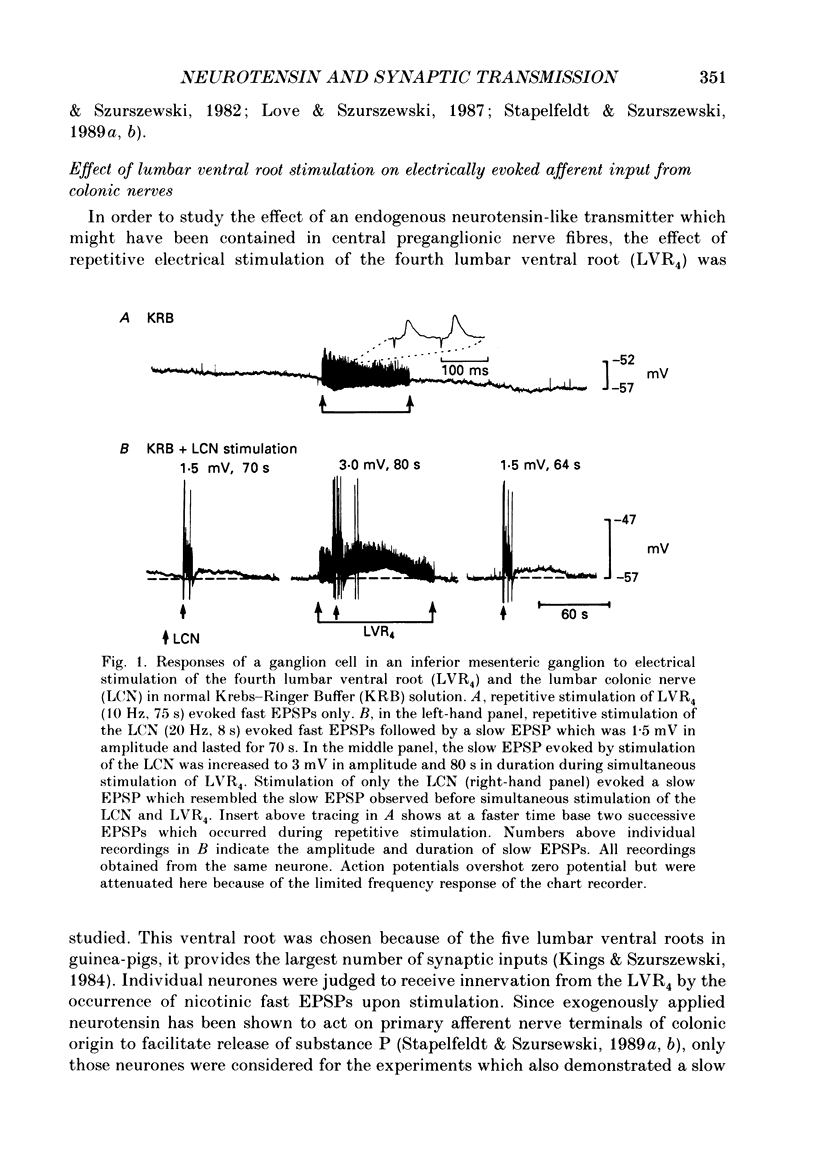
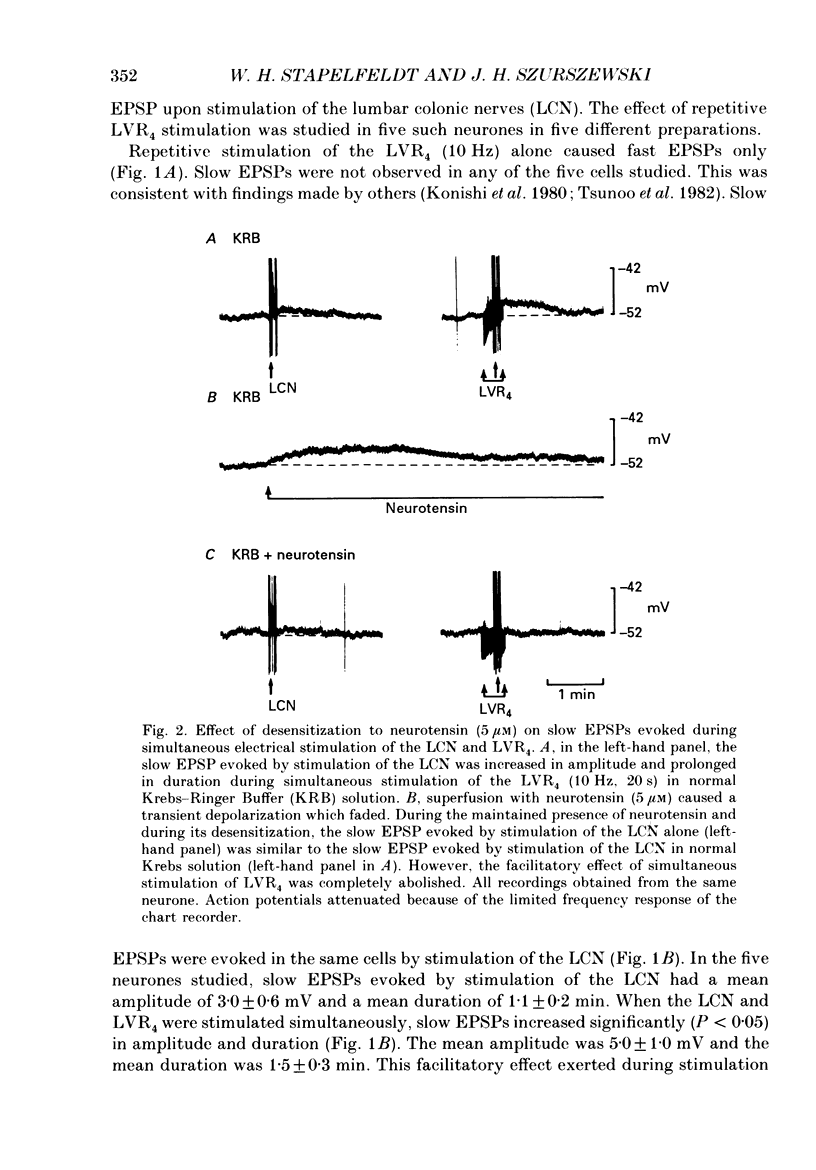
Abstract
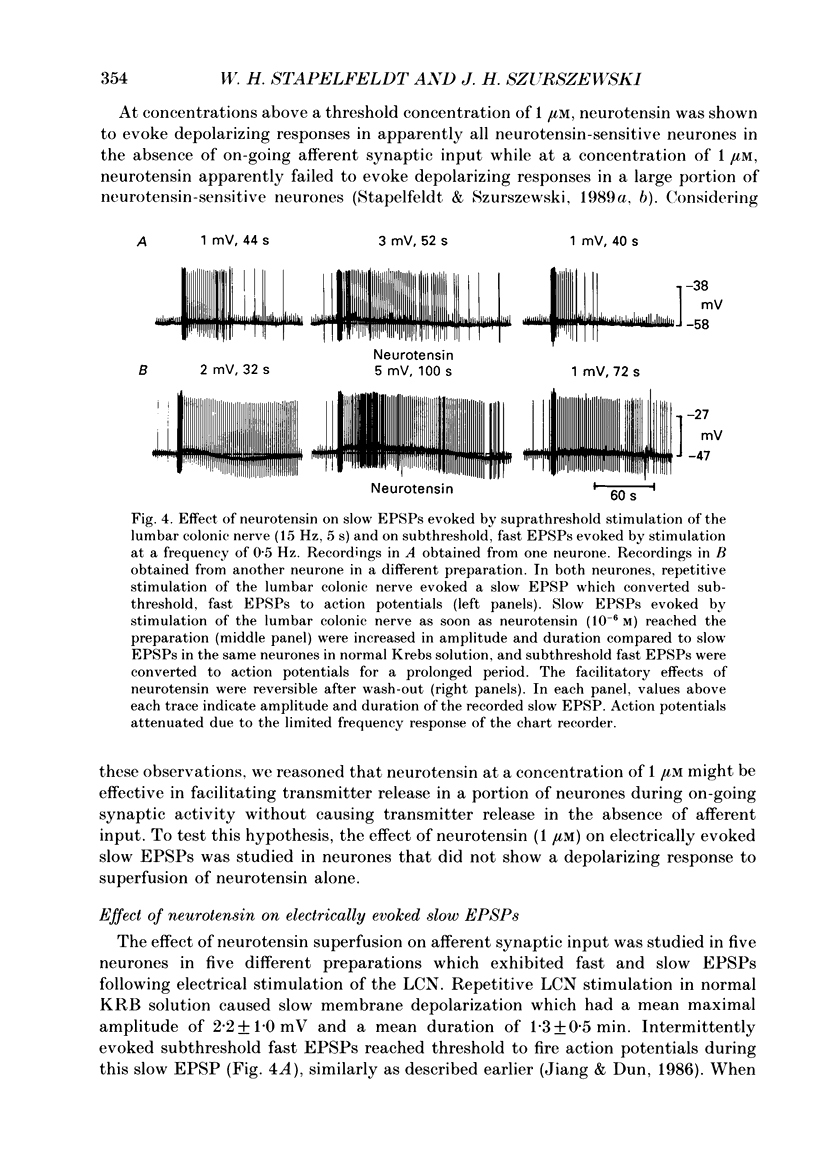
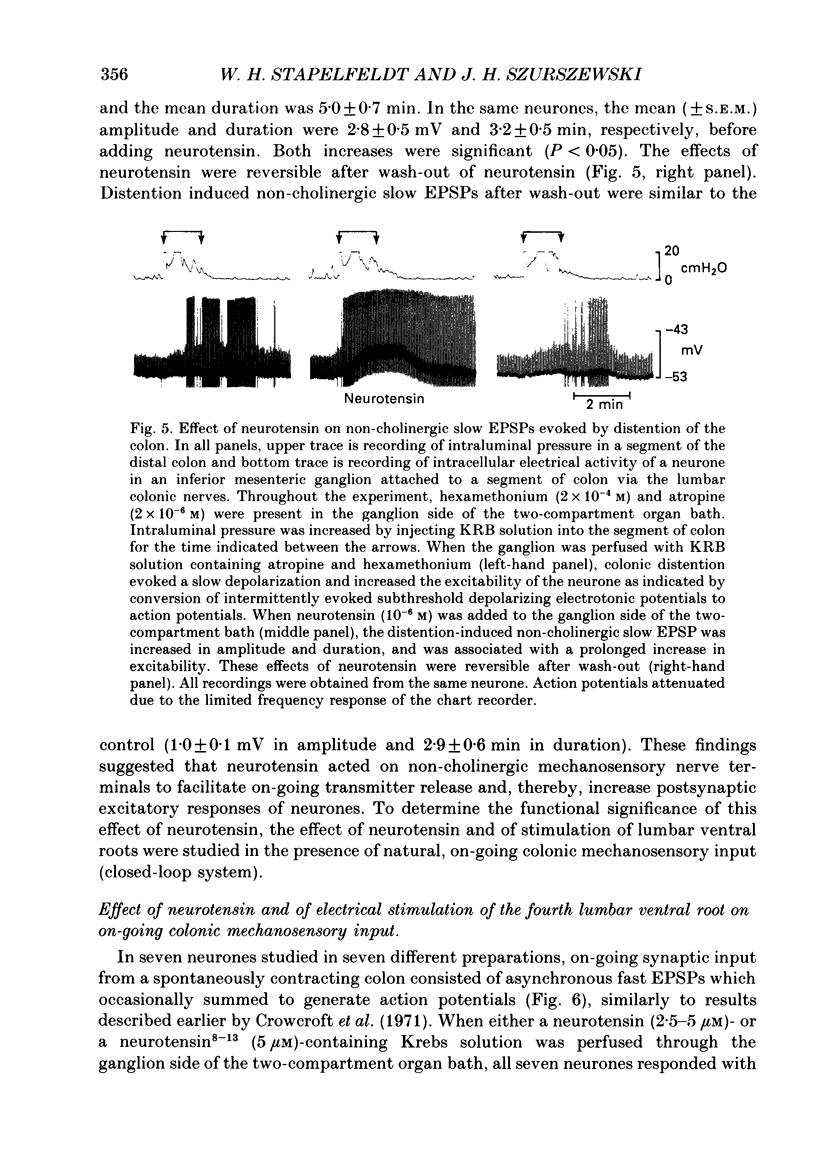
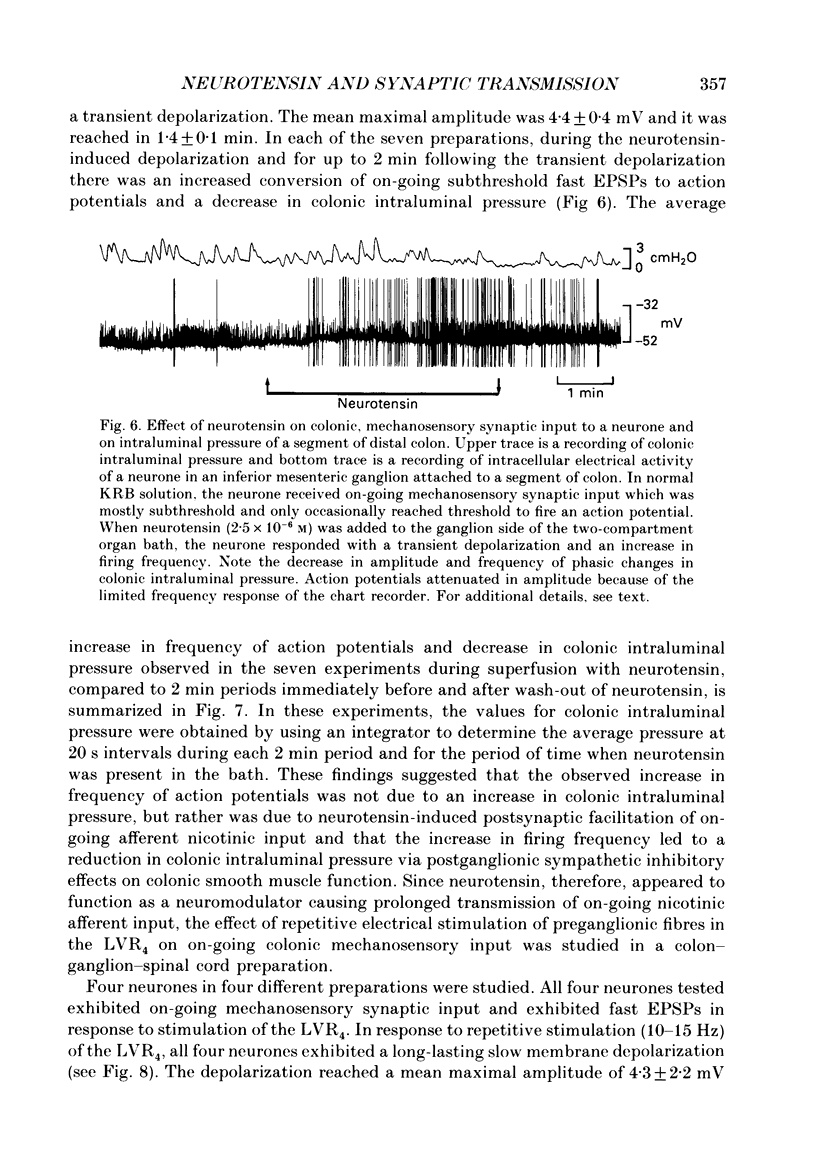
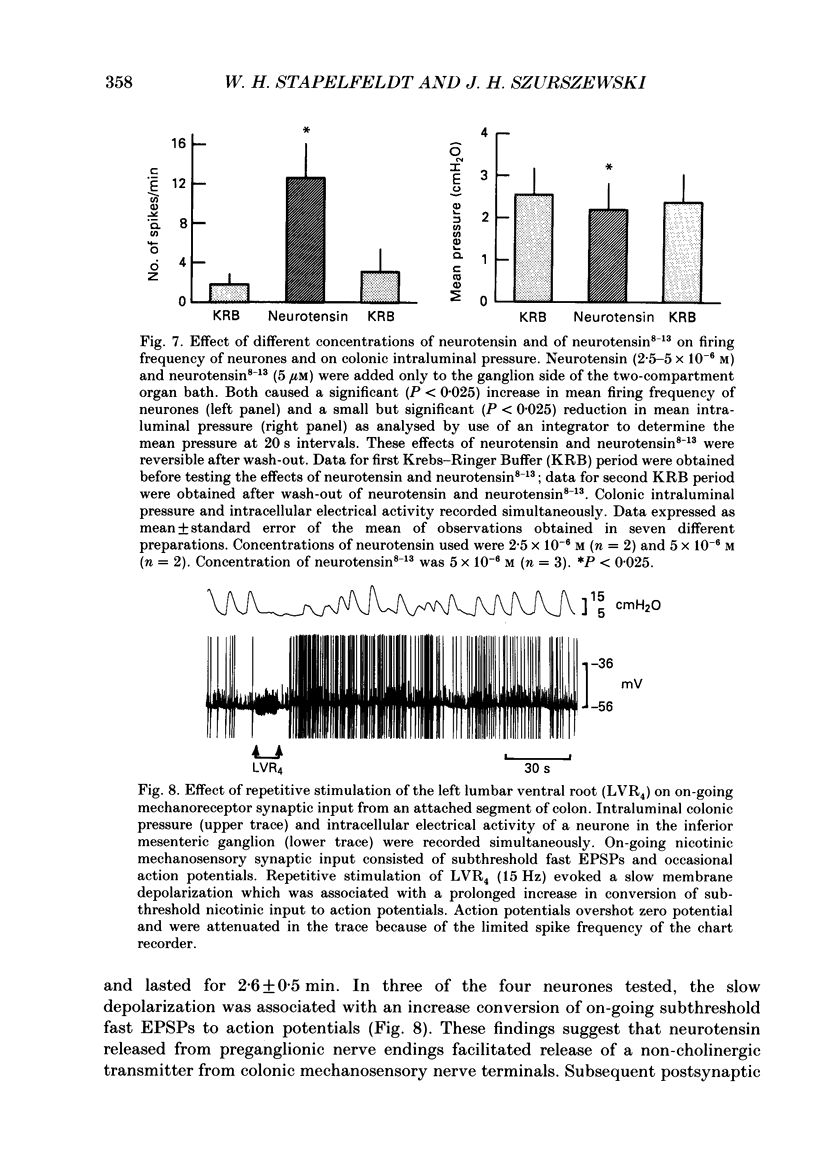
1. The effects of neurotensin and of stimulation of preganglionic nerves on peripheral afferent synaptic input from segments of distal colon to neurones in the inferior mesenteric ganglia of guinea-pigs were studied using intracellular recording techniques in vitro. 