Abstract
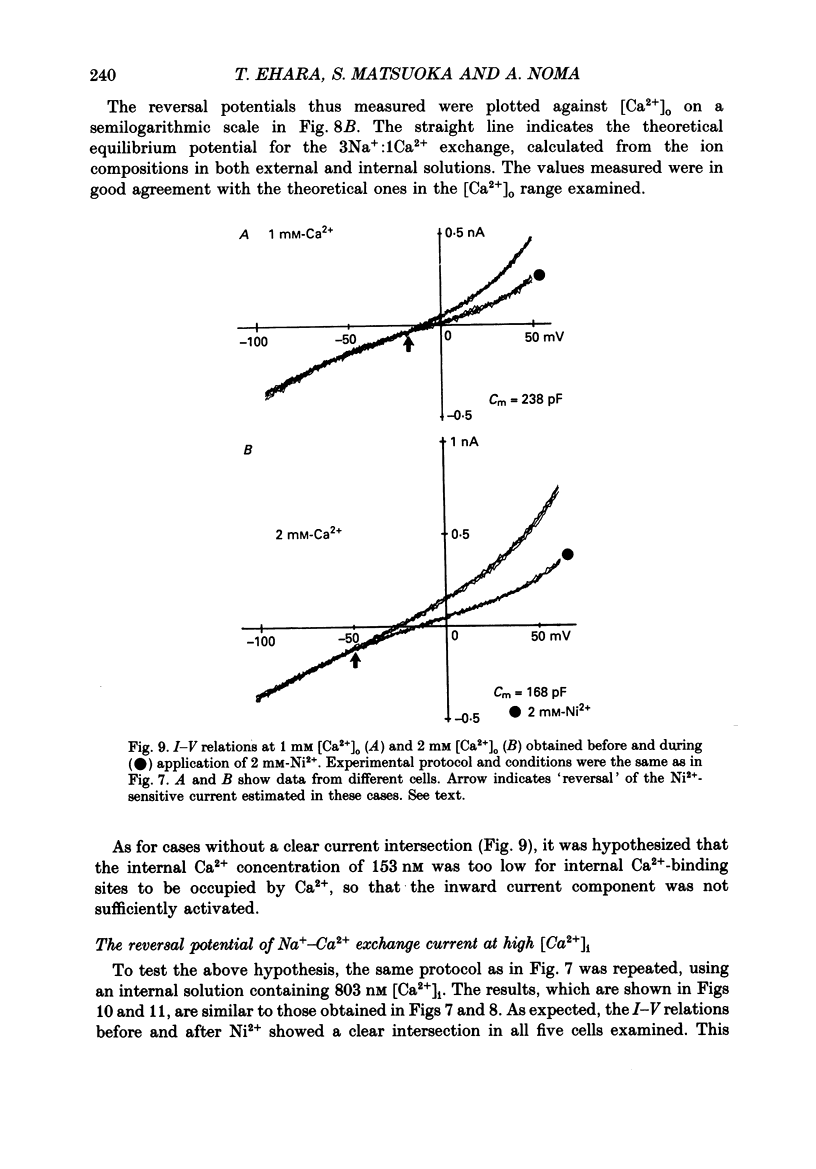
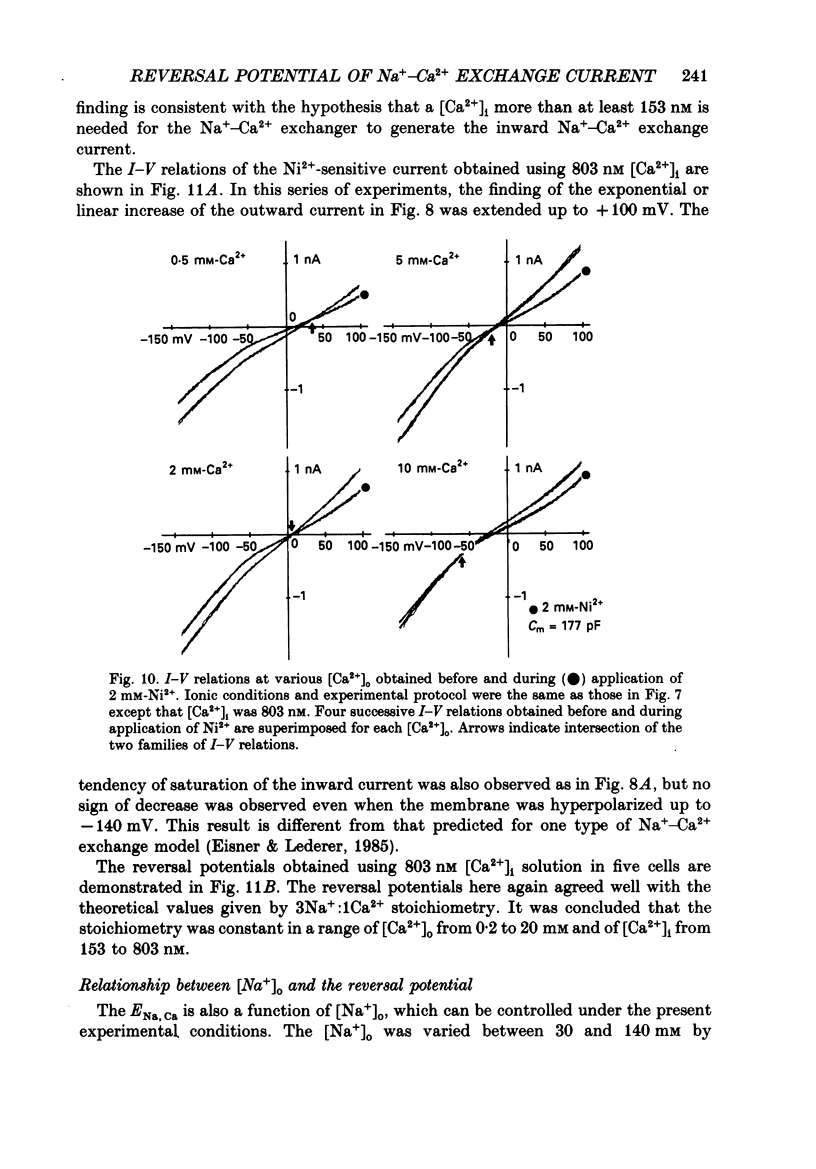
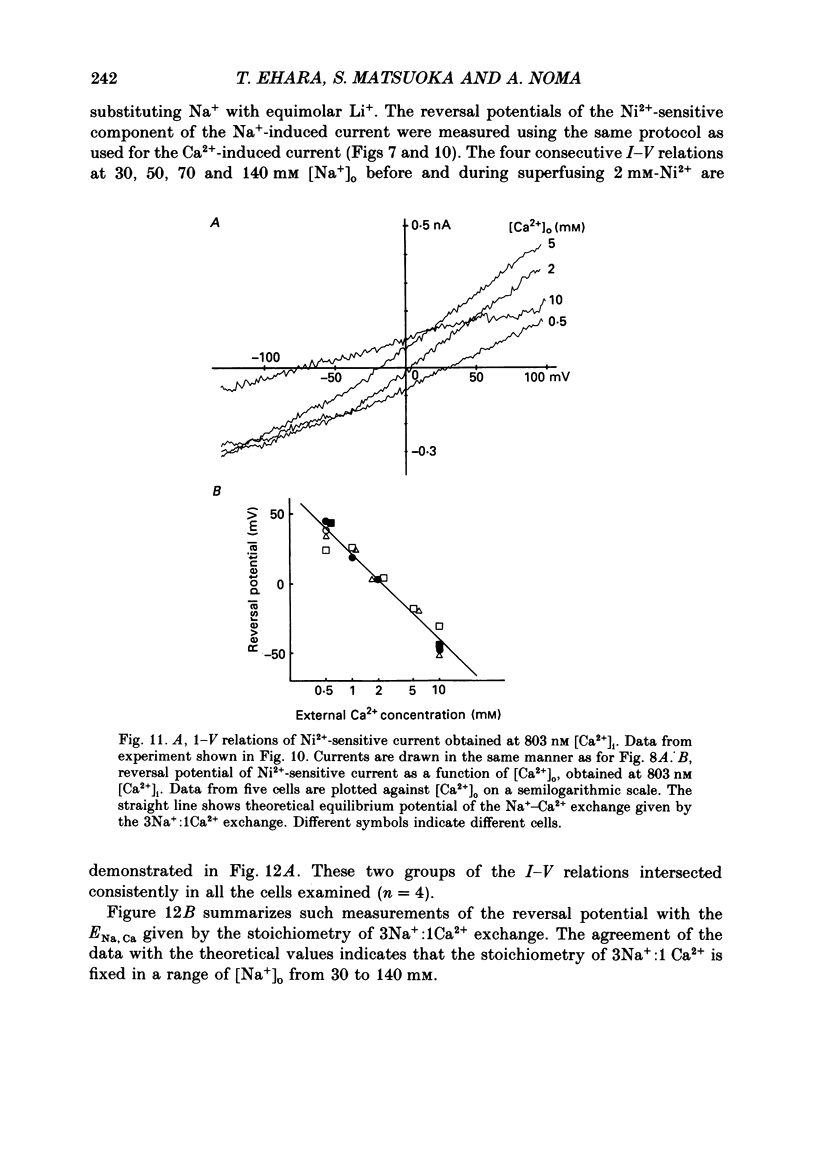
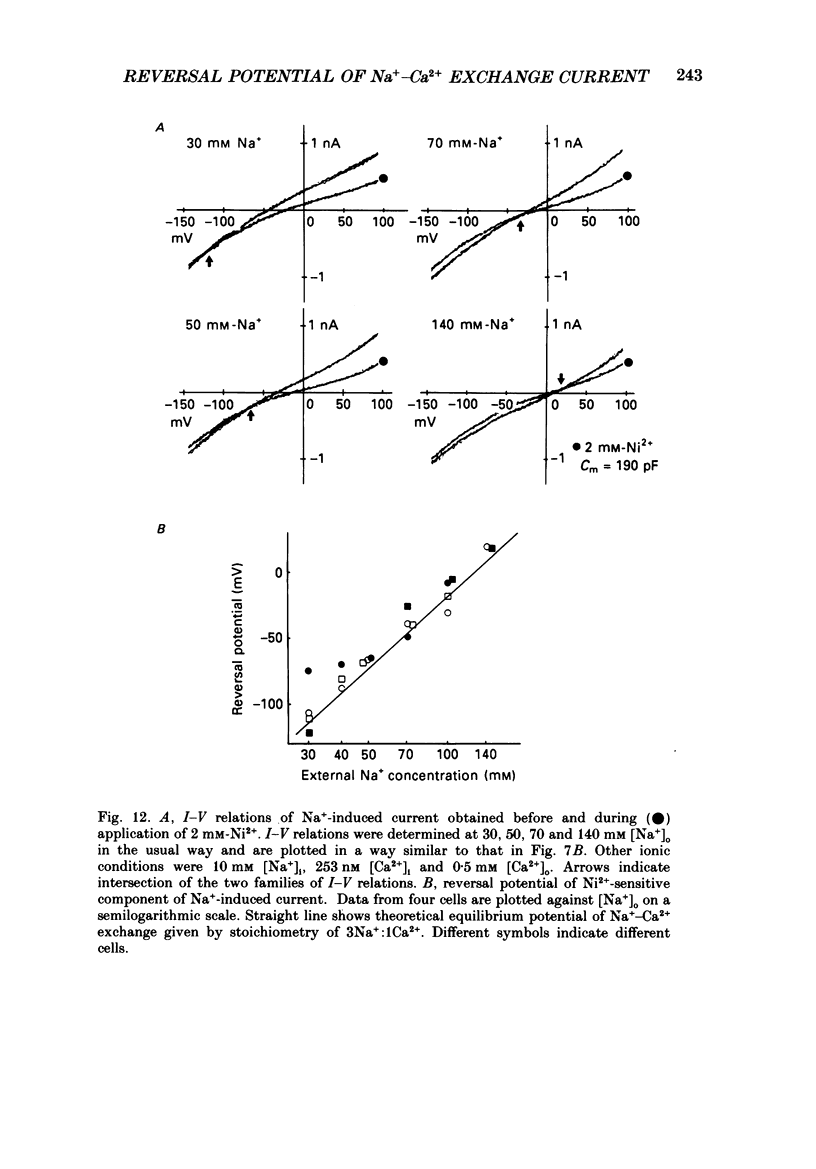
1. To identify the Na+- or Ca2+-induced current as Na+-Ca2+ exchange current and to determine the stoichiometry of the Na+-Ca2+ exchange, the reversal potential was measured in a wide range of external Na+ [( Na+]o) or Ca2+ [( Ca2+]o) concentrations. The Na+- or Ca2+-induced current was recorded in single ventricular cells enzymatically dispersed from guinea-pig hearts, using the technique of whole-cell voltage clamp combined with internal perfusion. 2. In the presence of 10-40 mM-Na+ and 55-803 nM-Ca2+ in the internal solution, an increase of [Ca2+]o from 0.1 to 0.5-20 mM or an increase of [Na+]o from 30 to 50-140 mM induced an extra current associated with an increase in membrane conductance. The reversal potential of these extra currents was determined from an intersection of the current-voltage (I-V) relations obtained in the absence and presence of a Na+-Ca2+ exchange blocker, Ni2+ (2 mM). 3. Ba2+ in the external solution failed to induce the extra current, but inhibited the background conductance having a reversal potential at around 0 mV. Thus, 1 mM-Ba2+ was added to all external solutions, so that a change in the background current was minimized during application of Ca2+ or Ni2+. 4. The relation between [Ca2+]o and amplitude of the Ca2+-induced current was examined in the presence and absence of Ni2+. Lineweaver-Burk analysis revealed that the action of Ni2+ on the extra current might be a mixed type of competitive and non-competitive inhibition. 