Abstract
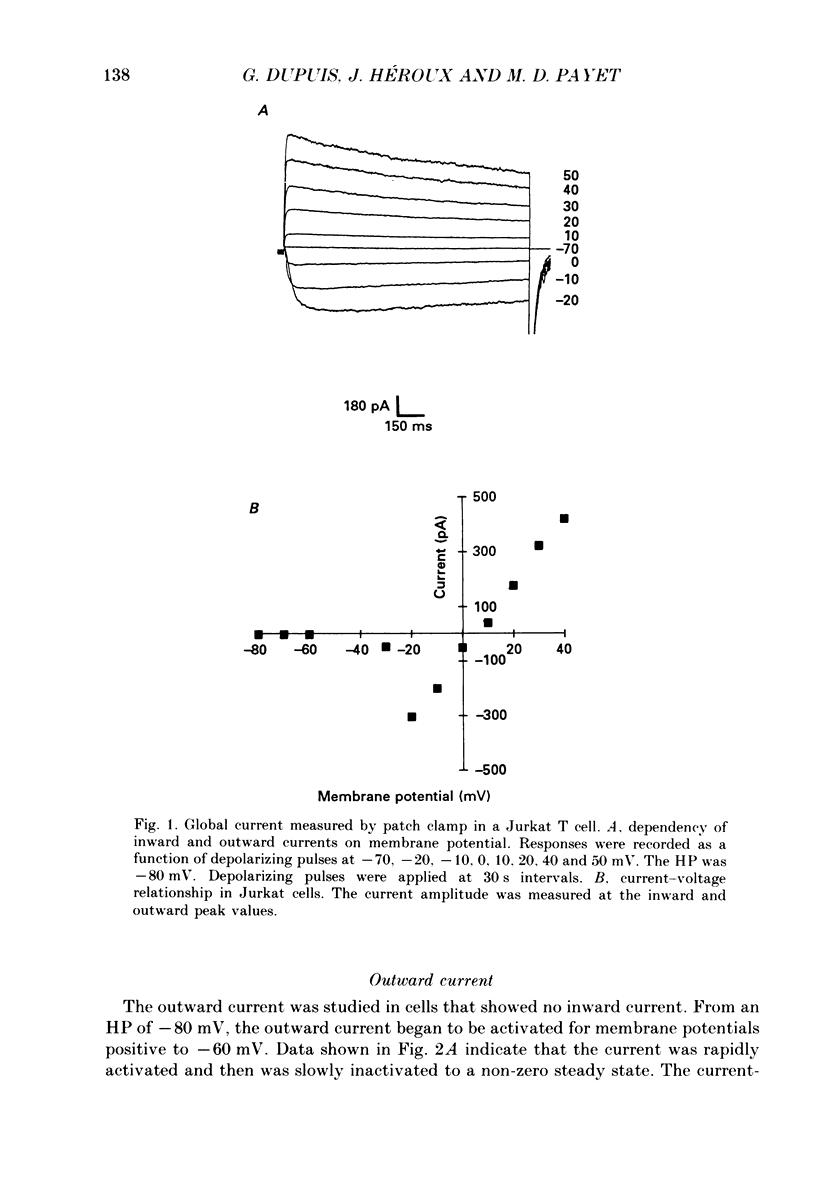
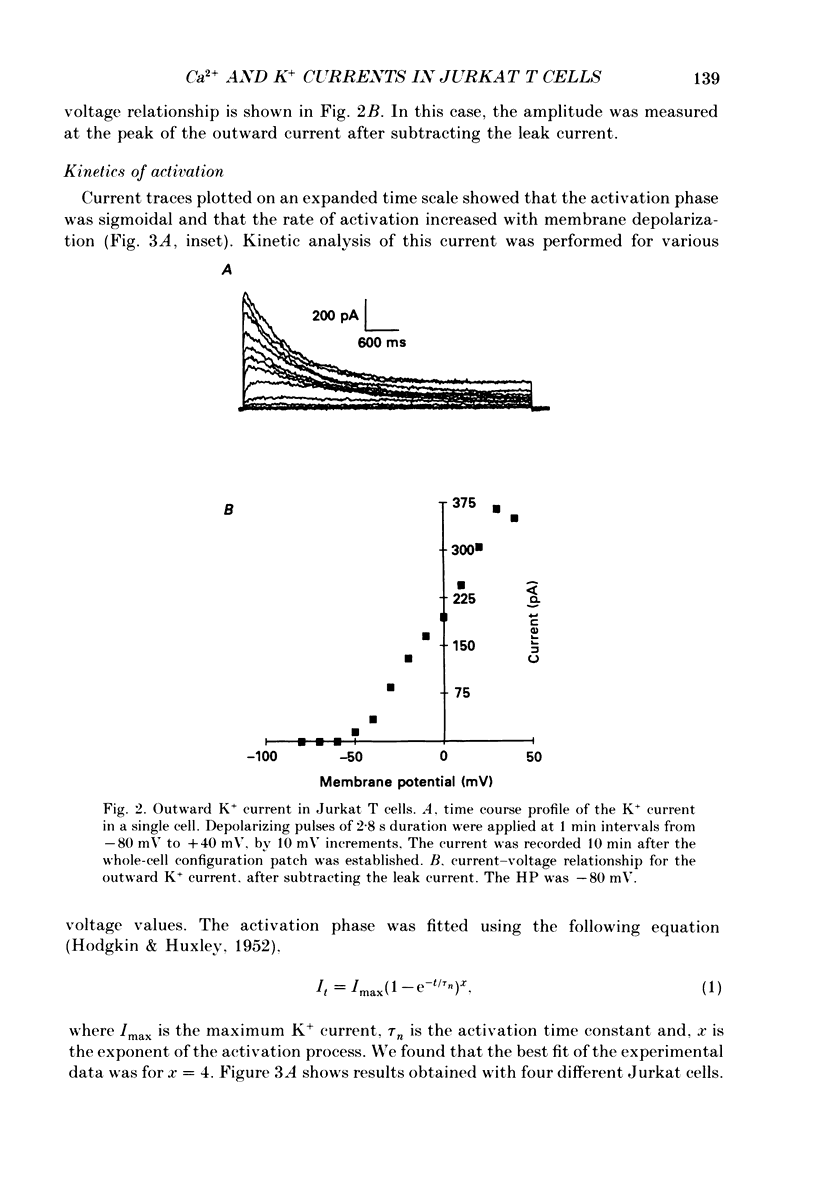
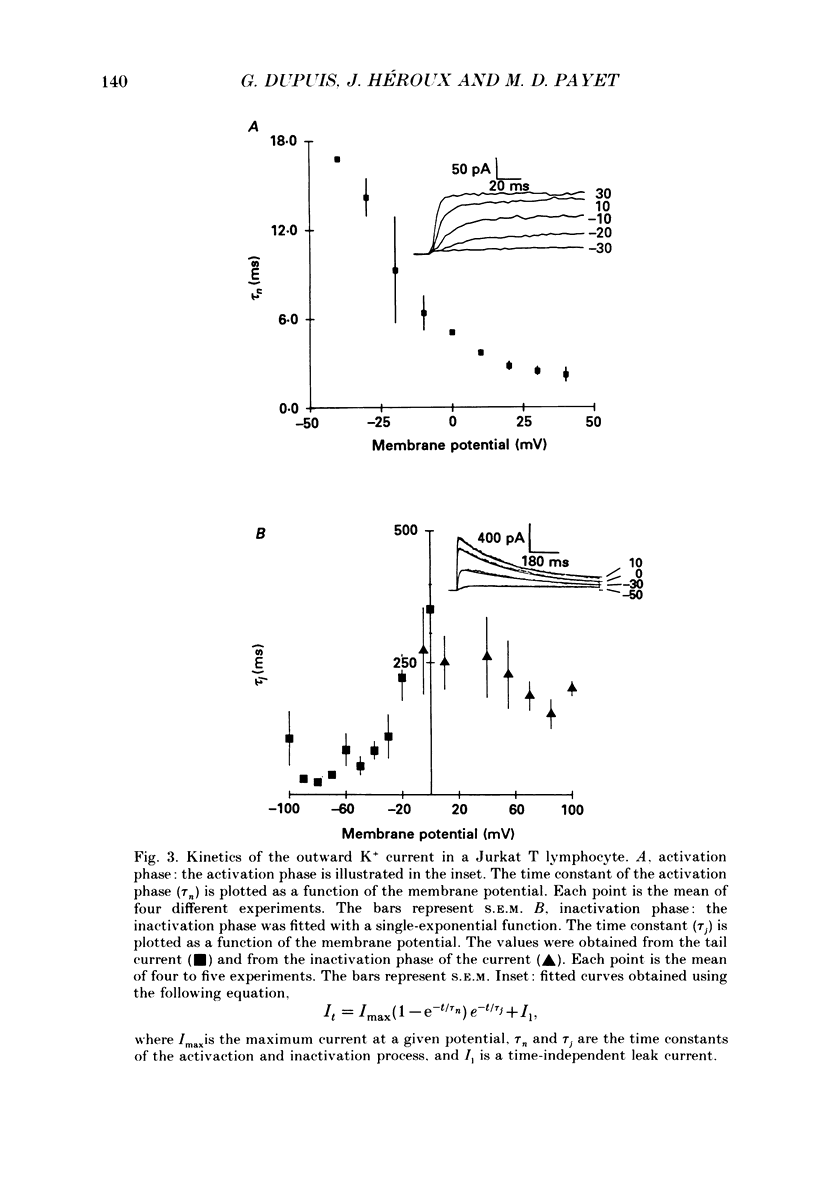
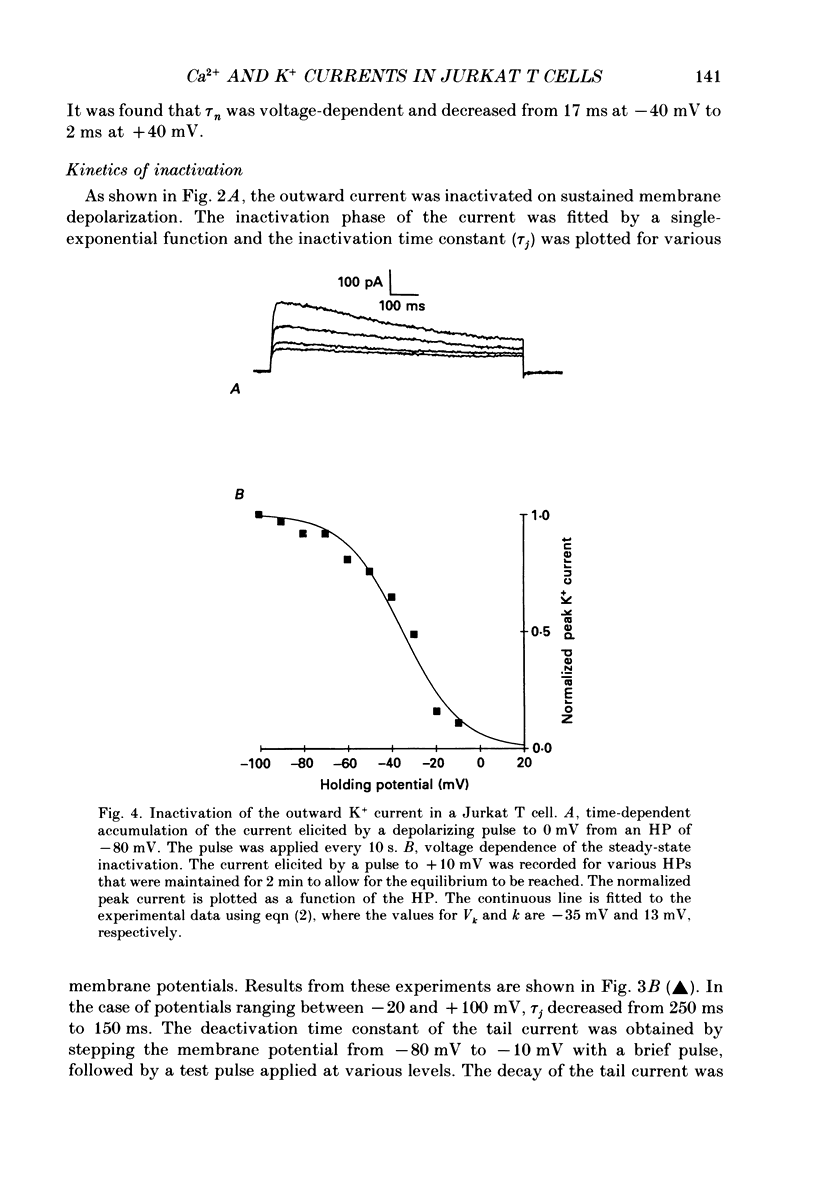
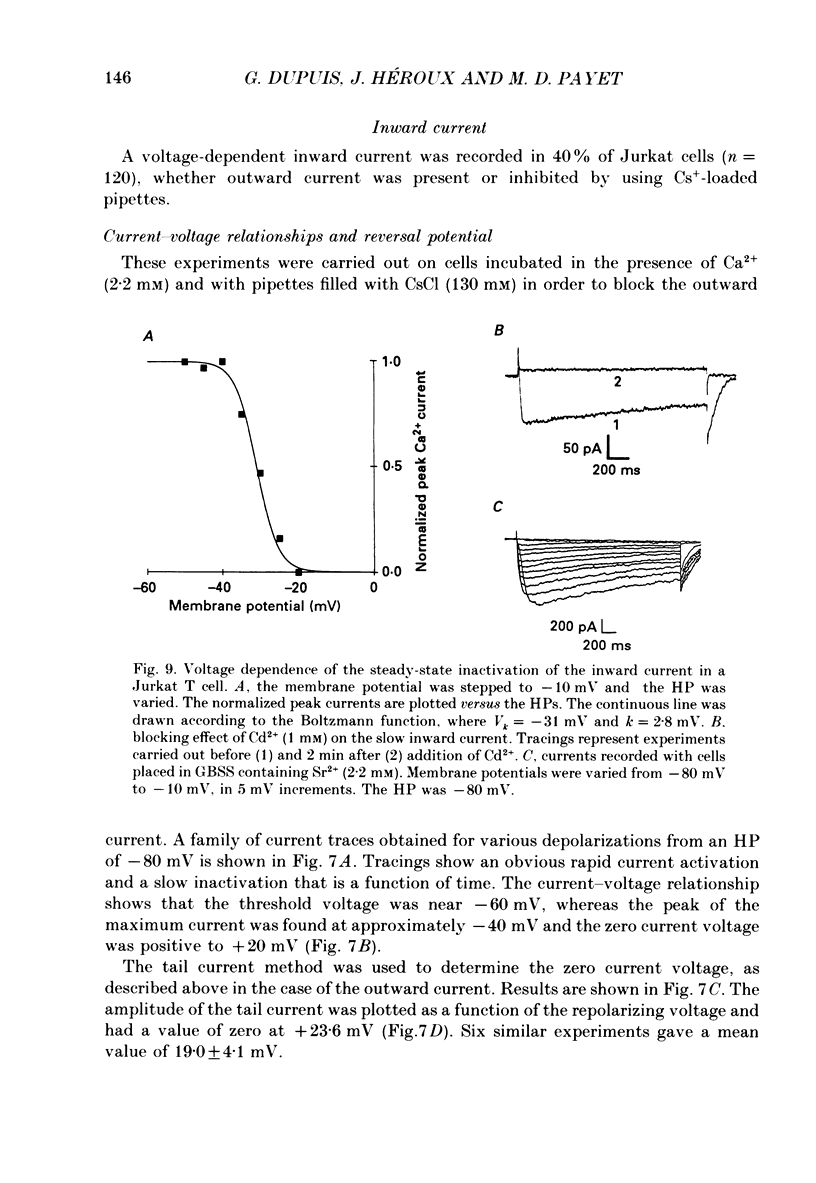
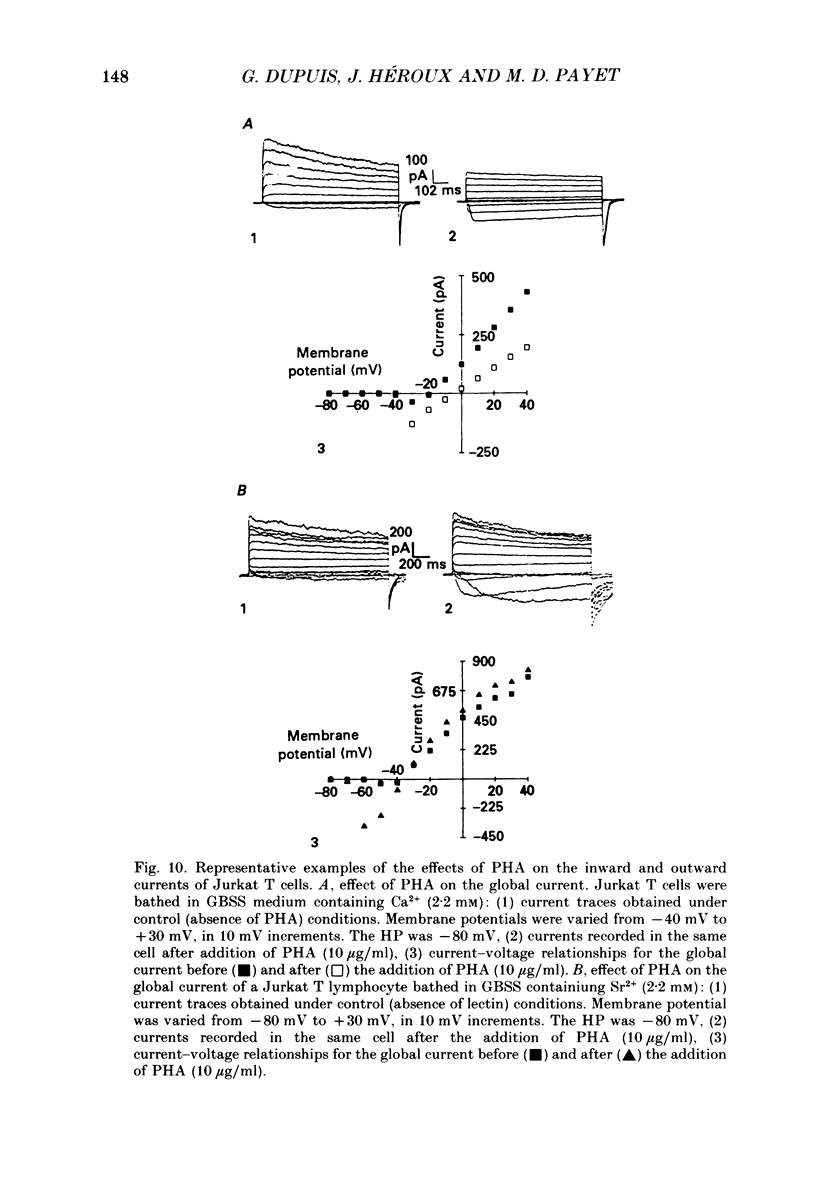
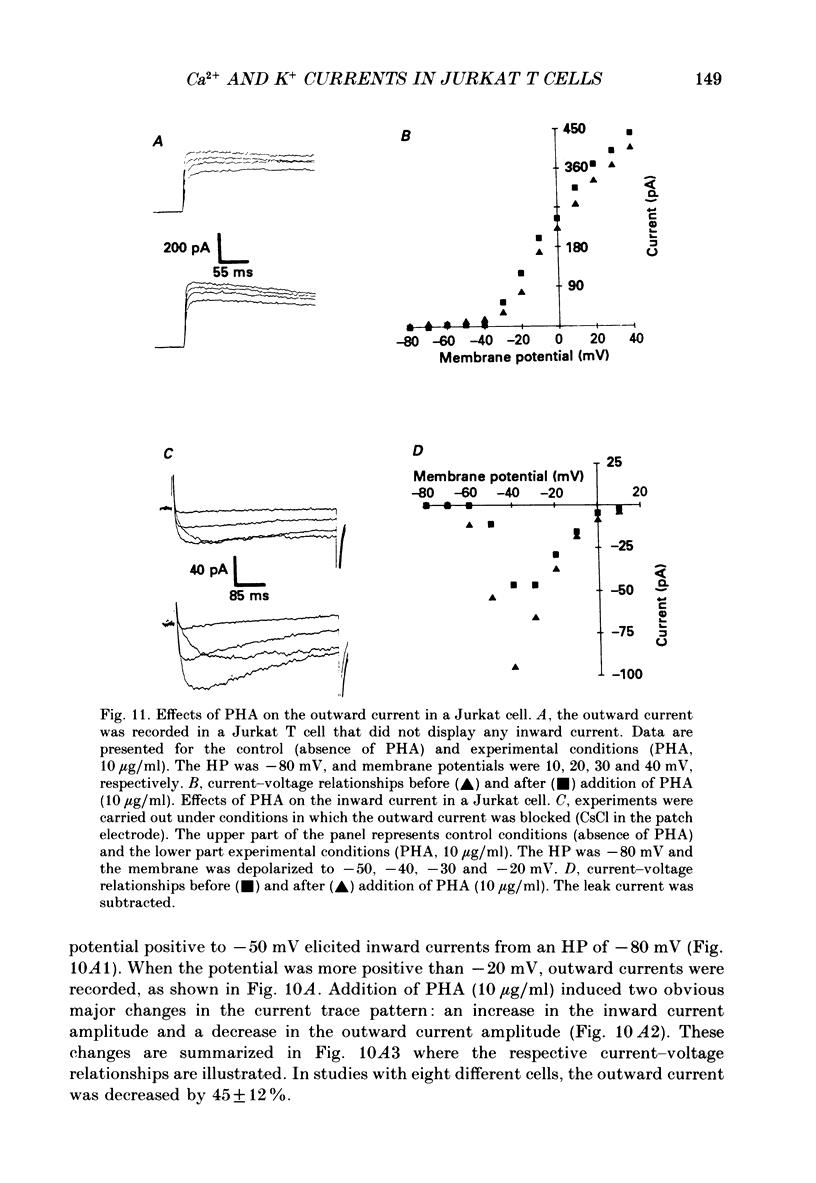
1. Inward and outward currents were recorded in the human Jurkat T cell line using the whole-cell configuration of the patch-clamp technique. 2. The transient outward current was activated at membrane potentials positive to -60 mV. The activation time constant-voltage relationship decreased from 17 ms to 2 ms for membrane potentials ranging from -40 to +40 mV. The inactivation phase could be fitted by a single-exponential function and the inactivation time constant decreased from 250 ms to 150 ms for membrane potentials ranging from -20 to +100 mV. 3. The steady-state inactivation-voltage relationship showed a mid-point potential of -32 +/- 2.6 mV, and the slope factor was 10.8 +/- 1.8 mv (n = 3). 4. The calcium ionophore A23187 provoked a decrease in the amplitude of the outward current, suggesting a dependence of this current on the cytosolic concentration of Ca2+. 5. The K+ outward current was blocked by tetraethylammonium (TEA, Michaelis-Menten constant (Km), 6 mM) and by the calcium channel blockers Ni2+, Co2+, Mn2+ and Cd2+. 