Abstract
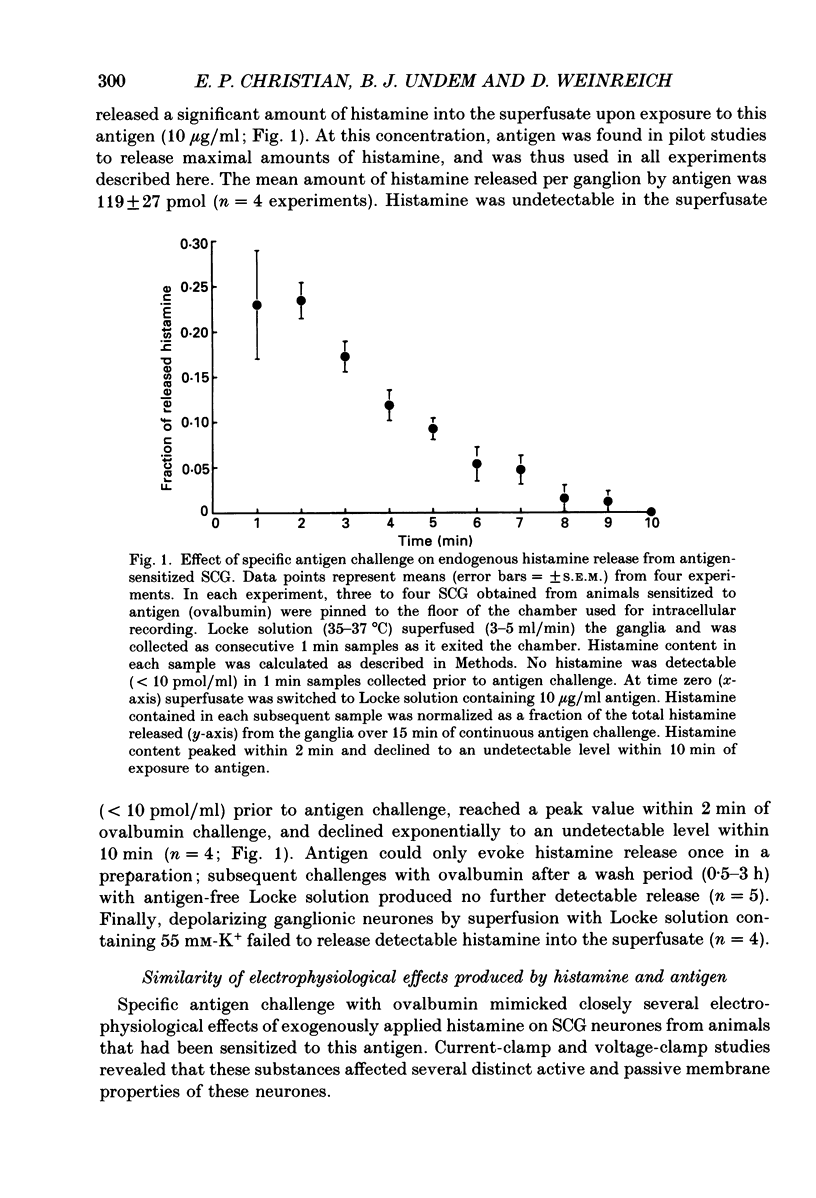
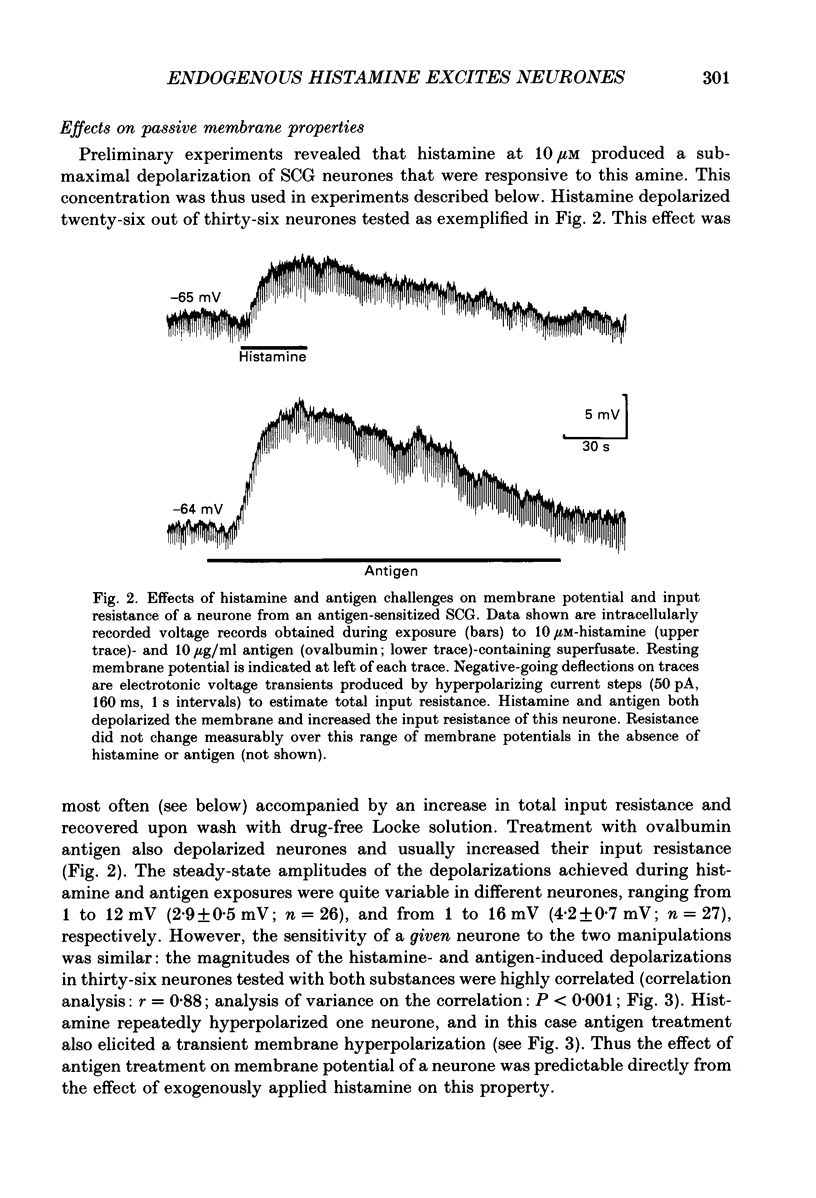
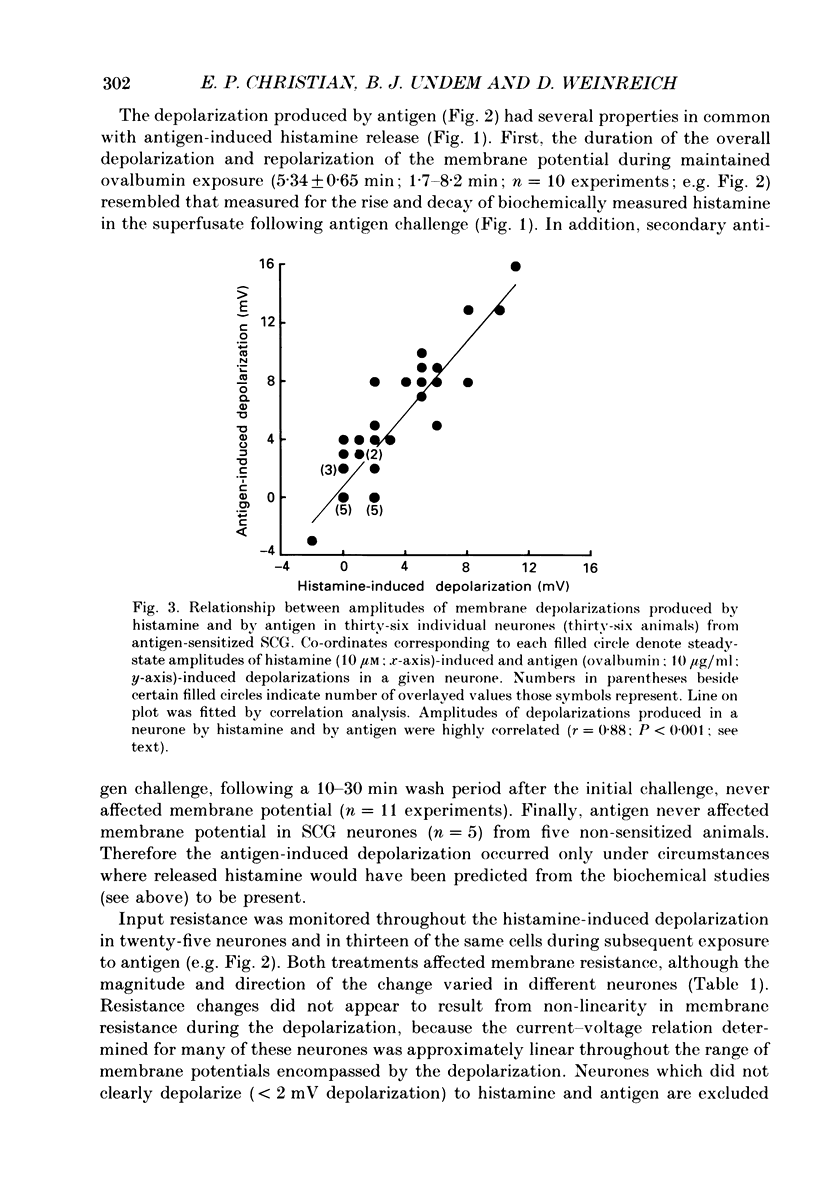
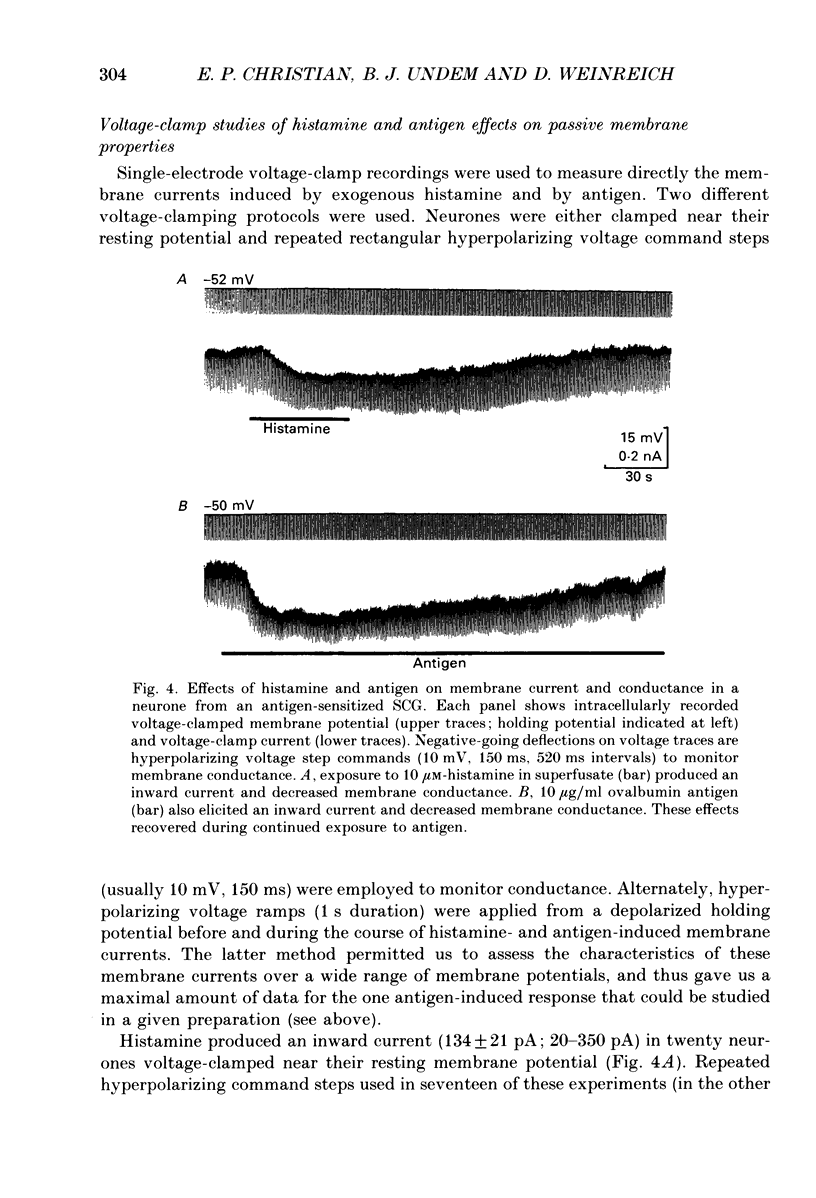
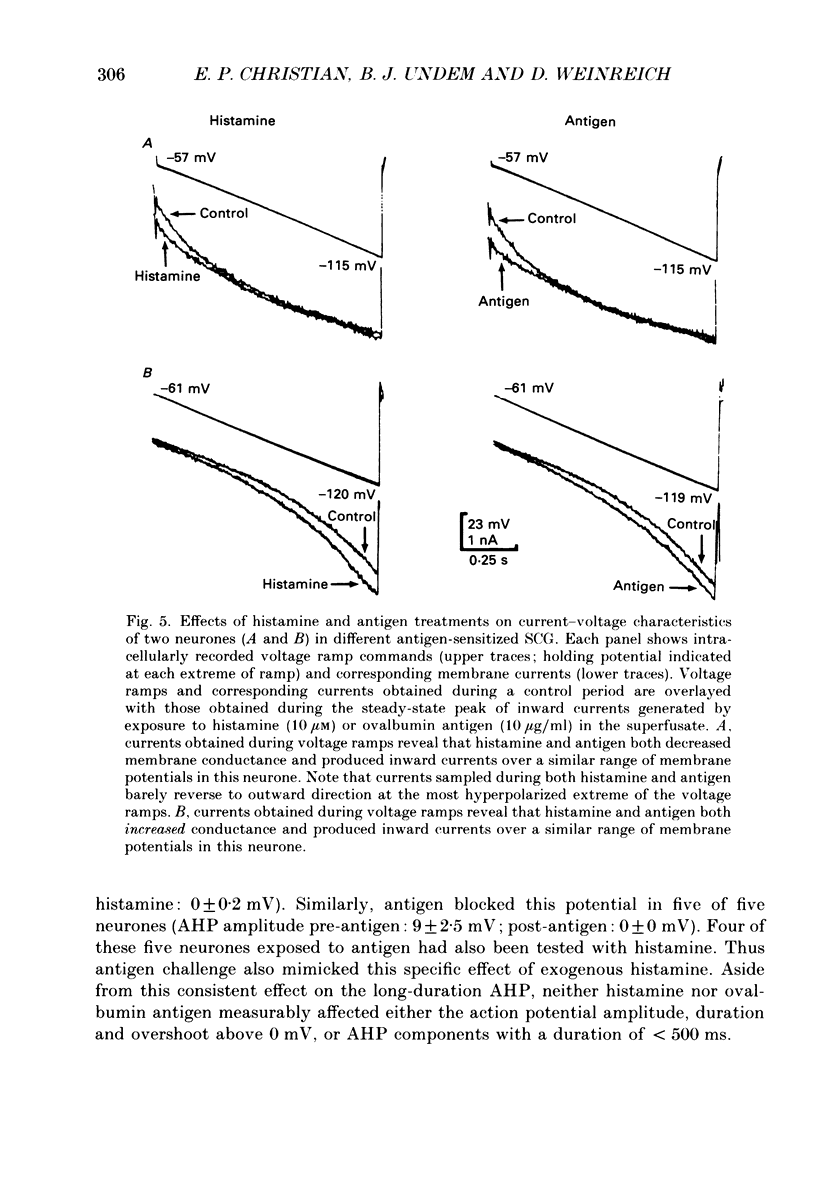
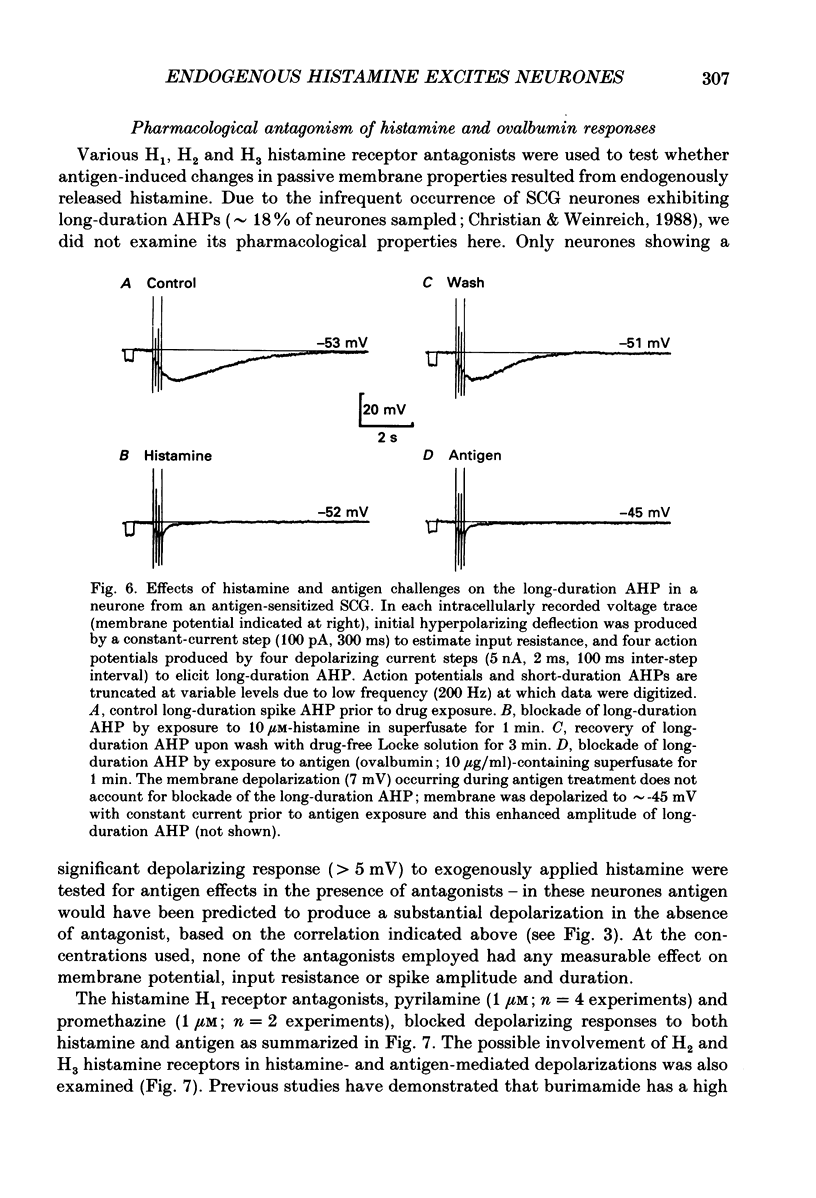
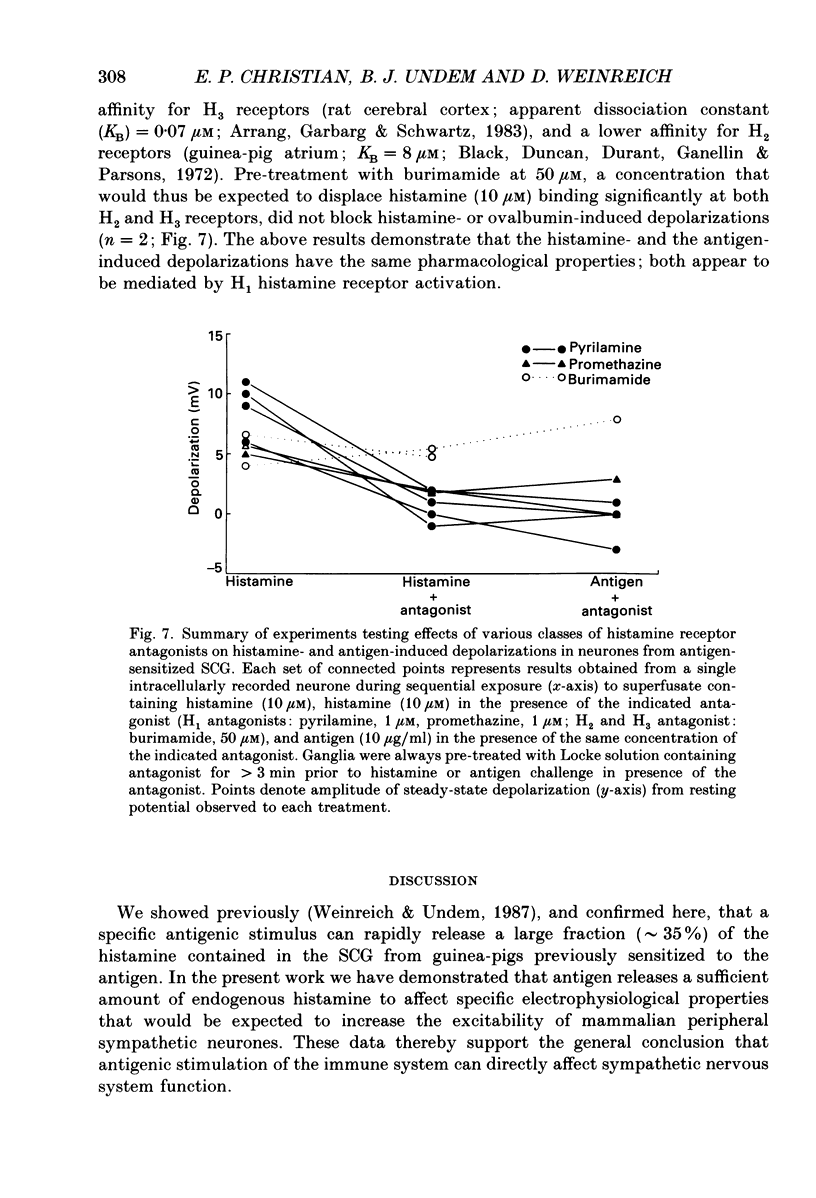
1. Intracellular recordings were obtained from neurones in the guinea-pig superior cervical ganglion (SCG) in vitro to study the electrophysiological effects of endogenously released histamine. 2. Guinea-pigs were actively sensitized to the specific antigen, ovalbumin. SCG removed from these animals rapidly released a significant proportion of their endogenous histamine stores into the extracellular space upon exposure to the sensitizing antigen. Several observations indicated that the released histamine was derived from ganglionic mast cells. 3. The electrophysiological effects produced by antigen challenge in a neurone mimicked qualitatively and quantitatively those effects produced by exogenously applied histamine in the same neurone. Under current clamp the membrane effects of antigen and histamine included a transient depolarization, an increase in input resistance and transient blockade of a long-duration component of the spike after-hyperpolarization. In voltage clamp histamine and antigen produced an inward current and decreased membrane conductance. 