Abstract
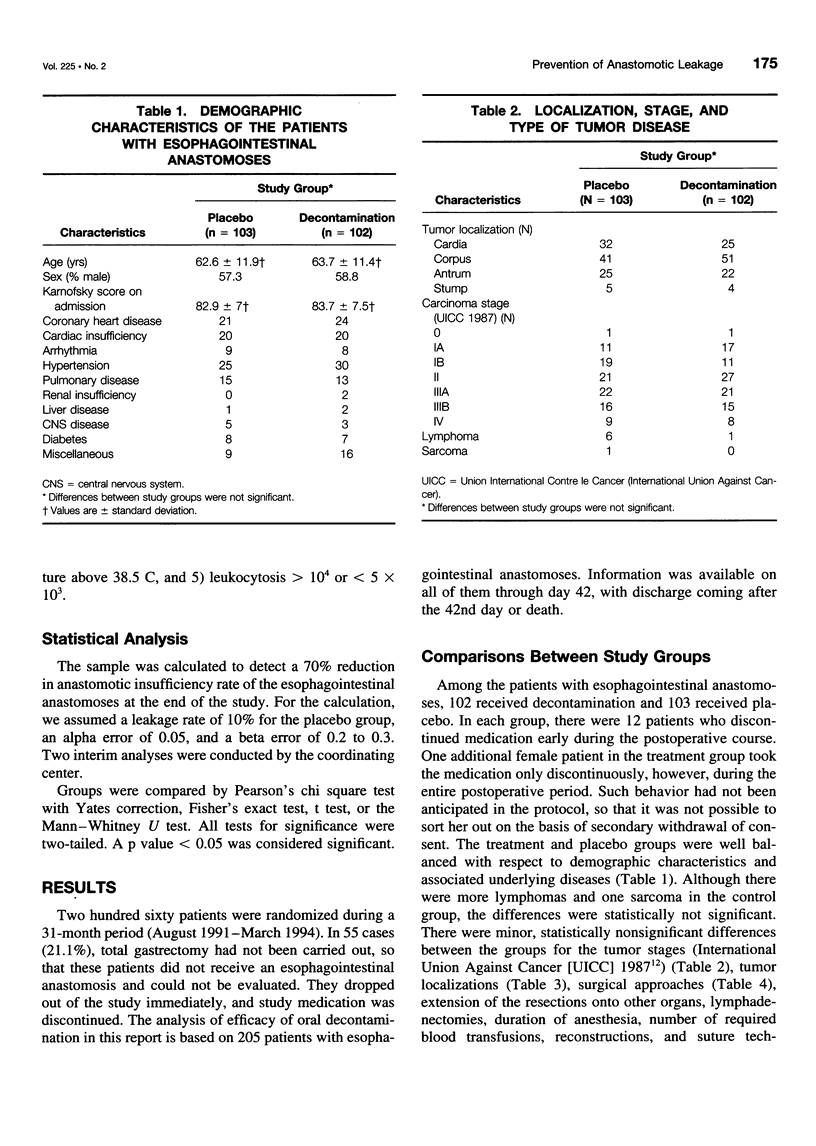
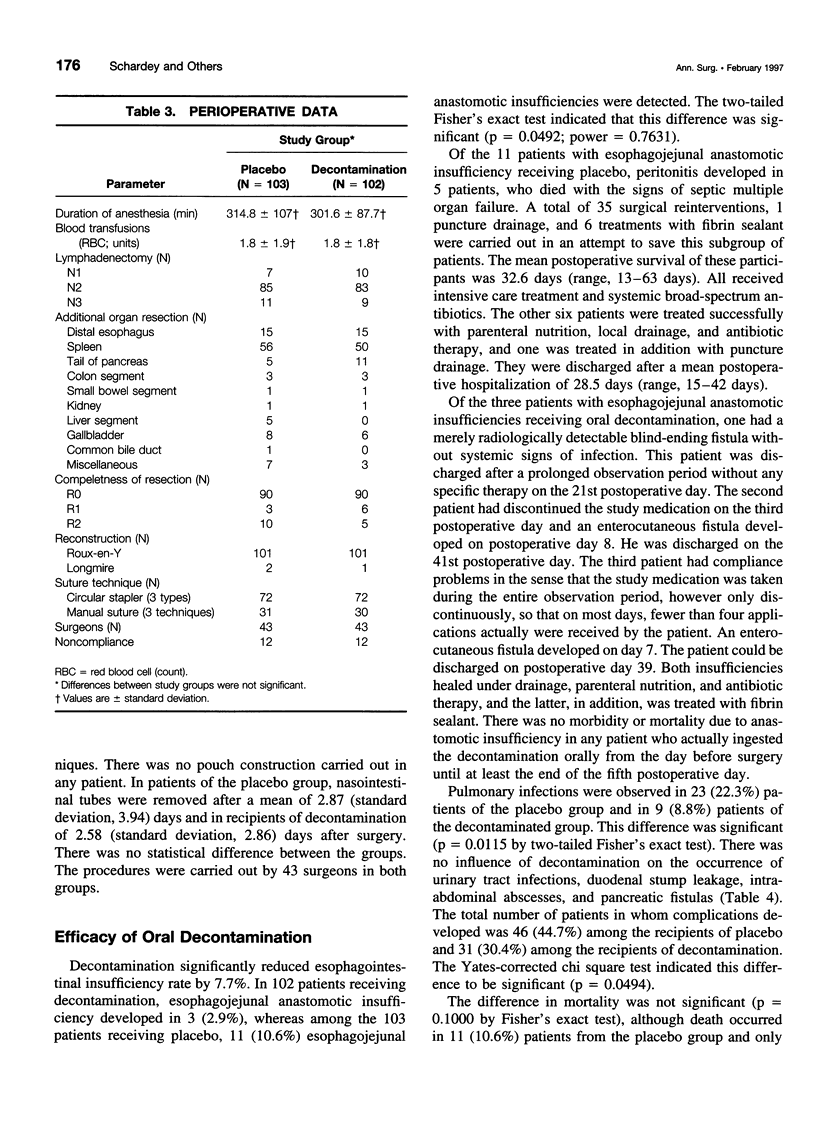
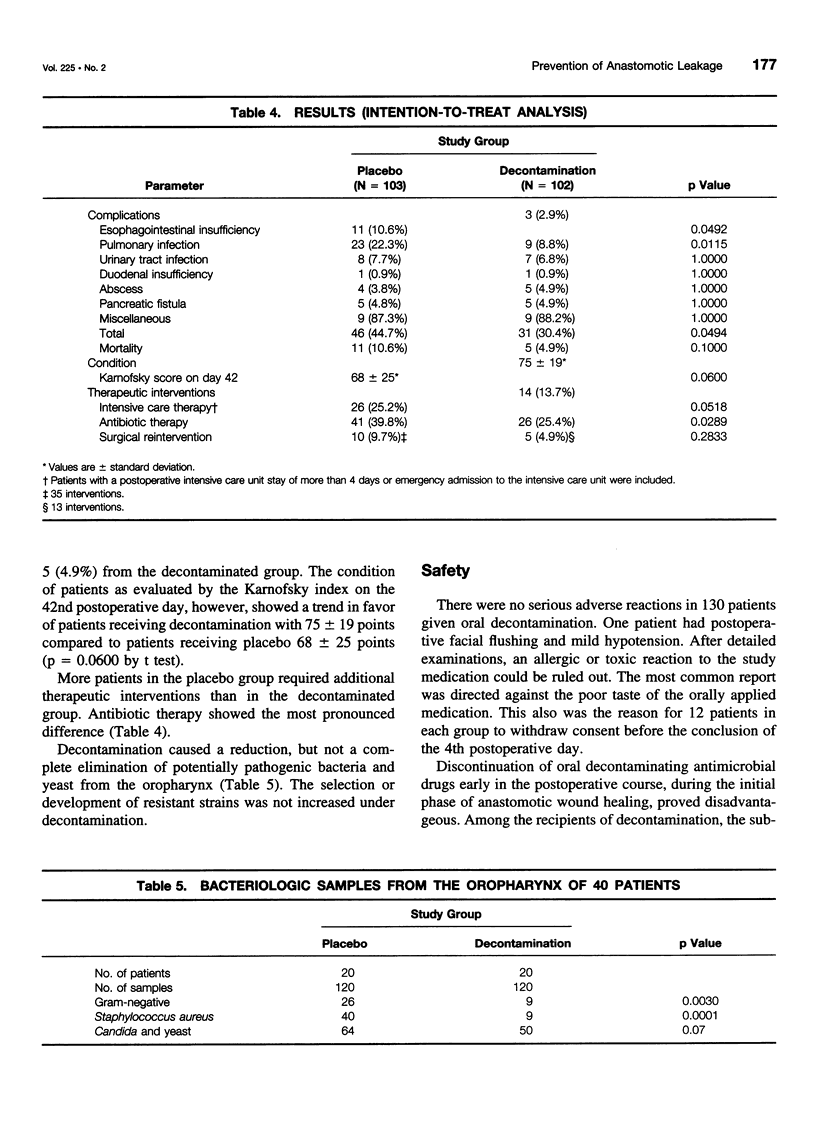
OBJECTIVE: A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled multicenter trial was undertaken in 205 patients treated with total gastrectomy for gastric malignancies to evaluate whether local antimicrobial measures reduce the incidence of esophagojejunal anastomotic leakage. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Anastomotic leakage of the esophagojejunostomy is always a septic complication of total gastrectomy for gastric malignancies, but it never has been attempted to prevent this complication with the administration of topical antimicrobial agents during the critical phase of anastomotic wound healing. METHODS: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of topical decontamination, the study was carried out as a prospective, randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled clinical multicenter trial in patients with total gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Patients received either placebo or decontamination with polymyxin B (100 mg), tobramycin (80 mg), vancomycin (125 mg), and amphotericin B (500 mg) four times per day orally from the day before the operation until the seventh postoperative day. All patients received a perioperative intravenous prophylaxis with cefotaxime 2 x 2 g. Other interventions including the administration of antibiotics and fluids, were not affected by the study protocol. RESULTS: Of 260 patients who were randomized, total gastrectomy was not carried out in 55 patients. They dropped out of the study. Patients receiving an esophagojejunostomy were observed until day 42, when they were discharged from the clinic or died. An intention-to-treat analysis of the data was carried out. Among the 103 recipients of placebo, there were 11 (10.6%) with an anastomotic leakage of the esophagojejunostomy, and among the 102 recipients of decontamination, there were 3 (2.9%) with an anastomotic leakage of the esophagojejunostomy (p = 0.0492). Pulmonary infections were observed in 23 patients (22.3%) receiving placebo and in 9 patients (8.8%) who were decontaminated (p = 0.02). There were 11 deaths (10.6%) among the recipients of placebo and 5 deaths (4.9%) among the recipients of decontamination (p = 0.1). CONCLUSIONS: Decontamination with polymyxin, tobramycin, vancomycin, and amphotericin B during anastomotic wound healing is safe and effective in the prevention of esophagojejunal anastomotic leakage after total gastrectomy.