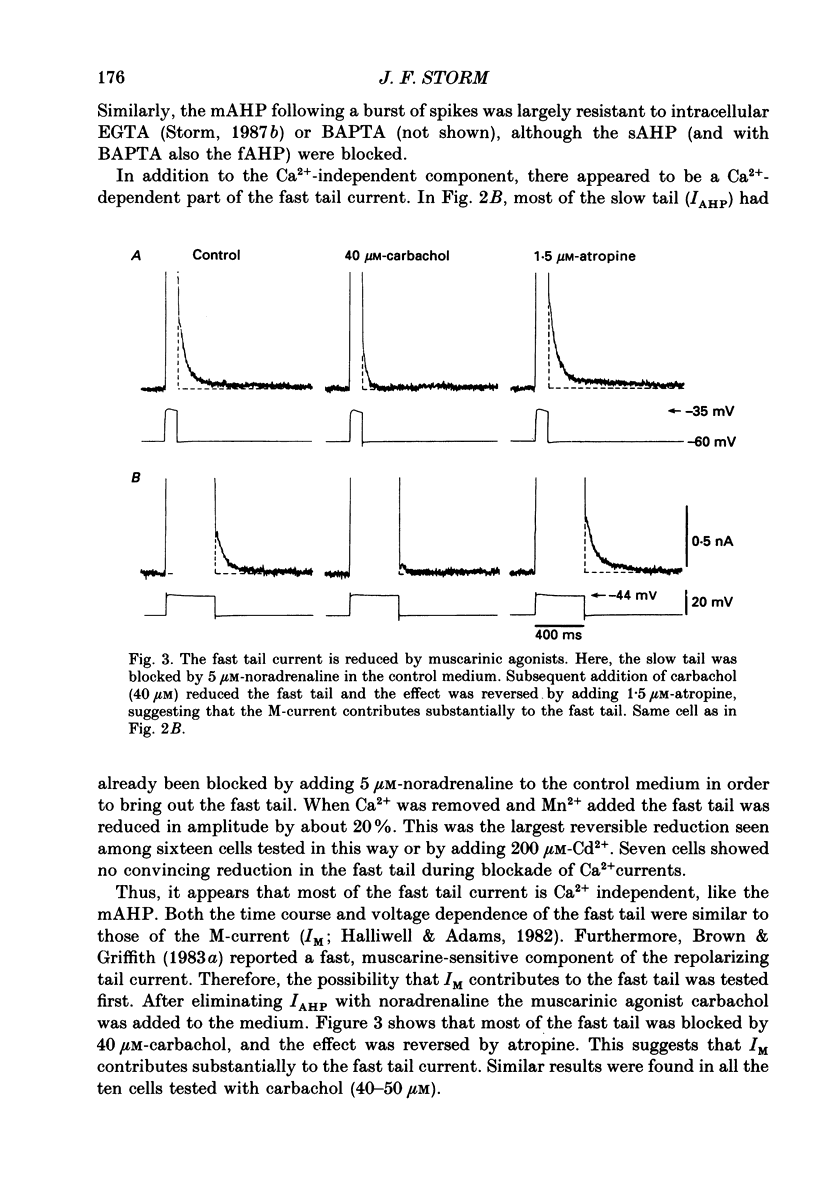
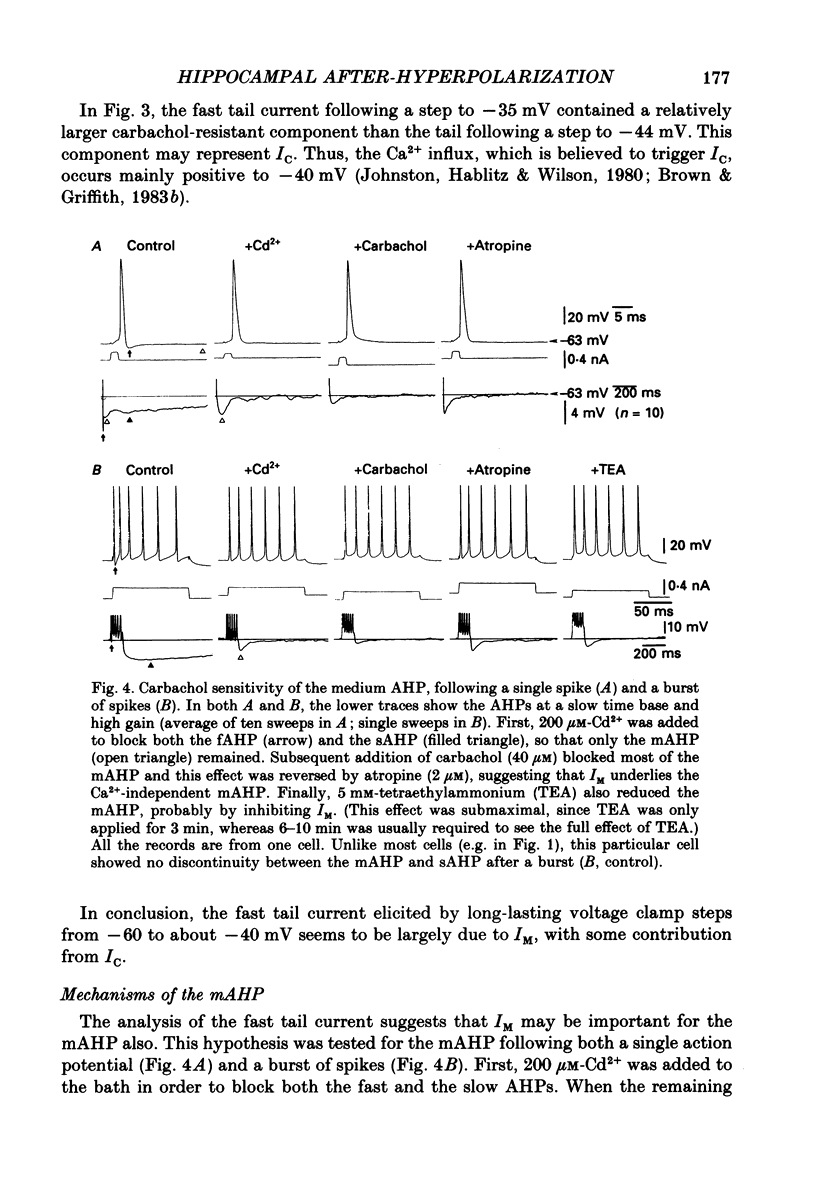
1. In hippocampal pyramidal cells, action potentials are followed by three after-hyperpolarizations (AHPs): a fast AHP (fAHP) lasting 2-5 ms, a medium AHP (mAHP) lasting 50-100 ms, and a slow AHP (sAHP) lasting more than 1 s. The mechanism underlying the mAHP was studied in CA1 cells (n = 46) in rat hippocampal slices, using injection of depolarizing current to elicit discharge. 2. The current underlying the mAHP was studied by single-electrode voltage clamp in two ways. Either the voltage clamp was activated following a burst of spikes, thus recording the early tail current underlying the mAHP (hybrid clamp), or, after blocking the spikes with tetrodotoxin, the early tail current following a depolarizing voltage clamp command (to -20 to -45 mV for 100-400 ms) was measured. In both cases, the early tail current (measured at -60 mV) showed the following characteristics: (a) it decayed exponentially with a time constant of about 50 ms; (b) it was substantially reduced by the muscarinic agonist carbachol (40-50 microM); (c) it was moderately reduced (by 20% or less) by Ca2+-free medium and Ca2+ channel blockers (Cd2+, Mn2+), which abolished the fAHP and the sAHP; (d) it was partly blocked by tetraethylammonium (TEA, 1-10 mM) both before and during Ca2+ channel blockade; (e) it was resistant to noradrenaline (5-10 microM), which blocked the sAHP, and to apamin (100 nM). 3. The mAHP itself, recorded under current clamp, showed properties corresponding to those of the early tail current. 4. Unlike the current underlying the sAHP, which was reduced and reversed by hyperpolarization, the early tail current appeared to be reduced only at potentials down to -80 mV, and to increase at more negative potentials. The early tail current and mAHP-like undershoot at hyperpolarized potentials was blocked by external Cs+, but not by carbachol, in contrast to the early tail current and mAHP at -60 mV. 5. It was concluded that two currents contribute to the mAHP: IM (a voltage-gated muscarine-sensitive K+ current) and IC (a Ca2+-dependent TEA-sensitive K+ current). TEA reduced both the IM (5 mM) and the IC (1 mM) component of the mAHP. When the cell is hyperpolarized, a third current, IQ (a Ca+-sensitive mixed Na+-K+ inward current activated by hyperpolarization), masks the reversal of the mAHP by causing a depolarizing sag which resembles the decay of the mAHP.
