Abstract
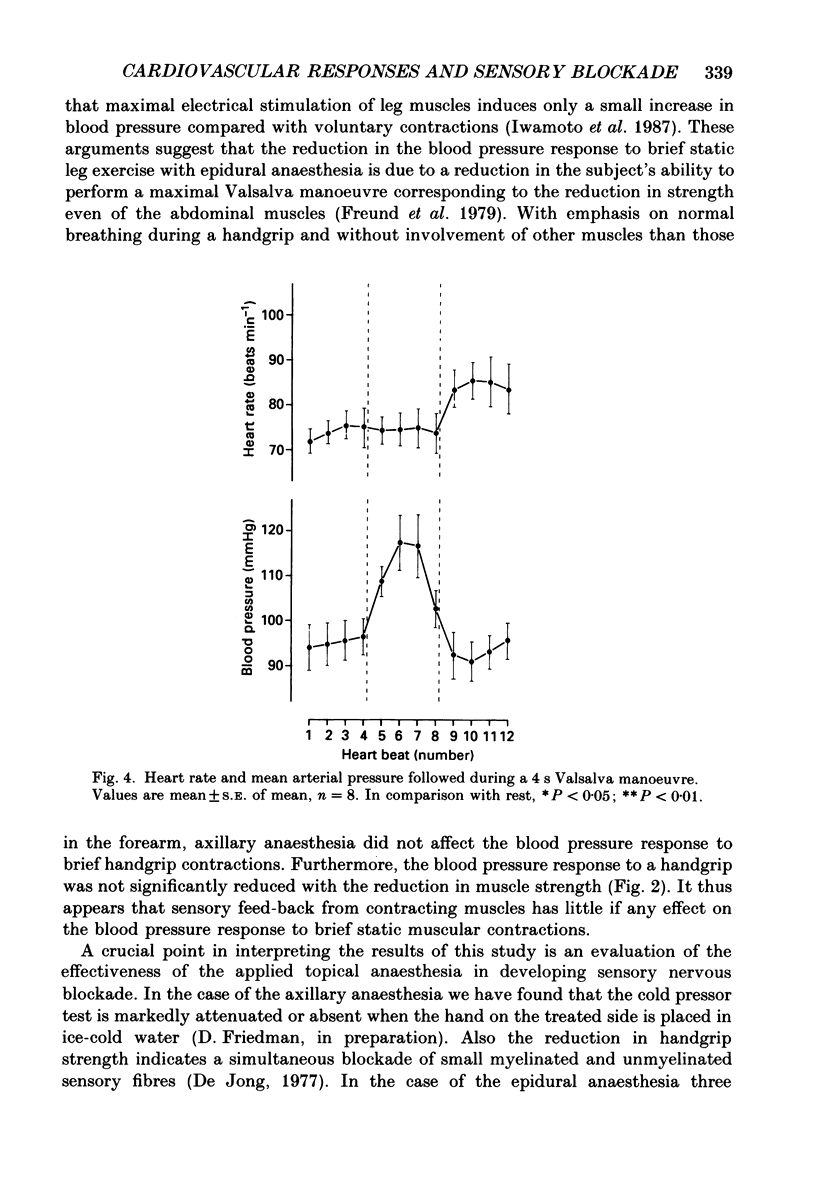
1. We tested the hypothesis that afferent nerves from working muscles are important in determining the heart rate and blood pressure responses to brief maximal static exercise. 2. In twenty human subjects, the heart rate and arterial blood pressure responses to a brief maximal voluntary handgrip were studied before and after axillary nerve anaesthesia or to maximal one-leg knee extension before and after epidural anaesthesia at L3-L4. Maximal knee extension could not be accomplished without performing a 'Valsalva-like' manoeuvre, but during handgrip it was possible to avoid the use of muscles other than those directly involved in the contraction. Heart rate and blood pressure were also monitored during a Valsalva manoeuvre of similar duration to the maximal voluntary contractions (4 s). 3. During handgrip with normal breathing, axillary nerve anaesthesia reduced the heart rate response but had no effect on the blood pressure response. 4. During a Valsalva manoeuvre, blood pressure increased but heart rate remained stable as long as expiratory pressure was maintained. During one-leg knee extension, epidural anaesthesia reduced the blood pressure response; however, the reduction in blood pressure was probably due to a reduction in the simultaneously performed 'Valsalva-like' manoeuvre. 5. The results of this study suggest that afferent input from the working muscles is of importance for the heart rate responses to brief static muscle contractions. That such influence may be important for the blood pressure response remains unproven.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam M., Smirk F. H. Observations in man upon a blood pressure raising reflex arising from the voluntary muscles. J Physiol. 1937 Jun 3;89(4):372–383. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1937.sp003485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund P. R., Rowell L. B., Murphy T. M., Hobbs S. F., Butler S. H. Blockade of the pressor response to muscle ischemia by sensory nerve block in man. Am J Physiol. 1979 Oct;237(4):H433–H439. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.237.4.H433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyschuss U. Cardiovascular adjustment to somatomotor activation. The elicitation of increments in heart rate, aortic pressure and venomotor tone with the initiation of muscle contraction. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1970;342:1–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs S. F., Gandevia S. C. Cardiovascular responses and the sense of effort during attempts to contract paralysed muscles: role of the spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jun 4;57(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto G. A., Mitchell J. H., Mizuno M., Secher N. H. Cardiovascular responses at the onset of exercise with partial neuromuscular blockade in cat and man. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:39–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjaer M., Secher N. H., Bach F. W., Galbo H. Role of motor center activity for hormonal changes and substrate mobilization in humans. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):R687–R695. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.253.5.R687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh A., Lindhard J. The regulation of respiration and circulation during the initial stages of muscular work. J Physiol. 1913 Oct 17;47(1-2):112–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1913.sp001616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard B., Mitchell J. H., Mizuno M., Rube N., Saltin B., Secher N. H. Partial neuromuscular blockade and cardiovascular responses to static exercise in man. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:365–379. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secher N. H. Heart rate at the onset of static exercise in man with partial neuromuscular blockade. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:481–490. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


