Abstract
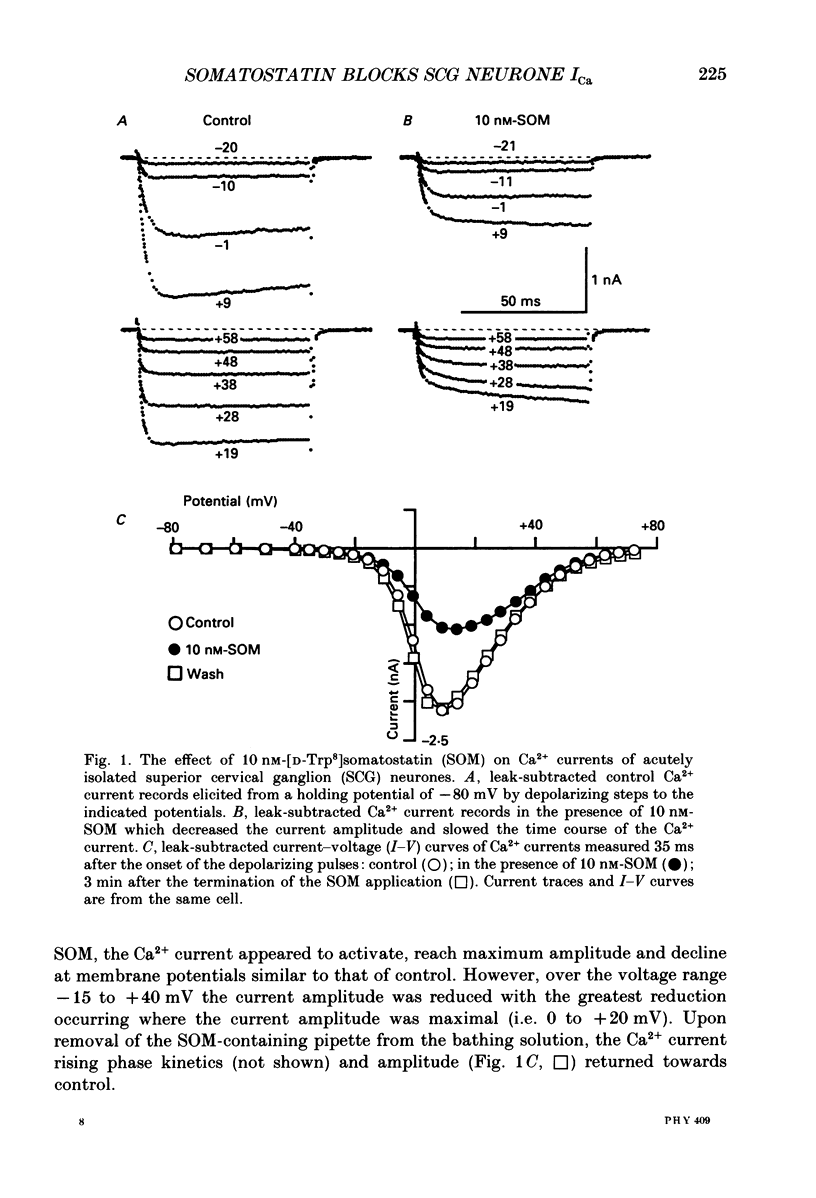
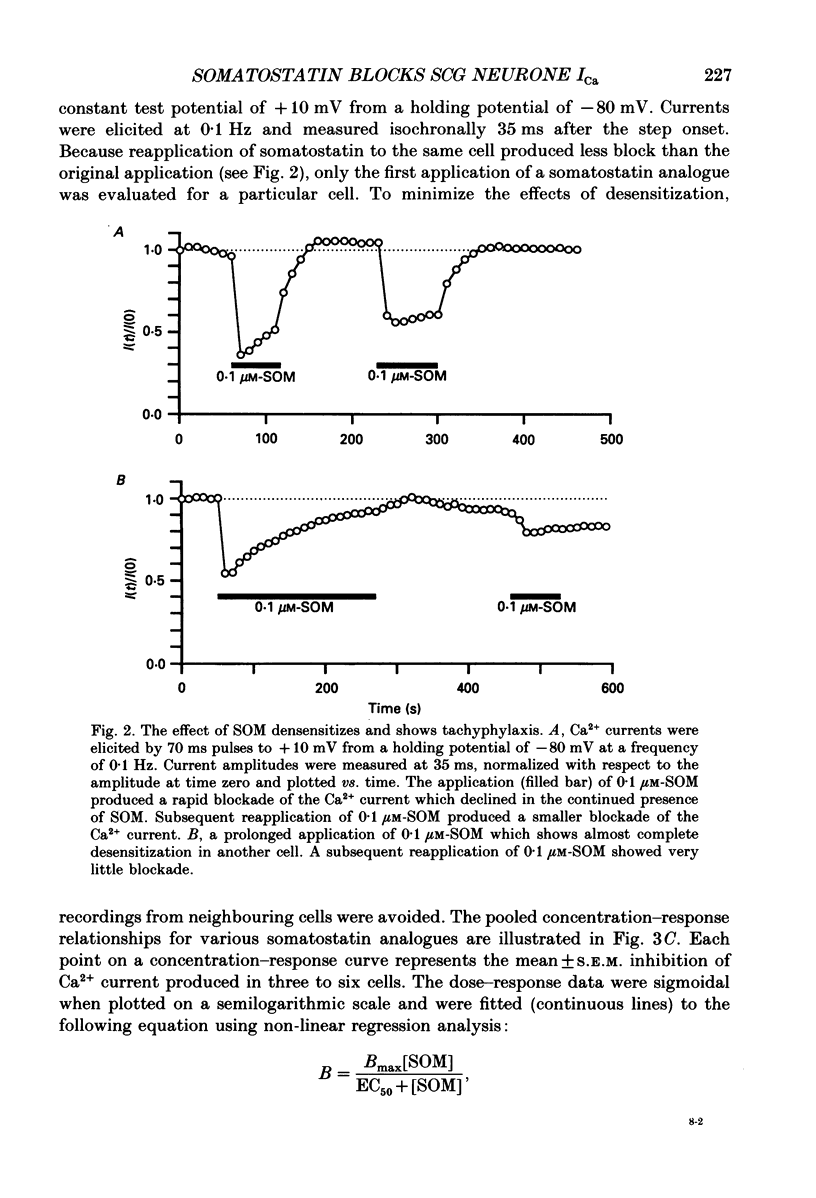
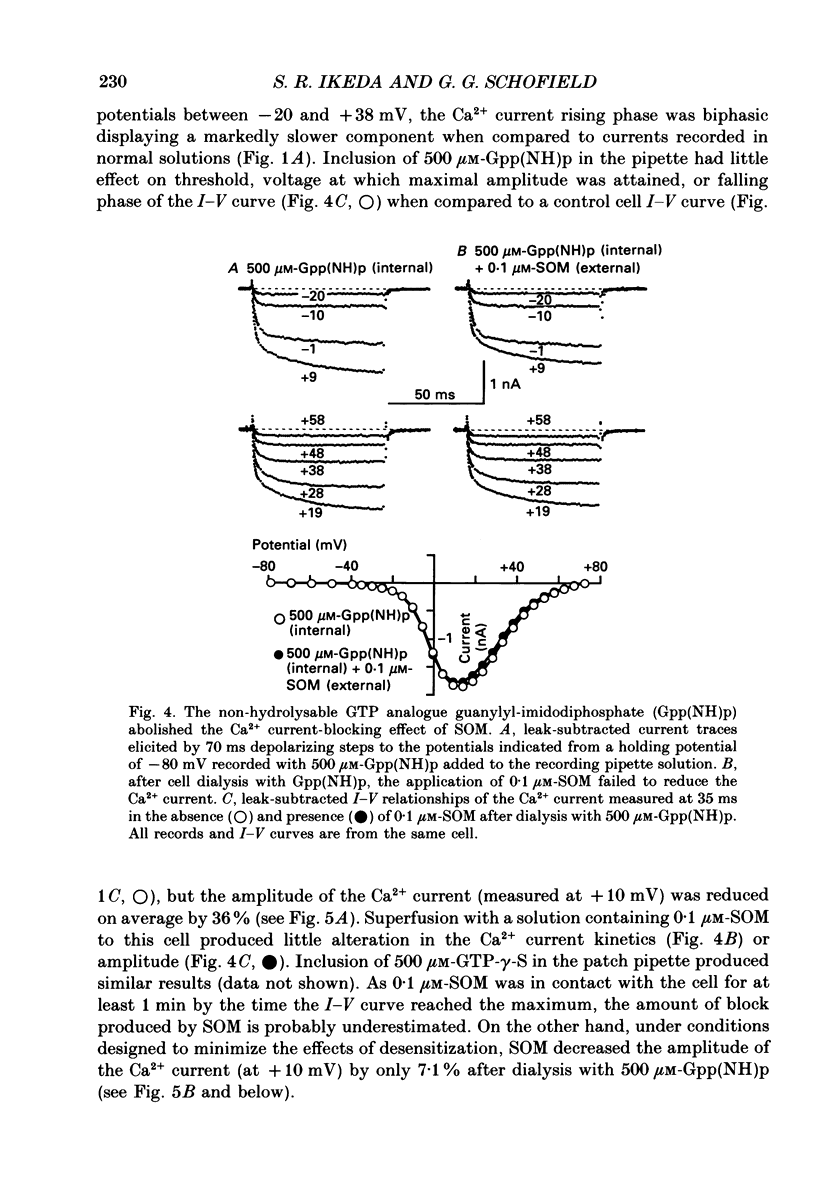
1. The effects of somatostatin and somatostatin analogues on a Ca2+ current from acutely isolated and short-term (24-48 h) cultured adult rat superior cervical ganglion (SCG) neurones were studied using the whole-cell variant of the patch-clamp technique. 2. [D-Trp8]Somatostatin (SOM) produced a rapid, reversible and concentration-dependent reduction of the Ca2+ current. Ca2+ current amplitude was reduced over the voltage range -15 to +40 mV with the greatest reduction occurring where the amplitude was maximal (ca +10 mV). In the presence of SOM, the Ca2+ current rising phase was slower and biphasic at potentials between 0 and +40 mV. 3. Application of 0.1 microM-SOM for greater than 10 s resulted in a desensitization of the response. During a 4 min application of 0.1 microM-SOM, Ca2+ current amplitude returned to about 90% of control. A second application of 0.1 microM-SOM produced less block than the initial application. 4. Concentration-response curves for SOM, somatostatin-14 (SOM-14) and somatostatin-28 (SOM-28) were fitted to a single-site binding isotherm. The concentrations producing half-maximal block and the maximal attainable blocks of the Ca2+ current for SOM, SOM-14 and SOM-28 were 3.3, 5.4 and 35 nM, respectively and 55, 51 and 54%, respectively. SOM-14 and SOM-28 slowed the Ca2+ current rising phase in a manner similar to that of SOM. Somatostatin-28 had no effect on the Ca2+ current at 1 microM. 