2. Electrical stimulation of colonic afferent nerve fibres evoked fast, nicotinic synaptic responses (fast EPSPs or action potentials) followed by a slow depolarizing response (slow EPSP). 3. Neurotensin (1 microM) increased the amplitude and duration of slow EPSPs evoked by stimulation of colonic afferents. 4. Distention of a segment of distal colon left attached to an inferior mesenteric ganglion evoked a slow depolarization. Neurotensin (1 microM) increased the amplitude and duration of distention-induced depolarizations. 5. Electrical stimulation of central preganglionic nerve fibres present in the third and fourth lumbar ventral roots increased the amplitude and duration of slow EPSPs evoked by electrical stimulation of colonic afferent nerves. This facilitatory effect was abolished after desensitization to neurotensin. 6. Slow depolarizations evoked by neurotensin and by stimulation of central preganglionic nerves converted subthreshold fast EPSPs due to mechanosensory synaptic input from an attached segment of distal colon to action potentials. This increase in firing rate of sympathetic ganglion cells led to a decrease in colonic intraluminal pressure. 7. Taken together these data support the hypothesis that neurotensin or a closely related substance contained in central preganglionic nerves facilitated release of a non-cholinergic excitatory transmitter from colonic mechanosensory nerves. The slow depolarization evoked by the non-cholinergic transmitter converted on-going subthreshold fast EPSPs to action potentials thereby increasing sympathetic output to the colon. 8. It is suggested that under normal in vivo conditions, central preganglionic fibres containing neurotensin or a closely related peptide modulate peripheral reflex activity through prevertebral ganglia in guinea-pigs.