5. During the application of Ca2+, the Ca2+-induced outward current decayed in a time-dependent manner, resulting in a shift of the I-V relations towards positive potentials. This current decay was inhibited by increasing the capacity of the internal Ca2+-buffer, using BAPTA (1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid) or higher concentrations of EGTA. The result indicates that [Ca2+]i, at least under the cell membrane, changes due to ion fluxes through the Na+-Ca2+ exchange and that control of the ion concentrations within the cell is prerequisite for measuring the reversal potential of the Na+-Ca2+ exchange. 6. The shift of both the holding current and the I-V relations during stimulation of the exchange was suppressed, when the membrane potential was clamped at the equilibrium potential of 3Na+:1Ca2+ exchange.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



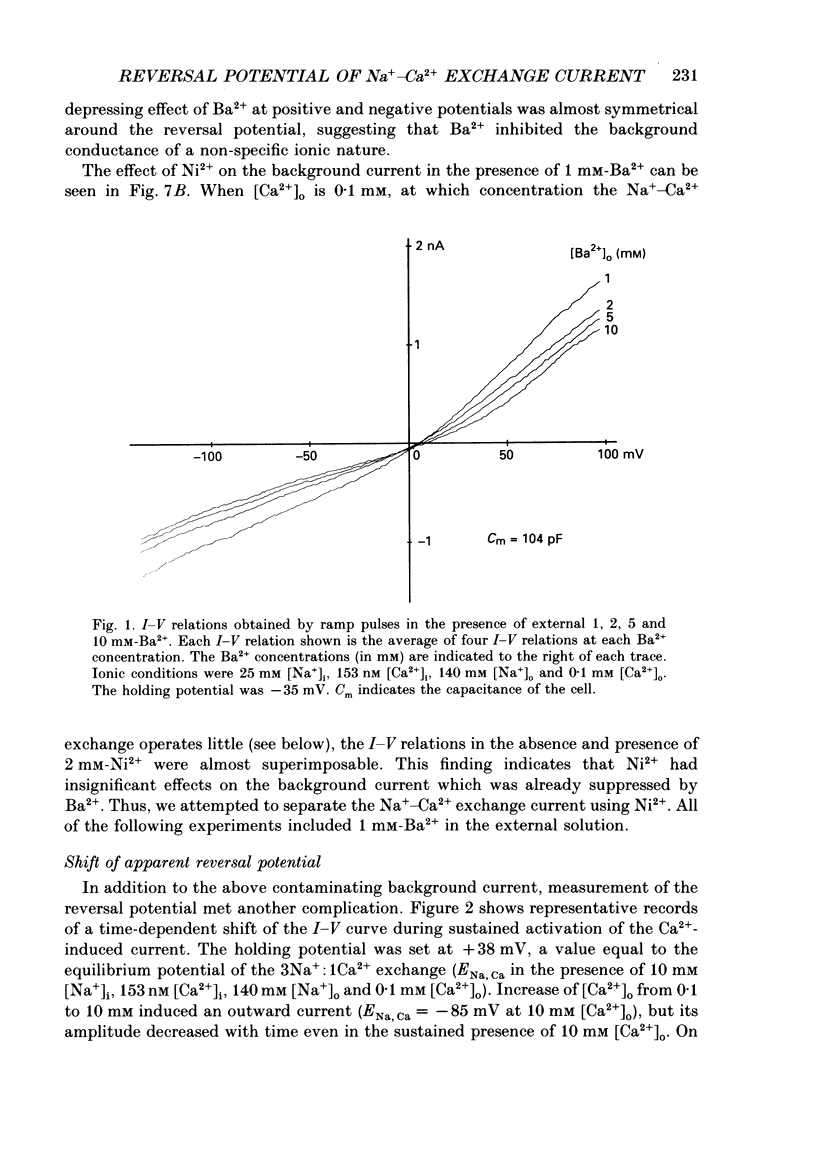
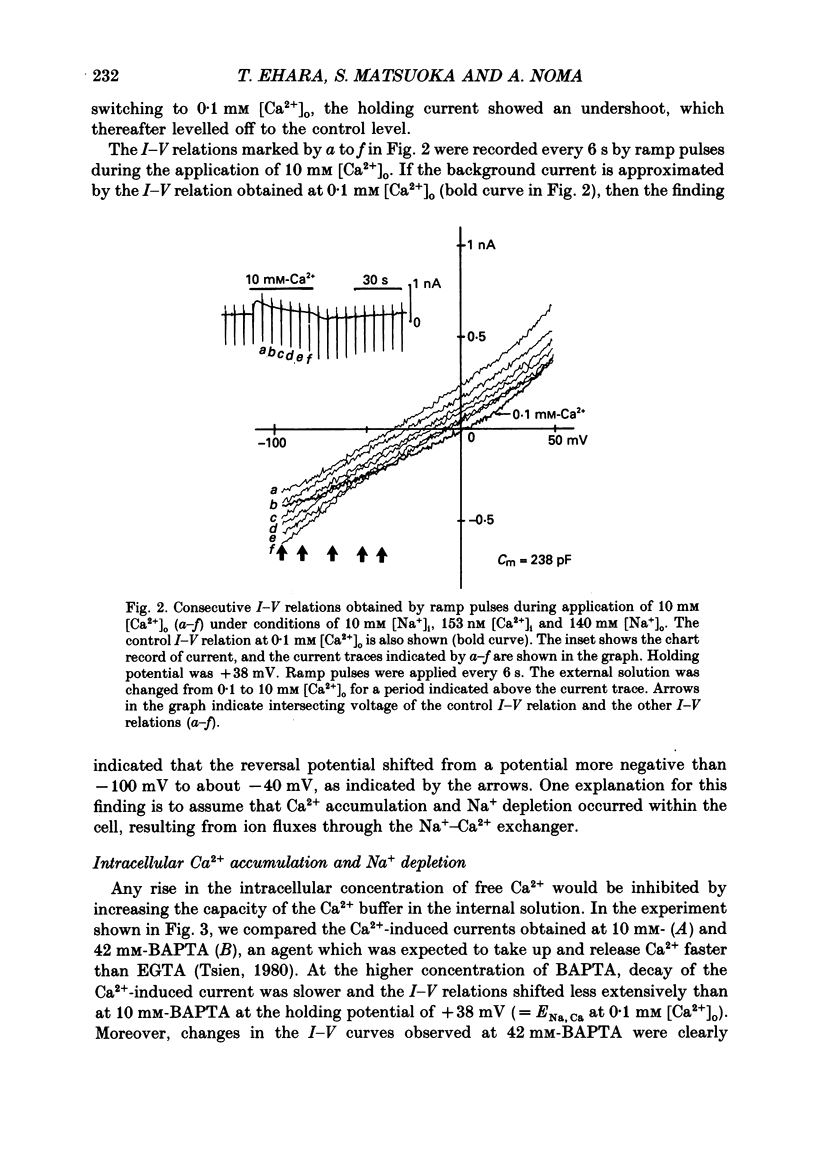
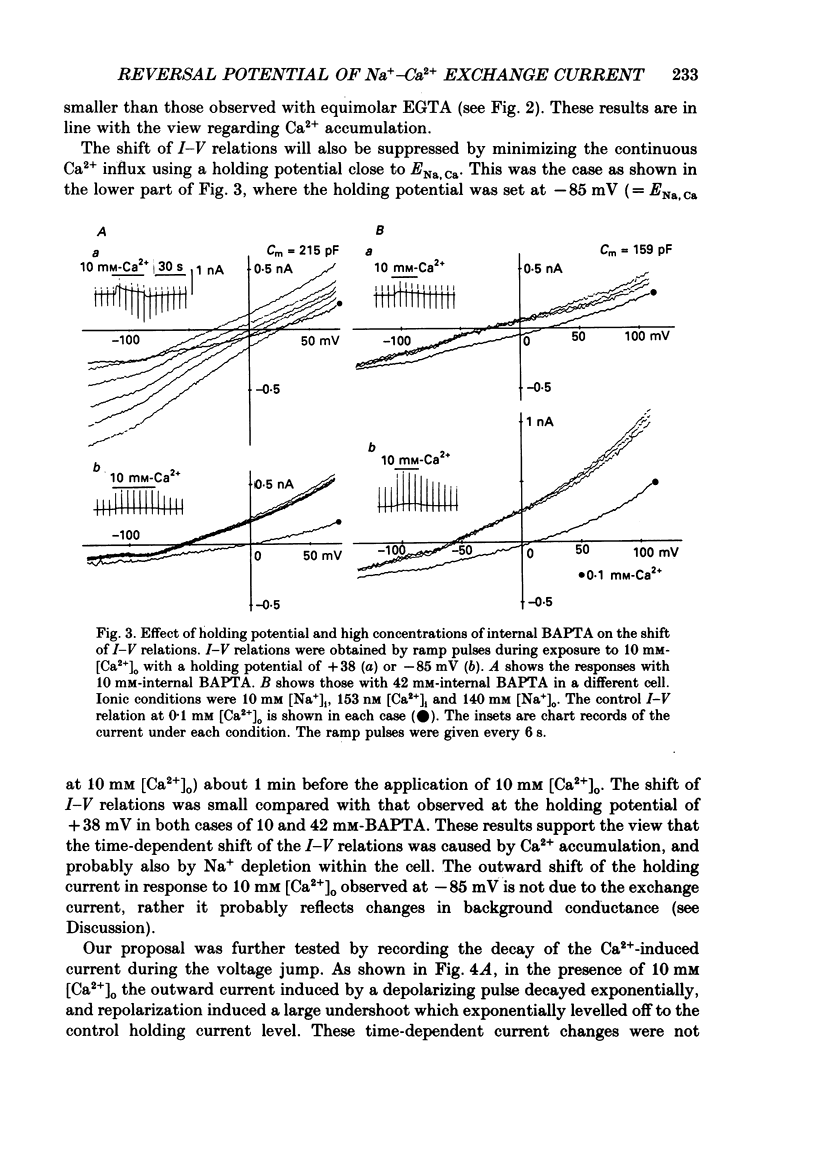
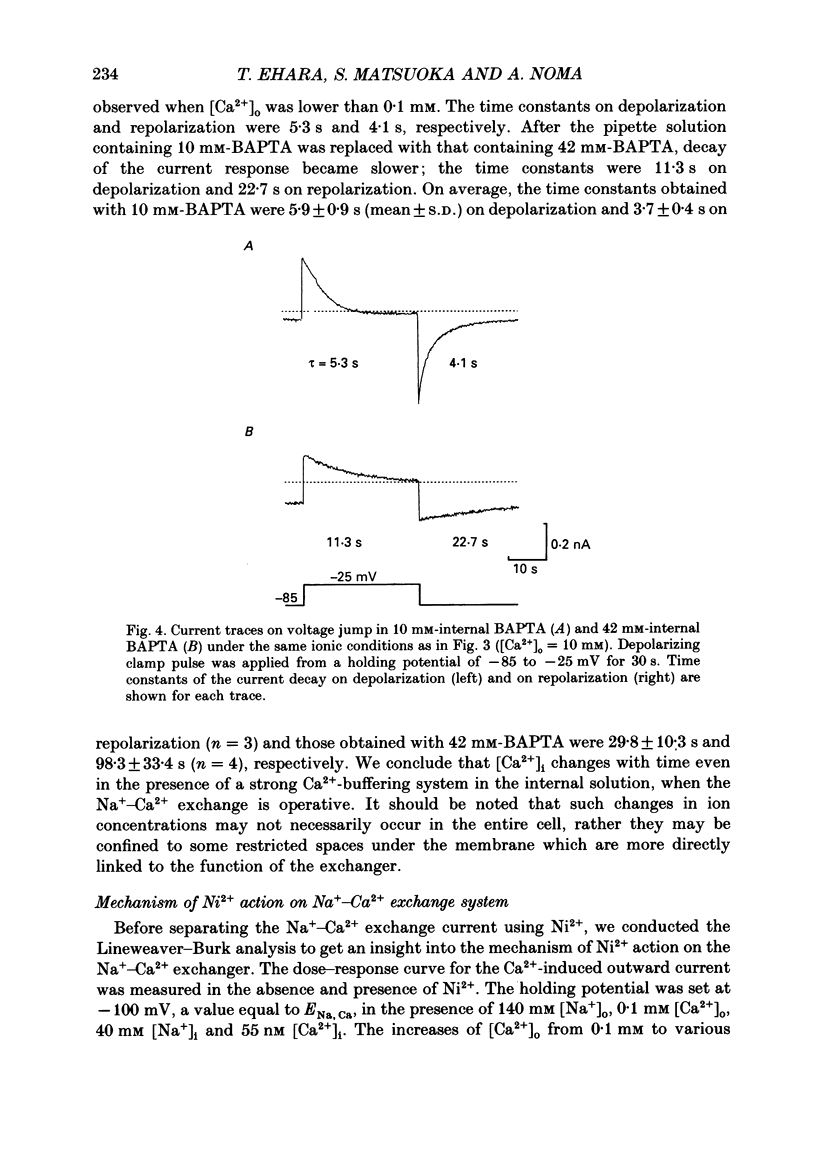
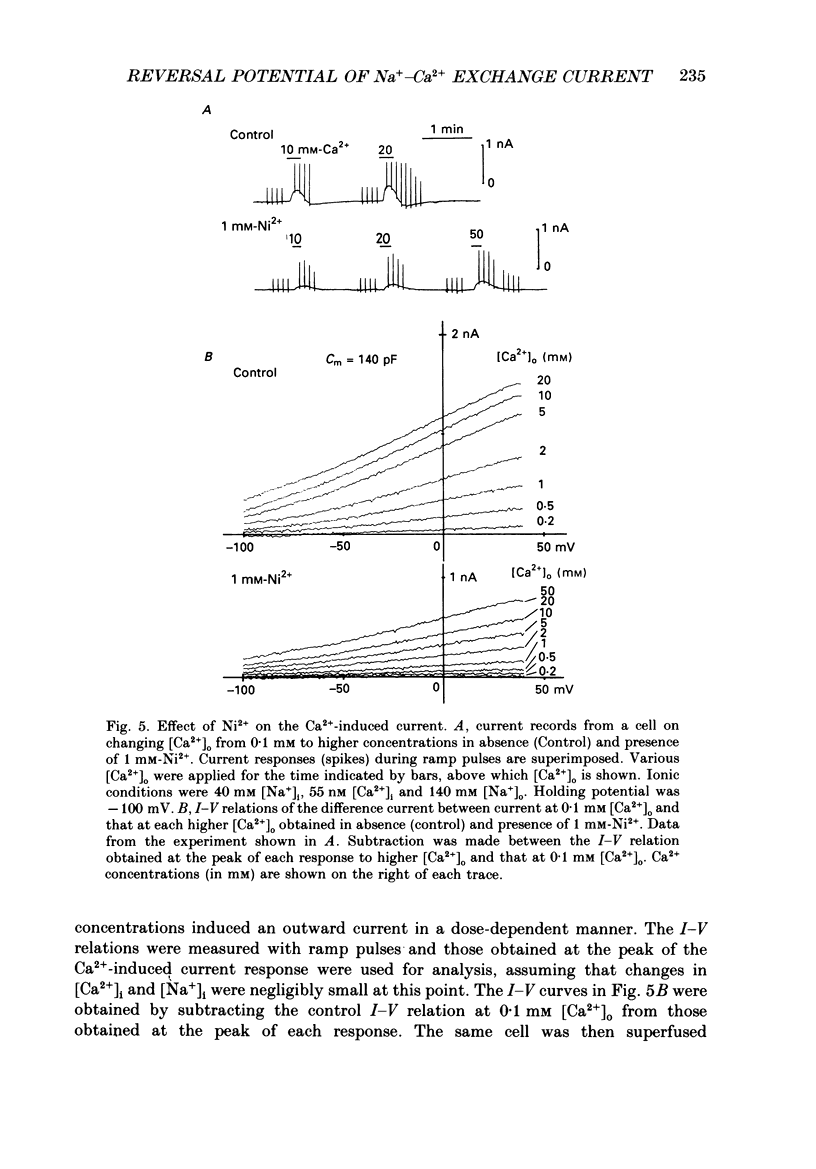
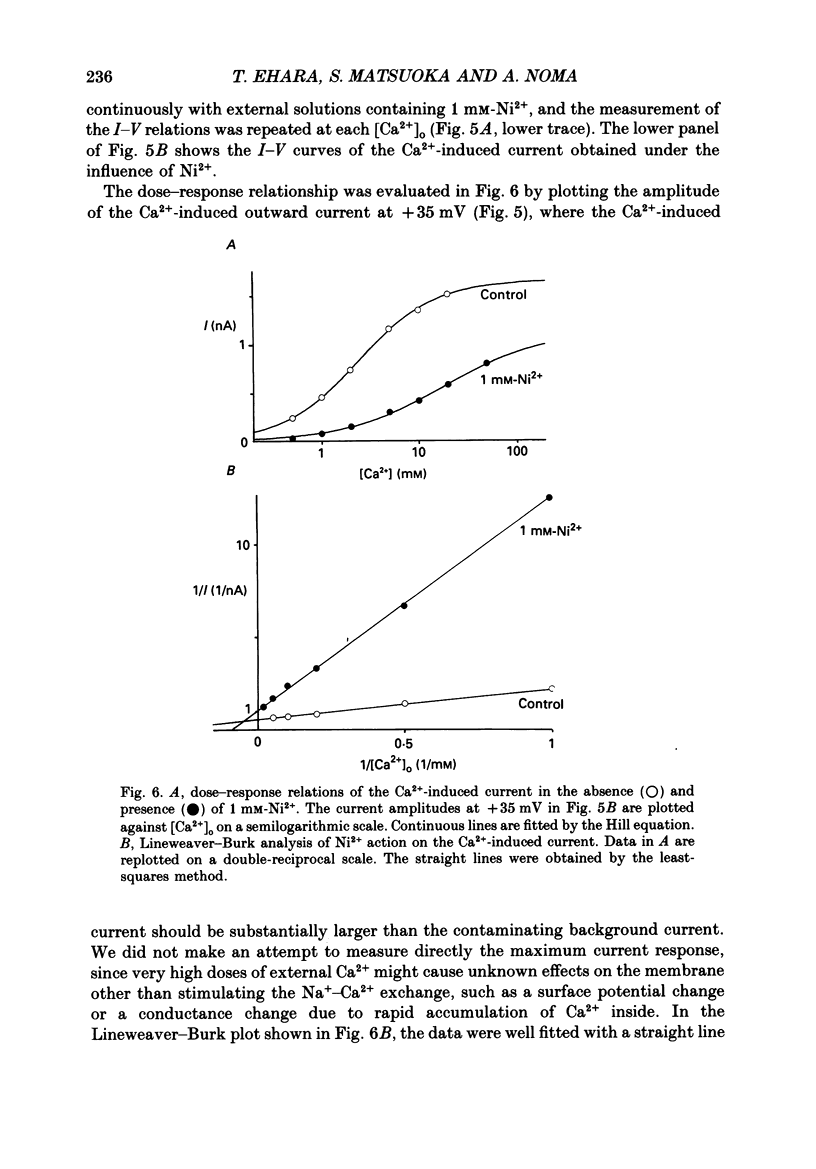

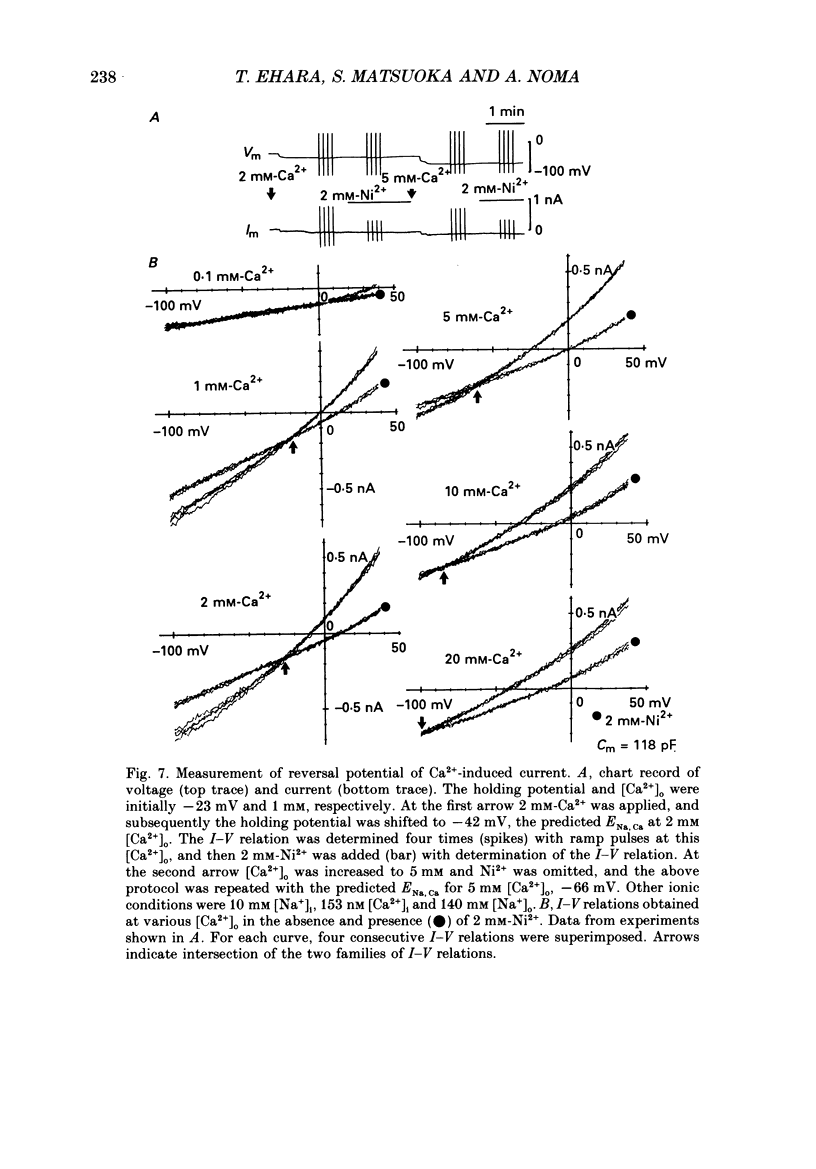
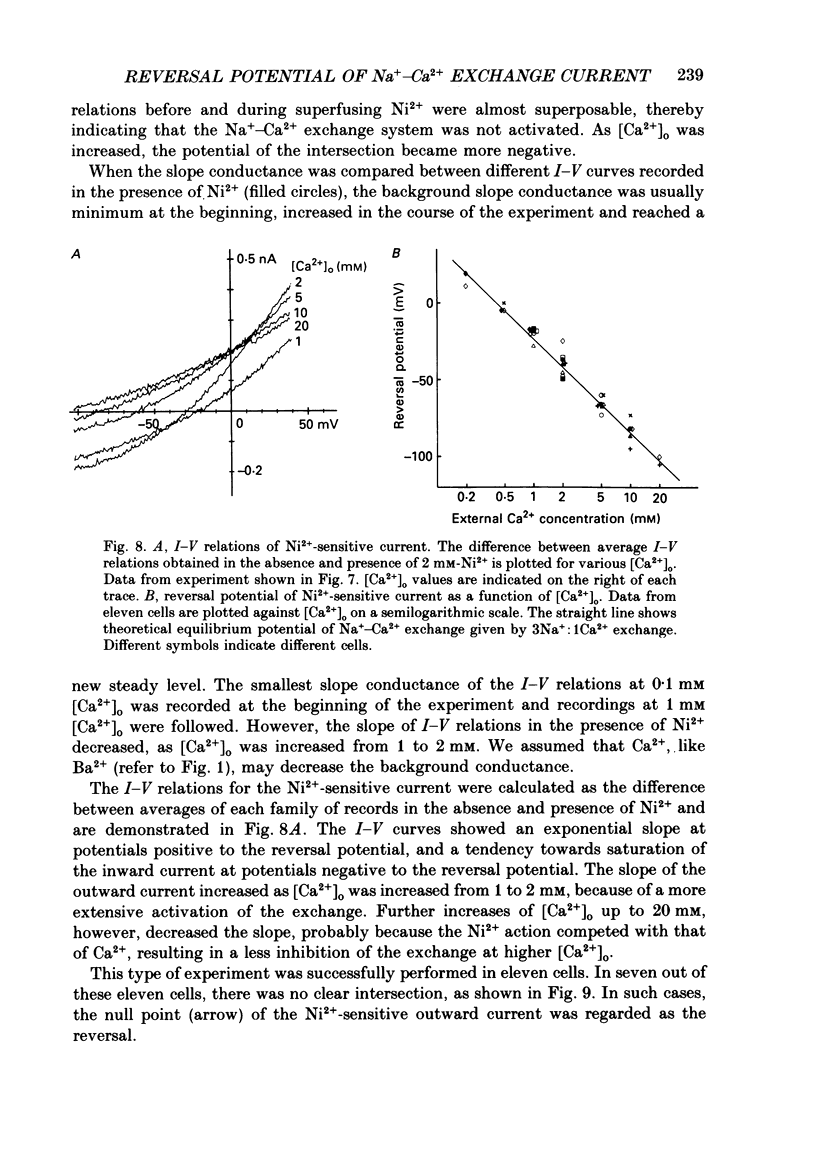






