Abstract
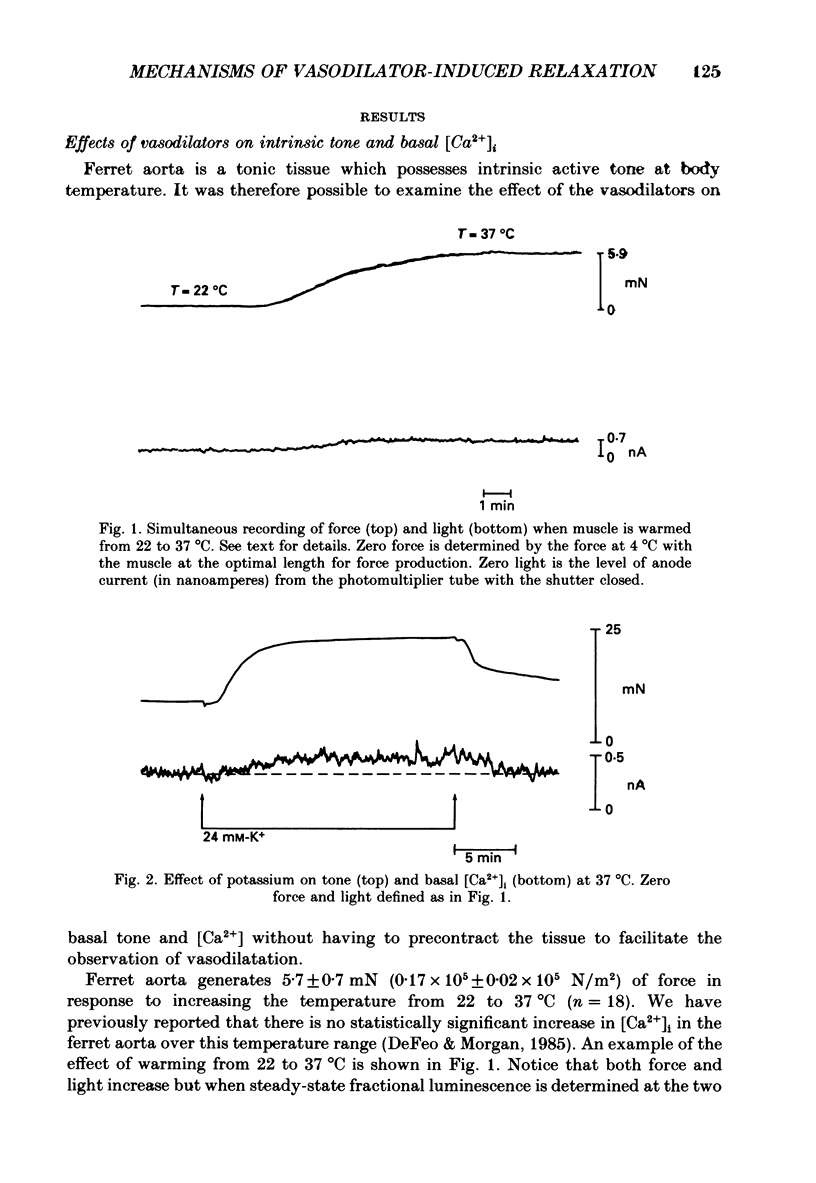
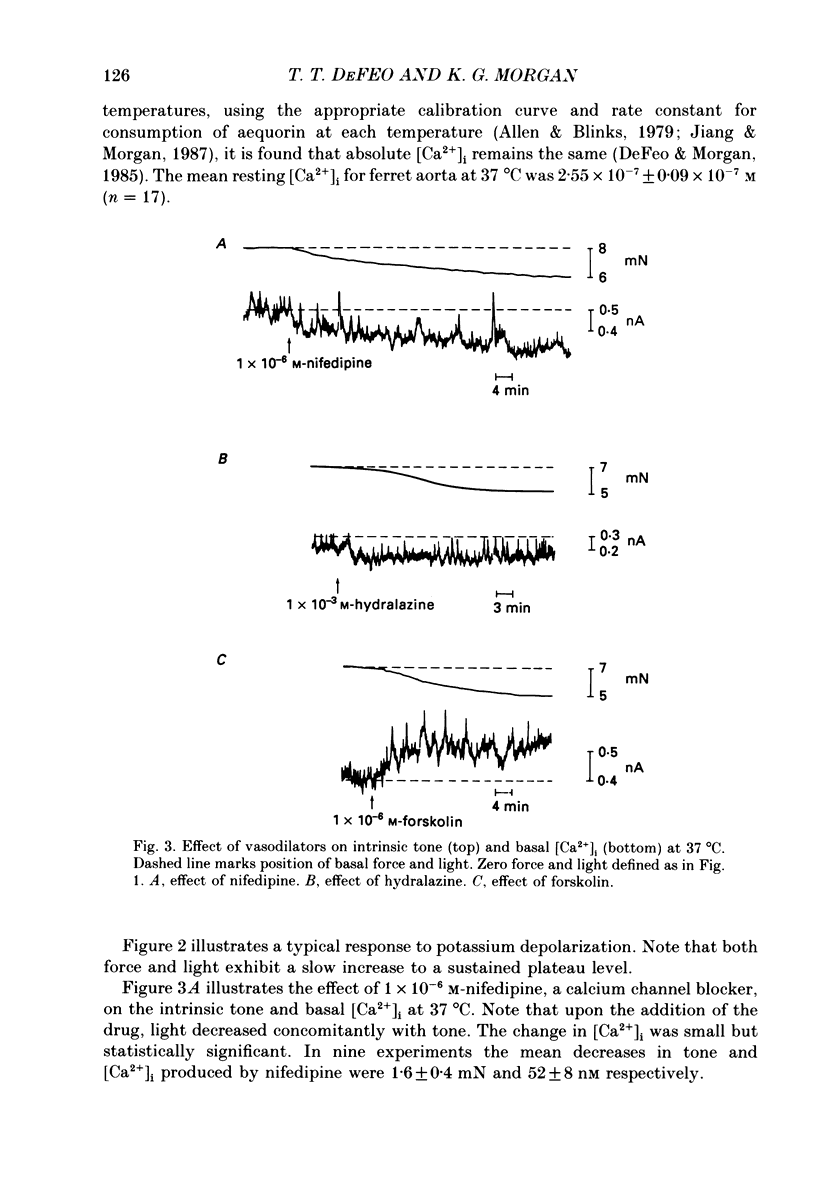
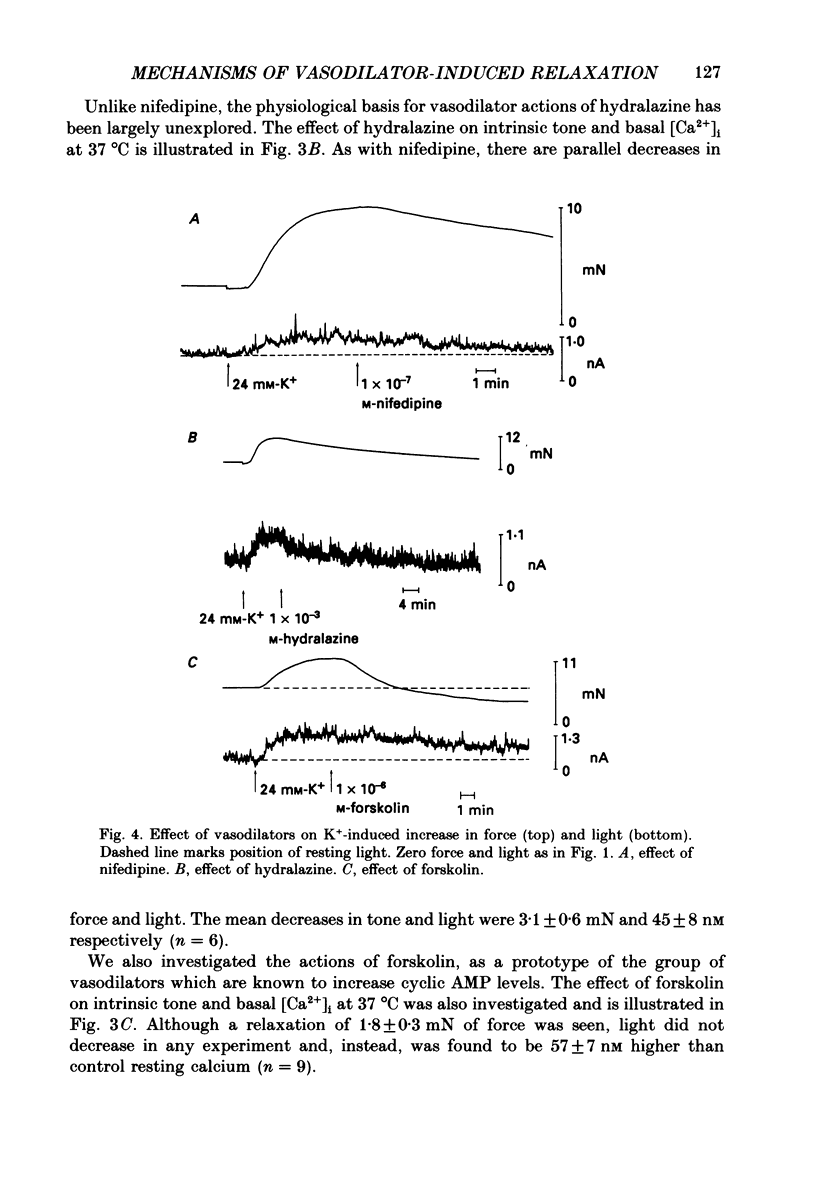
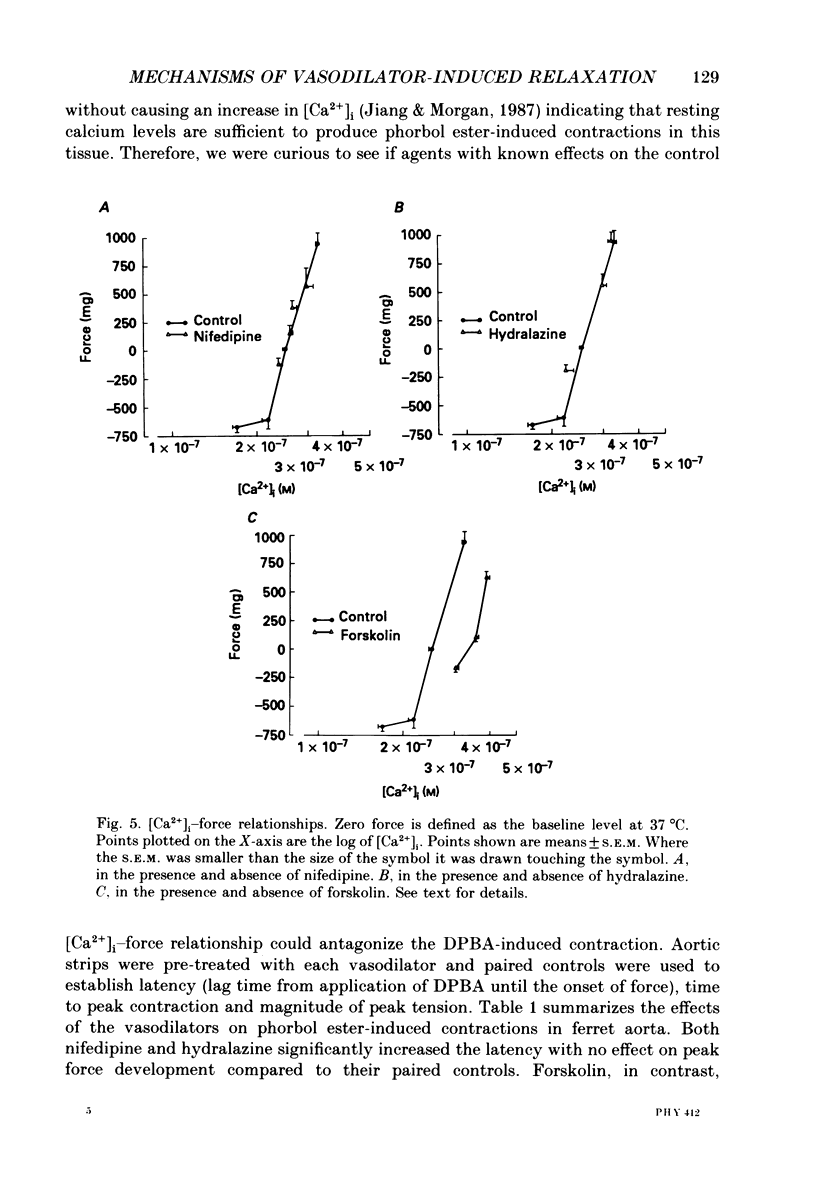
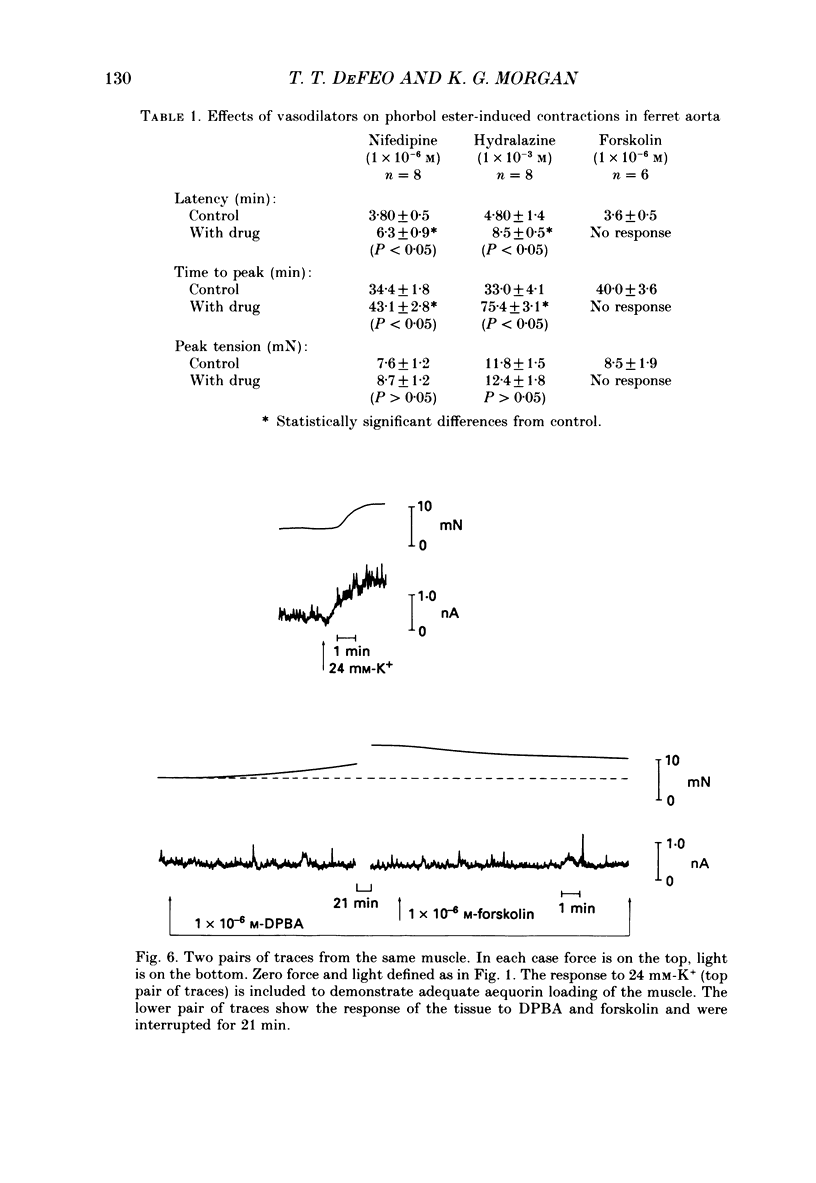
1. The effects of three vasodilators, nifedipine, hydralazine and forskolin, were determined on isometric force and intracellular ionized calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) as indicated by aequorin in ferret aorta. Three types of contraction were studied: the intrinsic tone induced by warming from 22 to 37 degrees C; the contraction to the phorbol ester 12-deoxyphorbol-13-isobutyrate-20-acetate (DPBA); and the contraction to potassium depolarization. 2. On warming there was no significant steady-state change in [Ca2+], even though 5.7 +/- 0.7 mN of tone developed. During potassium depolarization, [Ca2+]i rose to a sustained plateau while DPBA caused no significant rise in [Ca2+]i. 3. Nifedipine and hydralazine inhibited intrinsic