5. The magnitude of the Ca2+ current block produced by 0.1 microM-SOM was not significantly altered in the presence of 1 microM-idazoxan, atropine, naloxone or the somatostatin antagonist aminoheptanoyl-Phe-D-Trp-Lys-O-benzyl-Thr. 6. Internal dialysis with solutions containing 500 microM-guanylyl-imidodiphosphate (Gpp(NH)p) or guanosine-5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate)(GTP-gamma-S) decreased the Ca2+ current amplitude by 36 and 41%, respectively, and induced a biphasic rising phase in the Ca2+ current. Under these conditions, application of 0.1 microM-SOM produced significantly less block of Ca2+ current amplitude (7.1 and 14.7%, respectively) when compared with controls. 7. Internal dialysis with solutions containing 500 microM-guanosine-5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate)(GDP-beta-S) had no significant effect on either the Ca2+ current amplitude or block produced by 0.1 microM-SOM. 8. Internal dialysis with solutions containing 500 microM-cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cyclic AMP) and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine had no significant effect on either the Ca2+ current block produced by 0.1 microM-SOM or the Ca2+ current amplitude.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




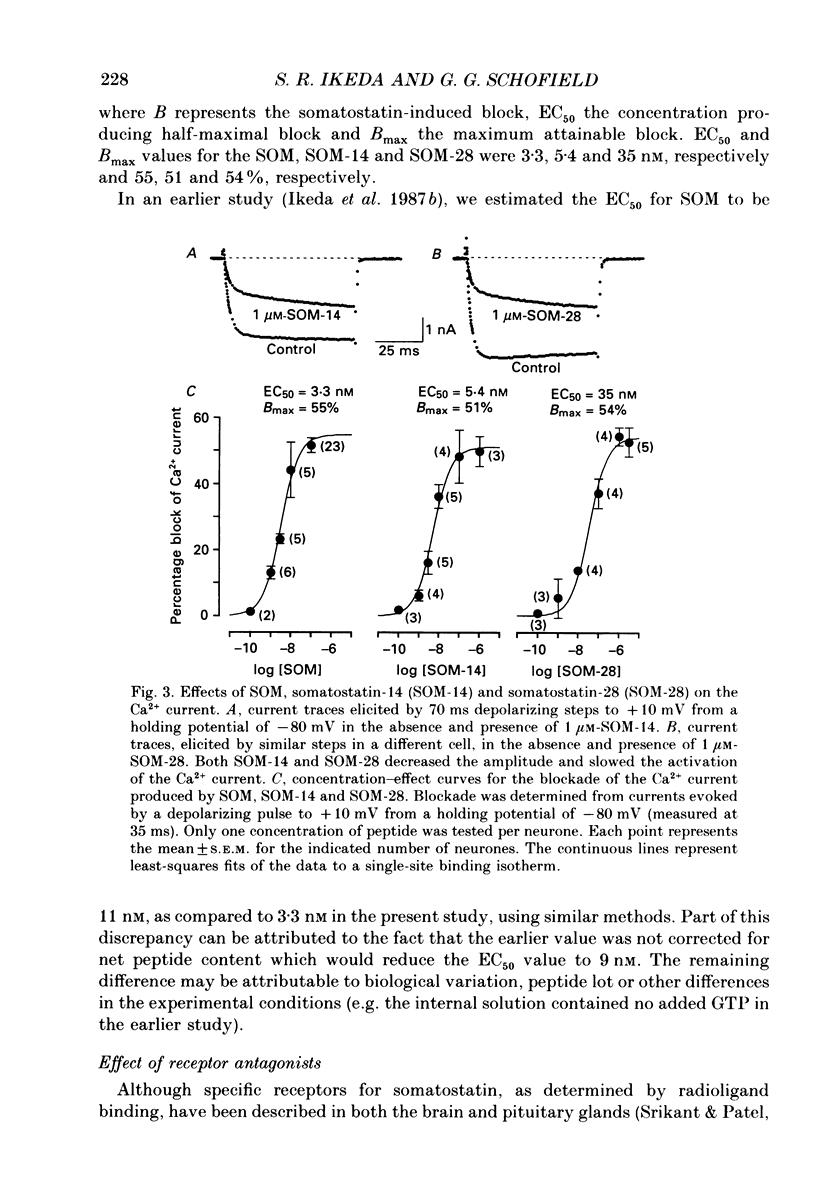







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
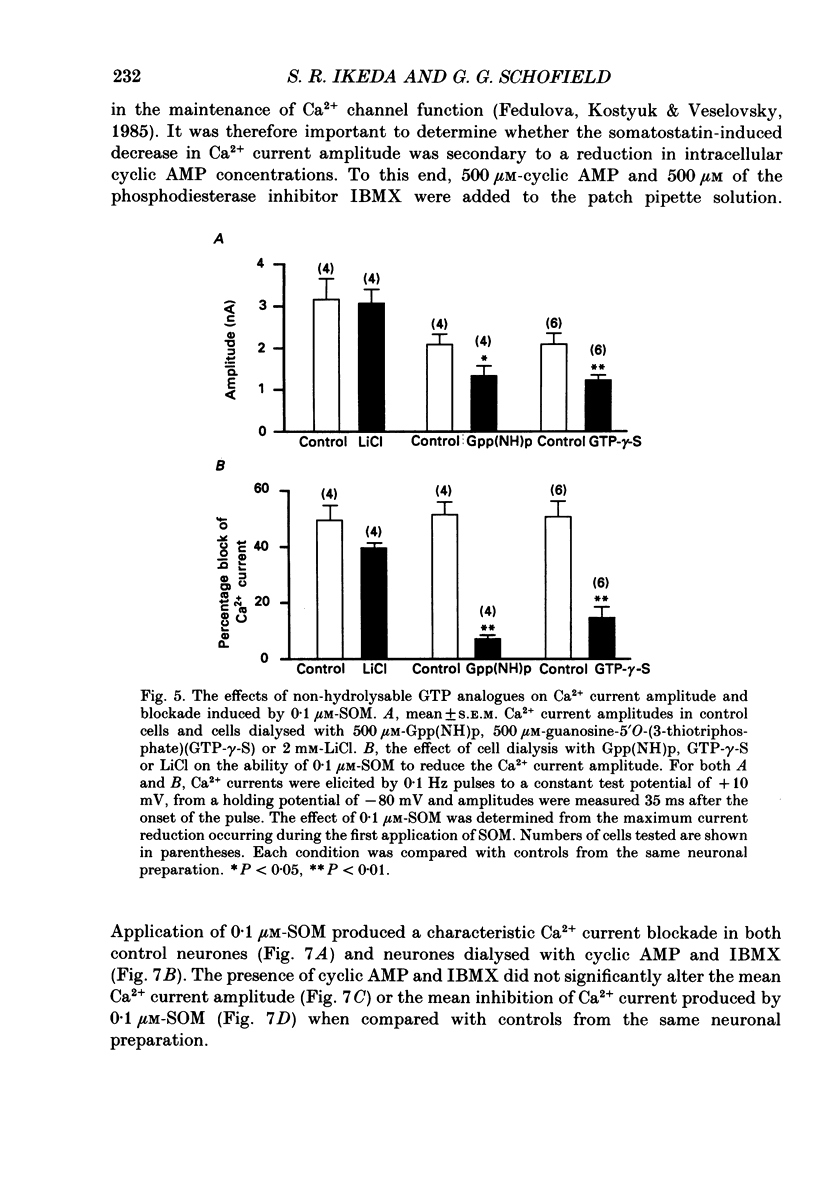
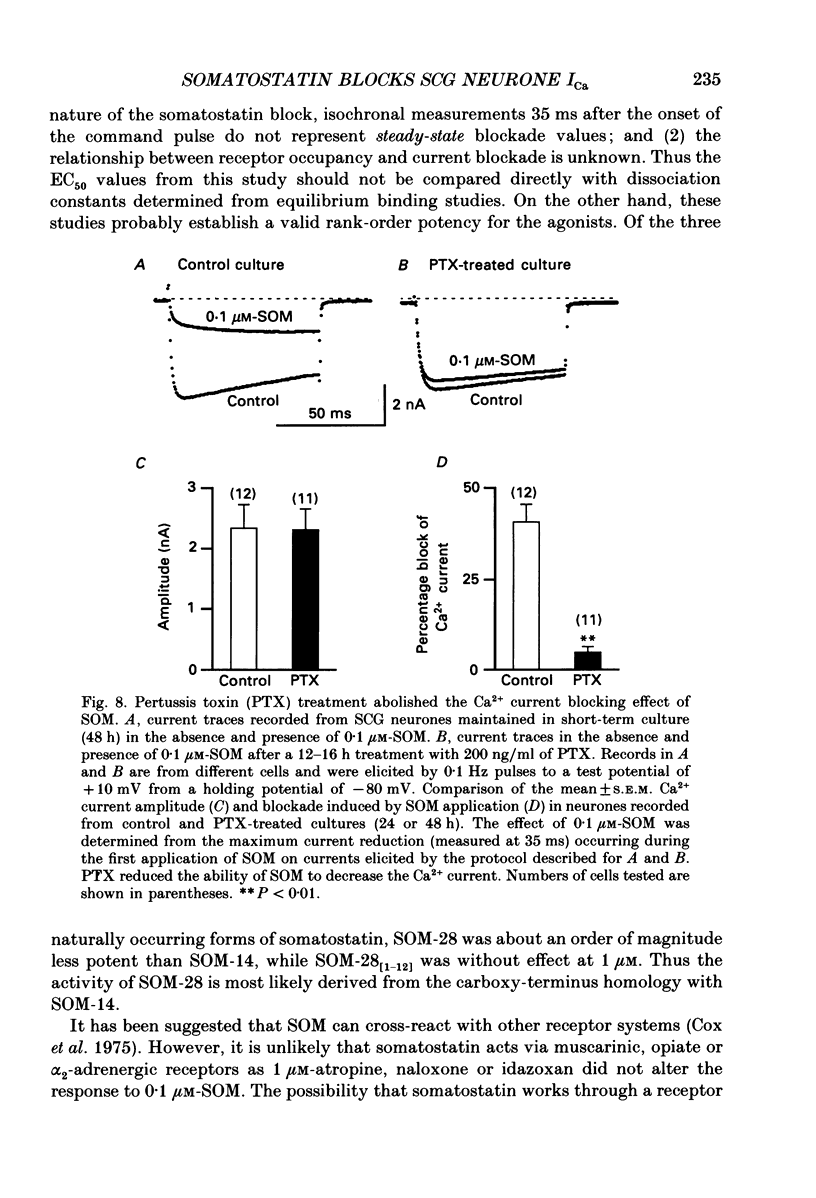
