Abstract
1. Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) and currents (IPSCs) were recorded from cultured hippocampal neurones of the embryonic rat at 22 degrees C, using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique with a low-Cl-, 145 mM-potassium gluconate solution in the patch pipette. Individual synaptic events were elicited at low frequency (0.05-0.1 Hz) by stimulating a presynaptic neurone either by direct intracellular current injection, or by applying a brief pulse of L-glutamate. 2. In target neurones voltage clamped at -40 mV, outwardly directed IPSCs of mean amplitude 0.23 nA were recorded. The IPSCs were depressed by the GABA antagonist bicuculline, and reversed polarity between -50 and -80 mV (mean -64 mV), as did current responses to gamma-aminobutyric acid. The IPSPs and IPSCs reversed as a single phase; no bicuculline-resistant 'late' synaptic event was observed. 3. The IPSCs had variable kinetics, with rise times between 1 and 5 ms (mean 2.9 ms) at -40 mV, and slower, monoexponential, decay phases (decay time constant, tau IPSC, 10-40 ms at -40 mV). In some cells, tau IPSC clearly increased with depolarization. 4. The IPSC reversal potential was -64 +/- 9 mV (n = 23) under the experimental conditions used; this suggests that the synaptically activated channels are approximately 25 times more permeable to Cl- than to the gluconate anion. 5. The peak conductance associated with the IPSC showed outward rectification. The synaptic conductance measured at -40 mV was 1.7 times greater than that measured at -100 mV; at -20 mV, synaptic conductance was 2.5 times greater than at -100 mV. This outward rectification can be explained by a constant field model under these experimental conditions of asymmetric Cl- concentrations.
Full text
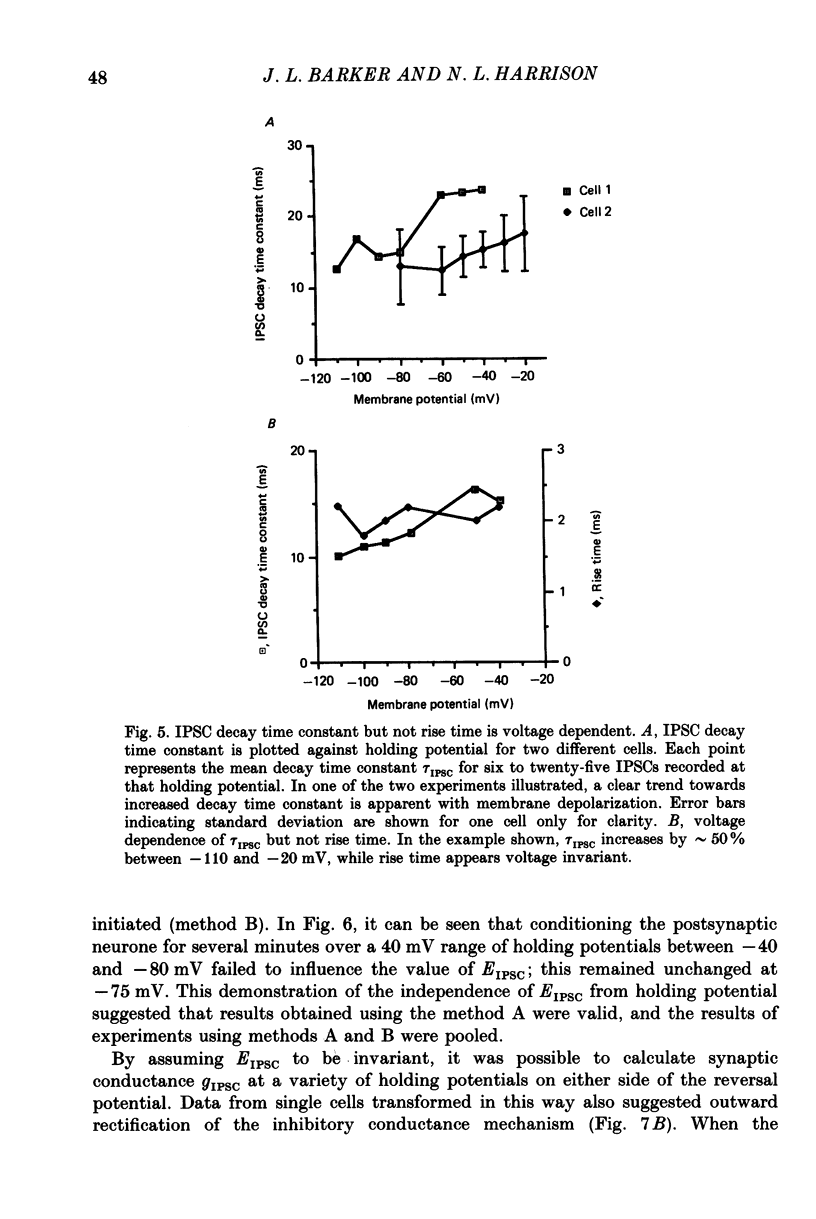
PDF


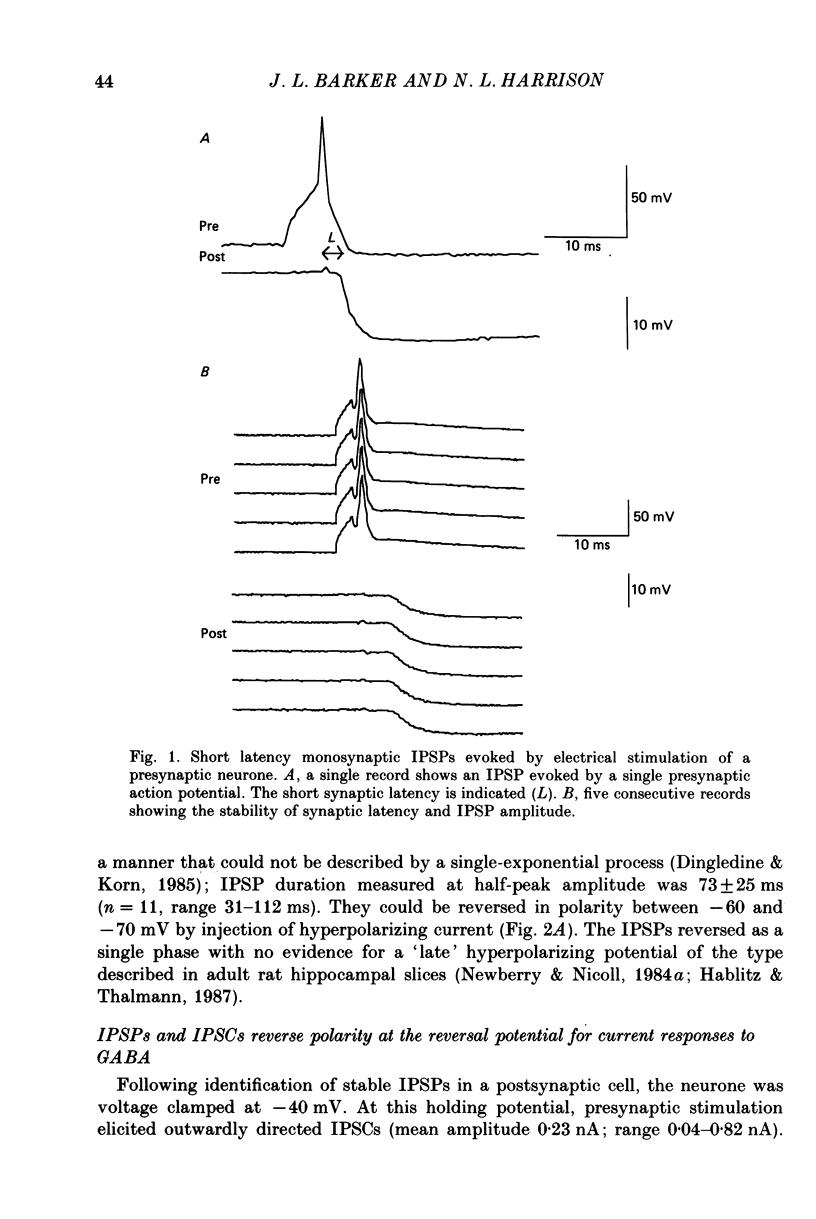
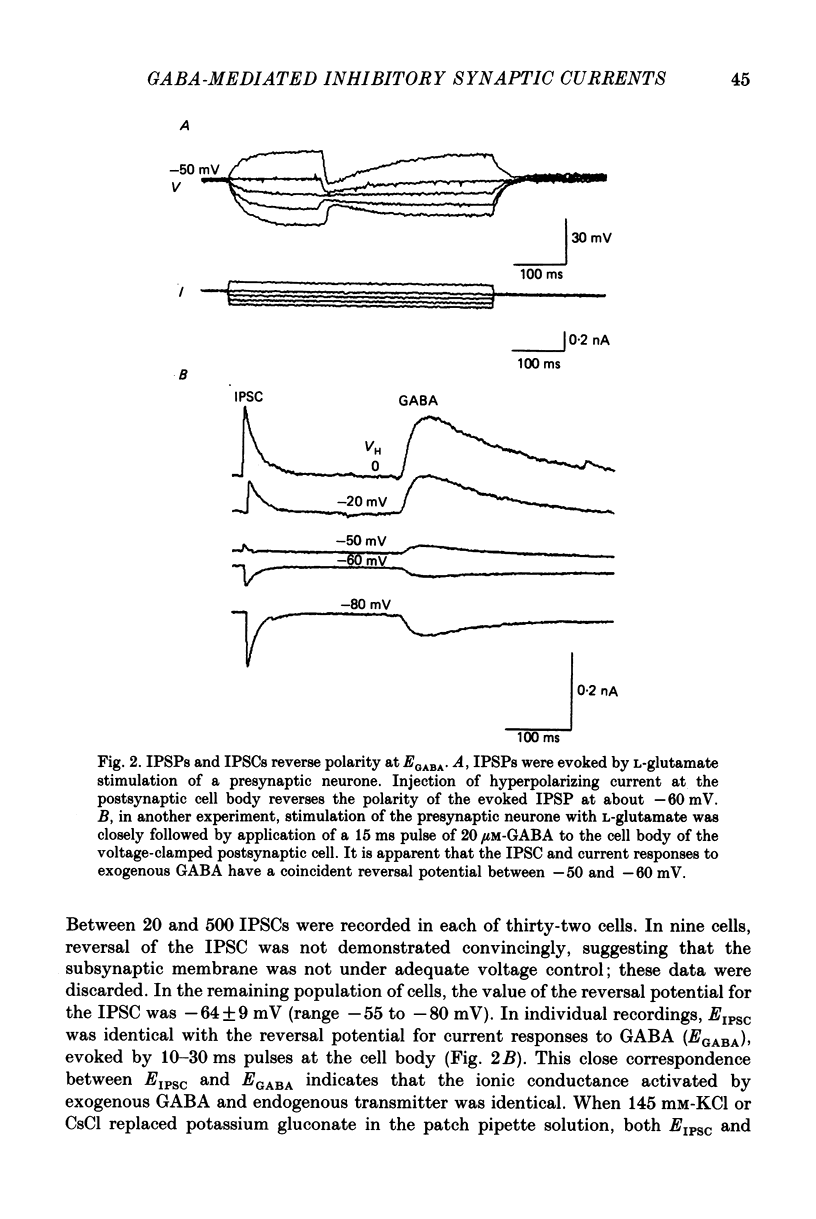
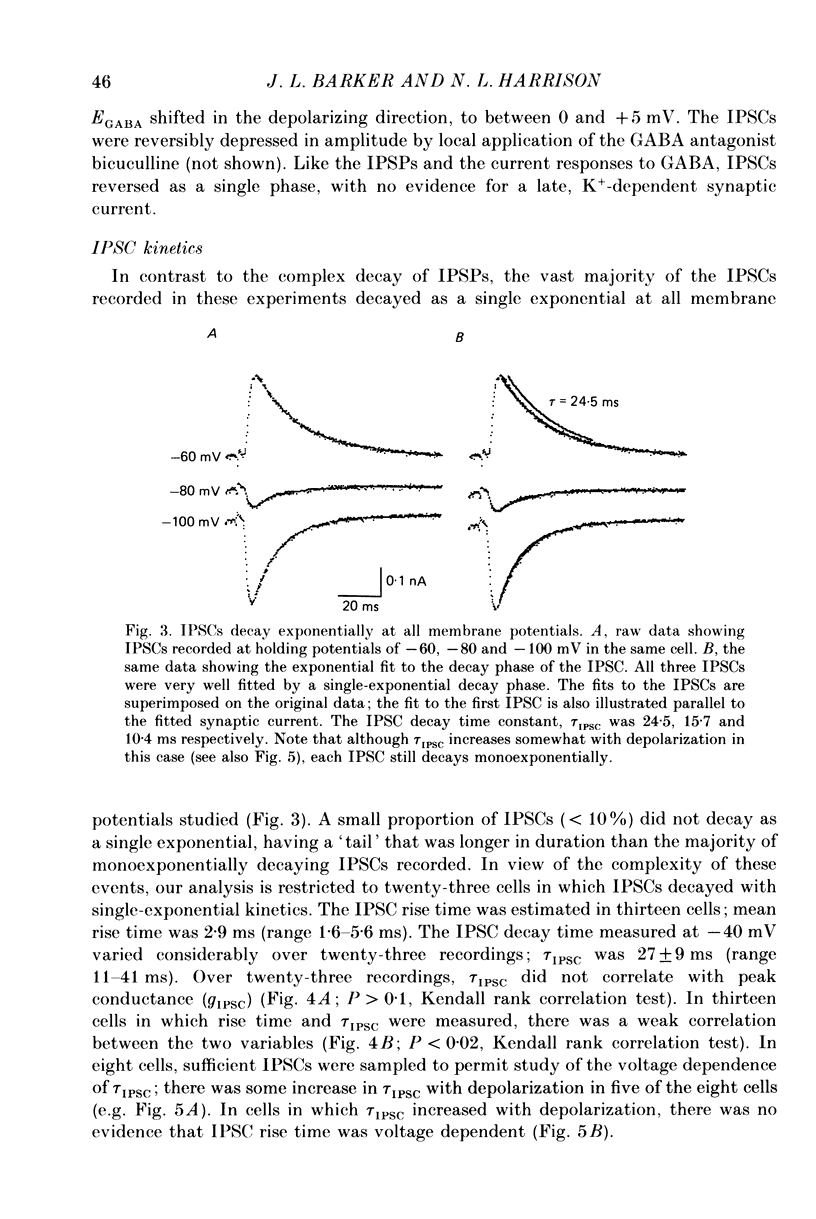
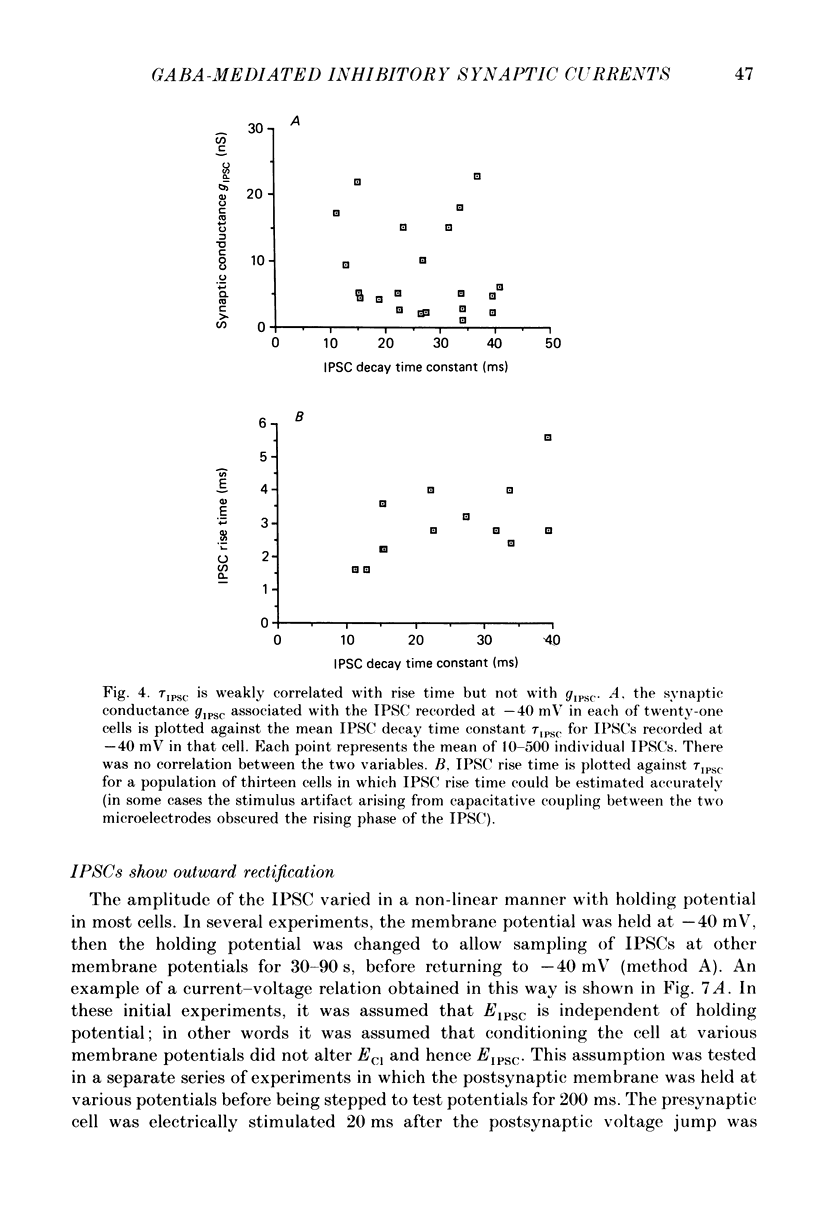
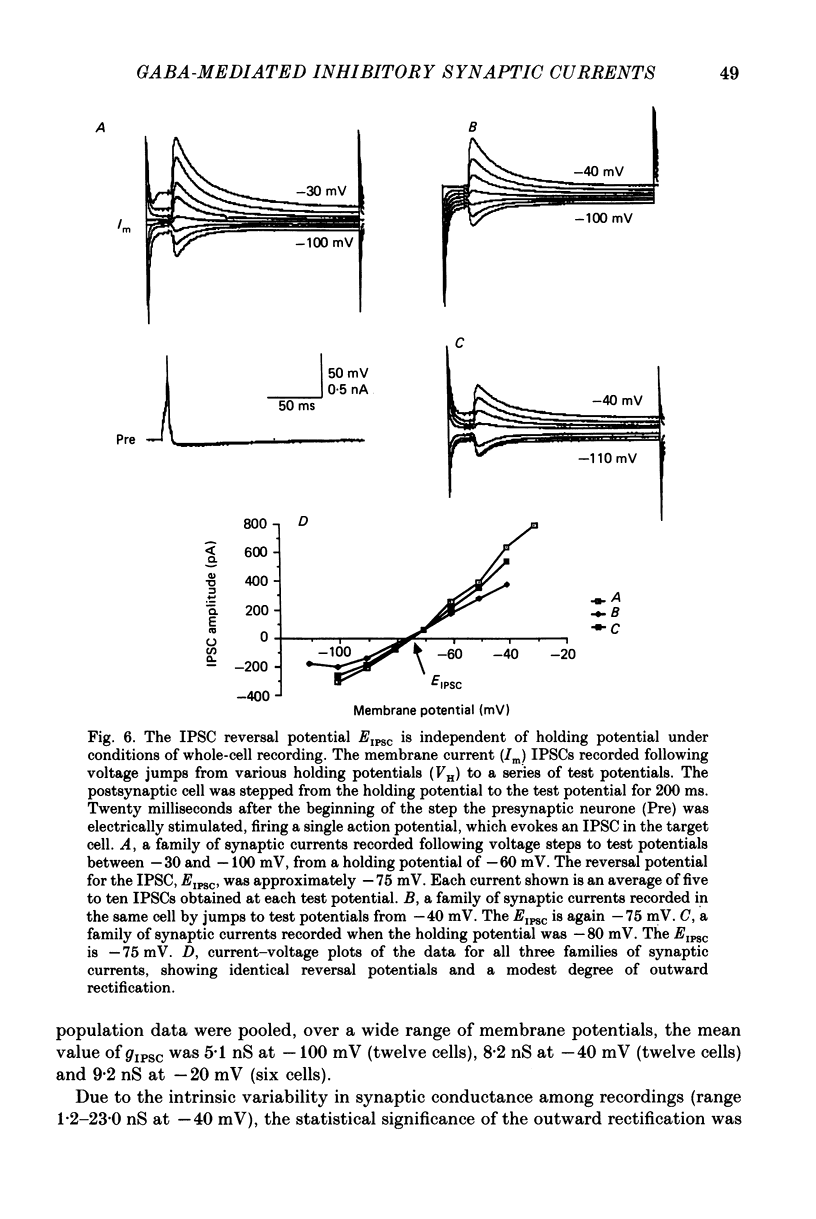




Selected References
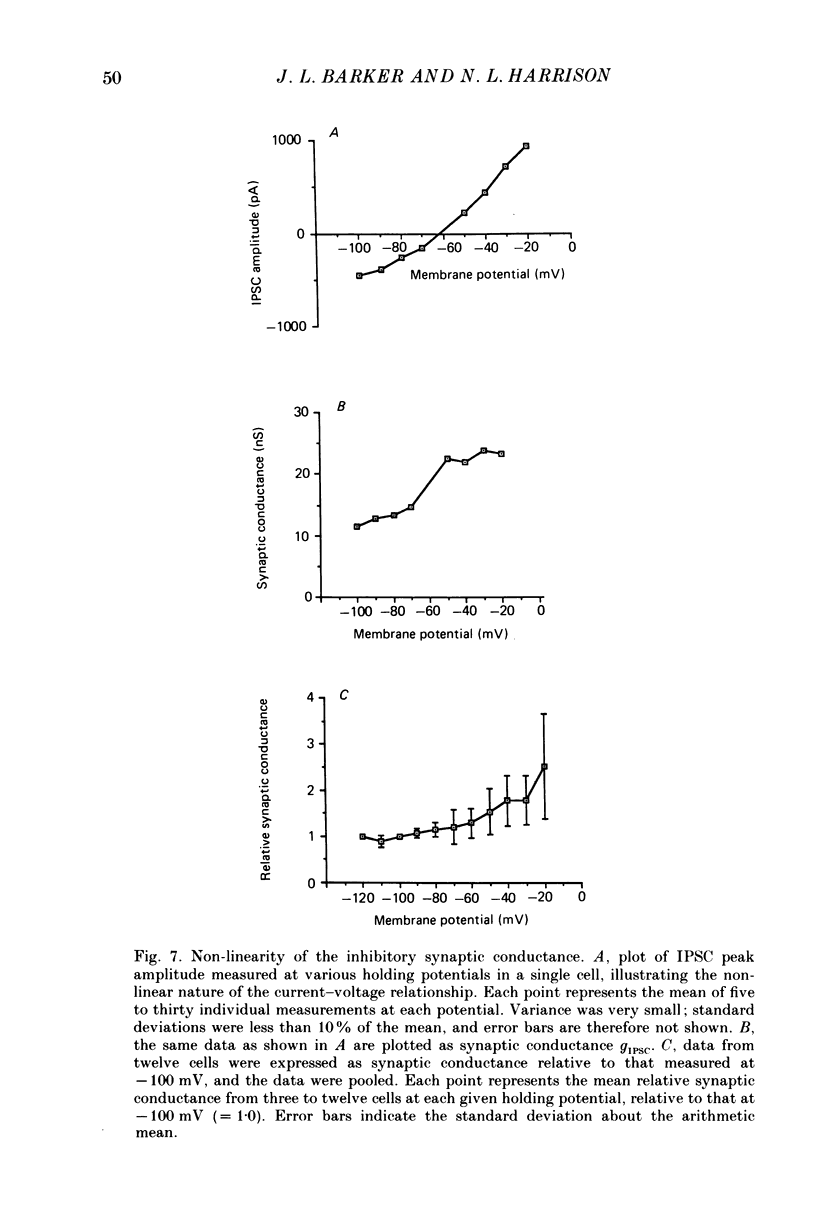
