Abstract
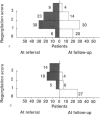
OBJECTIVE: The purpose of the study was to evaluate the long-term symptomatic and endoscopic outcome in gastroesophageal reflux disease with erosive esophagitis, comparing conservative with operative management. METHODS: The study comprised 105 of 120 patients consecutively referred for severe reflux symptoms to the gastroenterologic outpatient department of a teaching hospital, where erosive esophagitis was confirmed endoscopically. If conservative management (modified lifestyle and medication) failed to relieve symptoms and heal the esophagitis, antireflux surgery (Nissen fundoplication) was undertaken. Follow-up (median, 10.9 years) evaluation of all patients included comprehensive, standardized interviews; self-scoring of symptoms at the time of referral and currently; and observations at endoscopy. RESULTS: Nissen fundoplication was performed on 37 of the 105 patients. At follow-up of these 37 patients, (31) 84% had no or only occasional mild heartburn, (33) 89% were free from erosive esophagitis, and (2) 5% were taking H2 antagonists or omeprazole. The corresponding figures in the 68 patients with only conservative treatment were (36) 53%, (31) 45%, and (14) 21%. The mean change in symptom score between referral time and follow-up was 5.7 in the surgically treated group and 1.7 in the nonsurgically treated group. Fifteen new cases of Barrett's metaplasia were found at follow-up. CONCLUSIONS: In gastroesophageal reflux disease with erosive esophagitis, surgical treatment gave results subjectively and objectively superior to those from conservative management.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DeMeester T. R., Bonavina L., Albertucci M. Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Evaluation of primary repair in 100 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1986 Jul;204(1):9–20. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198607000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demeester T. R., Johnson L. F., Joseph G. J., Toscano M. S., Hall A. W., Skinner D. B. Patterns of gastroesophageal reflux in health and disease. Ann Surg. 1976 Oct;184(4):459–470. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197610000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen C. A., Sadek S. A., Cranford C., Sutton D., Kennedy N., Cuschieri A. Reflux oesophagitis and oesophageal transit: evidence for a primary oesophageal motor disorder. Gut. 1988 Apr;29(4):448–452. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.4.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glise H. Healing, relapse rates and prophylaxis of reflux esophagitis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1989;156:57–64. doi: 10.3109/00365528909091039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallerbäck B., Unge P., Carling L., Edwin B., Glise H., Havu N., Lyrenäs E., Lundberg K. Omeprazole or ranitidine in long-term treatment of reflux esophagitis. The Scandinavian Clinics for United Research Group. Gastroenterology. 1994 Nov;107(5):1305–1311. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heading R. C. Epidemiology of oesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1989;168:33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinder R. A., Filipi C. J., Wetscher G., Neary P., DeMeester T. R., Perdikis G. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is an effective treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg. 1994 Oct;220(4):472–483. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199410000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri J., Laippala P. Prevalence of symptoms suggestive of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in an adult population. Ann Med. 1995 Feb;27(1):67–70. doi: 10.3109/07853899509031939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Lydeard S. Prevalence of symptoms of dyspepsia in the community. BMJ. 1989 Jan 7;298(6665):30–32. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6665.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahrilas P. J., Dodds W. J., Hogan W. J., Kern M., Arndorfer R. C., Reece A. Esophageal peristaltic dysfunction in peptic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):897–904. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90692-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klauser A. G., Schindlbeck N. E., Müller-Lissner S. A. Symptoms in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Lancet. 1990 Jan 27;335(8683):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90287-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuster E., Ros E., Toledo-Pimentel V., Pujol A., Bordas J. M., Grande L., Pera C. Predictive factors of the long term outcome in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: six year follow up of 107 patients. Gut. 1994 Jan;35(1):8–14. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luostarinen M. Nissen fundoplication for reflux esophagitis. Long-term clinical and endoscopic results in 109 of 127 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1993 Apr;217(4):329–337. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199304000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E. D. The hiatus hernia-esophagitis-esophageal stricture complex. Twenty-year prospective study. Am J Med. 1968 Apr;44(4):566–579. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M., Sahba B., Avner D., Jhala N., Greski-Rose P. A., Jennings D. E. A comparison of lansoprazole and ranitidine in the treatment of erosive oesophagitis. Multicentre Investigational Group. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Feb;9(1):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1995.tb00347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruth M., Månsson I., Sandberg N. The prevalence of symptoms suggestive of esophageal disorders. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991 Jan;26(1):73–81. doi: 10.3109/00365529108996486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmark S., Carlsson R., Fausa O., Lundell L. Omeprazole or ranitidine in the treatment of reflux esophagitis. Results of a double-blind, randomized, Scandinavian multicenter study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988 Jun;23(5):625–632. doi: 10.3109/00365528809093923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P., Adamopoulos A., Taylor R. H., Colin-Jones D. G. Oesophageal motor function before and after healing of oesophagitis. Gut. 1992 Dec;33(12):1590–1596. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.12.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P., Taylor R. H., Colin-Jones D. G. Prolonged remission of oesophagitis does not alter the magnitude of oesophageal acid exposure. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994 Jan;29(1):11–16. doi: 10.3109/00365529409090430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor K. B., Silander T. A long-term randomized prospective trial of the Nissen procedure versus a modified Toupet technique. Ann Surg. 1989 Dec;210(6):719–724. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198912000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]