4. Histamine H1, but not H2 or H3 receptor antagonists prevented the membrane depolarization to both histamine and antigen treatments. 5. These convergent biochemical, physiological and pharmacological data demonstrate that a sufficient quantity of endogenous histamine is released by an antigenic stimulus in SCG from sensitized guinea-pigs to affect specific electrophysiological characteristics of neurones. Histamine may thus be involved in mediating interactions between the mammalian immune system and the peripheral sympathetic nervous system.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):832–837. doi: 10.1038/302832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bani-Sacchi T., Barattini M., Bianchi S., Blandina P., Brunelleschi S., Fantozzi R., Mannaioni P. F., Masini E. The release of histamine by parasympathetic stimulation in guinea-pig auricle and rat ileum. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:29–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienenstock J., Tomioka M., Matsuda H., Stead R. H., Quinonez G., Simon G. T., Coughlin M. D., Denburg J. A. The role of mast cells in inflammatory processes: evidence for nerve/mast cell interactions. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;82(3-4):238–243. doi: 10.1159/000234197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Duncan W. A., Durant C. J., Ganellin C. R., Parsons E. M. Definition and antagonism of histamine H 2 -receptors. Nature. 1972 Apr 21;236(5347):385–390. doi: 10.1038/236385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimble M. J., Wallis D. I. Histamine H1 and H2-receptors at a ganglionic synapse. Nature. 1973 Nov 16;246(5429):156–158. doi: 10.1038/246156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian E. P., Weinreich D. Long-duration spike afterhyperpolarizations in neurons from the guinea pig superior cervical ganglion. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jan 22;84(2):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dun N. J., Minota S. Effects of substance P on neurones of the inferior mesenteric ganglia of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:259–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J., Jordan C. Histamine release and vascular changes induced by neuropeptides. Agents Actions. 1983 Apr;13(2-3):105–116. doi: 10.1007/BF01967311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. P. HISTAMINE AND THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:1095–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. S., Guo Z. G., Levi R., Bailey W. H., Chenouda A. A. Release of histamine by sympathetic nerve stimulation in the guinea pig heart and modulation of adrenergic responses. A physiological role for cardiac histamine? Circ Res. 1984 May;54(5):516–526. doi: 10.1161/01.res.54.5.