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams W., Ctercteko G., Bilous M. Effect of an omental wrap on the healing and vascularity of compromised intestinal anastomoses. Dis Colon Rectum. 1992 Aug;35(8):731–738. doi: 10.1007/BF02050320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankey P., Fiegel V., Singh R., Knighton D., Cerra F. Hypoxia and endotoxin induce macrophage-mediated suppression of fibroblast proliferation. J Trauma. 1989 Jul;29(7):972–980. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198907000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum M. L., Anish D. S., Chalmers T. C., Sacks H. S., Smith H., Jr, Fagerstrom R. M. A survey of clinical trials of antibiotic prophylaxis in colon surgery: evidence against further use of no-treatment controls. N Engl J Med. 1981 Oct 1;305(14):795–799. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198110013051404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonenkamp J. J., Songun I., Hermans J., Sasako M., Welvaart K., Plukker J. T., van Elk P., Obertop H., Gouma D. J., Taat C. W. Randomised comparison of morbidity after D1 and D2 dissection for gastric cancer in 996 Dutch patients. Lancet. 1995 Mar 25;345(8952):745–748. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90637-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttcher K., Siewert J. R., Roder J. D., Busch R., Hermanek P., Meyer H. J. Risiko der chirurgischen Therapie des Magencarcinoms in Deutschland. Ergebnisse der Deutschen Magencarcinom-Studie 1992. Deutsche Magencarcinom-Studiengruppe (GGCS '92). Chirurg. 1994 Apr;65(4):298–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. R., Cornell C. N., Collins M. H., Sell J. E., Blanc W. A., Altman R. P. Healing of ischemic colonic anastomoses in the rat: role of antibiotic preparation. Surgery. 