6. Forty per cent (n = 120) of the patched Jurkat cells displayed an inward current. In a physiological medium containing Ca2+ (2.2 mM), the inward current threshold voltage was -60 mV, the maximum current was observed at -40 mV and the zero current voltage was positive to +20 mV. At negative membrane potentials, the time required to reach 50% of the maximum amplitude was 60 ms and grew shorter with increasing depolarization, reaching a value of 5 ms at -5 mV. The inactivation of the inward current was very slow and the time constant varied from 1200 ms at -35 mV to approximately 250 ms for potentials positive to -10 mV. 7. The current availability had a value of one for potentials negative to -50 mV and zero for potentials positive to -15 mV. The mid-point potential was -31 +/- 3.4 mV and the slope factor was 3.3 +/- 0.2 mV (n = 3). 8. The inward channels were permeable to Sr2+, but were blocked by classical Ca2+ channel inhibitors such as Co2+, Mn2+ and Ni2+. 9. Phaseolus vulgaris phytohaemagglutinin (PHA), an inducer of interleukin-2 production in Jurkat cells, increased the inward current amplitude by 32 +/- 20% (n = 4). This increase was concomitant with a decrease (45 +/- 12%) in the amplitude of the outward current, but only when the current was carried by Ca2+.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


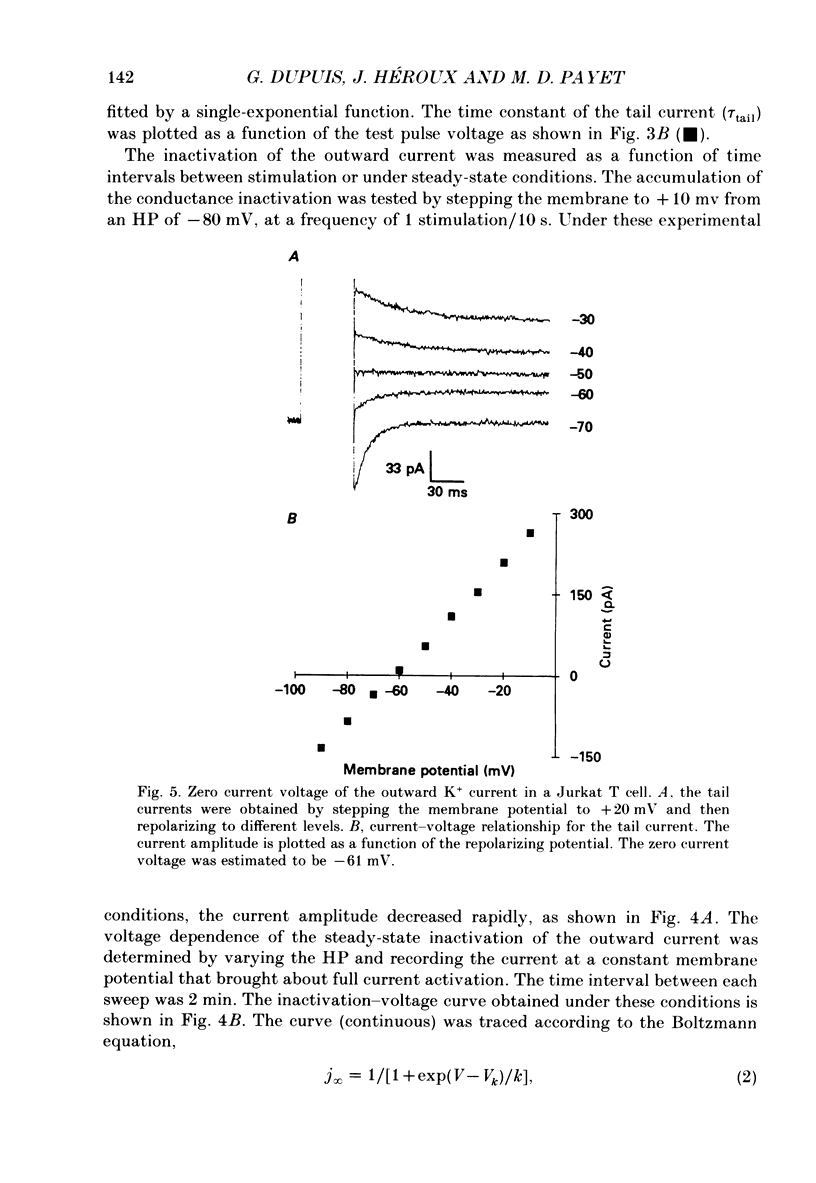
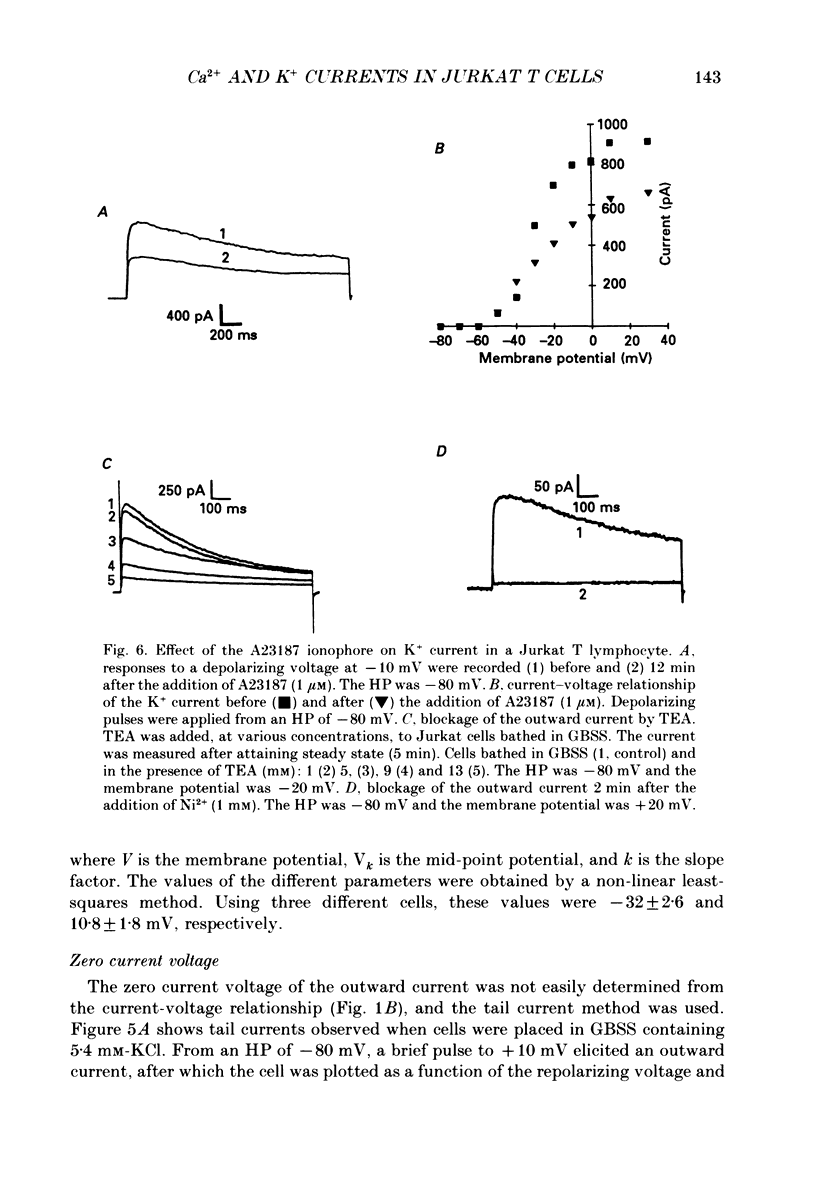
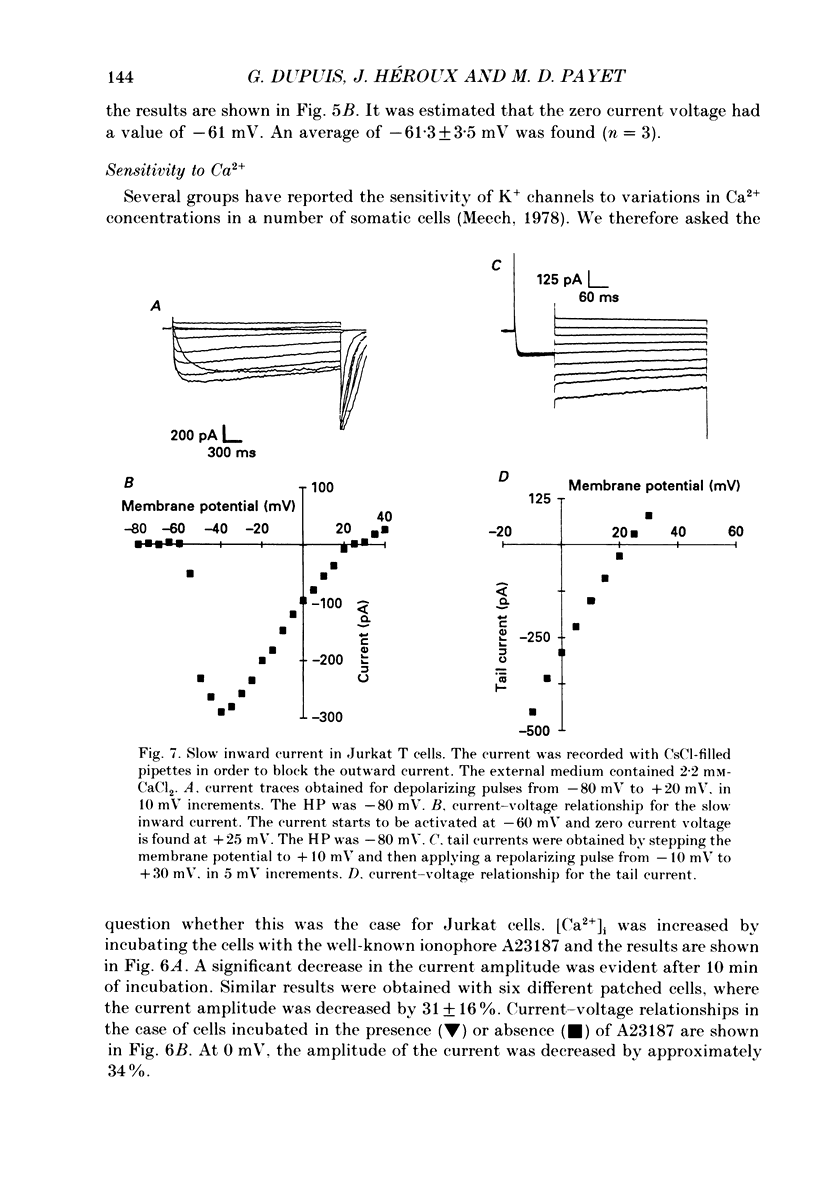
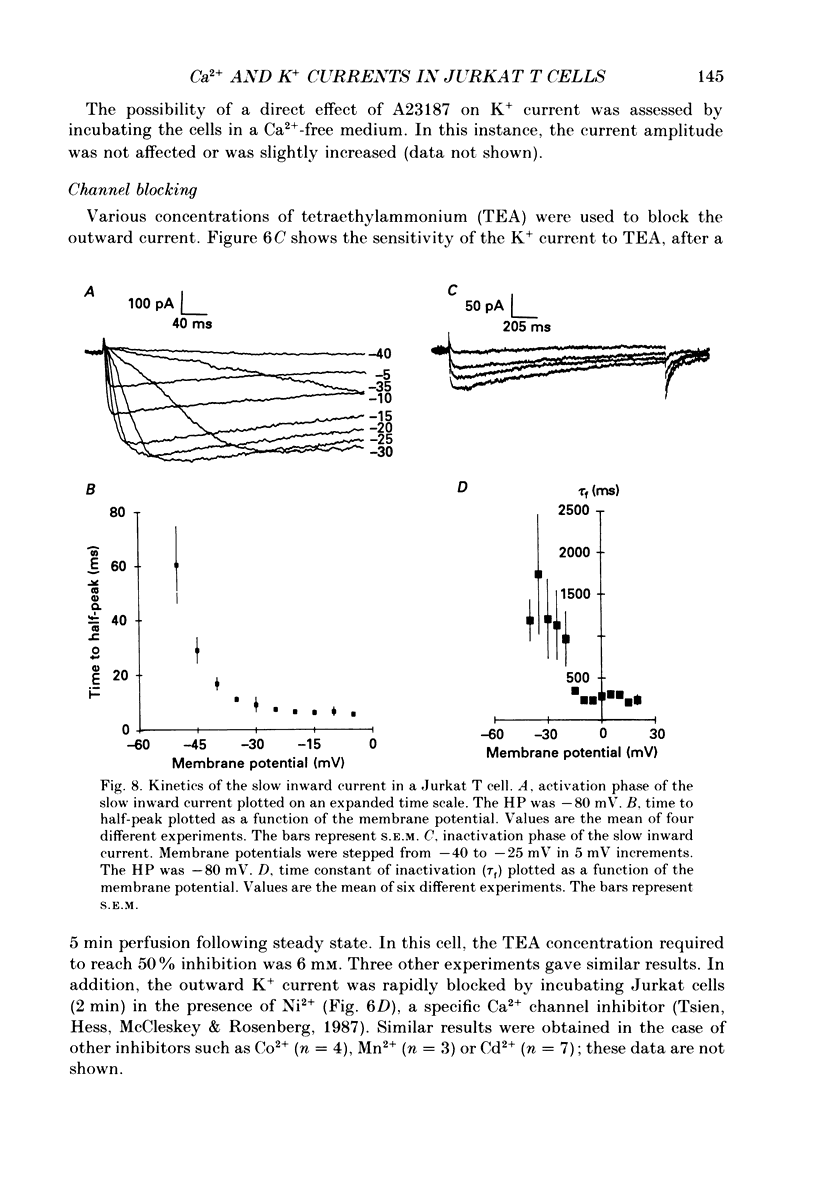






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcover A., Ramarli D., Richardson N. E., Chang H. C., Reinherz E. L. Functional and molecular aspects of human T lymphocyte activation via T3-Ti and T11 pathways. Immunol Rev. 1987 Feb;95:5–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregestovski P., Redkozubov A., Alexeev A. Elevation of intracellular calcium reduces voltage-dependent potassium conductance in human T cells. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):776–778. doi: 10.1038/319776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Gupta S. A voltage-gated potassium channel in human T lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:197–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Ransom J. T. Molecular mechanisms of transmembrane signaling in B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:175–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choquet D., Sarthou P., Primi D., Cazenave P. A., Korn H. Cyclic AMP-modulated potassium channels in murine B cells and their precursors. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1211–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.2434998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCoursey T. E., Chandy K. G., Gupta S., Cahalan M. D. Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes: a role in mitogenesis? Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):465–468. doi: 10.1038/307465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decoursey T. E., Chandy K. G., Gupta S., Cahalan M. D. Two types of potassium channels in murine T lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Mar;89(3):379–404. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.3.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch C., Price M. A. Cell calcium in human peripheral blood lymphocytes and the effect of mitogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 7;687(2):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis G., Bastin B. Lectin interactions with the Jurkat leukemic T-cell line: quantitative binding studies and interleukin-2 production. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Mar;43(3):238–247. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.3.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S. Currents carried by monovalent cations through calcium channels in mouse neoplastic B lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:255–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S., Henkart M. Potassium current in clonal cytotoxic T lymphocytes from the mouse. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:645–656. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S. Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel in mouse myeloma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2240–2242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W., Cheung R. K., Grinstein S. Mitogen-induced changes in Ca2+ permeability are not mediated by voltage-gated K+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11520–11523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W., Mills G. B., Cheung R. K., Lee J. W., Grinstein S. Transmembrane ion fluxes during activation of human T lymphocytes: role of Ca2+, Na+/H+ exchange and phospholipid turnover. Immunol Rev. 1987 Feb;95:59–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Watson J. Biochemical and biological characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. V. Identification of an interleukin 2-producing human leukemia T cell line. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1709–1719. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Weiss A. The T-cell antigen receptor regulates sustained increases in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ through extracellular Ca2+ influx and ongoing intracellular Ca2+ mobilization. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):695–700. doi: 10.1042/bj2470695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. G. Membrane cation transport and the control of proliferation of mammalian cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1978;40:19–41. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.40.030178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Gardner P. Ion channels activated by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in plasma membrane of human T-lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):301–304. doi: 10.1038/326301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Goronzy J., Weyand C. M., Gardner P. Single-channel and whole-cell recordings of mitogen-regulated inward currents in human cloned helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):269–273. doi: 10.1038/323269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Sabath D. E., Deutsch C., Prystowsky M. B. Increased voltage-gated potassium conductance during interleukin 2-stimulated proliferation of a mouse helper T lymphocyte clone. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1200–1208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linch D. C., Wallace D. L., O'Flynn K. Signal transduction in human T lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1987 Feb;95:137–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Nabholz M. T-cell activation. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:231–253. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Deutsch C. K channels in T lymphocytes: a patch clamp study using monoclonal antibody adhesion. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):468–471. doi: 10.1038/307468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen H. C., Terhorst C., Cantley L. C., Rosoff P. M. Stimulation of the T3-T cell receptor complex induces a membrane-potential-sensitive calcium influx. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens T., Kaplan J. G. Increased cationic fluxes in stimulated lymphocytes of the mouse: response of enriched B- and T-cell subpopulations to B- and T-cell mitogens. Can J Biochem. 1980 Oct;58(10):831–839. doi: 10.1139/o80-116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecht I., Corcia A., Liuzzi M. P., Alcover A., Reinherz E. L. Ion channels activated by specific Ti or T3 antibodies in plasma membranes of human T cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1935–1939. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichter L., Sidell N., Hagiwara S. K channels are expressed early in human T-cell development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5625–5629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider U., Schwenk H. U., Bornkamm G. Characterization of EBV-genome negative "null" and "T" cell lines derived from children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and leukemic transformed non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 1977 May 15;19(5):621–626. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Hess P., McCleskey E. W., Rosenberg R. L. Calcium channels: mechanisms of selectivity, permeation, and block. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:265–290. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. T-cell mitogens cause early changes in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ and membrane potential in lymphocytes. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):68–71. doi: 10.1038/295068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Shoback D., Stobo J. Role of T3 surface molecules in human T-cell activation: T3-dependent activation results in an increase in cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4169–4173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