Full text
PDF







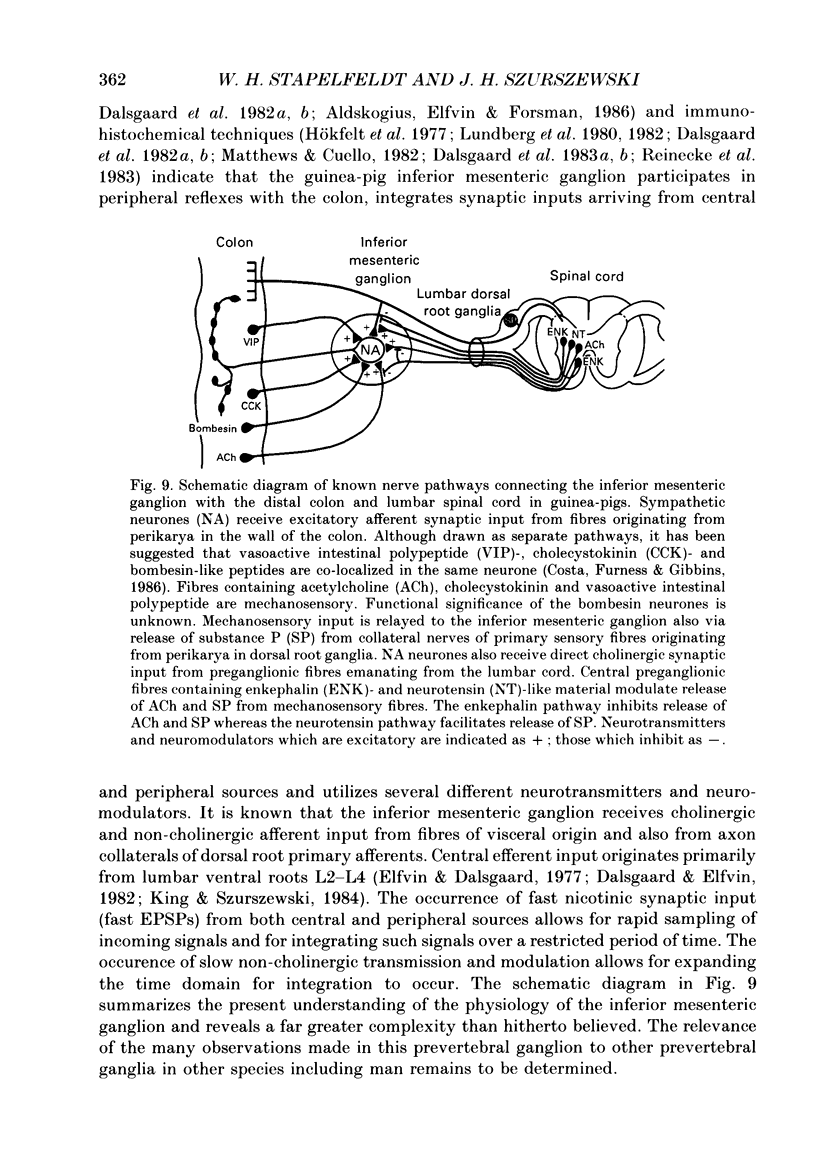



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldskogius H., Elfvin L. G., Forsman C. A. Primary sensory afferents in the inferior mesenteric ganglion and related nerves of the guinea pig. An experimental study with anterogradely transported wheat germ agglutinin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1986 Feb;15(2):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(86)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Vincent J. P., Kitabgi P. Neuromedin N: high affinity interaction with brain neurotensin receptors and rapid inactivation by brain synaptic peptidases. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul 31;126(3):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B., Gibbins I. L. Chemical coding of enteric neurons. Prog Brain Res. 1986;68:217–239. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowcroft P. J., Holman M. E., Szurszewski J. H. Excitatory input from the distal colon to the inferior mesenteric ganglion in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(2):443–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowcroft P. J., Szurszewski J. H. A study of the inferior mesenteric and pelvic ganglia of guinea-pigs with intracellular electrodes. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(2):421–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Elfvin L. G. Spinal origin of preganglionic fibers projecting onto the superior cervical ganglion and inferior mesenteric ganglion of the guinea pig, as demonstrated by the horseradish peroxidase technique. Brain Res. 1979 Aug 17;172(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90901-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Elfvin L. G. Structural studies on the connectivity of the inferior mesenteric ganglion of the guinea pig. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1982 May;5(3):265–278. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(82)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Hökfelt T., Elfvin L. G., Skirboll L., Emson P. Substance P-containing primary sensory neurons projecting to the inferior mesenteric ganglion: evidence from combined retrograde tracing and immunohistochemistry. Neuroscience. 1982 Mar;7(3):647–654. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Hökfelt T., Elfvin L. G., Terenius L. Enkephalin-containing sympathetic preganglionic neurons projecting to the inferior mesenteric ganglion: evidence from combined retrograde tracing and immunohistochemistry. Neuroscience. 1982;7(9):2039–2050. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Hökfelt T., Schultzberg M., Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Dockray G. J., Goldstein M. Origin of peptide-containing fibers in the inferior mesenteric ganglion of the guinea-pig: immunohistochemical studies with antisera to substance P, enkephalin, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, cholecystokinin and bombesin. Neuroscience. 1983 May;9(1):191–211. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Vincent S. R., Hökfelt V. T., Christensson I., Terenius L. Separate origins for the dynorphin and enkephalin immunoreactive fibers in the inferior mesenteric ganglion of the guinea pig. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Dec 20;221(4):482–489. doi: 10.1002/cne.902210410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dun N. J., Jiang Z. G. Non-cholinergic excitatory transmission in inferior mesenteric ganglia of the guinea-pig: possible mediation by substance P. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:145–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfvin L. G., Dalsgaard C. J. Retrograde axonal transport of horseradish perioxidase in afferent fibers of the inferior mesenteric ganglion of the guinea pig. Identification of the cells of origin in dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res. 1977 Apr 22;126(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90221-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry R. C. The nervous control of the caudal region of the large bowel in the cat. J Physiol. 1933 Mar 15;77(4):422–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp002977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heym C., Reinecke M., Weihe E., Forssmann W. G. Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase-, neurotensin-, substance P-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide- and enkephalin-immunohistochemistry of paravertebral and prevertebral ganglia in the cat. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;235(2):411–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00217867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Elfvin L. G., Schultzberg M., Goldstein M., Nilsson G. On the occurrence of substance P-containing fibers in sympathetic ganglia: immunohistochemical evidence. Brain Res. 1977 Aug 19;132(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90704-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Z. G., Dun N. J. Facilitation of nicotinic response in the guinea pig prevertebral neurons by substance P. Brain Res. 1986 Jan 15;363(1):196–198. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90679-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King B. F., Szurszewski J. H. Mechanoreceptor pathways from the distal colon to the autonomic nervous system in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:93–107. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi S., Tsunoo A., Otsuka M. Enkephalin as a transmitter for presynaptic inhibition in sympathetic ganglia. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):80–82. doi: 10.1038/294080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi S., Tsunoo A., Otsuka M. Enkephalins presynaptically inhibit cholinergic transmission in sympathetic ganglia. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):515–516. doi: 10.1038/282515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreulen D. L., Peters S. Non-cholinergic transmission in a sympathetic ganglion of the guinea-pig elicited by colon distension. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:315–334. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krier J., Szurszewski J. H. Effect of substance P on colonic mechanoreceptors, motility, and sympathetic neurons. Am J Physiol. 1982 Oct;243(4):G259–G267. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.243.4.G259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krukoff T. L. Coexistence of neuropeptides in sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the cat. Peptides. 1987 Jan-Feb;8(1):109–112. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(87)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love J. A., Szurszewski J. H. The electrophysiological effects of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the guinea-pig inferior mesenteric ganglion. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:67–84. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Anggård A., Uvnäs-Wallensten K., Brimijoin S., Brodin E., Fahrenkrug J. Peripheral peptide neurons: distribution, axonal transport, and some aspects on possible function. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1980;22:25–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Rökaeus A., Hökfelt T., Rosell S., Brown M., Goldstein M. Neurotensin-like immunoreactivity in the preganglionic sympathetic nerves and in the adrenal medulla of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Jan;114(1):153–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb06965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews M. R., Cuello A. C. Substance P-immunoreactive peripheral branches of sensory neurons innervate guinea pig sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1668–1672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Neuromedin N: a novel neurotensin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):542–549. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mo N., Dun N. J. Cholecystokinin octapeptide depolarizes guinea pig inferior mesenteric ganglion cells and facilitates nicotinic transmission. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Mar 14;64(3):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mo N., Dun N. J. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide facilitates muscarinic transmission in mammalian sympathetic ganglia. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Nov 23;52(1-2):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S., Kreulen D. L. Fast and slow synaptic potentials produced in a mammalian sympathetic ganglion by colon distension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1941–1944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinecke M., Forssmann W. G., Thiekötter G., Triepel J. Localization of neurotensin-immunoreactivity in the spinal cord and peripheral nervous system of the guinea pig. Neurosci Lett. 1983 May 27;37(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90501-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann M. A., Kreulen D. L. Action of cholecystokinin octapeptide and CCK-related peptides on neurons in inferior mesenteric ganglion of guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Nov;239(2):618–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C., Thim L., Conlon J. M. [Ser7]neurotensin: isolation from guinea pig intestine. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 7;202(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80684-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu H. D., Love J. A., Szurszewski J. H. Effect of enkephalins on colonic mechanoreceptor synaptic input to inferior mesenteric ganglion. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 1):G128–G135. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.1.G128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapelfeldt W. H., Szurszewski J. H. Neurotensin facilitates release of substance P in the guinea-pig inferior mesenteric ganglion. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:325–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
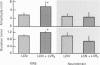
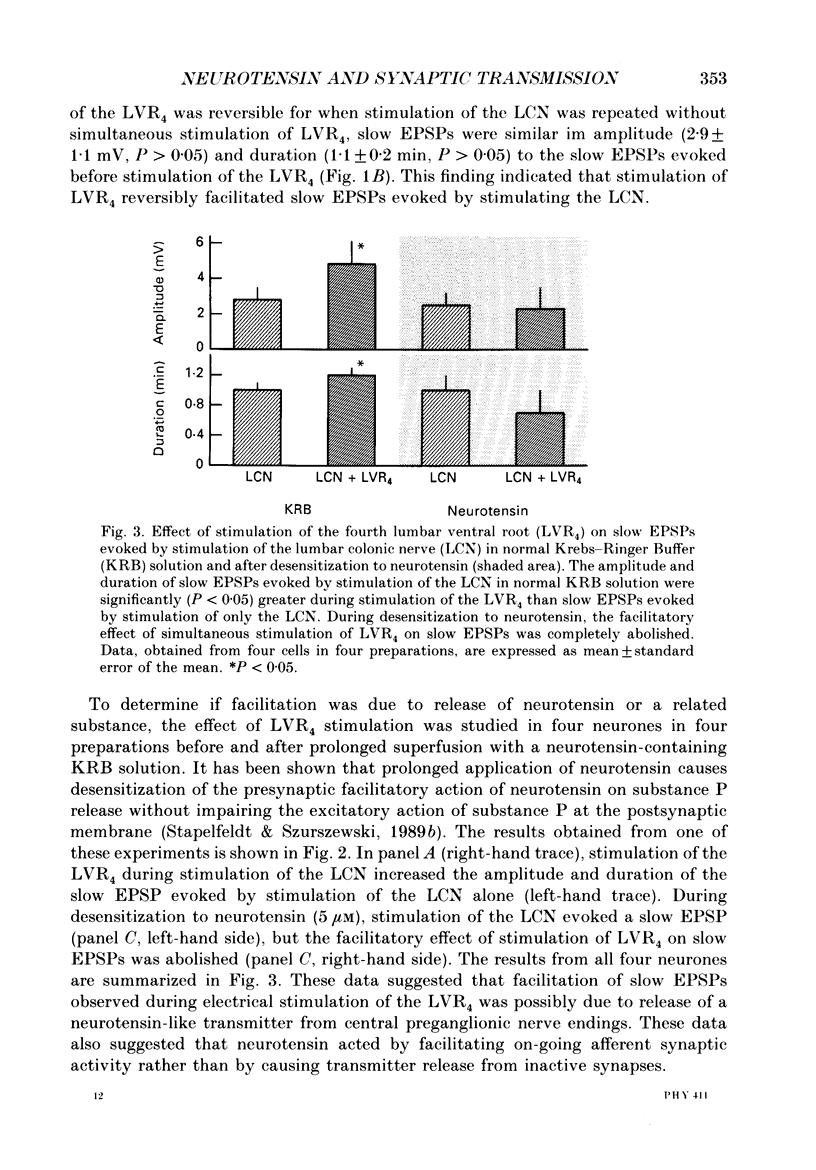
- Stapelfeldt W. H., Szurszewski J. H. The electrophysiological effects of neurotensin on neurones of guinea-pig prevertebral sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:301–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szurszewski J. H. Physiology of mammalian prevertebral ganglia. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:53–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.000413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szurszewski J. H., Weems W. A. A study of peripheral input to and its control by post-ganglionic neurones of the inferior mesenteric ganglion. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(3):541–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunoo A., Konishi S., Otsuka M. Substance P as an excitatory transmitter of primary afferent neurons in guinea-pig sympathetic ganglia. Neuroscience. 1982;7(9):2025–2037. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weems W. A., Szurszewski J. H. Modulation of colonic motility by peripheral neural inputs to neurons of the inferior mesenteric ganglion. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):273–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]