- Birnbaumer L., Codina J., Mattera R., Cerione R. A., Hildebrandt J. D., Sunyer T., Rojas F. J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Iyengar R. Regulation of hormone receptors and adenylyl cyclases by guanine nucleotide binding N proteins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1985;41:41–99. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571141-8.50006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
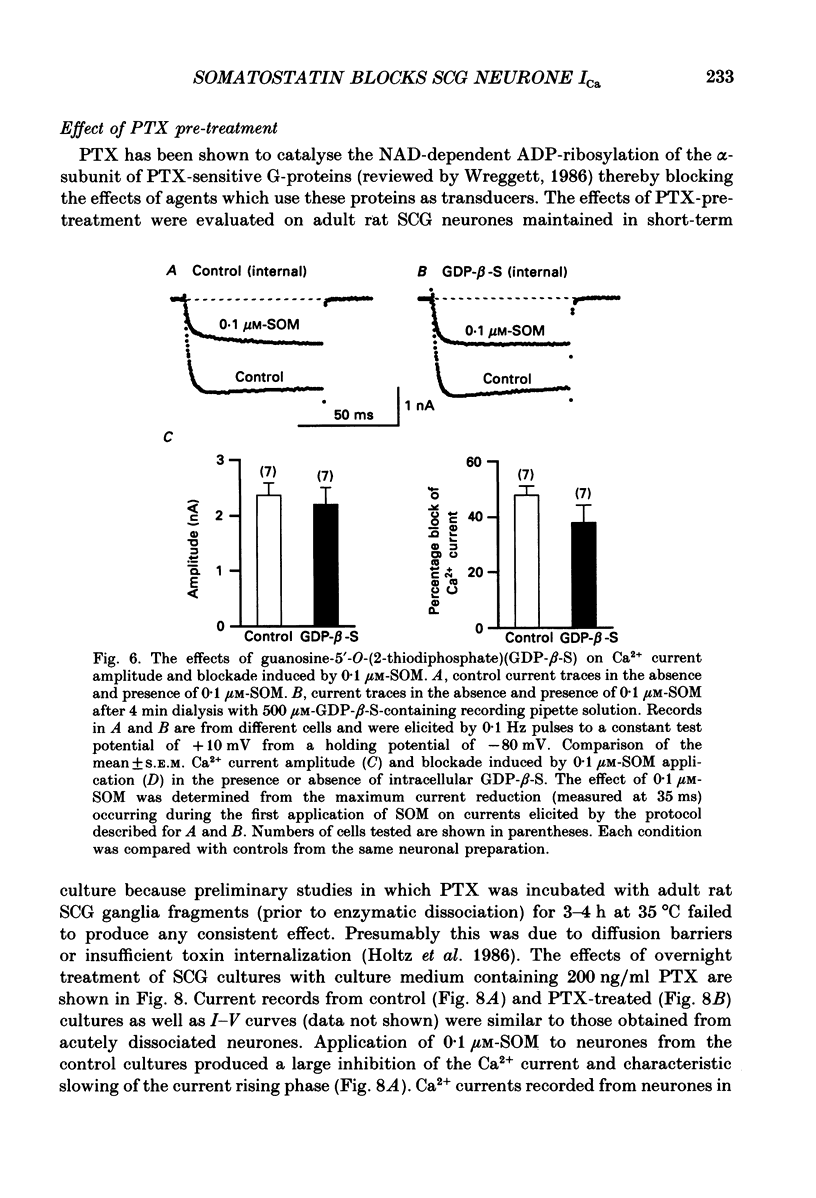
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Mechanism of adenylate cyclase activation by cholera toxin: inhibition of GTP hydrolysis at the regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
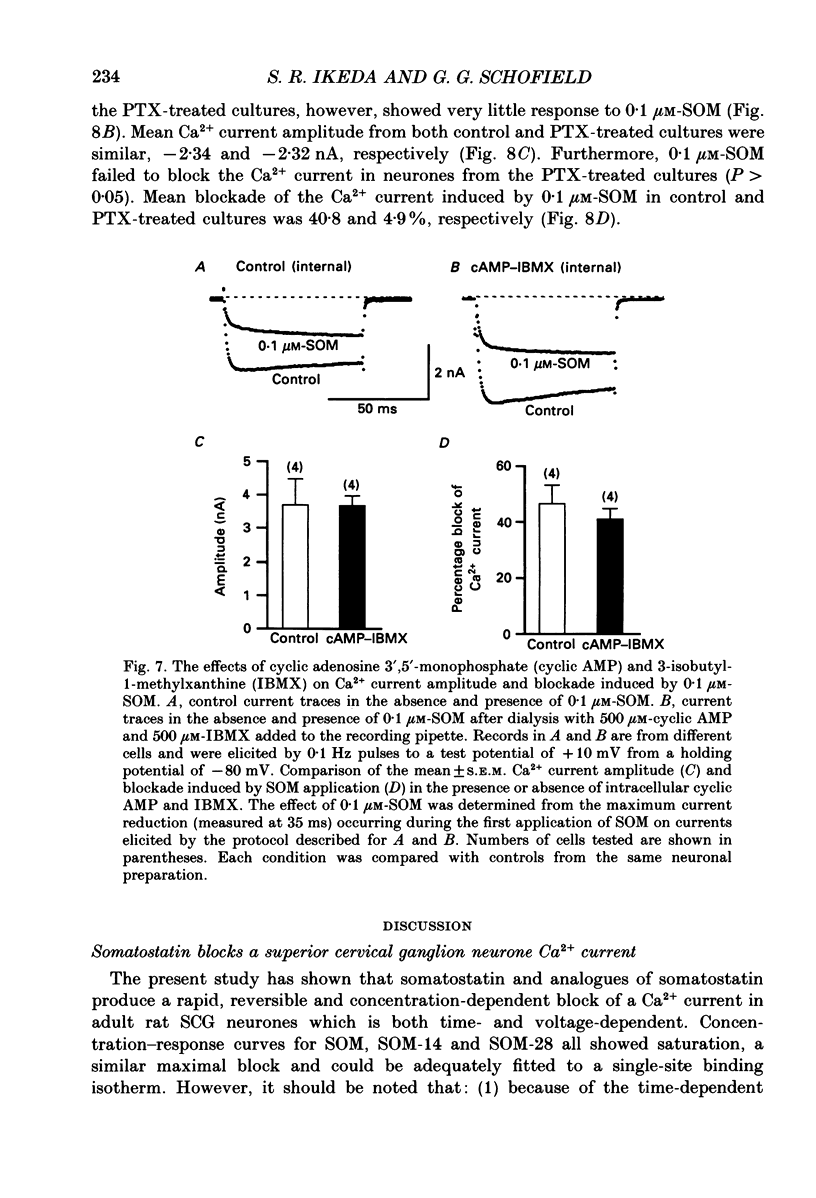
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Rosing E., Wiley K. S., Slater I. H. Somatostatin inhibits adrenergic and cholinergic neurotransmission in smooth muscle. Life Sci. 1978 Oct 23;23(16):1659–1664. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Opheim K. E., Teschemacher H., Goldstein A. A peptide-like substance from pituitary that acts like morphine. 2. Purification and properties. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1777–1782. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coy D. H., Murphy W. A., Lance V. A., Hocart S. J., Sueiras-Diaz J., Mezo I. Somatostatin agonists and antagonists--peptide control of growth hormone secretion. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;188:325–337. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7886-4_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfs J. R., Dichter M. A. Effects of somatostatin on mammalian cortical neurons in culture: physiological actions and unusual dose response characteristics. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1176–1188. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01176.