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Konnerth A. Histamine and noradrenaline decrease calcium-activated potassium conductance in hippocampal pyramidal cells. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):432–434. doi: 10.1038/302432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Koketsu K. Analysis of the slow excitatory postsynaptic potential in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26(6):651–669. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.26.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Sejnowski T. J. Peptidergic and muscarinic excitation at amphibian sympathetic synapses. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:257–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski H. Histamine in nervous tissue. J Physiol. 1943 Jun 30;102(1):32–41. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1943.sp004011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN L. M., OSLER A. G. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISMS OF HYPERSENSITIVITY PHENOMENA. IX. HISTAMINE RELEASE FROM HUMAN LEUKOCYTES BY RAGWEED POLLEN ANTIGEN. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:507–530. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff A. R., Stimler N. P., Munoz N. M., Shioya T., Tallet J., Dame C. Augmentation of respiratory mast cell secretion of histamine caused by vagus nerve stimulation during antigen challenge. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1066–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindl T., Behrendt H., Heinl-Sawaja M. C., Teufel E., Cramer H. Effects of compound 48/80 on mast cells, histamine, and cyclic AMP in isolated superior cervical ganglia. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;286(3):283–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00498311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindl T. Effects of histamine agonists and antagonists (H1 and H2) on ganglionic transmission and on accumulation of cyclic nucleotides (cAMP and cGMP) in rat superior cervical ganglion in vitro. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Feb;22(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth P. R., Ort C. A., Wood J. D. Intracellular study of effects of histamine on electrical behaviour of myenteric neurones in guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1984 Oct;355:411–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. Central and synaptic transmission in the nervous system; pharmacological aspects. Annu Rev Physiol. 