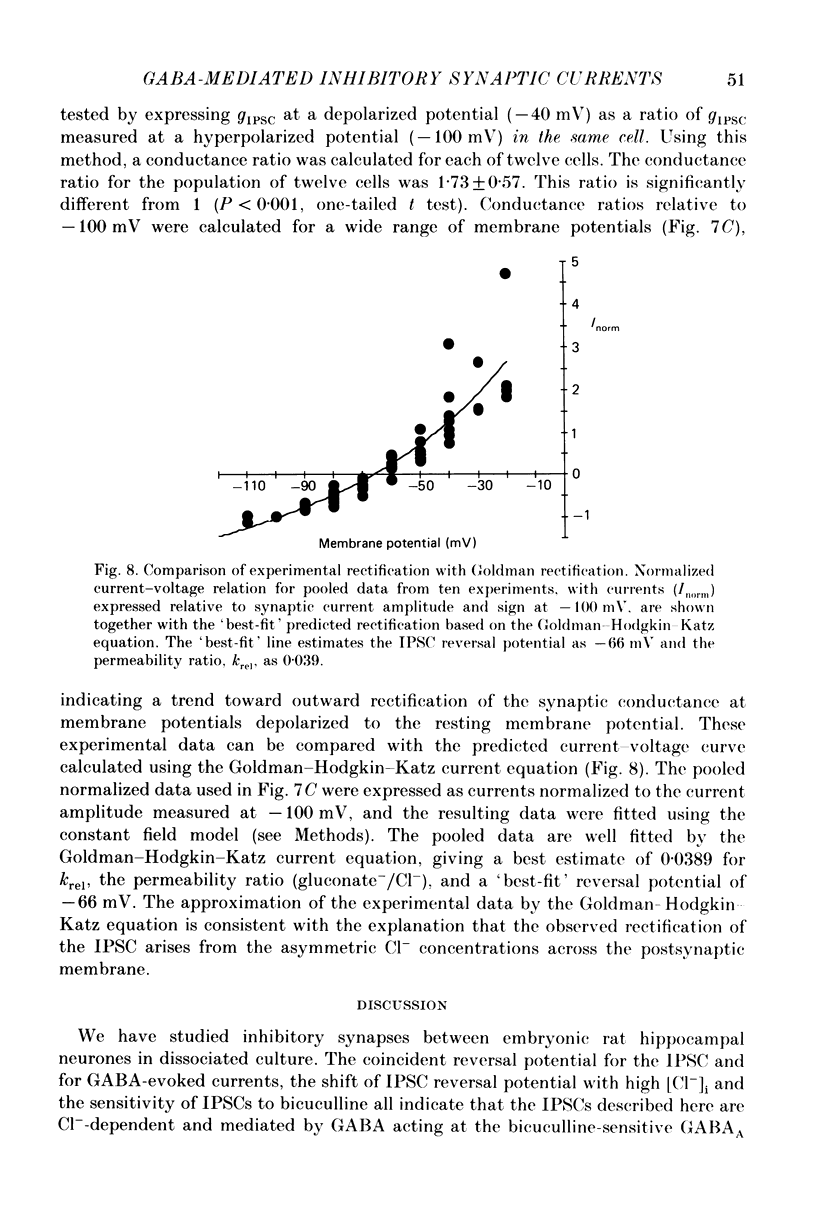
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W., Hamill O. P. Inhibitory postsynaptic currents at Aplysia cholinergic synapses: effects of permeant anions and depressant drugs. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Feb 22;214(1196):335–350. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Banks F. W. Voltage clamp analysis of inhibitory synaptic action in crayfish stretch receptor neurons. Fed Proc. 1981 Sep;40(11):2637–2641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwood T. J., Collingridge G. L., Herron C. E., Wheal H. V. Voltage-clamp analysis of somatic gamma-aminobutyric acid responses in adult rat hippocampal CA1 neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:27–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Johnston D. Voltage-clamp analysis of mossy fiber synaptic input to hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Aug;50(2):487–507. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.2.