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Scott R. H. Calcium channel currents and their inhibition by (-)-baclofen in rat sensory neurones: modulation by guanine nucleotides. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:1–17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F., Cassel D., Levkovitz H., Lowe M., Selinger Z. Guanosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate). An inhibitor of adenylate cyclase stimulation by guanine nucleotides and fluoride ions. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9829–9834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedulova S. A., Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S. Two types of calcium channels in the somatic membrane of new-born rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forscher P., Oxford G. S. Modulation of calcium channels by norepinephrine in internally dialyzed avian sensory neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1985 May;85(5):743–763. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.5.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvan M., Adams P. R. Control of calcium current in rat sympathetic neurons by norepinephrine. Brain Res. 1982 Jul 22;244(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90911-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiman M. L., Murphy W. A., Coy D. H. Differential binding of somatostatin agonists to somatostatin receptors in brain and adenohypophysis. Neuroendocrinology. 1987 Jun;45(6):429–436. doi: 10.1159/000124788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henon B. K., McAfee D. A. The ionic basis of adenosine receptor actions on post-ganglionic neurones in the rat. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:607–620. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirning L. D., Fox A. P., McCleskey E. W., Olivera B. M., Thayer S. A., Miller R. J., Tsien R. W. Dominant role of N-type Ca2+ channels in evoked release of norepinephrine from sympathetic neurons. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):57–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2447647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Elfvin L. G., Elde R., Schultzberg M., Goldstein M., Luft R. Occurrence of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in some peripheral sympathetic noradrenergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3587–3591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R., Schofield G. G. Tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium current of rat nodose neurones: monovalent cation selectivity and divalent cation block. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:255–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R., Schofield G. G., Weight F. F. Somatostatin blocks a calcium current in acutely isolated adult rat superior cervical ganglion neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Oct 16;81(1-2):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. L., Weight F. F., Luini A. A guanine nucleotide-binding protein mediates the inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current by somatostatin in a pituitary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9035–9039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luini