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen T. J., Baker P. F. Intracellular Ca indicator Quin-2 inhibits Ca2+ inflow via Na/Ca exchange in squid axon. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):755–756. doi: 10.1038/315755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen P. H., Bridge J. H. Electrochemical ion gradients and the Na/Ca exchange stoichiometry. Measurements of these gradients are thermodynamically consistent with a stoichiometric coefficient greater than or equal to 3. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Mar;85(3):471–475. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahinski A., Nakao M., Gadsby D. C. Potassium translocation by the Na+/K+ pump is voltage insensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3412–3416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., McNaughton P. A. Kinetics and energetics of calcium efflux from intact squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(1):103–144. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Ellis D. Intracellular calcium and sodium activity in sheep heart Purkinje fibres. Effect of changes of external sodium and intracellular pH. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Apr;393(2):171–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00582941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L. The effect of cyanide on the efflux of calcium from squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):497–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Santiago E. M. Effects of internal and external cations and of ATP on sodium-calcium and calcium-calcium exchange in squid axons. Biophys J. 1977 Oct;20(1):79–111. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85538-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridge J. H., Bassingthwaighte J. B. Uphill sodium transport driven by an inward calcium gradient in heart muscle. Science. 1983 Jan 14;219(4581):178–180. doi: 10.1126/science.6849128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Carafoli E. The regulation of the Na+ -Ca2+ exchanger of heart sarcolemma. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 16;132(3):451–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPolo R., Beaugé L. Characterization of the reverse Na/Ca exchange in squid axons and its modulation by Cai and ATP. Cai-dependent Nai/Cao and Nai/Nao exchange modes. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Oct;90(4):505–525. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.4.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPolo R., Beaugé L. The calcium pump and sodium-calcium exchange in squid axons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:313–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.001525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Lederer W. J. Na-Ca exchange: stoichiometry and electrogenicity. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C189–C202. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., McNaughton P. A., Nunn B. J. Measurement of sodium-calcium exchange in salamander rods. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:347–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nunn B. J. The effect of ions on sodium-calcium exchange in salamander rods. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:371–398. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume J. R., Uehara A. "Creep currents" in single frog atrial cells may be generated by electrogenic Na/Ca exchange. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jun;87(6):857–884. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.6.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume J. R., Uehara A. Properties of "creep currents" in single frog atrial cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jun;87(6):833–855. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.6.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Klockner U. Calcium tolerant ventricular myocytes prepared by preincubation in a "KB medium". Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):6–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00584963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Miyamae S., Noma A. Identification of sodium-calcium exchange current in single ventricular cells of guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:199–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Noma A., Irisawa H. Na-Ca exchange current in mammalian heart cells. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):596–597. doi: 10.1038/319596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer G. A. Sodium-calcium exchange in the heart. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:435–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledvora R. F., Hegyvary C. Dependence of Na+-Ca2+ exchange and Ca2+-Ca2+ exchange on monovalent cations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 23;729(1):123–136. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90463-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J. A mechanism for Na/Ca transport. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Dec;70(6):681–695. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.6.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J., Brinley F. J., Jr Sensitivity of calcium efflux from squid axons to changes in membrane potential. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Feb;65(2):135–152. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.2.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Gadsby D. C. Voltage dependence of Na translocation by the Na/K pump. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):628–630. doi: 10.1038/323628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson K. D. Sodium-calcium exchange in plasma membrane vesicles. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:561–571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts B. J. Stoichiometry of sodium-calcium exchange in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. Coupling to the sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6232–6235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell T., Terrar D. A., Twist V. W. Electrical properties of individual cells isolated from adult rat ventricular myocardium. J Physiol. 