1958;20:431–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.20.030158.002243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellmar T. C. Histamine decreases calcium-mediated potassium current in guinea pig hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Apr;55(4):727–738. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves D. Functional and structural changes in mammalian sympathetic neurones following interruption of their axons. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(2):429–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Histamine modulates reactivity of hippocampal CA3 neurons to afferent stimulation in vitro. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 1;213(2):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Histamine produces a Ca2+-sensitive depolarization of hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Aug;19(1):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90257-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P. An automated continuous-flow system for the extraction and fluorometric analysis of histamine. Anal Biochem. 1974 Feb;57(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow R. W., Weinreich D. Presynaptic and postsynaptic effects of histamine and histamine agonists in the superior cervical ganglion of the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Jul;26(7A):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90237-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORP A. Histamine and mast cells in nerves. Med Exp Int J Exp Med. 1961;4:180–182. doi: 10.1159/000135010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Minota S., Kuba K. Regulation of two ion channels by a common muscarinic receptor-transduction system in a vertebrate neuron. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Oct 16;81(1-2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villena F., Montoya G. A., Roa J., Jofré A., Goset C. Mast cells and synaptic transmission in sympathetic ganglia. Cell Mol Biol. 1986;32(3):253–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D. Multiple sites of histamine storage in superior cervical ganglia. Exp Neurol. 1985 Oct;90(1):36–43. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(85)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D., Undem B. J. Immunological regulation of synaptic transmission in isolated guinea pig autonomic ganglia. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1529–1532. doi: 10.1172/JCI112984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R. Criteria for identification of a central nervous system transmitter. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1966 Aug;18(4):745–766. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(66)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