A., Lewis D., Guild S., Schofield G., Weight F. Somatostatin, an inhibitor of ACTH secretion, decreases cytosolic free calcium and voltage-dependent calcium current in a pituitary cell line. J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;6(11):3128–3132. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-11-03128.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léránth C., Williams T. H., Jew J. Y., Arimura A. Immuno-electron microscopic identification of somatostatin in cells and axons of sympathetic ganglia in the guinea pig. Cell Tissue Res. 1980;212(1):83–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00234035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti C., Carbone E., Lux H. D. Effects of dopamine and noradrenaline on Ca channels of cultured sensory and sympathetic neurons of chick. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Feb;406(2):104–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00586670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrion N. V., Smart T. G., Brown D. A. Membrane currents in adult rat superior cervical ganglia in dissociated tissue culture. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jun 1;77(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90606-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., Nishi S., North R. A., Surprenant A. A non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic slow inhibitory post-synaptic potential in neurones of the guinea-pig submucous plexus. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:357–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., North R. A., Surprenant A. Somatostatin increases an inwardly rectifying potassium conductance in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:335–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller A. L., Kunkel D. D., Schwartzkroin P. A. Electrophysiological actions of somatostatin (SRIF) in hippocampus: an in vitro study. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1986 Dec;6(4):363–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00711406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman Q. J., Siggins G. R. Somatostatin hyperpolarizes hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. Brain Res. 1981 Sep 28;221(2):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90791-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisine T., Zhang Y. L., Sekura R. Pertussis toxin treatment blocks the inhibition of somatostatin and increases the stimulation by forskolin of cyclic AMP accumulation and adrenocorticotropin secretion from mouse anterior pituitary tumor cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jan;232(1):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield G. G., Ikeda S. R. Sodium and calcium currents of acutely isolated adult rat superior cervical ganglion neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1988 May;411(5):481–490. doi: 10.1007/BF00582368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikant C. B., Patel Y. C. Somatostatin receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;188:291–304. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7886-4_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suidan H., Tamir A., Tolkovsky A. M. A simple test for enhanced guanyl nucleotide exchange in brain adenylate cyclase systems activated by neurotransmitters. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10524–10529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunoo A., Yoshii M., Narahashi T. Block of calcium channels by enkephalin and somatostatin in neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9832–9836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanke E., Ferroni A., Malgaroli A., Ambrosini A., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Activation of a muscarinic receptor selectively inhibits a rapidly inactivated Ca2+ current in rat sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4313–4317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreggett K. A. Bacterial toxins and the role of ADP-ribosylation. J Recept Res. 1986;6(2):95–126. doi: 10.3109/10799898609073927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Imoto Y., Reeves J. P., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. A G protein directly regulates mammalian cardiac calcium channels. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2446390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Sekura R. D., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Reconstitution of somatostatin and muscarinic receptor mediated stimulation of K+ channels by isolated GK protein in clonal rat anterior pituitary cell membranes. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Apr;1(4):283–289. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-4-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