1985 Apr;97(4):443–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn I., Jr Intestinal antisepsis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1970 Jun;130(6):1006–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeVeen H. H., Wapnick S., Falk G., Olivas O., Bhat D., Gaurdre M., Patel M. Effects of prophylactic antibiotics on colonic healing. Am J Surg. 1976 Jan;131(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(76)90419-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger Z., Hoffeld J. T., Oppenheim J. J. Suppression of fibroblast proliferation by activated macrophages: involvement of H2O2 and a non-prostaglandin E product of the cyclooxygenase pathway. Cell Immunol. 1986 Jul;100(2):501–514. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. L., Smith J. W. Intragastric microbial colonization in common disease states of the stomach and duodenum. Ann Surg. 1975 Nov;182(5):557–561. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197511000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Bartlett J. G., Louie T., Sullivan-Seigler N., Gorbach S. L. Microbial synergy in experimental intra-abdominal abscess. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):22–26. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.22-26.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou J. P., Cohen J. R., Johnson H., Jr Factors influencing wound dehiscence. Am J Surg. 1992 Mar;163(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(92)90014-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. D., Böttcher K., Siewert J. R., Busch R., Hermanek P., Meyer H. J. Prognostic factors in gastric carcinoma. Results of the German Gastric Carcinoma Study 1992. Cancer. 1993 Oct 1;72(7):2089–2097. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19931001)72:7<2089::aid-cncr2820720706>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schardey H. M., Kamps T., Rau H. G., Gatermann S., Baretton G., Schildberg F. W. Bacteria: a major pathogenic factor for anastomotic insufficiency. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Nov;38(11):2564–2567. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.11.2564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer K., Loeweneck H., Stanka H., Ernst R., Zumtobel V. Mikrozirkulationsstörungen bei Colonanastomosen und ihre Bedeutung für die Pathogenese der Nahtinsuffizienz. Langenbecks Arch Chir. 1990;375(1):24–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00186117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstedt S., Kager L., Heimdahl A., Nord C. E. Microbial colonization of tumors in relation to the upper gastrointestinal tract in patients with gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg. 1988 Mar;207(3):341–346. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198803000-00020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstedt S., Levin P., Malmborg A. S., Bergman U., Kager L. Septic complications in relation to factors influencing the gastric microflora in patients undergoing gastric surgery. J Hosp Infect. 1989 Feb;13(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(89)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoutenbeek C. P., van Saene H. K., Miranda D. R., Zandstra D. F. The effect of selective decontamination of the digestive tract on colonisation and infection rate in multiple trauma patients. Intensive Care Med. 1984;10(4):185–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00259435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetteroo G. W., Wagenvoort J. H., Castelein A., Tilanus H. W., Ince C., Bruining H. A. Selective decontamination to reduce gram-negative colonisation and infections after oesophageal resection. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):704–707. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90813-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unertl K., Ruckdeschel G., Selbmann H. K., Jensen U., Forst H., Lenhart F. P., Peter K. Prevention of colonization and respiratory infections in long-term ventilated patients by local antimicrobial prophylaxis. Intensive Care Med. 1987;13(2):106–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00254795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Saene H. K., Unertl K. E., Alcock S. R., Stoutenbeek C. P., Hart C. A. Emergence of antibiotic resistance during selective digestive decontamination? J Hosp Infect. 1993 Jun;24(2):158–161. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(93)90079-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Waaij D. Colonization resistance of the digestive tract: clinical consequences and implications. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Oct;10(4):263–270. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.4.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