tone while causing an associated decrease in [Ca2+]i; but in the presence of forskolin, a similar inhibition of tone was accompanied by no significant decrease in [Ca2+]i. 4. Nifedipine and hydralazine prolonged the characteristic lag phase before force development in response to DPBA but did not cause a significant change in contraction amplitude. In contrast, forskolin caused an essentially total inhibition of the contraction. 5. During potassium depolarization, all three vasodilators caused significant decreases in [Ca2+]i coincident with decreases in steady-state force. Calcium-force curves were constructed by plotting the calibrated aequorin light signal against the resulting force. The control calcium-force curve was not shifted by nifedipine or hydralazine but was significantly shifted to the right by forskolin.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baraban J. M., Gould R. J., Peroutka S. J., Snyder S. H. Phorbol ester effects on neurotransmission: interaction with neurotransmitters and calcium in smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):604–607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley A. B., Morgan K. G. Alterations in cytoplasmic calcium sensitivity during porcine coronary artery contractions as detected by aequorin. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:437–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo T. T., Morgan K. G. A comparison of two different indicators: quin 2 and aequorin in isolated single cells and intact strips of ferret portal vein. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Apr;406(4):427–429. doi: 10.1007/BF00590948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo T. T., Morgan K. G. Calcium-force relationships as detected with aequorin in two different vascular smooth muscles of the ferret. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:269–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. Mechanism of action of hydralazine on vascular smooth muscle. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 15;33(18):2915–2919. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90216-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang M. J., Morgan K. G. Intracellular calcium levels in phorbol ester-induced contractions of vascular muscle. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 2):H1365–H1371. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.6.H1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisheri K. D., van Breemen C. Effects of beta-adrenergic stimulation on calcium movements in rabbit aortic smooth muscle: relationship with cyclic AMP. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:429–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Alteration of cytoplasmic ionized calcium levels in smooth muscle by vasodilators in the ferret. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:539–551. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Stimulus-specific patterns of intracellular calcium levels in smooth muscle of ferret portal vein. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:155–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Vascular smooth muscle: the first recorded Ca2+ transients. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):75–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00584972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Perspectives on the role of protein kinase C in stimulus-response coupling. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Mar;76(3):363–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Haeusler G., Somlyo A. P. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate: potassium-dependent action on vascular smooth muscle membrane potential. Science. 1970 Jul 31;169(3944):490–491. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3944.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