Full text
PDF


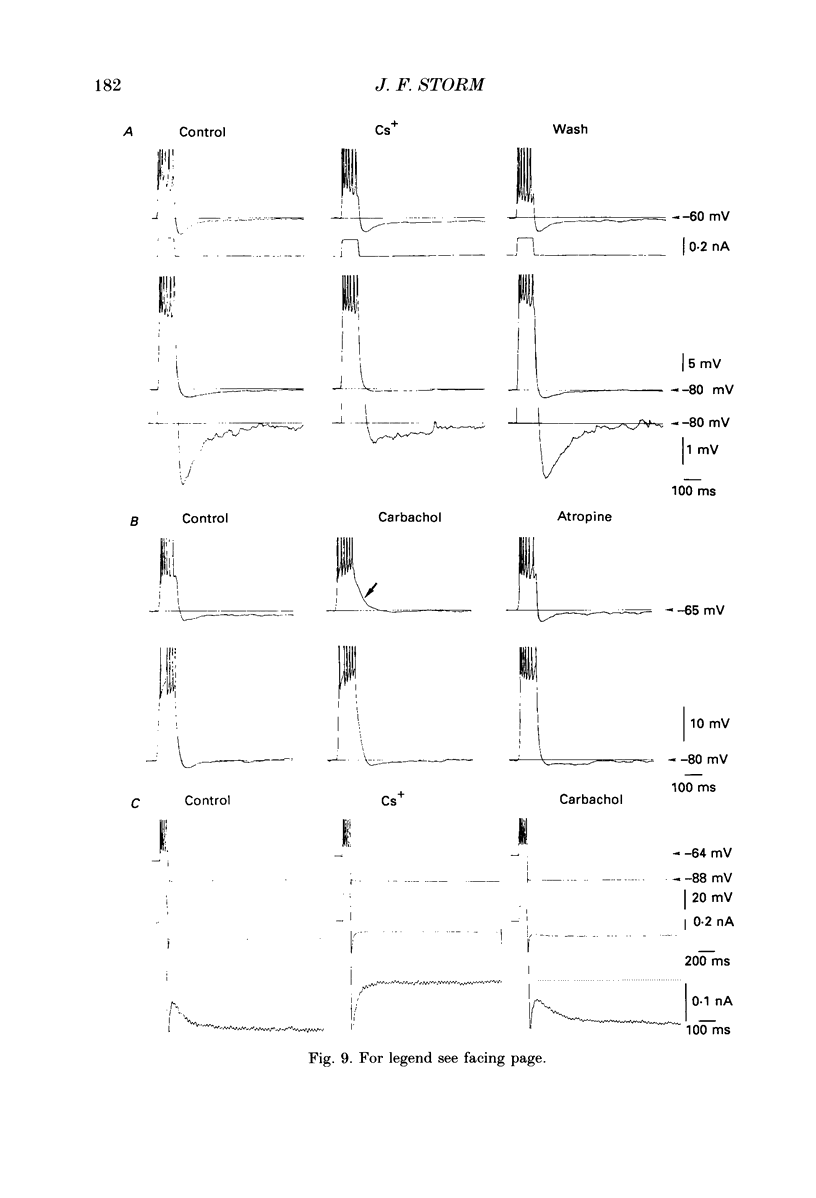

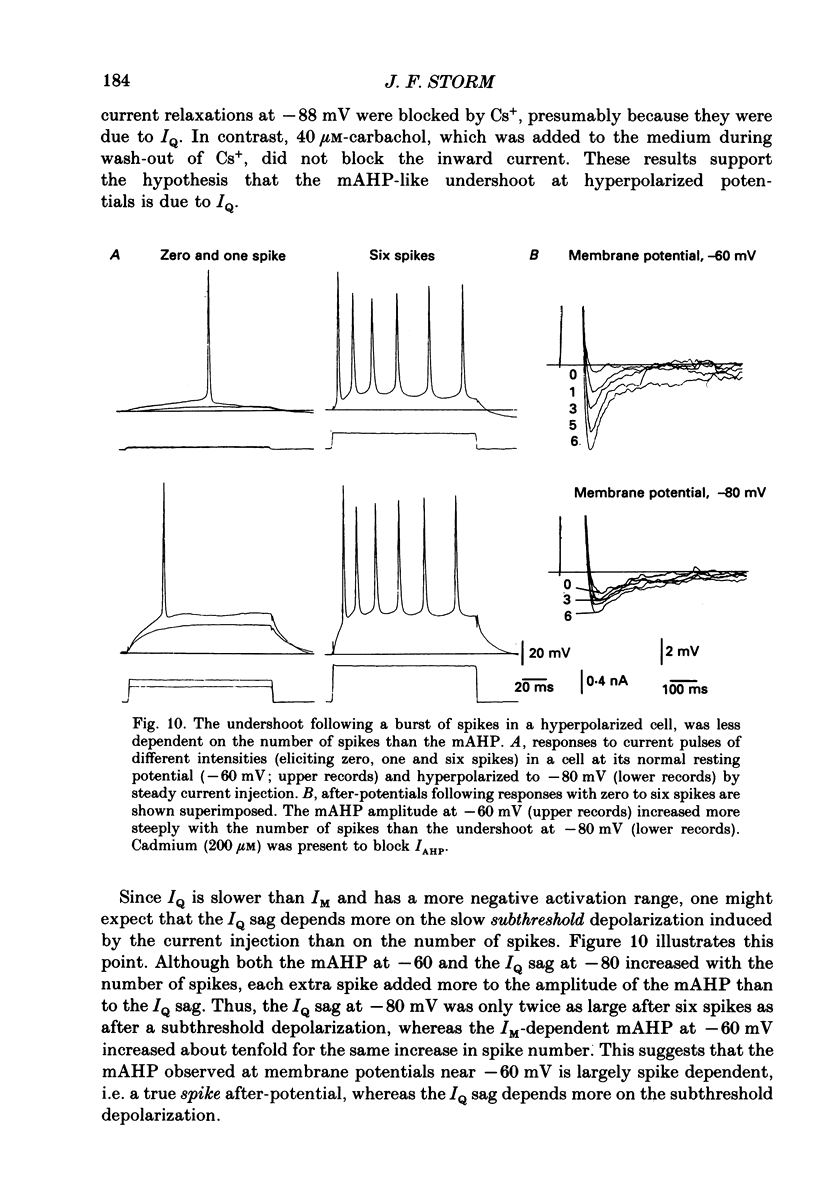






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:537–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alger B. E., Nicoll R. A. Epileptiform burst afterhyperolarization: calcium-dependent potassium potential in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Science. 1980 Dec 5;210(4474):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.7444438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade R., Nicoll R. A. Pharmacologically distinct actions of serotonin on single pyramidal neurones of the rat hippocampus recorded in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:99–124. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benardo L. S., Prince D. A. Ionic mechanisms of cholinergic excitation in mammalian hippocampal pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 14;249(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Griffith W. H. Calcium-activated outward current in voltage-clamped hippocampal neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:287–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Griffith W. H. Persistent slow inward calcium current in voltage-clamped hippocampal neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:303–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Johnston D. Voltage-clamp analysis of mossy fiber synaptic input to hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Aug;50(2):487–507. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.2.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Nicoll R. A. Acetylcholine mediates a slow synaptic potential in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Science. 1983 Sep 23;221(4617):1299–1301. doi: 10.1126/science.6612345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Nicoll R. A. Characterization of a slow cholinergic post-synaptic potential recorded in vitro from rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Nicoll R. A. The pharmacology of cholinergic excitatory responses in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1984 Jul 9;305(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90434-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colino A., Halliwell J. V. Differential modulation of three separate K-conductances in hippocampal CA1 neurons by serotonin. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):73–77. doi: 10.1038/328073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Brown D. A. M-Currents in voltage-clamped mammalian sympathetic neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jul 17;24(3):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Sim J. A. Calcium-dependent potassium conductance in guinea-pig olfactory cortex neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:173–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The after-effects of impulses in the giant nerve fibres of Loligo. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):341–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel A. S., Redman S. Theory and operation of a single microelectrode voltage clamp. J Neurosci Methods. 1984 Jun;11(2):101–127. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(84)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Wigström H. Evidence for two types of afterhyperpolarization in CA1 pyramidal cells in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 16;206(2):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90548-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Greene R. W. Adenosine enhances afterhyperpolarization and accommodation in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Nov;402(3):244–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00585506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Greene R. W. Effects of histamine on hippocampal pyramidal cells of the rat in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1986;62(1):123–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00237408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Konnerth A. Histamine and noradrenaline decrease calcium-activated potassium conductance in hippocampal pyramidal cells. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):432–434. doi: 10.1038/302432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell J. V., Adams P. R. Voltage-clamp analysis of muscarinic excitation in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 28;250(1):71–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90954-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotson J. R., Prince D. A. A calcium-activated hyperpolarization follows repetitive firing in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;43(2):409–419. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Brown T. H. Interpretation of voltage-clamp measurements in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Aug;50(2):464–486. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.2.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Hablitz J. J., Wilson W. A. Voltage clamp discloses slow inward current in hippocampal burst-firing neurones. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):391–393. doi: 10.1038/286391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Adams P. R. Calcium-dependent current generating the afterhyperpolarization of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jun;55(6):1268–1282. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.6.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Properties of two calcium-activated hyperpolarizations in rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:187–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Wheal H. V. The synaptically evoked late hyperpolarisation in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells is resistant to intracellular EGTA. Neuroscience. 1984 May;12(1):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Voltage clamp analysis of cholinergic action in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):733–741. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00733.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Control of the repetitive discharge of rat CA 1 pyramidal neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:319–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Noradrenaline blocks accommodation of pyramidal cell discharge in the hippocampus. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):636–638. doi: 10.1038/299636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. Dopamine decreases the calcium-activated afterhyperpolarization in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1986 Aug 6;379(2):210–215. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90773-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numann R. E., Wadman W. J., Wong R. K. Outward currents of single hippocampal cells obtained from the adult guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:331–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellmar T. C. Histamine decreases calcium-mediated potassium current in guinea pig hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Apr;55(4):727–738. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennefather P., Lancaster B., Adams P. R., Nicoll R. A. Two distinct Ca-dependent K currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3040–3044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purpura D. P., Prelevic S., Santini M. Hyperpolarizing increase in membrane conductance in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1968 Feb;7(2):310–312. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Stafstrom C. E. Effects of EGTA on the calcium-activated afterhyperpolarization in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells. Science. 1980 Dec 5;210(4474):1125–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.6777871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindt P. C., Spain W. J., Foehring R. C., Stafstrom C. E., Chubb M. C., Crill W. E. Multiple potassium conductances and their functions in neurons from cat sensorimotor cortex in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Feb;59(2):424–449. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.2.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Barker J. L. Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: potassium conductances. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Jun;51(6):1409–1433. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.6.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain W. J., Schwindt P. C., Crill W. E. Anomalous rectification in neurons from cat sensorimotor cortex in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1987 May;57(5):1555–1576. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.5.1555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm J. F. Action potential repolarization and a fast after-hyperpolarization in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:733–759. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm J. F. Intracellular injection of a Ca2+ chelator inhibits spike repolarization in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 1;435(1-2):387–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91631-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Masukawa L. M., Prince D. A. Temperature dependence of intrinsic membrane properties and synaptic potentials in hippocampal CA1 neurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1985 Mar;5(3):817–824. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-03-00817.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokimasa T. Intracellular Ca2+-ions inactivate K+-current in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Brain Res. 1985 Jul 1;337(2):386–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zbicz K. L., Weight F. F. Transient voltage and calcium-dependent outward currents in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Apr;53(4):1038–1058. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.4.1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Krnjević K. Apamin depresses selectively the after-hyperpolarization of cat spinal motoneurons. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Feb 10;74(1):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