1980 May;302:131–153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasgado-Flores H., Blaustein M. P. Na/Ca exchange in barnacle muscle cells has a stoichiometry of 3 Na+/1 Ca2+. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):C499–C504. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.5.C499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Hale C. C. The stoichiometry of the cardiac sodium-calcium exchange system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7733–7739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato R., Noma A., Kurachi Y., Irisawa H. Effects of intracellular acidification on membrane currents in ventricular cells of the guinea pig. Circ Res. 1985 Oct;57(4):553–561. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.4.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheu S. S., Fozzard H. A. Na/Ca exchange in the intact cardiac cell. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Mar;85(3):476–478. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheu S. S., Fozzard H. A. Transmembrane Na+ and Ca2+ electrochemical gradients in cardiac muscle and their relationship to force development. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Sep;80(3):325–351. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima M., Noma A. Mode of regulation of the ACh-sensitive K-channel by the muscarinic receptor in rabbit atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00587544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi J., Kokubun S., Noma A., Irisawa H. Spontaneously active cells isolated from the sino-atrial and atrio-ventricular nodes of the rabbit heart. Jpn J Physiol. 1981;31(4):547–558. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.31.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada K., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Blocking actions of Ca2+ antagonists on the Ca2+ channels in the smooth muscle cell membrane of rabbit small intestine. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(6):552–557. doi: 10.1007/BF00581155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbits G. F., Philipson K. D. Na+-dependent alkaline earth metal uptake in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 25;817(2):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J. Neutral carrier ion-selective microelectrodes for measurement of intracellular free calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul;599(2):623–638. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Goshima K. Kinetic studies on sodium-dependent calcium uptake by myocardial cells and neuroblastoma cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 20;642(1):158–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Nakatani K. Electrogenic Na-Ca exchange in retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):661–663. doi: 10.1038/311661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