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Gage P. W., Robertson B. Inhibitory post-synaptic currents in rat hippocampal CA1 neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:551–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G. Inhibitory synaptic currents in voltage-clamped locust muscle fibres desensitized to their excitatory transmitter. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 May 22;221(1224):375–383. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G. Miniature and evoked inhibitory junctional currents and gamma-aminobutyric acid-activated current noise in locust muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:179–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Korn S. J. Gamma-aminobutyric acid uptake and the termination of inhibitory synaptic potentials in the rat hippocampal slice. J Physiol. 1985 Sep;366:387–409. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Voltage dependence of amplitude and time course of inhibitory synaptic current in crayfish muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Oct 19;371(1-2):167–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00580786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. Membrane-potential effects on an inhibitory post-synaptic conductance in Aplysia buccal ganglia. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:165–180. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. Membrane-potential effects on an inhibitory post-synaptic conductance in Aplysia buccal ganglia. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:165–180. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D., Stevens C. F. Rate-limiting step of inhibitory post-synaptic current decay in Aplysia buccal ganglia. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:145–164. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H., Brown D. A. GABAB-receptor-activated K+ current in voltage-clamped CA3 pyramidal cells in hippocampal cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1558–1562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hablitz J. J., Thalmann R. H. Conductance changes underlying a late synaptic hyperpolarization in hippocampal CA3 neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Jul;58(1):160–179. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.1.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Bormann J., Sakmann B. Activation of multiple-conductance state chloride channels in spinal neurones by glycine and GABA. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):805–808. doi: 10.1038/305805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Lange G. D., Barker J. L. (-)-Baclofen activates presynaptic GABAB receptors on GABAergic inhibitory neurons from embryonic rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Feb 15;85(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G. 3H-baclofen and 3H-GABA bind to bicuculline-insensitive GABA B sites in rat brain. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):149–152. doi: 10.1038/290149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarren M., Alger B. E. Use-dependent depression of IPSPs in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Feb;53(2):557–571. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.2.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Pun R. Y., Westbrook G. L. Synaptic excitation in cultures of mouse spinal cord neurones: receptor pharmacology and behaviour of synaptic currents. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:169–190. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. A bicuculline-resistant inhibitory post-synaptic potential in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:239–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. Direct hyperpolarizing action of baclofen on hippocampal pyramidal cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):450–452. doi: 10.1038/308450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera K., Takeuchi A. An analysis of the inhibitory post-synaptic current in the voltage-clamped crayfish muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:265–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Barker J. L. Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: properties of GABA-activated Cl- ion conductance. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Mar;51(3):500–515. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.3.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Barker J. L. Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: voltage-clamp analysis of inhibitory synaptic connections. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Sep;52(3):469–487. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.52.3.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: responses to electrical and chemical stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Dec;50(6):1249–1264. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.6.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicini S., Wroblewski J. T., Costa E. Pharmacological modulation of GABAergic transmission in cultured cerebellar neurons. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Feb;25(2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



